使用 Python 构建推荐系统
4.71/5 (5投票s)
本文将帮助您使用 Python 构建不同类型的基本推荐系统。
引言
每当谈到数据科学或机器学习时,我们首先想到的是预测、推荐系统或类似的东西。实际上,推荐系统在当今非常普遍。如果我们谈论一些最受欢迎的网站,如亚马逊、eBay、yts,更不用说 Facebook,您都会看到这些推荐系统在运行。您肯定会遇到一些带有“**您可能感兴趣**”、“**您可能认识这个人**”或“**人们还搜索了**”之类的标签。所以我决定看看这些东西是如何工作的,然后就有了这篇文章。我们将讨论一些基本且常见的推荐系统类型、它们如何工作以及我们将使用 Python 开发它们。需要注意的一点是;这些系统在质量、复杂性或准确性方面与科技公司使用的系统不匹配,但只会给您一个想法和起点。
环境设置
Ipython notebook,现在称为 Jupyter notebook,是科学计算最常用的技术之一。它之所以被使用的主要原因是它在文学编程方面表现出色。换句话说,它能够重新运行程序的一部分,这在处理大型数据集时非常方便。获取 Jupyter notebook 应用程序最简单的方法是安装科学 Python 发行版;其中最常见的是 Anaconda。您可以从 https://anaconda.net.cn/download/ 下载 Anaconda 发行版,然后只需使用默认设置安装它以供单个用户使用。
我们的环境都已设置好,现在我们实际做点什么。创建一个名为 *图书推荐系统* 的新文件夹(之所以这样命名,是因为我们要构建图书推荐系统,您可以随意命名)。现在启动 Anaconda 命令提示符并通过输入以下命令启动一个新笔记本
$ jupyter notebook
您应该看到以下屏幕

它所做的是在我们的指定文件夹中创建一个空笔记本,并将为您启动一个基于网络的交互式环境供您工作。现在让我们讨论一些常用的推荐系统,并看看它们是如何工作的。
注意
本文假设您对使用 Python 的数据科学库有非常基本的了解。即使您是新手,也可以继续阅读,因为我试图将事情分解得简单。此外,我将用于本文的数据集是一个相当小的数据集,基于从亚马逊和 goodreads 收集的数据。您可以下载它并随意实验。代码也适用于任何其他数据集。
基于流行度的推荐器
这是最基本的推荐系统,它根据流行度向每个用户提供通用推荐。但即使它很简单,也确实有道理。让我们以冰淇淋店为例。每位顾客都点巧克力口味,因此巧克力在顾客中确实更受欢迎,并且是该冰淇淋店的热销产品。因此,如果一位新顾客走进来询问最好的,他会被建议尝试巧克力口味。这同样适用于旅游景点、酒店推荐、电影、书籍、音乐等,任何在公众中更受欢迎的东西,都更有可能推荐给新顾客。
如前所述,这类推荐器提供的是通用推荐,而不是个性化推荐。这意味着该系统不会考虑“个人”偏好或选择,而是会告诉您某个特定事物受到大多数用户的喜爱。
构建一个将阐明其背后的思想。让我们开始吧。
# In[1]:
#importing libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
pandas 和 numpy 是 Python 提供的两个用于科学计算、数据操作和数据分析的强大库。numpy 最重要的是提供高性能、多维数组以及操作它的工具。而 pandas 则以其数据结构和数据操作闻名。我们将在这篇文章中使用这两个库。
# In[2]:
#reading the files
data = pd.read_csv('listing.csv', encoding = 'latin-1')
books = pd.read_csv('books.csv', encoding = 'latin-1')
# In[3]:
#using head() function to view first 5 rows for the object based on position.
Just to test if we have right data.
data.head()

# In[4]:
books.head()

# In[5]:
# Getting recommendation based on No. Of ratings
rating_count = pd.DataFrame(books, columns=['book_id','no_of_ratings'])
# Sorting and dropping the duplicates
rating_count.sort_values('no_of_ratings', ascending=False).drop_duplicates().head(10)

# In[6]:
# getting the detail of 5 most rated books
most_rated_books = pd.DataFrame([4755, 2409, 2194, 4696, 1616], index=np.arange(5), columns=['book_id'])
detail = pd.merge(most_rated_books, data, on='book_id')
detail

