使用 Spring Security 保护 Spring Boot Web 应用程序
在本文中,我将向读者展示如何使用 Spring Security 和标签来保护基于 Spring Boot 和 WAR 归档的 Web 应用程序。该应用程序将有一个登录页面,基于用户角色的页面访问,登录失败和访问被拒绝的页面。
引言
不久前,我发表了一篇题为《使用 Spring Boot 和 JSP 及 WAR 归档创建 MVC Web 应用程序》的文章。在其中,我描述了如何使用 Spring Boot 创建 MVC 应用程序。这是创建 Web 应用程序的一种非常酷的方式。现在,我将更进一步,使用 Spring Security 来锁定应用程序。
对于本教程中的示例应用程序,我将添加一个登录页面,一个用于认证和授权用户的用户服务,一种退出登录的方式,以及只能由具有特定角色的用户访问的页面。我还添加了两个页面,一个用于登录失败,另一个用于未经授权的访问错误。在我 walkthrough 代码时,读者将看到让这样的应用程序正常运行是多么有趣和令人兴奋。
文件结构
在深入研究实际代码之前,我想向您展示目录结构和文件位置。
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/App.java
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/security/UserAuthenticationService.java
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/controllers/LoginController.java
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/controllers/SecuredPageController.java
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/config/WebAppSecurityConfig.java
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/application.properties
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/static/test.html
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/static/assets/bootstrap/<all the Bootstrap files in some sub folders>
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/static/css/index.css
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/static/jquery/js/jquery.min.js
<base-dir>/src/main/resources/static/js/test.js
<base-dir>/src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/jsp/<all the jsp template files>
<base-dir>/pom.xml
在我之前的文章中,我说过使用 Spring Boot,Web 应用程序变得非常简单。这是不正确的。任何涉及安全性并具有多个页面的应用程序的项目都会有很多文件。这些文件会增加整个项目的复杂性。但不要因此而害怕。整个项目仍然很简单。
POM 文件
POM 文件是指定项目如何编译和打包的文件。就像我在《使用 Spring Boot 和 JSP 及 WAR 归档创建 MVC Web 应用程序》的上一篇文章中所做的那样,本教程中的示例应用程序仍打包为 war 文件。它的运行方式相同。但它增加了一些额外功能。在深入了解这些新功能之前,让我们看一下 POM 文件的内容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>boot-war</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>Hanbo Boot War Sample App</name>
<description>An example of Spring Boot, JSP and WAR</description>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-taglibs</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
在此 POM 文件中,我仅添加了两个新依赖项:Spring Security 和 Spring Security taglib。它们是
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-taglibs</artifactId>
</dependency>
这两个依赖项是必要的原因是
- 我们需要 spring-boot-starter-security 来为 Web 应用程序设置核心安全配置。
- 我们需要 spring-security-taglibs,以便我们可以在 jsp 文件中使用 Spring Security 标签。
当我们 walkthrough 代码时,我会指出每个依赖项的使用位置。
除了这两个新依赖项之外,该文件与我上次教程中的 POM 文件相同。接下来,我将向您展示示例应用程序的安全配置。
Spring Security 配置
在开始安全配置之前,我只想指出,本示例应用程序的主入口类与我之前教程中的相同。我在这里不列出它。您可以在那里查看。除了这个主入口类之外,我还必须添加另一个类来进行安全配置。
我添加的这个新类称为 WebAppSecurityConfig。它位于
<base-dir>/src/main/java/org/hanbo/boot/app/config/WebAppSecurityConfig.java
这个类是此示例应用程序中最复杂的类。您会发现即使它也相当简单。要正确完成 Spring Security 配置,您需要知道要调用的方法的组合。在我开始之前,我想向您展示代码。
package org.hanbo.boot.app.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher;
import org.hanbo.boot.app.security.UserAuthenticationService;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = true)
public class WebAppSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
{
@Autowired
private UserAuthenticationService authenticationProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception
{
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**", "/assets/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/secure/index", true).failureUrl("/public/authFailed")
.successHandler(new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
.and()
.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/public/accessDenied")
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
.logoutSuccessUrl("/public/logout").permitAll();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder authMgrBuilder)
throws Exception
{
authMgrBuilder.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
}
这是一个典型的类,它有三个注解
@Configuration:这意味着当 Spring 应用程序启动时,它将从该类中查找配置信息。该类有一个名为configure()的方法,该方法将在启动时调用。@EnableWebSecurity:这告诉 Spring 在应用程序启动时将启用 Web 安全。也就是说,将调用configure()方法来设置用于保护 Web 应用程序的安全配置。@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity:这是一个非常特殊的东西。为了保护我的 Web 应用程序控制器类中的操作方法,我必须使用@PreAuthorize()之类的注解。此配置注解将允许我这样做。
最复杂的部分是 configure() 方法。它接受一个 HttpSecurity 类型的参数。我们可以通过链式调用此类型对象的系列方法来保护 Web 应用程序。目标是设置应用程序中的哪些页面可以被所有人访问,哪些页面只能被登录用户访问。这是一个高层概述,这是 configure() 方法的代码。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception
{
