绘制序列 Logo
用 VisualBasic 实现的序列 Logo 绘制器
引言

图 1. 从 RegPrecise 数据库绘制的噬草菌属 LexA 序列标志:http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/regulog.jsp?regulog_id=680
在生物信息学中,序列标志(sequence logo)是对核苷酸(DNA/RNA链)或氨基酸(蛋白质序列)的序列保守性进行图形化表示。序列标志由一组比对的序列集合创建,并展示了共识序列和序列的多样性。序列标志常用于表示序列特征,例如 DNA 中的蛋白质结合位点或蛋白质中的功能单元。(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_logo)
在本文中,我想介绍如何使用 Visual Basic 语言创建这个序列标志图。
背景
有许多工具可以创建用于绘制序列标志的基序模型。如果数据要求不那么严格,可以使用 MEGA 或 Clustal 软件从多序列比对生成一个简单的序列标志模型;但在大多数情况下,基序应该从 PWM(概率矩阵)生成,而 meme suite 软件 在基序 PWM 发现和创建方面做得最好。

图 2. 在 GCModeller 中绘制序列标志
基序中的一些概念
1. Fasta 序列
最常用的数据库格式,用于在文本文件中存储生物序列。一个 fasta 序列以标题行开始,其第一个字符必须是 >
然后从第二行开始是生物序列数据,这是一个简单的核苷酸序列的例子
>XC_0012:21_Sigma54
-------TGCTGCTGTT--GCTGC---
>XC_0013:35_Sigma54
-------AGGCACAGGAAGTGC-----
GCModeller for .NET 语言中已经实现了 fasta 序列数据库的解析器,它位于命名空间:LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel.FASTA.FastaFile
使用这个解析器就足够简单了
Imports LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel
' Parsing the fasta database from the specific file
Dim fasta As New FASTA.FastaFile(path)
2. 字母相对频率
蛋白质和 DNA 之间的字母不同。DNA 序列只有 ATGC 4 个字母,而蛋白质序列有 20 个字符:
''' <summary>
''' Enumeration for nucleotide residues
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public ReadOnly Property NT As IReadOnlyCollection(Of Char) = {"A"c, "T"c, "G"c, "C"c}
''' <summary>
''' Enumeration for amino acid.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public ReadOnly Property AA As IReadOnlyCollection(Of Char) = {
"A"c, "R"c, "N"c, "D"c, "C"c, "E"c, "Q"c, "G"c,
"H"c, "I"c, "L"c, "K"c, "M"c, "F"c, "P"c, "S"c,
"T"c, "W"c, "Y"c, "V"c
}

