重塑神经网络 - 第三部分
4.60/5 (7投票s)
现在我们已经完成了基础知识,是时候进行改进了!
完整系列
- 第 1 部分:我们从头开始创建整个
NeuralNetwork类。 - 第 2 部分:我们在 Unity 中创建一个环境,以便在该环境中测试神经网络。
- 第 3 部分:我们通过向代码添加一种新型的变异,对已经创建的神经网络进行重大改进。
引言
在我开始之前,我得承认我 16 岁了,因为我有点注意到人们在知道这件事后会打嗝,所以我想...也许如果人们知道,我会从中得到更多。只是说说而已。
欢迎回来伙计们!大约一个月前,我发布了本系列的第 2 部分。之后,我真的忙于做一堆其他的事情,这让我无法继续做我真正想做的事情(对此感到抱歉)。然而,几天前,Michael Bartlett 向我发送了一封电子邮件,询问一种名为安全变异(或简称 SA)的 GA 运算符(参考这篇论文)。
背景
为了理解本文,您需要具备基本的 C# 和 Unity 编程知识。 另外,您需要阅读本系列的第 1 部分和第 2 部分。
理解理论
根据 Michael 发送的论文,似乎有两种类型的 SM 运算符
- 通过重新缩放的安全变异:简而言之,这就像稍微调整权重以了解这个位对输出的影响有多大,并据此进行明智的变异。
- 通过梯度的安全变异:这与反向传播中使用的获取每个权重的梯度的方法类似,并据此也进行明智的变异。
然而,这仍然没有给我足够的开始编码的信息,所以我一直寻找直到我找到这篇论文。 这篇论文表明,如果您仅仅使用一些就在您面前的信息,您可以获得多么大的改进。 如果您查看该论文中的图 4,您会看到无偏突变会产生最差的结果,而节点突变会产生指数级更好的结果! 好吧,它甚至可以匹配交叉!


它甚至与安全变异(通过梯度)和反向传播在图 7 和 8 中进行了比较。 它要么与安全变异打成平手,而节点变异击败了反向传播......


好吧... 那么什么是神奇的“Mutate Nodes”运算符? 好吧... 普通的突变只是选择一些权重并按如下方式对它们进行突变

然而,节点突变选择一些节点并突变所有进入它的权重
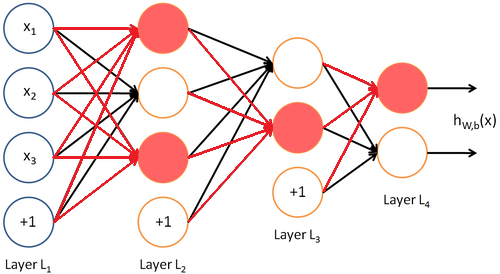
Using the Code
好吧,代码非常简单。 首先,将 MutateNodes 函数添加到 NeuralSection 类
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralSection's Nodes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a node is going
/// to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">The maximum amount
/// a Mutated Weight would change.</param>
public void MutateNodes(double MutationProbablity, double MutationAmount)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[0].Length; j++) // For each output node
{
if (TheRandomizer.NextDouble() < MutationProbablity) // Check if we are going
// to mutate this node
{
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++) // For each input node
// connected to the
// current output node
{
Weights[i][j] = TheRandomizer.NextDouble() *
(MutationAmount * 2) - MutationAmount; // Mutate the
// weight connecting both nodes
}
}
}
}
然后,将调用函数添加到 NeuralNetwork 类
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralNetwork's Nodes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a node
/// is going to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">
/// The maximum amount a Mutated Weight would change.</param>
public void MutateNodes(double MutationProbablity = 0.3, double MutationAmount = 2.0)
{
// Mutate each section
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Sections[i].MutateNodes(MutationProbablity, MutationAmount);
}
}
这几乎就是它了! 这就是 NeuralNetwork.cs 现在应该的样子
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
public class NeuralNetwork
{
public UInt32[] Topology // Returns the topology in the form of an array
{
get
{
UInt32[] Result = new UInt32[TheTopology.Count];
TheTopology.CopyTo(Result, 0);
return Result;
}
}
ReadOnlyCollection<UInt32> TheTopology; // Contains the topology of the NeuralNetwork
NeuralSection[] Sections; // Contains the all the sections of the NeuralNetwork
Random TheRandomizer; // It is the Random instance used
// to mutate the NeuralNetwork
private class NeuralSection
{
private double[][] Weights; // Contains all the weights of the section
// where [i][j] represents the weight from
// neuron i in the input layer and neuron j
// in the output layer
private Random TheRandomizer; // Contains a reference to the Random instance
// of the NeuralNetwork
/// <summary>
/// Initiate a NeuralSection from a topology and a seed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="InputCount">The number of input neurons in the section.</param>
/// <param name="OutputCount">The number of output neurons in the section.</param>
/// <param name="Randomizer">The Ransom instance of the NeuralNetwork.</param>
public NeuralSection(UInt32 InputCount, UInt32 OutputCount, Random Randomizer)
{
// Validation Checks
if (InputCount == 0)
throw new ArgumentException("You cannot create a Neural Layer
with no input neurons.", "InputCount");
else if (OutputCount == 0)
throw new ArgumentException("You cannot create a Neural Layer
with no output neurons.", "OutputCount");
else if (Randomizer == null)
throw new ArgumentException("The randomizer cannot be set to null.",
