[树莓派系列] 使用 4511 IC 的高级 7 段显示驱动器
4.50/5 (3投票s)
源代码可在 Github 上获取 背景 在本系列的第一篇文章中,我讨论了一种通过树莓派 2 直接驱动 7 段显示的非常简单的方法。虽然这确实有效,但在实践中,它存在许多警告和限制。首先,每个 LED 的电流受到限制
源代码可在 Github 上获取
背景
在我本系列的第一篇文章中,我讨论了一种通过树莓派 2 直接驱动 7 段显示的非常简单的方法。虽然这确实有效,但在实践中,它存在许多警告和限制。首先,每个 LED 的电流受到树莓派上每个 GPIO 引脚可以提供的电流的限制。其次,如果所有段都点亮,则进入 GPIO 输入引脚的累积电流超过建议的输入电流。虽然我毫不怀疑树莓派可以处理它,但我不会建议长期使用它。
引言
为了改进之前的帖子并以更有效的方式驱动七段显示器,我将进行两个重大更改。首先,我将使用 CMOS4511 集成电路芯片从二进制输入驱动 7 段显示器。其次,为了保护 GPIO 输入,将使用晶体管来打开和关闭显示器,并且电路将接地而不是 GPIO 引脚。
先决条件
1 x 树莓派 2
1 x Cmos 4511 IC
4 x NPN 晶体管(或多或少取决于显示器上的位数)
1 x 5641AS 7 段显示器(或类似的 7 段显示器)
7 x 220 欧姆电阻
4 x 1 kOhm 电阻(与晶体管数量相同)
Fritzing
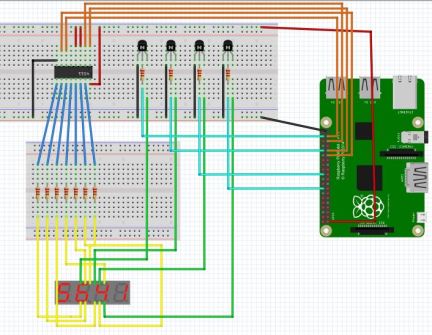
电路
上面的 Fritzing 图显示了演示中使用的完整电路。 如果需要,可以使用不同的 GPIO 引脚输出到 4511 和 GPIO。
CMOS4511 IC 用于将二进制输入转换为 7 段显示输出。 4511 的引脚排列可以在 数据表中找到。 4 个输入 D0 – D3 连接到树莓派,7 个输出 a 到 g 通过 220 欧姆电阻连接到显示器上的相应段。Vcc、BL 和 LT 都应连接到电源 [建议 3.3v],并且接地应连接到地。 LE 可以保持未连接状态。
从显示器上,每个数字显示引脚应连接到 NPN 晶体管的集电极,并且每个晶体管发射极可以连接到地。 每个晶体管基极可以通过 1 kOhm 电阻连接到 GPIO 引脚。
代码
由于核心代码与之前的驱动程序相同,因此从之前的代码中抽象出我们的新驱动程序是有意义的。 为此,我们需要进行一些小的更改。
首先,由于我们将使用 4 个引脚而不是 7 个引脚来驱动我们的显示器,我们需要覆盖现有类中的 SetDisplay 方法,因此现在应将其设置为 virtual 以允许我们这样做。我们还需要覆盖 ClearDisplay() 方法,因此也将其设置为 virtual。
除此之外,由于我们使用的是一组不同的 GPIO 引脚,我们需要能够提供不同的构造函数,但是由于我们不想使用原始的基本构造函数,因此我们必须提供另一个构造函数,在这种情况下是无参数构造函数。 由于我们只希望派生类能够使用它,因此我们可以将构造函数设置为受保护。 我们还可以利用此构造函数来设置先前在主构造函数中设置的取消令牌,从而无需提供对这些字段的受保护访问器。
protected Display()
{
this.cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
this.token = new CancellationToken();
}
我们需要对原始类做的最后一件事是使显示器数组可供派生类访问
protected GpioPin[] Displays
{
get
{
return this.displays;
}
set
{
this.displays = value;
}
}
现在我们准备好创建新的派生类。 应创建一个类似于我们原始基类的新构造函数,但我们只需要提供 4 个输出引脚 [用于 4511 D0-D3],然后是我们的显示引脚。 然后按照基类执行引脚的初始化。
接下来,我们可以提供重写的 SetDisplay 方法。 此版本不是将提供的 int 转换为其 7 段表示形式,而是将提供的 int 转换为其二进制表示形式。
protected override void SetDisplay(GpioPin displayPin, int value)
{
this.ClearDisplay();
switch (value)
{
case 0:
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 1:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 2:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd1 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 3:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 4:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd2 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 5:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd2 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd1,this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 6:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2});
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 7:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd3 });
break;
case 8:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd3 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2 });
break;
case 9:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd3 });
this.SetLow(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2 });
break;
case 10: // Clear Display
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
default:
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { this.pinBcd0, this.pinBcd1, this.pinBcd2, this.pinBcd3 });
break;
}
this.SetHigh(new GpioPin[] { displayPin });
}
此方法中还有另一个更改。 也就是说,这次我们设置 GPIO 为高电平,而不是将 GPIO 引脚设置为低电平以打开显示数字。 这是因为我们现在设置引脚为高电平,而不是将引脚设置为低电平以允许电流流入 GPIO 引脚,然后该引脚“切换”晶体管,从而允许电流流动并流入地线。 因此,我们还覆盖了 ClearDisplays 方法以将所有 GPIO 引脚设置为低电平 [而不是高电平]。
protected override void ClearDisplay()
{
this.SetLow(this.Displays);
}
视频
下面的视频展示了项目的实际效果