图 3. 字母相对频率统计
要计算字母相对频率,只需统计每个字母在每一列中出现的频率。下面是统计字母频率的简化版本
- 字母的计数是它们在某一列中出现的次数;
- 然后用出现次数除以序列的总数
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic.Linq
Imports LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel.FASTA
''' <summary>
''' Simple function for statics the alphabet frequency in the fasta source.
''' The returns matrix, alphabet key char is Upper case.
''' (返回来的数据之中的残基的字符是大写的)
''' </summary>
''' <param name="source">
''' Fasta sequence source, and all of the fasta sequence
''' in this source must in the same length.
''' </param>
''' <returns></returns>
<ExportAPI("NT.Frequency")>
Public Function Frequency(source As IEnumerable(Of FastaToken)) As PatternModel
Dim len As Integer = source.First.Length
Dim n As Integer = source.Count
Dim alphabets As Char() =
If(source.First.IsProtSource,
Polypeptides.ToChar.Values.ToArray, New Char() {"A"c, "T"c, "G"c, "C"c})
' Converts the alphabets in the sequence data to upper case.
Dim fasta As New FastaFile(source.ToArray(Function(x) x.ToUpper))
Dim LQuery = (From pos As Integer
In len.Sequence.AsParallel
Select pos,
row = (From c As Char
In alphabets
Select c, ' Statics for the alphabet frequency at each column
f = __frequency(fasta, pos, c, n)).ToArray
Order By pos Ascending).ToArray
Dim Model As IEnumerable(Of SimpleSite) =
From x
In LQuery.SeqIterator
Let freq As Dictionary(Of Char, Double) =
x.obj.row.ToDictionary(Function(o0) o0.c, Function(o0) o0.f)
Select New SimpleSite(freq, x.Pos)
Return New PatternModel(Model)
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Statics of the occurence frequency for the specific alphabet at specific
''' column in the fasta source.
''' (因为是大小写敏感的,所以参数<see cref="Fasta"/>里面的所有的序列数据都必须是大写的)
''' </summary>
''' <param name="Fasta"></param>
''' <param name="p">The column number.</param>
''' <param name="C">Alphabet specific for the frequency statics</param>
''' <param name="numOfFasta">The total number of the fasta sequence</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function __frequency(Fasta As IEnumerable(Of FastaToken),
p As Integer,
C As Char,
numOfFasta As Integer) As Double
Dim LQuery As Integer = (From nt As FastaToken
In Fasta
Let chr As Char = nt.SequenceData(p)
Where C = chr
Select 1).Sum
Dim f As Double = LQuery / numOfFasta
Return f
End Function
此字母频率统计函数代码可在命名空间中找到:LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel.Patterns.PatternsAPI
使用代码
如图 2 所示,要在 VisualBasic 中绘制序列标志,我们需要创建一个绘图模型来进行可视化。绘制序列标志需要以下 3 种信息:
- 残基的字母
- 每一列字母的高度
- 该序列标志图将表示的基序的列
字母渲染
首先,我们来看看如何渲染残基字母。
由于 fasta 序列数据库可以存储两种类型的序列,因此我们需要两种颜色方案来绘制序列标志,分别对应 DNA 序列和蛋白质序列。以下是颜色定义:
核苷酸序列的颜色方案
''' <summary>
''' Color schema for the nucleotide sequence.(核酸Motif的profiles)
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public ReadOnly Property NucleotideSchema As Dictionary(Of Char, Image)
Get
Return New Dictionary(Of Char, Image) From {
{"A"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Green, "A")},
{"T"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Red, "T")},
{"G"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Yellow, "G")},
{"C"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Blue, "C")}
}
End Get
End Property
蛋白质残基字母的颜色方案
''' <summary>
''' Color schema for the protein residues alphabets.(蛋白质Motif的profiles)
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public ReadOnly Property ProteinSchema As Dictionary(Of Char, Image)
Get
Return New Dictionary(Of Char, Image) From {
{"A"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.CadetBlue, "A")}, 'Alanine Ala
{"R"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Black, "R")}, 'Arginine Arg
{"N"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Chocolate, "N")}, 'Asparagine Asn
{"D"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Coral, "D")}, 'Aspartic acid Asp
{"C"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Chartreuse, "C")}, 'Cysteine Cys
{"E"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Cyan, "E")}, 'Glutamic acid Glu
{"Q"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.LawnGreen, "Q")}, 'Glutamine Gln
{"G"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.DarkMagenta, "G")}, 'Glycine Gly
{"H"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Gold, "H")}, 'Histidine His
{"I"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.HotPink, "I")}, 'Isoleucine Ile
{"L"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.LightSlateGray, "L")}, 'Leucine Leu
{"K"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Yellow, "K")}, 'Lysine Lys
{"M"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Teal, "M")}, 'Methionine Met
{"F"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.SaddleBrown, "F")}, 'Phenylalanine Phe
{"P"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Red, "P")}, 'Proline Pro
{"S"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.RoyalBlue, "S")}, 'Serine Ser
{"T"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Tomato, "T")}, 'Threonine Thr
{"W"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.MediumSeaGreen, "W")}, 'Tryptophan Trp
{"Y"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.SkyBlue, "Y")}, 'Tyrosine Tyr
{"V"c, ColorSchema.__getTexture(Color.Maroon, "V")} 'Valine Val
}
End Get
End Property
由于使用 DrawString 方法直接控制序列标志图上的字符串绘图样式很困难,而 gdi+ 的 DrawImage 方法可以通过 x, y, width 和 height 这些函数参数直接控制图像的绘制位置和大小,因此我为每个字母创建了图像缓存,这些字母是标志字母所必需的。然后,这些字母的图像缓存可以使后续的标志绘制程序更加容易。以下是将字母字符串转换为图像缓存的代码:
''' <summary>
''' Creates the image cache for the alphabet.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="color"></param>
''' <param name="alphabet"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function __getTexture(color As Color, alphabet As String) As Image
Dim bitmap As New Bitmap(680, 680)
Dim font As New Font(FontFace.Ubuntu, 650)
Dim br As New SolidBrush(color:=color)
Using gdi As Graphics = Graphics.FromImage(bitmap)
Dim size As SizeF = gdi.MeasureString(alphabet, font:=font)
Dim w As Integer = (bitmap.Width - size.Width) / 2
Dim h As Integer = (bitmap.Height - size.Height) * 0.45
Dim pos As New Point(w, h)
gdi.CompositingQuality = Drawing2D.CompositingQuality.HighQuality
gdi.CompositingMode = Drawing2D.CompositingMode.SourceOver
Call gdi.DrawString(alphabet, font, br, point:=pos)
End Using
Return bitmap
End Function
这些代码可以在模块中找到:
LANS.SystemsBiology.AnalysisTools.SequenceTools.SequencePatterns.SequenceLogo.ColorSchema
计算残基位点的比特(Bits)
衡量序列标志上绘制的字母高度的一个重要因素是比特(Bits)。整个残基堆的高度是以比特为单位的信息量。这个值与字母的频率和 fasta 源中的序列数量有关。参考维基百科,给出了计算此信息比特的公式:
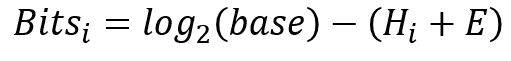
其中 base 的值与残基类型有关,对于 DNA 序列 base 为 4,对于蛋白质序列 base 为 20。例如,这是代码示例:
Dim base As Integer = If(fasta.First.IsProtSource, 20, 4)
E 的值也与 base 相关,并且还与对齐源中 fasta 序列的数量相关。

