Repository Pattern For .Net
4.71/5 (15投票s)
针对领域对象模型上的多个数据源或资源的存储库模式示例
引言
所有的 .Net 开发者都听说过 Entity Framework 的 Repository Pattern。但我们不能总是只使用 Entity Framework。有时我们希望以不同的方式存储数据,例如 XML 文件、Web 服务、NoSQL 数据库。那么!我们该怎么办,是不是就不使用 Repository Pattern 了?不,我们必须将其他数据源适配到 Repository Pattern 中。本文的主题是如何在 Repository Pattern 中实现多数据源。
背景
我想强调的是如何在多个数据源或资源上使用单一的 Repository Pattern。因此,我无法为您提供 Entity Framework 或其他上下文技术的细节。上下文层创建起来很简单。通常,这些技术用于 Web 应用程序或服务应用程序。 但我们使用控制台应用程序来方便演示。
使用代码
解决方案包含五个项目。它们分别是 Core、EFSource、XMLSource、Repository 和 Console。
第一个项目,看名字 Core。

这里有两个代码文件。现在创建一个 IEntity.cs 文件。
namespace RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs
{
public interface IEntity<TKey>
{
TKey Id { get; set; }
}
}
TKey Id 的意思是……我们必须在所有领域对象中使用它。因为我们不知道 Id 的类型(主键可以是 int、uniqueidentifier 等),因此我们在 Repository 类中定义了相同的函数返回值。
现在创建一个 Student.cs 领域对象文件。
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs
{
[Serializable]
[Table("Student")]
public partial class Student: IEntity<int>
{
[Key]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(50)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(50)]
public string SurName { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(5)]
public string Classroom { get; set; }
}
}
这里有两个重要的点。一个是用于 EF 的 EF Annotations,另一个是用于 XML 序列化的 Serialization Annotations。如果您想使用其他数据源或资源,您必须在此处添加相应的注解。
完成该项目,接下来是源项目。现在看名为 EFSource 的项目。

有一个名为 SchoolContext.cs 的文件。该文件是一个 EF context 类。在新项目中创建一个新的。
namespace RepositoryPattern.EFSource
{
using System.Data.Entity;
using Core.DomainObjecs;
public partial class SchoolContext : DbContext
{
public SchoolContext()
: base("name=SchoolContext")
{
}
public virtual DbSet<Student> Student { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
}
}
}
有一个来自 Student 领域对象的 DbSet,因为我们有一个领域对象。
在解决方案中完成该项目。现在看名为 XMLSource 的项目。

有一个名为 XMLSet.cs 的文件。该文件与 Context 类相同。为您的新项目创建一个新的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Xml.Serialization;
namespace RepositoryPattern.XMLSource
{
public class XMLSet<TModel> where TModel : class
{
private string m_filename;
private ICollection<TModel> m_models;
public XMLSet(string FileName)
{
this.m_filename = FileName;
}
public ICollection<TModel> Data
{
get
{
try
{
if (m_models == null) Load();
}
catch (Exception)
{
m_models = new List<TModel>();
}
return m_models;
}
set
{
m_models = value;
Save();
}
}
public void Save()
{
XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<TModel>));
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(this.m_filename);
serializer.Serialize(sw, this.m_models);
sw.Close();
sw.Dispose();
}
public void Load()
{
XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(List<TModel>));
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(this.m_filename);
this.m_models = serializer.Deserialize(sr) as List<TModel>;
sr.Close();
sr.Dispose();
}
}
}
该文件包含用于保存和加载操作的基本 context 方法。因此,它不能包含与 Entity Framework Context 相同的模型属性。但是,该类可以作为 context 和模型容器的多重继承。如果您想单独开发 XMLContext 和 XMLSet 对象,这是可能的。但这超出了主题范围,也许以后再讲。
该类需要知道两项信息。第一项是来自 T 的模型类,第二项是通过构造函数参数 FileName 传递的保存文件名。我们将把它交给 repository。
在解决方案中完成该项目。现在看名为 Repository 的项目。

