如何在 Servlet 中调用 RESTful API Web 服务
在本文中,我将介绍如何在 servlet 中调用 RESTful API。
引言
在本文中,我将介绍如何在 servlet 中调用 RESTful API。
背景
假设我们需要搜索并显示指定城市的天气状况。互联网上有很多第三方 Web 服务。 我将使用百度天气 Web 服务来演示这一点。现在,让我们开始执行以下步骤。
Using the Code
- 转到您选择使用的 Web 服务的网站,注册一个帐户并为您获取一个 apikey。
- 查找并理解 API 描述。以百度为例。
- API 地址: http://apis.baidu.com/heweather/weather/free
- 请求方法:
GET - 请求参数在 Header 中
名称
类型
必需
location
描述
默认值
apikey字符串是
header
来自您的 Web 服务提供商的 APIkey
apikey
- Url 参数
名称
类型
必需
location
描述
默认值
city字符串是
urlParam城市名称北京 - Json 格式的结果
"HeWeather data service 3.0": [ { "status": "ok", //status, "basic": { //basic info "city": "Beijing", //city name "cnty": "China", //country "id": "CN101010100", //city id "lat": "39.904000", //latitude of city "lon": "116.391000", //longitude of city "update": { //update time "loc": "2015-07-02 14:44", //locate time "utc": "2015-07-02 06:46" //UTC time } }, "now": { // the weather at this time "cond": { //weather condition "code": "100", //weather condition code "txt": "sunny day" //weather condiftion description }, ,...... //Omitted } ] }
- 为了方便地测试 REST API,请在您的计算机上查找或安装一些工具,例如 restclient、fiddler 等。 如果您使用的是 Chrome 或 Firefox 浏览器,您还可以安装 REST 客户端插件。 我在我的 Chrome 浏览器上安装了 Advanced REST Client。
- 启动 rest 客户端。 请输入 API 地址和 apikey,如下图所示,然后单击 Send 按钮。 您将获得一个 json
string结果。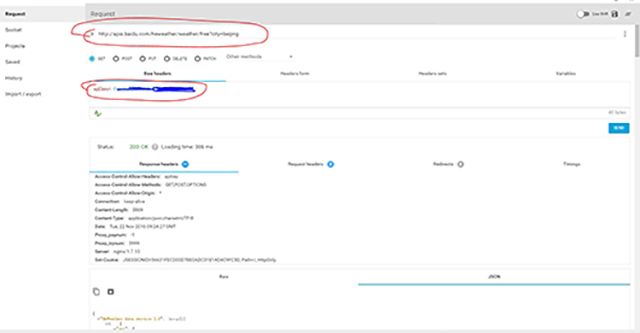
- 启动 http://www.jsonschema2pojo.org/ 并复制 json 字符串结果并将其粘贴到页面中以生成 javabean 类。 然后,在 Eclipse 中创建一个动态 Web 项目后,下载 zip 文件并将其解压缩到您的项目文件夹中。

