关于Hibernate - One To Many的注意事项
Hibernate一对多映射。
背景
这是一篇关于 Hibernate 单对多映射的笔记。在开始示例之前,我想先澄清几个 Hibernate 中常用的术语。
SessionFactory 与 Session
- SessionFactory - Hibernate 中的
SessionFactory是一个包含如何连接到数据库的所有配置信息的对象。- A
SessionFactory是不可变的; SessionFactory的行为由配置时提供的属性控制;- 创建
SessionFactory是一个缓慢且开销很大的过程; - 一个应用程序通常只有一个
SessionFactory; SessionFactory对象是线程安全的。
- A
- Session - Hibernate 中的
session是一个与数据库通信的对象。- 每个
session都有自己的数据库连接; session是由SessionFactory对象的openSession()方法创建的;- 创建
session对象是一个轻量级的过程; session应在数据库操作完成后关闭,以释放数据库连接;session对象不是线程安全的。
- 每个
瞬态 (Transient) vs. 持久化 (Persistent) vs. 游离 (Detached)
根据 Hibernate Session 文档,实体对象可以有三种状态。
- 如果一个实体对象在
Hibernate session外部创建,并且从未与Hibernate session关联,则它是瞬态的; - 如果一个实体对象已与
Hibernate session关联,则它是持久化的;- 瞬态对象可以通过
session.save()或session.persist()方法添加到session中; - 如果实体对象是通过
Hibernate session从数据库加载/获取的,则它是持久化状态。
- 瞬态对象可以通过
- 如果
session被关闭,或者在该对象上调用了 Session.evict() 方法,则持久化对象会变成游离对象。
FlushMode
FlushMode 代表一种刷新策略。刷新过程通过检测状态变化并执行 SQL 语句来同步数据库状态与 session 状态。Hibernate 有四种刷新模式。
ALWAYS-Session在每次查询之前都会被刷新;AUTO-Session有时会在查询执行前刷新,以确保查询永远不会返回过时的状态;COMMIT-Session在调用Transaction.commit()时被刷新;MANUAL-Session仅在应用程序显式调用Session.flush()时才被刷新。
示例

附带的是一个 Maven 项目,它对与单对多映射相关的实体执行一组单元测试 CRUD 操作。该示例使用 MySQL 数据库。如果您不熟悉 MySQL,可以参考 我之前的笔记。您可以使用以下 SQL 来创建测试中使用的表。
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS experimentA;
CREATE DATABASE experimentA;
USE experimentA;
CREATE TABLE Parent (
Id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
Name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
CREATE TABLE Child (
Id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
ParentID int(11) NOT NULL,
Name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Id),
FOREIGN KEY (ParentID) REFERENCES Parent (Id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
CREATE TABLE GrandChild (
Id int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
ParentID int(11) NOT NULL,
Name varchar(45) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Id),
FOREIGN KEY (ParentID) REFERENCES Child (Id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
[Child] 表在 [Parent] 表上有一个外键引用,[GrandChild] 表在 [Child] 表上有一个外键引用。以下是对应的 Hibernate 实体类。
package com.song.example.hibernate.entities;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Parent")
public class Parent {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set<Child> children = new HashSet<Child>();
public Parent() {}
public Parent(String name) { this.name = name; }
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "Id")
public Integer getId() { return this.id; }
public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; }
@Column(name = "Name", length = 100)
public String getName() { return this.name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "parent", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
public Set<Child> getChildren() { return this.children; }
public void setChildren(Set<Child> children) { this.children = children; }
}
package com.song.example.hibernate.entities;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "Child")
public class Child {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Parent parent;
private Set<GrandChild> grandChildren = new HashSet<GrandChild>();
public Child() {}
public Child(String name, Parent parent) {
this.name = name;
this.parent = parent;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "Id")
public Integer getId() { return this.id; }
public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; }
@Column(name = "Name", length = 100)
public String getName() { return this.name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "ParentID", nullable = false)
public Parent getParent() { return this.parent; }
public void setParent(Parent parent) { this.parent = parent; }
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "parent", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
public Set<GrandChild> getChildren() { return this.grandChildren; }
public void setChildren(Set<GrandChild> grandChildren) {
this.grandChildren = grandChildren;
}
}
package com.song.example.hibernate.entities;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "GrandChild")
public class GrandChild {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Child parent;
public GrandChild() {}
public GrandChild(String name, Child parent) {
this.name = name;
this.parent = parent;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "Id")
public Integer getId() { return this.id; }
public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; }
@Column(name = "Name", length = 100)
public String getName() { return this.name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "ParentID", nullable = false)
public Child getParent() { return this.parent; }
public void setParent(Child parent) { this.parent = parent; }
}
为了创建 Hibernate SessionFactory,将以下 hibernate.cfg.xml 文件添加到 resources 目录。
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
</property>
<property name="connection.url">
jdbc:mysql:///experimentA
</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">password</property>
<property name="dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
</property>
<property name="cache.provider_class">
org.hibernate.cache.NoCacheProvider
</property>
<property name="org.hibernate.flushMode">MANUAL</property>
<property name="show_sql">false</property>
<property name="format_sql">false</property>
<mapping class="com.song.example.hibernate.entities.Parent" />
<mapping class="com.song.example.hibernate.entities.Child" />
<mapping class="com.song.example.hibernate.entities.GrandChild" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