该项目包含很多文件。我们按级别顺序查看文件。
IRepository.cs
这是 repository 类的接口。有一些用于 CRUD 操作的函数模板。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public interface IRepository<TEntity, TKey> where TEntity : class
{
ICollection<TEntity> GetAll();
ICollection<TEntity> Find(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate);
TEntity Get(TKey id);
TKey Insert(TEntity model);
bool Update(TEntity model);
bool Remove(TKey id);
bool Delete(TKey id);
}
}
我之前提到的 TKey 在这里被使用。
IStudentRepository.cs
这是 Student 领域模型的接口,也指定了来自 IRepository 的参数。请注意继承点。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public interface IStudentRepository: IRepository<Student, int>
{
}
}
其目的是定制 repository。
EFRepositoryBase.cs
这是一个 Entity Framework 的基类 repository。它包含许多用于管理 context 类的 CRUD 操作的函数。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public abstract class EFRepositoryBase<TContext, TEntity, TKey> : IRepository<TEntity, TKey> where TEntity : class where TContext : DbContext
{
private readonly DbContext m_dbContext;
public EFRepositoryBase()
: this(Activator.CreateInstance<TContext>())
{
}
public EFRepositoryBase(DbContext context)
{
this.m_dbContext = context;
}
public virtual bool Delete(TKey id)
{
try
{
var model = this.Get(id);
this.GetSet().Remove(model);
this.m_dbContext.SaveChanges();
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
public ICollection<TEntity> Find(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate)
{
try
{
return this.GetSet().Where(predicate).ToList();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return new List<TEntity>();
}
}
public TEntity Get(TKey id)
{
try
{
return this.GetSet().Find(id);
}
catch (Exception)
{
return null;
}
}
public ICollection<TEntity> GetAll()
{
try
{
return this.GetSet().ToList();
}
catch (Exception)
{
return new List<TEntity>();
}
}
public TKey Insert(TEntity model)
{
try
{
this.GetSet().Add(model);
this.m_dbContext.SaveChanges();
IEntity<TKey> entity = model as IEntity<TKey>;
return entity.Id;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return Activator.CreateInstance<TKey>();
}
}
public bool Remove(TKey id)
{
try
{
var entity = this.GetSet().Find(id);
GetSet().Remove(entity);
this.m_dbContext.SaveChanges();
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
public bool Update(TEntity model)
{
try
{
this.GetSet().Attach(model);
this.m_dbContext.Entry(model).State = EntityState.Modified;
this.m_dbContext.SaveChanges();
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
protected DbSet<TEntity> GetSet()
{
return this.m_dbContext.Set<TEntity>();
}
}
}
有三个泛型参数。第一个 TContext 用于我们的 context 类。看行末,where TContext : DbContext。这意味着 TContext 类型继承自 DbContext。您知道第二个和第三个参数的含义。我们已经从其他代码中知道了。
我们来看 insert 方法。它返回插入对象的标识符。这里用到了 IEntity 接口。因为 IEntity 只知道 Id 字段的类型。因此,我们将我们的实体转换为 IEntity 接口,以便返回 TKey 类型。
此类为所有领域对象提供了便利。现在您看到了。
StudentEFRepository.cs
此文件的意思是 Student 领域对象的 repository。只有一些参数。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
using RepositoryPattern.EFSource;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public class StudentEFRepository: EFRepositoryBase<SchoolContext, Student, int>, IStudentRepository
{
}
}
很简单!它提供了 context、领域模型和键类型。您想,您有几百个领域模型?不用担心,这样很简单。
XMLRepositoryBase.cs
此文件与 EFRepositoryBase.cs 相同。但有一些微小的区别。首先看文件内容。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public class XMLRepositoryBase<TContext, TEntity, TKey> : IRepository<TEntity, TKey> where TContext : XMLSource.XMLSet<TEntity> where TEntity : class
{
private XMLSource.XMLSet<TEntity> m_context;
public XMLRepositoryBase(string fileName)
{
m_context = new XMLSource.XMLSet<TEntity>(fileName);
}
public bool Delete(TKey id)
{
try
{
List<IEntity<TKey>> items = m_context.Data as List<IEntity<TKey>>;
items.Remove(items.First(f => f.Id.Equals(id)));
m_context.Data = items as ICollection<TEntity>;
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
public ICollection<TEntity> Find(Expression<Func<TEntity, bool>> predicate)
{
try
{
var list = m_context.Data.AsQueryable().Where(predicate).ToList();
return list as ICollection<TEntity>;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return null;
}
}
public TEntity Get(TKey id)
{
try
{
List<IEntity<TKey>> items = m_context.Data as List<IEntity<TKey>>;
return items.FirstOrDefault(f => f.Id.Equals(id)) as TEntity;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return null;
}
}
public ICollection<TEntity> GetAll()
{
return m_context.Data;
}
public TKey Insert(TEntity model)
{
var list = m_context.Data;
list.Add(model);
m_context.Data = list;
return default(TKey);
}
public bool Remove(TKey id)
{
return Delete(id);
}
public bool Update(TEntity model)
{
try
{
IEntity<TKey> imodel = model as IEntity<TKey>;
List<IEntity<TKey>> items = m_context.Data as List<IEntity<TKey>>;
items.Remove(items.FirstOrDefault(f => f.Id.Equals(imodel.Id)));
items.Add(imodel);
m_context.Data = items as ICollection<TEntity>;
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
return false;
}
}
}
}
看方法体。我们的 XMLSource 没有 context 技术。因此,我们在保存和加载操作中进行了过滤、裁剪和添加。如果您还记得,EF 会自己处理这些操作。我们只调用 SaveChanges() 方法。但我们必须将保存的数据返回给 XMLSource。
StudentXmlRepository.cs
此文件与 StudentEFRepository.cs 相同。唯一的区别在于构造函数中的文件名。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
using RepositoryPattern.XMLSource;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public class StudentXMLRepository: XMLRepositoryBase<XMLSet<Student>, Student, int>, IStudentRepository
{
public StudentXMLRepository()
:base("student.xml")
{
}
}
}
ContextTypes.cs
我们将在下一个时间创建一个工厂类。此文件包含将要在工厂类中使用的源类型的类型。
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public enum ContextTypes
{
EntityFramework,
XMLSource
}
}
RepositoryFactory.cs
此文件的目的是创建源类型对象。看内容。
namespace RepositoryPattern.Repository
{
public static class RepositoryFactory
{
public static TRepository Create<TRepository>(ContextTypes ctype) where TRepository: class
{
switch (ctype)
{
case ContextTypes.EntityFramework:
if (typeof(TRepository) == typeof(IStudentRepository))
{
return new StudentEFRepository() as TRepository;
}
return null;
case ContextTypes.XMLSource:
if (typeof(TRepository) == typeof(IStudentRepository))
{
return new StudentXMLRepository() as TRepository;
}
return null;
default:
return null;
}
}
}
}
我们只有一个领域对象,因此只检查一种类型。如果您创建了一些领域对象,您必须在它们的 repository 中进行检查。
在解决方案中完成该项目。现在创建一个控制台应用程序进行测试。program.cs 代码如下。
using RepositoryPattern.Core.DomainObjecs;
using RepositoryPattern.Repository;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace RepositoryPattern.Console
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool isRun = true;
while (isRun)
{
System.Console.Clear();
System.Console.WriteLine("Select a process");
System.Console.WriteLine("1 - List Students");
System.Console.WriteLine("2 - Create a Student");
System.Console.WriteLine("3 - Exit");
string inputKey = System.Console.ReadLine();
System.Console.Clear();
if (inputKey == "1")
{
System.Console.WriteLine("Select source");
System.Console.WriteLine("1 - Entity Framework");
System.Console.WriteLine("2 - XML Source");
inputKey = System.Console.ReadLine();
if (inputKey == "1")
{
var source = RepositoryFactory.Create<IStudentRepository>(ContextTypes.EntityFramework);
var items = source.GetAll();
foreach (var item in items)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(item.Name + " " + item.SurName + ": " + item.Classroom);
}
}
else if (inputKey == "2")
{
var source = RepositoryFactory.Create<IStudentRepository>(ContextTypes.XMLSource);
var items = source.GetAll();
foreach (var item in items)
{
System.Console.WriteLine(item.Name + " " + item.SurName + ": " + item.Classroom);
}
}
System.Console.Write("Press any key to continue...");
System.Console.ReadKey();
}
else if (inputKey == "2")
{
Student student = new Student();
System.Console.Write("Name: ");
student.Name = System.Console.ReadLine();
System.Console.Write("SurName: ");
student.SurName = System.Console.ReadLine();
System.Console.Write("Classroom: ");
student.Classroom = System.Console.ReadLine();
System.Console.Clear();
System.Console.WriteLine("Select source");
System.Console.WriteLine("1 - Entity Framework");
System.Console.WriteLine("2 - XML Source");
inputKey = System.Console.ReadLine();
IStudentRepository source = null;
if (inputKey == "1")
{
source = RepositoryFactory.Create<IStudentRepository>(ContextTypes.EntityFramework);
}
else if (inputKey == "2")
{
source = RepositoryFactory.Create<IStudentRepository>(ContextTypes.XMLSource);
}
try
{
source.Insert(student);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
System.Console.Write(ex);
System.Console.ReadKey();
continue;
}
}
else if (inputKey == "3")
{
isRun = false;
}
}
}
}
}
好的,现在开始测试。