您也可以按如下方式获取评分最高的书籍
# In[7]:
# getting the most rated book
most_rated_book = pd.DataFrame(books, columns=['book_id', 'user_id', 'avg_rating', 'no_of_ratings'])
most_rated_book.max()

# In[8]:
#getting description for most rated book
most_rated_book.describe()

您也可以使用相同的函数获取任何列的描述。
# In[9]:
# description for author
data['author'].describe()

基于相关性的推荐器
由于这是一个“个性化”事物越来越多的时代,因此基于流行度的推荐器不足以满足需求。因此,存在基于相关性的推荐器,它将根据项目的相似性(我们谈论的是评论相似性)进行推荐。其基本思想是,如果您喜欢这个项目,您很可能也会喜欢与之相似的项目。基于相关性的推荐器是**基于协同过滤的推荐器**的更简单形式。它们会给您带来更多个性化的感觉,因为它们会推荐与之前选择的项目最相似的项目。
我们将使用 **Pearson 相关性** 用于我们的推荐系统。此推荐系统将使用基于项目的相似性;根据用户评分关联项目。
# In[1]:
# importing libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# In[2]:
# reading files
data = pd.read_csv('listing.csv', encoding = 'latin-1')
books = pd.read_csv('books.csv', encoding = 'latin-1')
# In[3]:
# Checking the data using head function
books.head()

# In[4]:
# calculating the mean
rating = pd.DataFrame(books.groupby('book_id')['no_of_ratings'].mean())
rating.head()

# In[5]:
# getting the description of rating
rating.describe()

# In[6]:
# sorting based on no of ratings that each book got
rating.sort_values('no_of_ratings', ascending=False).head()

# In[7]:
# Preparing data table for analysis
ratings_pivot = pd.pivot_table(data=books, values='user_rating', index='user_id', columns='book_id')
ratings_pivot.head()

由于我们有兴趣找到两个变量之间的相关性,因此我们将使用 Pearson 相关性,它将简单地测量线性相关性。在这种情况下,我们有兴趣了解基于用户评分的两本书之间的关系。
# In[8]:
correlation_matrix = user_rating.corr(method='pearson')
correlation_matrix.head(10)
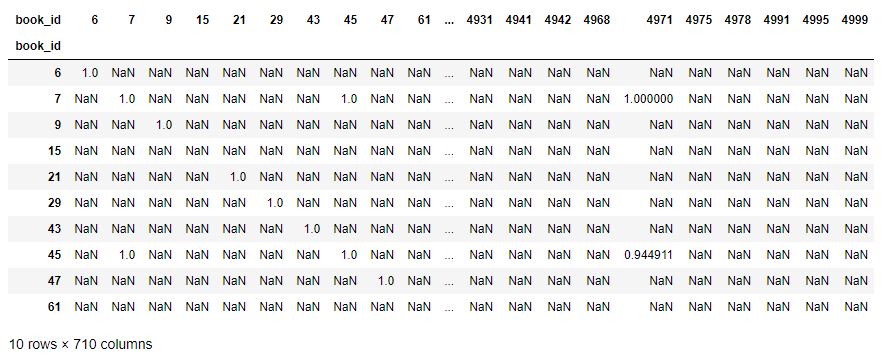
如您所见,现在我们的表格包含皮尔逊相关系数的值。
# getting the users who rated this particular book (most rated) and making sure rating is not zero
OneManOut_rating = ratings_pivot[4755]
OneManOut_rating[OneManOut_rating>=0]

# In[9]:
# finidng similar books to One Man Out book using Pearson correlation
similar_to_OneManOut = ratings_pivot.corrwith(OneManOut_rating)
corr_OneManOut = pd.DataFrame(similar_to_OneManOut, columns=['PearsonR'])
corr_OneManOut.dropna(inplace=True)
corr_OneManOut.head()
您会遇到一个运行时警告,因为遇到了除以零的情况。

但这不会妨碍我们,所以可以忽略。我们仍然会得到如下输出

# In[10]:
OneManOut_corr_summary = corr_OneManOut.join(rating)
# In[11]:
# getting the most similar book
OneManOut_corr_summary.sort_values('PearsonR', ascending=False).head(10)