SessionFactoryInstance.java 用于创建一个单例 SessionFactory 实例。这可能不是创建 SessionFactory 的最佳方法,但对于小型单元测试项目来说,它可以节省我一些打字的时间。
package com.song.example.hibernate;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public final class SessionFactoryInstance {
private SessionFactoryInstance(){}
public final static SessionFactory Instance
= new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
}
SessionFactory 在 PCG_Test.java 中用于执行 CRUD 操作的单元测试。
package com.song.example.hibernate;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.hibernate.FlushMode;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import com.song.example.hibernate.entities.Child;
import com.song.example.hibernate.entities.GrandChild;
import com.song.example.hibernate.entities.Parent;
public class PCG_Test {
private final SessionFactory sessionFactory
= SessionFactoryInstance.Instance;
private Parent parent = null;
private Child child = null;
private GrandChild grandChild = null;
@BeforeTest
public void Init() {
Assert.assertNotNull(sessionFactory);
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
FlushMode flushmode = session.getHibernateFlushMode();
Assert.assertEquals(flushmode, FlushMode.MANUAL);
session.doWork(connection -> {
try (Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.execute("SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 0");
statement.execute("TRUNCATE TABLE GrandChild;");
statement.execute("TRUNCATE TABLE Child;");
statement.execute("TRUNCATE TABLE Parent;");
statement.execute("SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS = 1");
}
});
}
// Initiate test data
this.parent = new Parent("Parent");
this.child = new Child("Child", this.parent);
this.grandChild = new GrandChild("Grand child", this.child);
this.parent.getChildren().add(this.child);
this.child.getChildren().add(this.grandChild);
}
@Test
public void Insert_Test() {
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Transaction tx = session.getTransaction();
try {
tx.begin();
session.save(parent);
session.flush();
tx.commit();
}
catch(Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
Assert.fail("Failed - Insert_Test");
}
}
// Validate data is inserted
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, this.parent.getId());
Child child = parent.getChildren().iterator().next();
GrandChild grandChild = child.getChildren().iterator().next();
Assert.assertEquals(parent.getName(), this.parent.getName());
Assert.assertEquals(child.getName(), this.child.getName());
Assert.assertEquals(grandChild.getName(), this.grandChild.getName());
}
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = {"Insert_Test"})
public void Update_Test() {
final String newParentName = "New Parent Name";
final String newChildName = "New Child Name";
final String newGrandChildName = "New Grand Child Name";
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Transaction tx = session.getTransaction();
Integer id = this.parent.getId();
try {
tx.begin();
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, id);
Child child = parent.getChildren().iterator().next();
GrandChild grandChild = child.getChildren().iterator().next();
parent.setName(newParentName);
child.setName(newChildName);
grandChild.setName(newGrandChildName);
session.flush();
tx.commit();
}
catch(Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
Assert.fail("Failed - Update_Test");
}
}
// Validate data is updated
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, this.parent.getId());
Child child = parent.getChildren().iterator().next();
GrandChild grandChild = child.getChildren().iterator().next();
Assert.assertEquals(parent.getName(), newParentName);
Assert.assertEquals(child.getName(), newChildName);
Assert.assertEquals(grandChild.getName(), newGrandChildName);
}
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = {"Update_Test"})
public void Delete_Child_Test() {
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Transaction tx = session.getTransaction();
Integer id = this.parent.getId();
try {
tx.begin();
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, id);
Child child = parent.getChildren().iterator().next();
parent.getChildren().remove(child);
session.delete(child);
session.flush();
tx.commit();
}
catch(Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
Assert.fail("Failed - Delete_Child_Test");
}
}
// Validate child is deleted
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, this.parent.getId());
Assert.assertEquals(parent.getChildren().size(), 0);
}
}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = {"Delete_Child_Test"})
public void Delete_ALL_Test() {
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Transaction tx = session.getTransaction();
Integer id = this.parent.getId();
try {
tx.begin();
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, id);
session.delete(parent);
session.flush();
tx.commit();
}
catch(Exception e) {
tx.rollback();
Assert.fail("Failed - Delete_ALL_Test");
}
}
// Validate all data is deleted
try (Session session = sessionFactory.openSession()) {
Parent parent = session.get(Parent.class, this.parent.getId());
Assert.assertNull(parent);
}
}
}
Init()方法清除数据库中的所有数据,为测试提供一个全新的开始;Insert_Test()方法将所有数据插入数据库。session.save()只应用于父对象,但所有子对象和孙对象都会级联保存;Update_Test()方法更新已保存在数据库中的数据;Delete_Child_Test()方法从父对象中删除一个子对象;Delete_ALL_Test()方法删除数据库中的所有对象。session.delete()只应用于父对象,但所有子对象和孙对象都会级联删除。
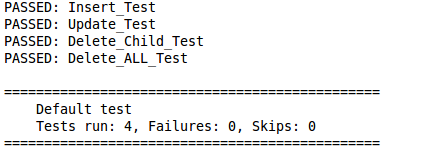
运行单元测试
要运行单元测试,您需要运行 MySQL 服务器。您可以通过以下命令在 Linux 系统中启动 MySQL 服务器。
sudo service mysql start
然后您就可以通过 Maven 命令运行单元测试了。
mvn test
如果您将项目加载到 Eclipse 中,也可以通过 TestNG 插件运行单元测试。
关注点
- 这是一篇关于 Hibernate 单对多映射的笔记。
- 希望您喜欢我的帖子,也希望这篇笔记能以某种方式帮助到您。
历史
- 2017年12月24日:首次修订
