WPF 中的数据绑定表达式
5.00/5 (8投票s)
在本文中,我们将探讨WPF提供的不同类型的数据绑定表达式。
有许多文章讨论了绑定概念,并解释了如何使用StaticResources和DynamicResources绑定属性。这些概念使用了WPF提供的数据绑定表达式。在本文中,我们将探讨WPF提供的不同类型的数据绑定表达式。
引言
数据绑定是一种强大的技术,允许UI元素和业务模型之间的数据流动。它会在业务模型中的数据发生变化时自动将变化反映到UI元素。
数据绑定模式
| 调式 | 描述 |
| OneWay(单向) | 源 → 目标 |
| TwoWay(双向) | 源 ←→ 目标 |
| OneWayToSource(单向到源) | 源 ← 目标 |
| OneTime(一次性) | 源 → 目标(仅一次) |
这可以通过WPF提供的不同类型的数据绑定表达式来实现。
数据绑定表达式类型
- DataContext 绑定
- RelativeSource 绑定
- 集合当前项绑定
DataContext 绑定
DataContext是一个依赖属性,是绑定的默认源。DataContext沿着逻辑树继承。因此,如果您将DataContext设置给一个控件,逻辑树中的所有子元素也将引用相同的DataContext,除非明确指定了另一个源。
让我们举个例子来更详细地理解它
- 创建如下所示的
Book类
public class Book
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Author { get; set; }
}
- 添加XAML文件DataContextBinding.xaml并放置四个TextBlock,如下所示
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="40"/>
<RowDefinition Height="40"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock Text="Book Name:" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<TextBlock Grid.Column="1" />
<TextBlock Text="Author:" FontWeight="Bold" Grid.Row="1"/>
<TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1"/>
</Grid>
- 现在我们来看看这个
DataContext属性是如何用于显示数据的它有两种使用方式
- 使用 {Binding} 表达式 - 用于直接绑定
DataContext。创建
Book类的实例,初始化其属性,并将类的Name属性分配给Window的DataContext属性。public partial class DataContextBinding : Window { public DataContextBinding() { InitializeComponent(); //Create the instance Book book = new Book(); //initialize the properties book.Name = "Computer Networking"; //Assign the Property as DataContext this.DataContext = book.Name; } }由于
Datacontext沿着逻辑树继承,并且数据book.Name绑定到Control Window,Window的所有子元素也将引用相同的对象(book.Name)要显示数据,将
DataContext与Textblock绑定,如下所示<TextBlock Text="Book Name:" FontWeight="Bold"/> <TextBlock Text="{Binding}" Grid.Column="1" />输出

- 使用 {Binding Property} 表达式 - 绑定Datacontext的属性。
创建
Book类的实例,初始化其属性,并将类的实例(book)分配给Window的DataContext属性。Book book = new Book(); //initialize the properties book.Name = "Computer Networking"; book.Author = "James F. Kurose"; //Assign the instance as DataContext this.DataContext = book;
现在让我们看看输出。

由于绑定表达式 {Binding} 用于绑定类型为
Book的DataContext对象,因此将调用其ToString()方法,数据将以字符串形式显示。要以正确格式显示数据,我们必须将数据对象的属性与Textblock绑定,如下所示
<TextBlock Text="Book Name:" FontWeight="Bold"/> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Name}" Grid.Column="1" /> <TextBlock Text="Author:" FontWeight="Bold" Grid.Row="1" /> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Author}" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1"/>绑定表达式 {Binding Name} 用于绑定已绑定
DataContext的Name属性。输出

- 使用 {Binding} 表达式 - 用于直接绑定
RelativeSource 绑定
RelativeSource是一个属性,它设置绑定源与绑定目标的相对关系。此扩展主要用于将一个元素的属性绑定到同一元素的另一个属性。
RelativeSource有四种类型
- Self
- FindAncestor
- TemplatedParent
- PreviousData
让我们逐一详细探讨它们。
Self
Self用于绑定源和绑定目标相同的情况。对象的某个属性与同一对象的另一个属性绑定。
例如:让我们取一个高度和宽度相同的椭圆
在XAML文件中添加以下代码。Width属性与height属性相对绑定。
<Grid>
<Ellipse Fill="Black" Height="100"
Width="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self},Path=Height}">
</Ellipse>
</Grid>
输出

如果椭圆的高度改变,宽度也会相对改变。
FindAncestor
顾名思义,这在绑定源是绑定目标的祖先(父级)之一时使用。使用FindAncestor扩展,您可以查找任何级别的祖先。
让我们举个例子来更清楚地理解它。
步骤
创建一个XAML,表示以下元素逻辑树