其中变量 n 是比对中 fasta 序列的数量,可以通过 FastaFile 类中的属性获得。
Dim n As Integer = FastaFile.NumberOfFasta
Dim base As Integer = If(fa.First.IsProtSource, 20, 4)
Dim E As Double = (1 / Math.Log(2)) * ((base - 1) / (2 * n))
而每个残基位点 i 的不确定性信息(bits)可以通过以下方式计算:

其中 i 是基序矩阵中的列,f(a) 是我们之前创建的字母相对频率。a 是字母,如果序列是 DNA,则相对频率函数的参数 a 属于 "ATGC";否则,对于蛋白质序列,它是 20 种氨基酸残基字母。计算不确定性信息 Hi 的代码如下所示:
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic.Linq
Dim H As Double() = f.Residues.ToArray(Function(x) x.Alphabets.__hi)
''' <summary>
'''
''' </summary>
''' <param name="f"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks>
''' If n equals ZERO, then log2(0) is NaN, n * Math.Log(n, 2) could not be measure,
''' due to the reason of ZERO multiple any number is ZERO, so that if n is ZERO,
''' then set n * Math.Log(n, 2) its value to Zero directly.
''' </remarks>
<Extension>
Private Function __hi(f As Dictionary(Of Char, Double)) As Double
Dim h As Double = f.Values.Sum(Function(n) If(n = 0R, 0, n * Math.Log(n, 2)))
h = 0 - h
Return h
End Function
然后,当我们计算了每个残基的比特信息后,再结合之前统计的相对字母频率矩阵,我们就有足够的信息来描述一个序列基序作为序列标志。
这是创建频率基序模型的完整代码,位于命名空间:LANS.SystemsBiology.AnalysisTools.SequenceTools.SequencePatterns.Motif.PWM
Imports System.Runtime.CompilerServices
Imports LANS.SystemsBiology.AnalysisTools.SequenceTools.SequencePatterns.SequenceLogo
Imports LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel.FASTA
Imports LANS.SystemsBiology.SequenceModel.Patterns
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic.Language
Imports Microsoft.VisualBasic.Linq
''' <summary>
''' Build probability matrix from clustal multiple sequence alignment, this matrix model can be
''' used for the downstream sequence logo drawing visualization.
''' (从Clustal比对结果之中生成PWM用于SequenceLogo的绘制)
''' </summary>
''' <param name="fa">A fasta sequence file from the clustal multiple sequence alignment.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function FromMla(fa As FastaFile) As MotifPWM
Dim f As PatternModel = PatternsAPI.Frequency(fa)
Dim n As Integer = fa.NumberOfFasta
Dim base As Integer = If(fa.First.IsProtSource, 20, 4)
Dim E As Double = (1 / Math.Log(2)) * ((base - 1) / (2 * n))
Dim H As Double() = f.Residues.ToArray(Function(x) x.Alphabets.__hi)
Dim PWM As ResidueSite() =
LinqAPI.Exec(Of SimpleSite, ResidueSite) _
(f.Residues) <= Function(x, i) __residue(x.Alphabets, H(i), E, base, i)
If base = 20 Then
Return MotifPWM.AA_PWM(PWM)
Else
Return MotifPWM.NT_PWM(PWM)
End If
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Construct of the residue model in the PWM
''' </summary>
''' <param name="f">ATGC</param>
''' <param name="h"></param>
''' <param name="en"></param>
''' <param name="n"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function __residue(f As Dictionary(Of Char, Double), h As Double, en As Double, n As Integer, i As Integer) As ResidueSite
Dim R As Double = Math.Log(n, 2) - (h + en)
Dim alphabets As Double()
If n = 4 Then
alphabets = {f("A"c), f("T"c), f("G"c), f("C"c)}
Else
alphabets = LinqAPI.Exec(Of Double) <= From c As Char In ColorSchema.AA Select f(c)
End If
Return New ResidueSite With {
.Bits = R,
.PWM = alphabets,
.Site = i
}
End Function
''' <summary>
'''
''' </summary>
''' <param name="f"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks>
''' If n equals ZERO, then log2(0) is NaN, n * Math.Log(n, 2) could not be measure,
''' due to the reason of ZERO multiple any number is ZERO, so that if n is ZERO,
''' then set n * Math.Log(n, 2) its value to Zero directly.
''' </remarks>
<Extension>
Private Function __hi(f As Dictionary(Of Char, Double)) As Double