# In[12]:
# getting the details for most similar books
book_corr_OneManOut = pd.DataFrame([2629, 493, 4755, 4571, 2900, 1417, 2681, 1676, 2913, 1431],
index = np.arange(10), columns=['book_id'])
summary = pd.merge(book_corr_OneManOut, data,on='book_id')
summary

现在,如果您看到我们数据集中评分最高的书籍是《**One Man Out: Curt Flood Versus Baseball**》,它属于法律类型,但我们的推荐引擎给我们混合了旅行、法律等推荐。这是因为我们正在利用评分之间的关系进行推荐。这本书在我们的数据集中被评分了 4 次,也是我们的推荐引擎首先推荐的。这意味着我们的推荐器正在运行。
内容推荐器
还存在另一种类型的推荐器,称为基于内容的推荐器。这种推荐器使用项目的描述来推荐下一个最相似的项目。基于内容的推荐器也进行“个性化”推荐。基于相关性的推荐器和基于内容的推荐器之间的主要区别在于,前者考虑“用户行为”,而后者考虑内容进行推荐。基于内容的推荐器使用产品特征或描述中使用的关键词来查找项目之间的相似性。让我们看看如何构建一个。
# In[1]:
# importing libraries
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import linear_kernel
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
linear_kernel 用于计算两个变量之间的线性核。我们将使用此函数而不是 cosine_similarities(),因为它速度更快,并且由于我们也使用 TF-IDF 向量化,一个简单的点积将给我们相同的余弦相似度分数。那么什么是 TF-IDF 向量?我们无法以它在我们的 dataset 中的形式计算给定描述之间的相似性。这实际上是不可能的。为此,计算所有文档的 Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF),它将简单地返回一个矩阵,其中每个单词代表一个列。sklearn 的 TfidfVectorizer 将在几行代码中为我们完成此操作
# In[2]:
# reading file
book_description = pd.read_csv('description.csv', encoding = 'latin-1')
# In[3]:
# checking if we have the right data
book_description.head()

# In[4]:
# removing the stop words
books_tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words='english')
# filling the missing values with empty string
book_description['description'] = book_description['description'].fillna('')
# computing TF-IDF matrix required for calculating cosine similarity
book_description_matrix = books_tfidf.fit_transform(book_description['description'])
# In[5]:
# Let's check the shape of computed matrix
book_description_matrix.shape

上面的形状表示在我们的 dataset 中使用了 4186 个单词来描述 143 本书。
# computing cosine similarity matrix using linear_kernal of sklearn
cosine_similarity = linear_kernel(book_description_matrix, book_description_matrix)
# In[6]:
indices = pd.Series(book_description['name'].index)
# In[7]:
# Function to get the most similar books
def recommend(index, cosine_sim=cosine_similarity):
id = indices[index]
# Get the pairwsie similarity scores of all books compared to that book,
# sorting them and getting top 5
similarity_scores = list(enumerate(cosine_sim[id]))
similarity_scores = sorted(similarity_scores, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
similarity_scores = similarity_scores[1:6]
# Get the books index
books_index = [i[0] for i in similarity_scores]
# Return the top 5 most similar books using integer-location based indexing (iloc)
return book_description['name'].iloc[books_index]
# In[8]:
# getting recommendation for book at index 2
recommend(2)

# In[9]:
# getting recommendation for book at index 6
recommend(6)

如果您注意到我们得到的结果;根据我们的推荐引擎,索引 2 的书与索引 6 的书相似。让我们沿着描述看看我们的推荐器是否有效。
根据 goodreads;以下是《**安吉拉的灰烬**》的简短描述:
"当我回顾我的童年时,我不知道自己是如何幸存下来的。那当然是一个悲惨的童年:幸福的童年几乎不值得你关注。比普通悲惨的童年更糟糕的是悲惨的爱尔兰童年,更糟糕的是悲惨的爱尔兰天主教童年。"
而《**剪刀手奔跑**》则如下:
“一个无法无天的童年的真实故事,在那里规则闻所未闻,圣诞树全年都在,安定片像糖果一样被消耗,如果事情变得无聊,电击疗法机器可以提供娱乐。”
这表明故事概要之间存在某种相似性。此外,这两本书都属于“传记与回忆录”类型。这表明我们的推荐在所有简单性上都足够好。
致读者
包含数据集和 Jupyter 笔记本的完整存储库也存在于 github 上。您可以在此处下载。
