WCF 服务中的异步通信
4.70/5 (17投票s)
WCF 服务与控制台客户端之间的异步通信。
引言
本文将分步介绍 WCF 中异步通信的实现。
背景
异步模式是一种在基于执行的系统中非常知名且常见的*设计模式*。
与其他许多技术一样,此模式在 Windows Communication Foundation 中也有实现。
NET Framework 提供了两种*设计模式*用于异步操作
- 使用
IAsyncResult对象的异步操作。 - 使用事件的异步操作。
本文使用 IAsyncResult 实现进行异步通信。
异步通信的需求
对于应用程序中的长时间运行的执行,当前线程可能会停止执行,因为它可能会*阻止用户界面*。例如,当 Windows 应用程序进入新的状态以执行长时间运行的进程时,Windows 可能会*冻结甚至崩溃*。一种解决方案是将此执行*移至另一个线程*并让其在那里继续。
异步模式在此发挥作用以解决此问题,Microsoft 在其强大的 .NET Framework 中为该模式提供了*内置机制*。Microsoft 对此模式的实现*包括以下几个部分*
- 异步操作的*两种方法*。
- 实现
IAsyncCallback接口的*对象*。 - 回调*委托*。
这样,方法的执行*分为两个步骤*。第一步,您创建后台进程并启动它,第二步,您*监听进程的变化*并等待其完成。
使用代码
下面简要介绍*示例项目中使用的类*
AsyncResult
public class AsyncResult : IAsyncResult, IDisposable
{
AsyncCallback callback;
object state;
ManualResetEvent manualResentEvent;
public AsyncResult(AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
this.callback = callback;
this.state = state;
this.manualResentEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
}
AsyncResult 派生自 IAsyncResult。
AsyncResult 包含一些属性,例如 AsyncCallback、状态对象以及处理*异步操作等待*的 ManualResetEvent。有一个 IsCompleted 属性,它返回一个布尔值以指定操作是否*已异步完成*,简单的 WaitOne(0, false) 方法调用*始终为任何异步操作返回相应的值*。最后一点是关于 Complete() 方法。它*调用我的 ManualResetEvent 的 Set() 方法*以表明我的事件已被*发出信号*,并且任何其他等待的线程都可以继续。然后,如果回调*不是 null*,我会将当前对象传递给回调。
AddAsyncResult
public class AddAsyncResult : AsyncResult
{
public readonly int number1 = 0;
public readonly int number2 = 0;
private int result;
public AddDataContract AddContract { get; set; }
public Exception Exception { get; set; }
public int Result
{
get { return result; }
set { result = value; }
}
public AddAsyncResult(int num1, int num2, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
: base(callback, state)
{
this.number1 = num1;
this.number2 = num2;
}
public AddAsyncResult(AddDataContract input, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
: base(callback, state)
{
this.AddContract = input;
}
}
AddAsyncResult 派生自 AsyncResult;它还保存*输入和输出的数据契约/实体*。我们需要根据要求开发此类。
WCF 服务实现
IAddService
[ServiceContract()]
public interface IAddService
{
[OperationContract(AsyncPattern = true)]
[FaultContract(typeof(ErrorInfo))]
IAsyncResult BeginAddDC(AddDataContract input,
AsyncCallback callback, object state);
//[FaultContract(typeof(ErrorInfo))]
AddDataContract EndAddDC(IAsyncResult ar);
}
此服务具有 BeginAddDC 方法,该方法使用 AsyncPattern=true*声明为异步方法*。
AddService
public IAsyncResult BeginAddDC(AddDataContract input, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
AddAsyncResult asyncResult = null;
try
{
//throw new Exception("error intorduced here in BeginAddDC.");
asyncResult = new AddAsyncResult(input, callback, state);
//Queues a method for execution. The method executes
//when a thread pool thread becomes available.