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**", "/assets/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/secure/index", true).failureUrl("/public/authFailed")
.successHandler(new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
.and()
.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/public/accessDenied")
.and()
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
.logoutSuccessUrl("/public/logout").permitAll();
}
此方法用于配置如何处理用户的 HTTP 请求。以下是我配置的规则:首先,对 <context root>/public/** 和 <context root>/assets/** 的任何请求都将无需身份验证即可处理。所有其他请求,用户必须经过身份验证才能获得访问权限。
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**", "/assets/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
基于表单的登录将通过 POST 请求到 <context root>/login 来处理,登录页面可以通过 GET 请求到 <context root>/login 访问。在登录表单上,应该有一个名为“username”的文本输入框,以及一个名为“password”的文本输入框。如果用户直接访问登录页面,成功登录后,用户将看到 <context root>/secure/index 处的默认页面。当用户登录尝试失败时,用户将被重定向到 <context root>/public/authFailed 页面。如果用户有特定安全页面想要访问,成功登录后,successHandler 将使用 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 类型的对象来完成此操作。
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.usernameParameter("username")
.passwordParameter("password")
.defaultSuccessUrl("/secure/index", true).failureUrl("/public/authFailed")
.successHandler(new SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler())
对于经过身份验证的用户尝试访问没有权限访问的页面,我为此添加了一个异常处理程序。
.exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/public/accessDenied")
对于退出登录,它将是一个 GET 请求到 <context root>/logout。如果退出登录操作成功,用户将被重定向到页面 <context root>/public/logout。
.logout()
.logoutRequestMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/logout"))
.logoutSuccessUrl("/public/logout").permitAll();
那么,这个类中的另一个方法是做什么的?另一个方法用于指定用户身份验证如何工作。在这种情况下,我创建了一个虚拟身份验证服务。它将检查用户的姓名和密码是否与一些预定义的用户名和相应密码匹配。一旦用户凭据(用户名和密码)得到验证,用户将被分配一个或多个角色。角色决定了用户可以访问哪些页面。
用户身份验证服务
我的用户身份验证服务非常简单。服务对象获取用户名和密码,并与三组预定义的用户名和密码进行匹配。如果找到匹配项,则会将与用户名和密码关联的一组角色分配给用户。
在解释代码之前,我想
package org.hanbo.boot.app.security;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserAuthenticationService
implements AuthenticationProvider
{
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication auth) throws AuthenticationException
{
Authentication retVal = null;
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuths = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>();
if (auth != null)
{
String name = auth.getName();
String password = auth.getCredentials().toString();
if (name.equals("admin") && password.equals("admin12345"))
{
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_STAFF"));
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
retVal = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
name, "", grantedAuths
);
}
else if (name.equals("staff1") && password.equals("staff12345"))
{
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_STAFF"));
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
retVal = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
name, "", grantedAuths
);
}
else if (name.equals("user1") && password.equals("user12345"))
{
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
retVal = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
name, "", grantedAuths
);
}
}
else
{
retVal = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
null, null, grantedAuths
);
}
return retVal;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> tokenType)
{
return tokenType.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
让我们从这个新类最简单的部分开始。我的类实现了 AuthenticationProvider,它需要我实现两个方法。
Authentication authenticate(Authentication auth)boolean supports(Class<?> tokenType)
supports() 方法用于告诉此 AuthenticationProvider 是否可以处理 Authentication 对象。对于本示例应用程序,登录表单将返回 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 类型的对象。因此,只有当 Authentication 对象类型正确时,此 supports() 才返回 true。然后 authenticate() 方法可以处理身份验证请求。
authenticate() 方法首先获取用户名和密码(密码值来自 getCredential())。然后,将用户名和密码与三组用户名和密码组合进行匹配。
admin:如果匹配,用户将获得三个角色:ROLE_ADMIN、ROLE_STAFF和ROLE_USER。staff:如果匹配,用户将获得两个角色:ROLE_STAFF和ROLE_USER。user:如果匹配,用户将只获得一个角色:ROLE_USER。
返回值是一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 类型的对象。此类型的对象可以包含三种不同的值。
- 用户名
- 凭据。通常是密码。所以我将其留空。
- 最后一个是角色列表。角色基本上是“
ROLE_”前缀开头的string。角色对象是SimpleGrantedAuthority类型。
所有角色名称都以“ROLE_”前缀开头很重要。没有这个前缀,使用 @PreAuthorize() 注解的角色授权将不起作用。
创建角色对象并将其添加到列表中的代码如下所示:
List<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuths = new ArrayList<GrantedAuthority>();
...
