ASP.NET Core 结合 Dapper 和 VS 2017 使用 JWT 身份验证 WEB API 并在 Angular2 客户端应用程序中使用
5.00/5 (4投票s)
ASP.NET Core 使用 JWT 身份验证 WEB API 并在 Angular2 客户端应用程序中使用,并进行适当的项目结构设置。
引言
我试图在 web API 中实现 JWT 身份验证。我想在我的 Angular 2 客户端应用程序中使用 Web API。但是在互联网上搜索时,我没有找到任何针对我的问题且具有**项目架构设置**的正确解决方案。最后,我终于找到了解决此问题的实际步骤,这可以帮助您节省大量时间来检查此解决方案中的内容。因此,以下是详细说明。
源代码链接:https://github.com/rajeshdas85/JwtAuthentication
- ASP.NET Core 中带有 JWT 身份验证的项目解决方案的 Web API
- Angular2/4 用于客户端应用程序
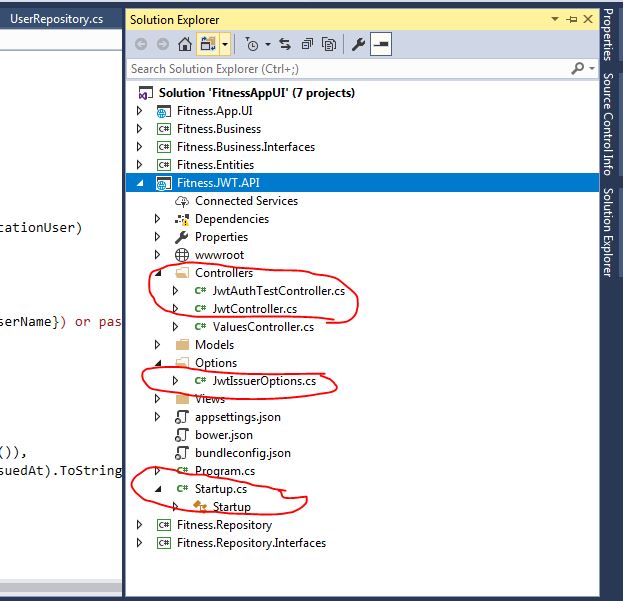
请参阅下面的项目结构
背景
步骤 1
创建 ASP.NET Core Web API 项目
Fitness.JWT.API 项目说明
我想解释一下项目源代码中突出显示的部分,以启用 Jwt 身份验证。
Using the Code
startup.cs
配置 secretkey,允许**跨域**并应用 使用策略身份验证。
//
public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; }
//SecretKey for Authentication
private const string SecretKey = "ABCneedtogetthisfromenvironmentXYZ";
private readonly SymmetricSecurityKey _signingKey =
new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(SecretKey));
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
// Add framework services.
// services.AddMvc();
// Add framework services.
// Add framework services.
services.AddCors(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CorsPolicy",//Allow Cross origin
builder => builder.AllowAnyOrigin()
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowCredentials());
});
services.AddOptions();
// Make authentication compulsory across the board (i.e. shut
// down EVERYTHING unless explicitly opened up).
services.AddMvc(config =>
{
var policy = new AuthorizationPolicyBuilder()
.RequireAuthenticatedUser()
.Build();
config.Filters.Add(new AuthorizeFilter(policy));
});
// Use policy auth.
services.AddAuthorization(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("FitnessJWT",
policy => policy.RequireClaim("FitnessJWT", "FitnessUser"));
});
// Get options from app settings
var jwtAppSettingOptions = Configuration.GetSection(nameof(JwtIssuerOptions));
// Configure JwtIssuerOptions
services.Configure<JwtIssuerOptions>(options =>
{
options.Issuer = jwtAppSettingOptions[nameof(JwtIssuerOptions.Issuer)];
options.Audience = jwtAppSettingOptions[nameof(JwtIssuerOptions.Audience)];
options.SigningCredentials = new SigningCredentials
(_signingKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
});
}
//
JwtIssuerOptions.cs
此类文件负责在服务器中创建 Auth 唯一票证。
//
public class JwtIssuerOptions
{
/// <summary>
/// "iss" (Issuer) Claim
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "iss" (issuer) claim identifies the principal that issued the
/// JWT. The processing of this claim is generally application specific.