"Randomizer");
// Set Randomizer
TheRandomizer = Randomizer;
// Initialize the Weights array
Weights = new double[InputCount + 1][]; // +1 for the Bias Neuron
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
Weights[i] = new double[OutputCount];
// Set random weights
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[i].Length; j++)
Weights[i][j] = TheRandomizer.NextDouble() - 0.5f;
}
/// <summary>
/// Initiates an independent Deep-Copy of the NeuralSection provided.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Main">The NeuralSection that should be cloned.</param>
public NeuralSection(NeuralSection Main)
{
// Set Randomizer
TheRandomizer = Main.TheRandomizer;
// Initialize Weights
Weights = new double[Main.Weights.Length][];
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
Weights[i] = new double[Main.Weights[0].Length];
// Set Weights
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[i].Length; j++)
{
Weights[i][j] = Main.Weights[i][j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Feed input through the NeuralSection and get the output.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Input">The values to set the input neurons.</param>
/// <returns>The values in the output neurons after propagation.</returns>
public double[] FeedForward(double[] Input)
{
// Validation Checks
if (Input == null)
throw new ArgumentException("The input array cannot be set to null.", "Input");
else if (Input.Length != Weights.Length - 1)
throw new ArgumentException
("The input array's length does not match the number of neurons
in the input layer.", "Input");
// Initialize Output Array
double[] Output = new double[Weights[0].Length];
// Calculate Value
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[i].Length; j++)
{
if (i == Weights.Length - 1) // If is Bias Neuron
Output[j] += Weights[i][j]; // Then, the value of the neuron
// is equal to one
else
Output[j] += Weights[i][j] * Input[i];
}
}
// Apply Activation Function
for (int i = 0; i < Output.Length; i++)
Output[i] = ReLU(Output[i]);
// Return Output
return Output;
}
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralSection.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a weight
/// is going to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">The maximum amount a Mutated Weight
/// would change.</param>
public void Mutate(double MutationProbablity, double MutationAmount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[i].Length; j++)
{
if (TheRandomizer.NextDouble() < MutationProbablity)
Weights[i][j] = TheRandomizer.NextDouble() *
(MutationAmount * 2) - MutationAmount;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralSection's Nodes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a node
/// is going to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">The maximum amount a Mutated Weight
/// would change.</param>
public void MutateNodes(double MutationProbablity, double MutationAmount)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Weights[0].Length; j++) // For each output node
{
if (TheRandomizer.NextDouble() < MutationProbablity) // Check if we are
// going to mutate this node
{
for (int i = 0; i < Weights.Length; i++) // For each input node
// connected to the current
// output node
{
Weights[i][j] = TheRandomizer.NextDouble() *
(MutationAmount * 2) - MutationAmount; // Mutate the weight
// connecting both nodes
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Puts a double through the activation function ReLU.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="x">The value to put through the function.</param>
/// <returns>x after it is put through ReLU.</returns>
private double ReLU(double x)
{
if (x >= 0)
return x;
else
return x / 20;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Initiates a NeuralNetwork from a Topology and a Seed.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Topology">The Topology of the Neural Network.</param>
/// <param name="Seed">The Seed of the Neural Network.