<Grid Name="Parent_3">
<StackPanel Name="Parent_2">
<Border Name="Parent_1">
<StackPanel x:Name="Parent_0" Orientation="Vertical" >
<Button></Button>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
现在让我们使用FindAncestor扩展将祖先的Name属性绑定到子元素Button的Content属性。
<Grid Name="Parent_3">
<StackPanel Name="Parent_2" HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="100">
<Border Name="Parent_1">
<StackPanel x:Name="Parent_0" Orientation="Vertical" >
<Button Height="50"
Content="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource FindAncestor,
AncestorType={x:Type StackPanel},
AncestorLevel=2},Path=Name}"></Button>
</StackPanel>
</Border>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
输出

祖先类型 "StackPanel" 与祖先级别 "2" 结合,将按钮的Content属性与StackPanel (Parent_2) 的Name属性绑定。
TemplatedParent
TemplatedParent是一个属性,它使您能够创建具有一些未知值的控件模板。这些值取决于应用了ControlTemplate的控件的属性。
让我们举个例子来更详细地理解它
步骤
- 创建一个按钮的
ControlTemplate,如下所示<Window.Resources> <ControlTemplate x:Key="template"> <Canvas> <Ellipse Height="110" Width="155" Fill="Black"/> <Ellipse Height="100" Width="150" Fill="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}, Path=Background}"> </Ellipse> <ContentPresenter Margin="35" Content="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent},Path=Content}"/> </Canvas> </ControlTemplate> </Window.Resources>在上述代码示例中,
Ellipse的Fill属性和ContentPresenter的Content属性取决于将应用此模板的控件的属性值。 - 添加一个按钮并应用模板
<Button Margin="50" Background="Beige" Template="{StaticResource template}" Height="0" Content="Click me" FontSize="22"> </Button>应用模板后,按钮的背景(米色)相对绑定到
Ellipse的Fill属性,内容(点击我)相对绑定到ContentPresenter的Content属性。评估依赖值并给出以下输出。输出

PreviousData
这是RelativeSource使用最少的模式。当需要分析数据并表示值相对于之前数据的变化时,它就会出现。
让我们举个例子来更详细地理解它
步骤
- 创建
Data类并实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口,如下所示public class Data : INotifyPropertyChanged { public int DataValue { get; set; } public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged(string PropertyName) { if (null != PropertyChanged) { PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(PropertyName)); } } } - 创建类型为
Data的列表并将其分配为DataContextpublic RelativeSourcePreviousData() { InitializeComponent(); List<Data> data = new List<Data>(); data.Add(new Data() { DataValue = 60 }); data.Add(new Data() { DataValue = 100 }); data.Add(new Data() { DataValue = 120 }); this.DataContext = data; } - 在XAML文件中添加
ItemsControl<ItemsControl ItemsSource="{Binding}"></ItemsControl> - 为其创建
ItemsPanel模板,如下所示<ItemsControl ItemsSource="{Binding}"> <ItemsControl.ItemsPanel> <ItemsPanelTemplate> <StackPanel Orientation="Vertical" /> </ItemsPanelTemplate> </ItemsControl.ItemsPanel> </ItemsControl> - 现在为了正确表示数据,创建
DataTemplate,如下所示<ItemsControl.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Grid Margin="30,20,0,0"> <Rectangle Width="80" Height="{Binding DataValue}" Fill="Blue"/> <TextBlock Foreground="White" Margin="35,0,0,0" Text="{Binding DataValue}"></TextBlock> </Grid> <TextBlock Margin="30,20,0,0" Text="Previous Data:"></TextBlock> <TextBlock VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5,20,0,0" Text="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource PreviousData}, Path=DataValue}"/> </StackPanel> </DataTemplate> </ItemsControl.ItemTemplate>输出