/// The "iss" value is a case-sensitive string containing a StringOrURI
/// value. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public string Issuer { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// "sub" (Subject) Claim
/// </summary>
/// <remarks> The "sub" (subject) claim identifies the principal that is the
/// subject of the JWT. The claims in a JWT are normally statements
/// about the subject. The subject value MUST either be scoped to be
/// locally unique in the context of the issuer or be globally unique.
/// The processing of this claim is generally application specific. The
/// "sub" value is a case-sensitive string containing a StringOrURI
/// value. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public string Subject { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// "aud" (Audience) Claim
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "aud" (audience) claim identifies the recipients that the JWT is
/// intended for. Each principal intended to process the JWT MUST
/// identify itself with a value in the audience claim. If the principal
/// processing the claim does not identify itself with a value in the
/// "aud" claim when this claim is present, then the JWT MUST be
/// rejected. In the general case, the "aud" value is an array of case-
/// sensitive strings, each containing a StringOrURI value. In the
/// special case when the JWT has one audience, the "aud" value MAY be a
/// single case-sensitive string containing a StringOrURI value. The
/// interpretation of audience values is generally application specific.
/// Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public string Audience { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// "nbf" (Not Before) Claim (default is UTC NOW)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "nbf" (not before) claim identifies the time before which the JWT
/// MUST NOT be accepted for processing. The processing of the "nbf"
/// claim requires that the current date/time MUST be after or equal to
/// the not-before date/time listed in the "nbf" claim. Implementers MAY
/// provide for some small leeway, usually no more than a few minutes, to
/// account for clock skew. Its value MUST be a number containing a
/// NumericDate value. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public DateTime NotBefore => DateTime.UtcNow;
/// <summary>
/// "iat" (Issued At) Claim (default is UTC NOW)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "iat" (issued at) claim identifies the time at which the JWT was
/// issued. This claim can be used to determine the age of the JWT. Its
/// value MUST be a number containing a NumericDate value. Use of this
/// claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public DateTime IssuedAt => DateTime.UtcNow;
/// <summary>
/// Set the timespan the token will be valid for (default is 3 min/180 seconds)
/// </summary>
public TimeSpan ValidFor { get; set; } = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1);
/// <summary>
/// "exp" (Expiration Time) Claim (returns IssuedAt + ValidFor)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "exp" (expiration time) claim identifies the expiration time on
/// or after which the JWT MUST NOT be accepted for processing. The
/// processing of the "exp" claim requires that the current date/time
/// MUST be before the expiration date/time listed in the "exp" claim.
/// Implementers MAY provide for some small leeway, usually no more than
/// a few minutes, to account for clock skew. Its value MUST be a number
/// containing a NumericDate value. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public DateTime Expiration => IssuedAt.Add(ValidFor);
/// <summary>
/// "jti" (JWT ID) Claim (default ID is a GUID)
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>The "jti" (JWT ID) claim provides a unique identifier for the JWT.
/// The identifier value MUST be assigned in a manner that ensures that
/// there is a negligible probability that the same value will be
/// accidentally assigned to a different data object; if the application
/// uses multiple issuers, collisions MUST be prevented among values
/// produced by different issuers as well. The "jti" claim can be used
/// to prevent the JWT from being replayed. The "jti" value is a case-
/// sensitive string. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.</remarks>
public Func<Task<string>> JtiGenerator =>
() => Task.FromResult(Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
/// <summary>
/// The signing key to use when generating tokens.
/// </summary>
public SigningCredentials SigningCredentials { get; set; }
}
//
JwtController.cs
它是匿名用户将登录的控制器,它创建 JWT 安全令牌并对其进行编码,然后将其作为带有策略的响应发送回客户端。
identity.FindFirst("FitnessJWT")
请参见下面的代码
[HttpPost]
[AllowAnonymous]
public async Task<IActionResult> Get([FromBody] ApplicationUser applicationUser)
{
var identity = await GetClaimsIdentity(applicationUser);
if (identity == null)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Invalid username ({applicationUser.UserName})
or password ({applicationUser.Password})");
return BadRequest("Invalid credentials");
}
var claims = new[]
{
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Sub, applicationUser.UserName),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Jti, await _jwtOptions.JtiGenerator()),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Iat,
ToUnixEpochDate(_jwtOptions.IssuedAt).ToString(), ClaimValueTypes.Integer64),
identity.FindFirst("FitnessJWT")
};
// Create the JWT security token and encode it.