Dim h As Double = f.Values.Sum(Function(n) If(n = 0R, 0, n * Math.Log(n, 2)))
h = 0 - h
Return h
End Function
构建绘图模型
如前文所述,绘制序列标志需要知道每个列位置的字母及其相对频率。为了衡量每个残基位的高度,需要根据字母相对频率和比对序列的数量来计算比特信息。因此,在数据模型计算完成后,就获得了绘制标志所需的所有信息。为了对来自多序列比对结果和 PWM 基序模型的序列标志进行统一操作,需要将频率模型或 PWM 转换为统一的 DrawingModel。以下是 DrawingModel 类的类型定义:
DrawingModel用于表示整个基序的数据模型Residue代表基序位点中的每个列位- 每一列的相对频率由
Alphabet类组成
''' <summary>
''' Drawing model for the sequence logo visualization.
''' </summary>
Public Class DrawingModel : Inherits ClassObject
''' <summary>
''' The motif model is consist of a sequence of residue sites.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Residues As Residue()
Public Property En As Double
''' <summary>
''' This drawing display title.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property ModelsId As String
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return ModelsId & " --> " & Me.GetJson
End Function
End Class
''' <summary>
''' A drawing site in the sequence logo drawing.(所绘制的序列logo图之中的一个位点)
''' </summary>
Public Class Residue : Implements IAddressHandle
''' <summary>
''' ATGC, 4 characters for nt, and aa is 20.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Alphabets As Alphabet()
''' <summary>
''' The total height of the letters depicts the information content Of the position, In bits.
''' (Bits的值是和比对的序列的数量是有关系的)
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Bits As Double
''' <summary>
''' Position value of this residue in the motif sequence.(这个残基的位点编号)
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Address As Integer Implements IAddressHandle.Address
End Class
''' <summary>
''' Alphabet model in the drawing motif model, nt for 4 and aa for 20
''' </summary>
Public Class Alphabet : Implements IComparable
''' <summary>
''' A alphabet character which represents one residue.(可以代表本残基的字母值)
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Alphabet As Char
''' <summary>
''' The relative alphabet frequency at this site position.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property RelativeFrequency As Double
End Class
这些类类型定义位于命名空间:LANS.SystemsBiology.AnalysisTools.SequenceTools.SequencePatterns.SequenceLogo
这就是表示序列标志数据模型所需的一切。此函数提供了将相对频率模型转换为 DrawingModel 以及最终进行序列标志绘制的接口。
''' <summary>
''' Drawing the sequence logo just simply modelling this motif site from
''' the clustal multiple sequence alignment.
''' (绘制各个残基的出现频率)
''' </summary>
''' <param name="Fasta">The alignment export data from the clustal software.</param>
''' <param name="title">The sequence logo display title.</param>
''' <returns></returns>
<ExportAPI("Drawing.Frequency")>
Public Function DrawFrequency(Fasta As FastaFile, Optional title As String = "") As Image
Dim PWM As MotifPWM = Motif.PWM.FromMla(Fasta)
Dim Model As DrawingModel = New DrawingModel
#If DEBUG Then
Dim m As String = New String(PWM.PWM.ToArray(Function(r) r.AsChar))
Call VBDebugger.WriteLine(m, ConsoleColor.Magenta)
#End If
If String.IsNullOrEmpty(title) Then
If Not String.IsNullOrEmpty(Fasta.FileName) Then
Model.ModelsId = Fasta.FileName.BaseName
Else
Model.ModelsId = New String(PWM.PWM.ToArray(Function(r) r.AsChar))
End If
Else
Model.ModelsId = title
End If
Model.Residues =
LinqAPI.Exec(Of ResidueSite, Residue)(PWM.PWM) <=
Function(rsd As ResidueSite) New Residue With {
.Bits = rsd.Bits,
.Address = rsd.Site,
.Alphabets = LinqAPI.Exec(Of Alphabet) <= From x As SeqValue(Of Double)
In rsd.PWM.SeqIterator
Select New Alphabet With {
.Alphabet = PWM.Alphabets(x.Pos),
.RelativeFrequency = x.obj
} ' alphabets
} ' residues
Return InvokeDrawing(Model, True)
End Function