蓝色框的高度是列表中项目的值,右侧显示了相对于框的先前数据。项目的第一个值是"60"。因此,第一个项目没有显示先前数据。
集合当前项绑定
当您使用集合时,会使用此功能。您可以使用此绑定表达式非常轻松地读取SelectedItem的属性。斜杠是用于处理集合中当前项的特殊运算符。
使用了三种表达式
- {Binding / }
- {Binding Collection / }
- {Binding Collection / Property}
{Binding / }
此表达式用于绑定DataContext中的当前项。
我们来看一个例子
在下面的例子中,DataContext是字符串类型的国家集合,并且与Listbox绑定
步骤
- 创建
Countries类并添加一个返回字符串数据类型国家集合的GetCountriesName()方法,如下所示public class Countries { public static List<string> GetCountriesName() { List<string> countries = new List<string>(); foreach (CultureInfo culture in CultureInfo.GetCultures(CultureTypes.SpecificCultures)) { RegionInfo country = new RegionInfo(culture.LCID); if (!countries.Contains(country.EnglishName)) countries.Add(country.EnglishName); } countries.Sort(); return countries; } } - 添加一个XAML文件,并添加
Listbox和TextBlock,如下所示<DockPanel Name="Collection"> <ListBox ItemsSource="{Binding}" IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem="True"> </ListBox> <TextBlock DockPanel.Dock="Top"/> </DockPanel> - 创建
Countries类的实例,并将Countries集合作为DataContextpublic CurrentItemCollection() { InitializeComponent(); Countries countries = new Countries(); this.DataContext = countries.GetCountriesName() } - 将TextBlock的
Text属性绑定到集合中当前选定的项目,如下所示<TextBlock DockPanel.Dock="Top" Text="{Binding /}" />输出
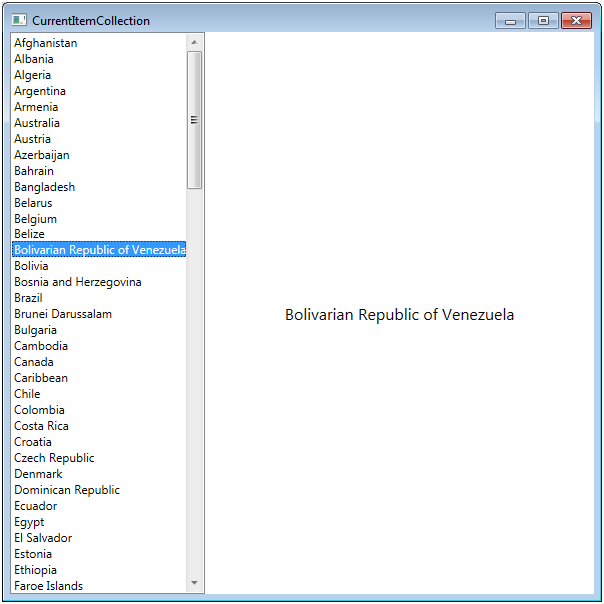
一旦项目被选中,它会在右侧显示选定的国家。
{Binding Collection / }
此表达式用于绑定DataContext中Collection属性的当前项。
示例
DataContext是Countries类
Collection属性是CounriesList,它与ListBox绑定
步骤
- 使用上面创建的
Countries类,略有不同。创建一个返回类型为RegionInfo的方法public static List<RegionInfo> GetCountries() { List<RegionInfo> countries = new List<RegionInfo>(); foreach (CultureInfo culture in CultureInfo.GetCultures(CultureTypes.SpecificCultures)) { RegionInfo country = new RegionInfo(culture.LCID); if (countries.Where(p => p.Name == country.Name).Count() == 0) countries.Add(country); } return countries.OrderBy(p => p.EnglishName).ToList(); } - 添加一个类型为
RegionInfo的CountriesList属性private List<RegionInfo> countries = null; public List<RegionInfo> CountriesList { get { if (countries == null) countries = GetCountries(); return countries; } }以下是
CountriesList集合中的值截图
- 将
Countries类指定为DataContext,并将Listbox与DataContext的CountriesList属性绑定<Window.Resources> <vm:Countries x:Key="Countries"></vm:Countries> </Window.Resources> <Grid> <DockPanel Name="Collection" DataContext="{StaticResource Countries}"> <ListBox ItemsSource="{Binding CountriesList}" IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem="True"> <ListBox.ItemTemplate> <DataTemplate> <TextBlock Text="{Binding EnglishName}"></TextBlock> </DataTemplate> </ListBox.ItemTemplate> </ListBox> </DockPanel> </Grid> - 为了评估
CountriesList属性的当前项,将TextBlock的Text属性绑定如下。<TextBlock DockPanel.Dock="Top" Text="{Binding CountriesList/}" HorizontalAlignment="Center" FontSize="16" VerticalAlignment="Center" />输出

右侧显示DataContext(Countries)中集合(CountriesList)的当前项
{Binding Collection / Property}
此表达式用于绑定DataContext中集合当前项的属性
例如,如果我们必须评估CountriesList集合中当前项的特定属性。
在此示例中,我想显示属性"EnglishName"的值。

为此,将TextBlock的Text属性绑定如下
<TextBlock DockPanel.Dock="Top"
Text="{Binding CountriesList/EnglishName}" />
输出

现在,当列表中选择项目时,它会显示属性"EnglishName"的值。
结论
我已详细介绍了所有数据绑定表达式。希望这能帮助您理解WPF提供的绑定概念和表达式。