- 当您使用 Eclipse 打开您的项目时,您将看到以下图像

- 为服务创建一个新的包,例如 com.BaiduWeather.Services。这里是调用 RESTfull API 的代理所在的位置。添加一个名为BaiduWeatherService.java的类,并将下面的代码行添加到其中。
Notice:
- 在此之前,您应该从 Maven Central 的 Gson 下载下载 gson-2.8.0.jar,将其复制到文件夹 WebContent/WEB-INF/lib/gson-2.8.0.jar 并将其添加到 Java 构建路径。
- 请记住将 apiKey 更改为您自己的。
package com.BaiduWeather.Services; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import java.net.URLEncoder; import com.BaiduWeather.Entities.Root; import com.google.gson.Gson; import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder; import com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException; /** * baidu weather service */ public class BaiduWeatherService { private static final String apiKey="0ae09eed4f3c024451ads12d1gsgsg1sg";//change this with yours private static final String baseBaiduUrl= "http://apis.baidu.com/heweather/weather/free?city=";//The constant url should be //stored in config file public static Root getWeatherInfo(String cityName) { String jsonResult=getWeatherJsonString(cityName); Root weatherInfoObject=toEntity(jsonResult); return weatherInfoObject; } //Covert json string to class object private static Root toEntity(String jsonString) { try{ Gson gson = new GsonBuilder().create(); Root weatherInfo = gson.fromJson(jsonString, Root.class); return weatherInfo; } catch(JsonSyntaxException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); return null; } } //Get the weather of the specific city private static String getWeatherJsonString(String cityName) throws RuntimeException{ //define a variable to store the weather api url and set beijing as it's default value String baiduUrl = baseBaiduUrl+"beijing"; //default value hard-coded 'beijing' //should be stored in config file try { if(cityName!=null && cityName!="") baiduUrl = baseBaiduUrl+URLEncoder.encode(cityName, "utf-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } StringBuilder strBuf = new StringBuilder(); HttpURLConnection conn=null; BufferedReader reader=null; try{ //Declare the connection to weather api url URL url = new URL(baiduUrl); conn = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection(); conn.setRequestMethod("GET"); conn.setRequestProperty("Accept", "application/json"); conn.setRequestProperty("apikey",apiKey); if (conn.getResponseCode() != 200) { throw new RuntimeException("HTTP GET Request Failed with Error code : " + conn.getResponseCode()); } //Read the content from the defined connection //Using IO Stream with Buffer raise highly the efficiency of IO reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(),"utf-8")); String output = null; while ((output = reader.readLine()) != null) strBuf.append(output); }catch(MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(reader!=null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(conn!=null) { conn.disconnect(); } } return strBuf.toString(); } } - 创建一个新的包
com.BaiduWeather.Servlets并在其下创建一个新的类 WeatherServlet.java。 在此 Java 文件中添加以下代码行package com.BaiduWeather.Servlets; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.BaiduWeather.Entities.HeWeatherDataService30; import com.BaiduWeather.Entities.Root; import com.BaiduWeather.Services.BaiduWeatherService; /** * Servlet implementation class WeatherServlet * * We can use 。jsp instead of servlet */ @WebServlet("/weather") public class WeatherServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#HttpServlet() */ public WeatherServlet() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //Get weather json info and convert it to object String city=request.getParameter("city"); Root wheatherInfoObject=BaiduWeatherService.getWeatherInfo(city); if(wheatherInfoObject!=null){ List<HeWeatherDataService30> weatherlist= wheatherInfoObject.getHeWeatherDataService30(); if(weatherlist!=null) { //output the weather content on web page. StringBuilder outputContent=new StringBuilder();//Unless the need of thread-safe, //Use StringBuilder not StringBuffer,because the latter takes more erformance overhead because of Synchronization //More cities can be store in a database or file,then load them into an array,then generators options of selection here outputContent.append("<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset=\"UTF-8\"> <title>Insert title here</title></head><body><form action=\"weather\" method=\"GET\"><select name=\"city\"><option value =\"beijing\">北京</option> <option value =\"shanghai\">上海</option><option value =\"xian\">西安</option> </select><input type=\"submit\" value=\"Submit\"></form>"); outputContent.append(weatherlist.get(0).getBasic().getCity()); outputContent.append("<br/>"); outputContent.append(weatherlist.get(0).getNow().getTmp()); outputContent.append("℃"); outputContent.append("<br/>"); outputContent.append(weatherlist.get(0).getNow().getCond().getTxt()); outputContent.append("<br/>"); outputContent.append(weatherlist.get(0).getNow().getWind().getDir()); outputContent.append("</body></html>"); response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8"); response.getWriter().write(outputContent.toString()); } } } /** * @see HttpServlet#doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub doGet(request, response); } } - 在 WebContent/WEB-INF/web.xml 中,添加以下配置项。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.1"> <display-name>BaiduWeather</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <!-- <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> --> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>weather</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <servlet> <!-- class name --> <servlet-name>WeatherServlet</servlet-name> <!-- package--> <servlet-class>com.BaiduWeather.Servlets.WeatherServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>WeatherServlet</servlet-name> <!-- address --> <url-pattern>/BaiduWeather/weather</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app> - 运行并调试此 servlet,您应该在 HTML 页面上获得天气信息。

感谢阅读!