下面两张图展示了 DrawingModel 组件之间的关系:
图 4. 残基与其字母之间的关系。
序列标志由一系列残基位点组成,每个残基位点由序列的所有字母组成,但每个字母在残基中的相对频率通常不相等。
图 5. 残基与 DrawingModel 类之间的关系
一个残基由所有字母组成,然后 DrawingModel 是这些残基的序列,每个残基位点的堆栈高度由比特信息量测量,比特信息量与每个残基位点的字母相对频率相关。
序列标志绘制函数
如上所述,字母高度与一个残基位点的比特信息量有关,而实际的绘制高度可以通过字母的相对频率与其在残基位点乘积来计算。

以及计算此字母高度的代码
' YHeight is the max height of current residue, and its value is calculate from its Bits value
YHeight = (n * DrawingDevice.Height) * (If(residue.Bits > MaxBits, MaxBits, residue.Bits) / MaxBits)
' H is the drawing height of the current drawing alphabet,
' this height value can be calculate from the formula that show above.
' As the YHeight variable is transform from the current residue Bits value, so that from this statement
' The drawing height of the alphabet can be calculated out.
Dim H As Single = Alphabet.RelativeFrequency * YHeight

图 6. 使用图像绘制比直接使用字符串绘制更容易控制字母的位置和大小。
' Due to the reason of the Y Axis in gdi+ is up side down, so that we needs Subtraction operation,
' and then this makes the next alphabet move up direction
Y -= H
gdi.Gr_Device.DrawImage(
colorSchema(Alphabet.Alphabet), ' Drawing alphabet
CSng(X), CSng(Y), ' position
CSng(DrawingDevice.WordSize), H) ' Size and relative height
序列标志绘制函数的完整代码可在命名空间中找到:
LANS.SystemsBiology.AnalysisTools.SequenceTools.SequencePatterns.SequenceLogo.DrawingDevice
使用示例
本文中的代码已实现为一个序列工具的 CLI 实用程序命令。该工具可以从 github release 下载。您可以尝试使用示例测试数据绘制序列标志,该数据位于 https://github.com/SMRUCC/Sequence-Patterns-Toolkit/blob/master/data/Xanthomonadales_MetR___Xanthomonadales.fasta,这个基序序列数据是从 RegPrecise 数据库下载的:http://regprecise.lbl.gov/RegPrecise/regulog.jsp?regulog_id=5789

打开 CMD 终端,然后使用命令 seqtools ? /logo 来获取有关如何使用此命令的详细信息。
这是一个绘制示例测试数据的命令行使用示例:
seqtools /logo /in ./data/Staphylococcaceae_LexA___Staphylococcaceae.fasta