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(CallbackDC), asyncResult);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "BeginAddDC faills");
throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
return asyncResult;
}
public AddDataContract EndAddDC(IAsyncResult ar)
{
AddDataContract result = null;
try
{
//throw new Exception("error intorduced here in EndAddDC.");
if (ar != null)
{
using (AddAsyncResult asyncResult = ar as AddAsyncResult)
{
if (asyncResult == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("IAsyncResult parameter is null.");
if (asyncResult.Exception != null)
throw asyncResult.Exception;
asyncResult.AsyncWait.WaitOne();
result = asyncResult.AddContract;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "EndAddDC faills");
throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
return result;
}
private void CallbackDC(object state)
{
AddAsyncResult asyncResult = null;
try
{
asyncResult = state as AddAsyncResult;
//throw new Exception("error intorduced here in CallbackDC.");
//throw new Exception("service fails");
asyncResult.AddContract = InternalAdd(asyncResult.AddContract);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
asyncResult.Exception = ex;
//ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "CallbackDC faills");
//throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
finally
{
asyncResult.Complete();
}
}
private int InternalAdd(int number1, int number2)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(20));
return number1 + number2;
}
BeginAddDC 将一个名为 CallBackDC 的方法*排入队列*,以便在*线程池中的线程可用时*执行它,并*立即返回给客户端*。然后,此 CallBackDC 方法*在单独的线程上执行*客户端请求的实际处理,并在完成处理后*发出 ManualResetEvent 的信号*。
EndAddDC 仅*从 IAsyncResult 中获取实际结果*并将其返回。
客户端
客户端*仅创建服务代理*并调用服务的 BeginAddDC 方法。除了业务相关的参数外,它还*传递一个回调方法*(一旦 WCF 服务执行完成,*控制就会在此处落下*)和一个*状态对象*。
IAsyncResult res = service.BeginAddDC(input, new AsyncCallback(AddCallbackDC), service);
客户端回调方法
static void AddCallbackDC(IAsyncResult ar)
{
try
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine("in AddCallbackDC");
IAddService res = ar.AsyncState as IAddService;
if (res != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Result returned from WCF service");
Console.WriteLine(res.EndAddDC(ar).Result.ToString());
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
finally
{
if (addProxy != null)
{
addProxy.CloseProxy();
Console.WriteLine("Proxy closed.");
}
Console.ResetColor();
}
此回调方法*从 IAsyncResult.AsyncState 中提取服务对象*,并调用 WCF 服务的 EndAddDC 以*在客户端端获取实际结果*。
输出
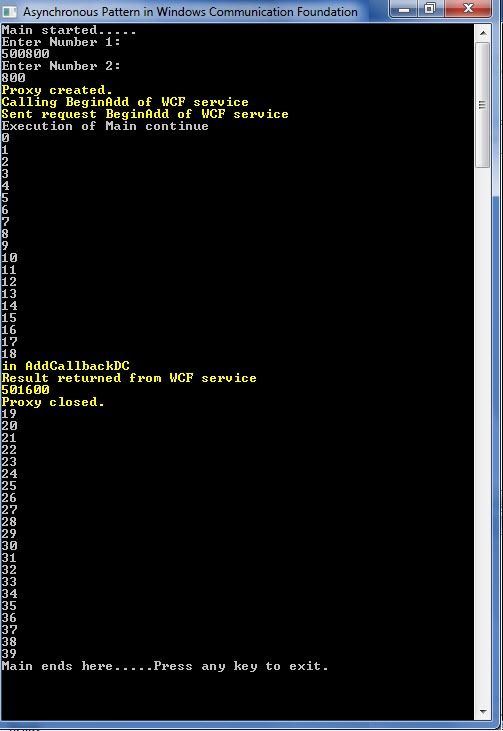
如下面的屏幕截图所示,在提供两个数字后,客户端会创建一个代理并调用其 BeginAddDC 方法,然后*立即返回到客户端并继续其执行*(开始打印数字),直到*收到 WCF 服务的响应*。收到响应后,它会显示响应并继续主执行。
处理 FaultException
如果在 WCF 服务中的 Begin/End 方法中*发生任何异常*,则可以直接*作为 FaultException 引发*。
catch (Exception ex)
{
ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "BeginAddDC faills");
throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
但是,如果*异常发生在 WCF 服务中*,在我们*在单独线程上运行的方法*(在本例中为 CallBackDC)中,该怎么办?
private void CallbackDC(object state)
{
AddAsyncResult asyncResult = null;
try
{
asyncResult = state as AddAsyncResult;
//throw new Exception("error intorduced here in CallbackDC.");
//throw new Exception("service fails");
asyncResult.AddContract = InternalAdd(asyncResult.AddContract);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
asyncResult.Exception = ex;
//ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "CallbackDC faills");
//throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
finally
{
asyncResult.Complete();
}
}
为了处理此类异常,我们可以*在 AsyncResult 中添加一个 Exception 属性*,并在服务中的回调方法中*发生异常时填充此属性*。然后,您可以在*相关的 End 方法中检查此 Exception 属性*。可以*从此 End 方法中引发 FaultException*。
public AddDataContract EndAddDC(IAsyncResult ar)
{
AddDataContract result = null;
try
{
//throw new Exception("error intorduced here in EndAddDC.");
if (ar != null)
{
using (AddAsyncResult asyncResult = ar as AddAsyncResult)
{
if (asyncResult == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("IAsyncResult parameter is null.");
if (asyncResult.Exception != null)
throw asyncResult.Exception;
asyncResult.AsyncWait.WaitOne();
result = asyncResult.AddContract;
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ErrorInfo err = new ErrorInfo(ex.Message, "EndAddDC faills");
throw new FaultException<ErrorInfo>(err, "reason goes here.");
}
return result;
}
在客户端端,您可以在*客户端的回调方法中捕获所有异常*。
需要注意的点
- 声明*两个相关方法*:一个名为
BeginMethodName,另一个名为EndMethodName。 - 将
[OperationContract(AsyncPattern = true)]*添加到相应的 Begin 方法*。 - *不要*将
OperationContract属性添加到*相应的 End 方法*。 - 在服务实现中,*实际处理应该放在一个方法中*,并且此方法*应该在单独的线程上运行*。为了确保这一点,请使用
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem。 - 在客户端端,*调用相应的 Begin 方法*,但*不要在此之后关闭代理*,因为 End 方法需要*相同的通道来获取结果*。您可以在调用 End 方法后在*客户端的回调中关闭它*。