第一个屏幕要求输入操作号。我们输入 1,然后看。

现在它要求输入源号。我们输入 1,然后看。
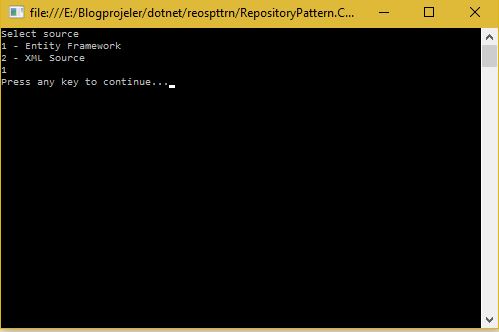
没有记录。XmlSource 也给出相同的结果。我们继续添加记录。按任意键返回第一个屏幕并输入 2。

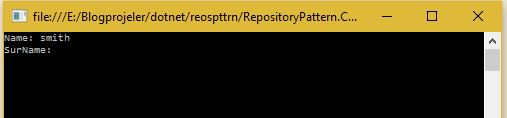


现在我们选择想要使用的资源。我选择 EF,表示 1。然后返回到第一个屏幕并选择 1 进行列表。然后选择 EF,表示 1。

哦,好的,smith jhon 在 8a 教室。此测试在 XMLSource 上返回类似的结果。
注意
如果您使用下载的项目,您必须编辑 app.config 文件中的连接字符串。您可以在 App_Data 目录中找到 student 表的创建 SQL 文件。您必须将 connectionstring 设置为适合您的环境。
历史
这是处理多数据源的好方法,但您需要使用一些技术。我通常使用依赖注入方法。我的项目通常有超过 100 个领域对象和几个数据源。例如 EF、ADO、XML、Web API 等。我有时需要多数据源,这种方法使之变得容易。