var jwt = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: _jwtOptions.Issuer,
audience: _jwtOptions.Audience,
claims: claims,
notBefore: _jwtOptions.NotBefore,
expires: _jwtOptions.Expiration,
signingCredentials: _jwtOptions.SigningCredentials);
var encodedJwt = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(jwt);
// Serialize and return the response
var response = new
{
access_token = encodedJwt,
expires_in = (int)_jwtOptions.ValidFor.TotalSeconds,
State=1,
expire_datetime= _jwtOptions.IssuedAt
};
var json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(response, _serializerSettings);
return new OkObjectResult(json);
}
JwtAuthTestController.cs
在此控制器中,我定义了策略 [Authorize(Policy = "FitnessJWT")] ,因此当用户请求该控制器时,它必须与策略和密钥匹配,然后响应才会返回给客户端。
[HttpGet("[action]")]
[Authorize(Policy = "FitnessJWT")]
public IActionResult WeatherForecasts()
{
var rng = new Random();
List<WeatherForecast> lstWeatherForeCast = new List<WeatherForecast>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
WeatherForecast obj = new WeatherForecast();
obj.DateFormatted = DateTime.Now.AddDays(i).ToString("d");
obj.TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55);
obj.Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)];
lstWeatherForeCast.Add(obj);
}
var response = new
{
access_token = lstWeatherForeCast,
State = 1
};
var json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(response, _serializerSettings);
return new OkObjectResult(json);
}
步骤 2:Angular2/4 用于客户端应用程序
我想添加一个。我不太关注 UI 部分,但是我尝试从 Angualar2/4 应用程序实现 JWT 身份验证。
Fitness.App.UI 解决方案
login.component.ts
使用 typescript 传递用户名和密码的登录模块
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import { AuthService } from "../../../app/services/auth.service";
import { LoginModel } from "../../model/login.model";
@Component({
selector: 'Fitness-Login',
templateUrl: './login.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./login.component.css'],
providers: [AuthService]
})
export class LoginComponent {
loginModel = new LoginModel();
constructor(private router: Router, private authService: AuthService) {
}
login() {
this.authService.login(this.loginModel.userName, this.loginModel.password)
.then(result => {
if (result.State == 1) {
this.router.navigate(["/nav-menu"]);
}
else {
alert(result.access_token);
}
});
}
}
auth.service.ts
身份验证服务,用于验证凭据并将重定向到主页。
login(userName: string, password: string): Promise<ResponseResult> {
let data = {
"userName": userName,
"password": password
}
let headers = new Headers({ 'Content-Type': 'application/json' });
let applicationUser = JSON.stringify(data);
let options = new RequestOptions({ headers: headers });
if (this.checkLogin()) {
return this.authPost(this.localUrl + '/api/Jwt', applicationUser, options);
}
else {
return this.http.post(this.localUrl + '/api/Jwt', applicationUser, options).toPromise()
.then(
response => {
let result = response.json() as ResponseResult;
if (result.State == 1) {
let json = result.access_token as any;
localStorage.setItem(this.tokeyKey, json);
localStorage.setItem(this.tokeyExpKey, result.expire_datetime);
this.sg['isUserExist'] = true;
}
return result;
}
)
.catch(this.handleError);
}
}
app.module.client.ts
{ provide: 'ORIGIN_URL', useValue: 'https://:57323' },JWT WEB API 上的路径。
您需要根据机器 URL 更改本地主机 API。
@NgModule({
bootstrap: sharedConfig.bootstrap,
declarations: sharedConfig.declarations,
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpModule,
...sharedConfig.imports
],
providers: [
//{ provide: 'ORIGIN_URL', useValue: location.origin },
{ provide: 'ORIGIN_URL', useValue: 'https://:57323' },
AuthService, AuthGuard, SimpleGlobal
]
})
export class AppModule {
}
要运行该应用程序,您需要将项目设置为如下
使用多个启动项目运行解决方案。
然后在浏览器中的两个选项卡中,客户端应用程序和 web API 服务都将启动。
应用程序上的输出如下
用户名:Test 和密码:Test
然后,它将重定向到导航菜单页面,如下所示
关注点
在撰写此博客时,我感到非常愉快。
历史
如果需要任何改进,请更新代码。