/// Set to 'null' to use a Timed Seed.</param>
public NeuralNetwork(UInt32[] Topology, Int32? Seed = 0)
{
// Validation Checks
if (Topology.Length < 2)
throw new ArgumentException("A Neural Network cannot contain
less than 2 Layers.", "Topology");
for (int i = 0; i < Topology.Length; i++)
{
if (Topology[i] < 1)
throw new ArgumentException("A single layer of neurons must contain,
at least, one neuron.", "Topology");
}
// Initialize Randomizer
if (Seed.HasValue)
TheRandomizer = new Random(Seed.Value);
else
TheRandomizer = new Random();
// Set Topology
TheTopology = new List<uint>(Topology).AsReadOnly();
// Initialize Sections
Sections = new NeuralSection[TheTopology.Count - 1];
// Set the Sections
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Sections[i] = new NeuralSection
(TheTopology[i], TheTopology[i + 1], TheRandomizer);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Initiates an independent Deep-Copy of the Neural Network provided.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Main">The Neural Network that should be cloned.</param>
public NeuralNetwork(NeuralNetwork Main)
{
// Initialize Randomizer
TheRandomizer = new Random(Main.TheRandomizer.Next());
// Set Topology
TheTopology = Main.TheTopology;
// Initialize Sections
Sections = new NeuralSection[TheTopology.Count - 1];
// Set the Sections
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Sections[i] = new NeuralSection(Main.Sections[i]);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Feed Input through the NeuralNetwork and Get the Output.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="Input">The values to set the Input Neurons.</param>
/// <returns>The values in the output neurons after propagation.</returns>
public double[] FeedForward(double[] Input)
{
// Validation Checks
if (Input == null)
throw new ArgumentException("The input array cannot be set to null.", "Input");
else if (Input.Length != TheTopology[0])
throw new ArgumentException("The input array's length does not match
the number of neurons in the input layer.", "Input");
double[] Output = Input;
// Feed values through all sections
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Output = Sections[i].FeedForward(Output);
}
return Output;
}
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralNetwork.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a weight
/// is going to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">The maximum amount a mutated weight would change.</param>
public void Mutate(double MutationProbablity = 0.3, double MutationAmount = 2.0)
{
// Mutate each section
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Sections[i].Mutate(MutationProbablity, MutationAmount);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Mutate the NeuralNetwork's Nodes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="MutationProbablity">The probability that a node
/// is going to be mutated. (Ranges 0-1)</param>
/// <param name="MutationAmount">The maximum amount a Mutated Weight would change.</param>
public void MutateNodes(double MutationProbablity = 0.3, double MutationAmount = 2.0)
{
// Mutate each section
for (int i = 0; i < Sections.Length; i++)
{
Sections[i].MutateNodes(MutationProbablity, MutationAmount);
}
}
}
而且... 不,我不会就这样离开你。 现在是时候对之前在 Unity 中制作的汽车演示进行一些小小的改动,这样我们就可以亲眼看到差异。 让我们首先转到我们 Unity 项目中的 EvolutionManager.cs 并在脚本的开头添加这个变量
[SerializeField] bool UseNodeMutation = true; // Should we use node mutation?
让我们也通过将 StartGeneration() 函数中对 Car.NextNetwork.Mutate() 的调用替换为以下内容来使用这个变量
if(UseNodeMutation) // Should we use Node Mutation
Car.NextNetwork.MutateNodes(); // Mutate its nodes
else
Car.NextNetwork.Mutate(); // Mutate its weights
这样,EvolutionManager.cs 最终应该看起来像这样
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class EvolutionManager : MonoBehaviour
{
public static EvolutionManager Singleton = null; // The current EvolutionManager Instance
[SerializeField] bool UseNodeMutation = true; // Should we use node mutation?
[SerializeField] int CarCount = 100; // The number of cars per generation
[SerializeField] GameObject CarPrefab; // The Prefab of the car to be created
// for each instance
[SerializeField] Text GenerationNumberText; // Some text to write the generation number
int GenerationCount = 0; // The current generation number
List<Car> Cars = new List<Car>(); // This list of cars currently alive
NeuralNetwork BestNeuralNetwork = null; // The best NeuralNetwork
// currently available
int BestFitness = -1; // The FItness of the best
// NeuralNetwork ever created
// On Start
private void Start()
{
if (Singleton == null) // If no other instances were created
Singleton = this; // Make the only instance this one
else
gameObject.SetActive(false); // There is another instance already in place.
// Make this one inactive.
BestNeuralNetwork = new NeuralNetwork(Car.NextNetwork); // Set the BestNeuralNetwork
// to a random new network
StartGeneration();
}
// Sarts a whole new generation
void StartGeneration ()
{
GenerationCount++; // Increment the generation count
GenerationNumberText.text = "Generation: " +
GenerationCount; // Update generation text
for (int i = 0; i < CarCount; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
Car.NextNetwork = BestNeuralNetwork; // Make sure one car uses the best network
else
{
Car.NextNetwork = new NeuralNetwork(BestNeuralNetwork); // Clone the best
// neural network and set it to be for the next car
if(UseNodeMutation) // Should we use Node Mutation
Car.NextNetwork.MutateNodes(); // Mutate its nodes
else
Car.NextNetwork.Mutate(); // Mutate its weights
}
Cars.Add(Instantiate(CarPrefab, transform.position,
Quaternion.identity, transform).GetComponent<Car>()); // Instantiate
// a new car and add it to the list of cars
}
}
// Gets called by cars when they die
public void CarDead (Car DeadCar, int Fitness)
{
Cars.Remove(DeadCar); // Remove the car from the list
Destroy(DeadCar.gameObject); // Destroy the dead car
if (Fitness > BestFitness) // If it is better that the current best car
{
BestNeuralNetwork = DeadCar.TheNetwork; // Make sure it becomes the best car
BestFitness = Fitness; // And also set the best fitness
}
if (Cars.Count <= 0) // If there are no cars left
StartGeneration(); // Create a new generation
}
}
将所有内容搅拌均匀并点击播放后,您将得到这个
关注点
仅仅通过进行一个非常简单的添加,就可以看到与上一篇文章相比,训练有了如此巨大的改进,真是太棒了。 既然我们有了一些改进,现在轮到你告诉我你对这一切的看法了。 你认为我下一步应该做什么? 而且,我应该制作关于人工智能之类的 youtube 视频,还是应该坚持写文章?
历史
- 版本 1.0:主要实现