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_STAFF"));
grantedAuths.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
使用用户名和角色创建 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象。
retVal = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(
name, "", grantedAuths
);
....
return retVal;
保护 Web 页面
编码的最后一部分是保护 Web 页面。更准确地说,我们想要保护那些会导致将 Web 页面发送回用户浏览器的方法。为了展示如何做到这一点,我创建了一个名为 SecuredPageController 的 controller 类。其中有三个操作方法(ASP.NET MVC 中常用的术语),每个方法都会显示一个页面。用户只能在登录并被分配了正确的用户角色后才能访问这些页面。以下是此类别的完整源代码。
package org.hanbo.boot.app.controllers;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
public class SecuredPageController
{
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')")
@RequestMapping(value="/secure/adminPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView adminPage()
{
ModelAndView retVal = new ModelAndView();
retVal.setViewName("webAccess");
retVal.addObject("pageInfo", "The AWESOME Admin Page");
retVal.addObject("userInfo", "Awesome Admin User.");
return retVal;
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_STAFF')")
@RequestMapping(value="/secure/staffPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView staffPage()
{
ModelAndView retVal = new ModelAndView();
retVal.setViewName("webAccess");
retVal.addObject("pageInfo", "The SUPPORTING Staff Page");
retVal.addObject("userInfo", "T.L.C Staff User.");
return retVal;
}
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_USER')")
@RequestMapping(value="/secure/userPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView userPage()
{
ModelAndView retVal = new ModelAndView();
retVal.setViewName("webAccess");
retVal.addObject("pageInfo", "The LAMMO User Page");
retVal.addObject("userInfo", "an ordinary User.");
return retVal;
}
}
我不会在这里逐一讲解每个方法。它们基本上做的事情相同。但是,@PreAuhorize() 注解对每个方法都不同。我将解释其中一个如何工作。
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_STAFF')")
@RequestMapping(value="/secure/staffPage", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView staffPage()
{
ModelAndView retVal = new ModelAndView();
retVal.setViewName("webAccess");
retVal.addObject("pageInfo", "The SUPPORTING Staff Page");
retVal.addObject("userInfo", "T.L.C Staff User.");
return retVal;
}
@PreAuhorize() 注解定义只有具有“ROLE_STAFF”角色的用户才能访问此方法。@RequestMapping() 注解定义了由此操作方法处理的 URL 路由。在这种情况下,以下 URL 路径将由该方法处理。
- https://:8080/secure/staffPage
它只处理此 URL 的 HTTP GET 请求。方法体创建一个 ModelAndView 对象,该对象使用一个名为“webAccess.jsp”的视图模板。ModelAndView 对象还包含两个 string 值,模板可以使用它们来创建实际页面。其他两个方法也使用示例视图模板做同样的事情,但是 URL 不同,并且访问每个页面所需的用户角色也不同。它们是
- https://:8080/secure/adminPage,仅限管理员用户访问。
- https://:8080/secure/userPage,仅限普通用户访问。
页面模板
既然我们已经看到了受保护页面的服务方式,现在该看看实际的页面模板了。从操作方法(在前一节列出)中可以看出,它们都引用同一个 JSP 视图模板,该模板称为“webAccess.jsp”。它看起来像这样。
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="sec" uri="http://www.springframework.org/security/tags" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<title>Admin Logged in - Home</title>
</sec:authorize>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_STAFF')">
<title>Staff Logged in - Home</title>
</sec:authorize>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')">
<title>Normal User Logged in - Home</title>
</sec:authorize>
<link href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet">
<link href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="row top-margin">
<div class="col-xs-offset-1 col-xs-10 col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-8 col-md-offset-3 col-md-6">
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-body">
<ol class="breadcrumb">
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<li><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/secure/adminPage">
Admin Access</a></li>
</sec:authorize>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_STAFF')">
<li><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/secure/staffPage">
Staff Access</a></li>
</sec:authorize>
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')">
<li><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/secure/userPage">
User Access</a></li>
</sec:authorize>
<li><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/logout">
<i class="glyphicon glyphicon-log-out"></i> Log Out</a></li>
</ol>
<h3>You are seeing this ${pageInfo} because...</h3>
<p>You are logged in as ${userInfo}</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/jquery/js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
当您以 staff 用户(用户名:staff1;密码:staff12345)登录,然后通过以下 URL 导航到页面时...
https://:8080/secure/staffPage
...您将看到类似以下的屏幕截图。

页面的主要正文就是这个。
<h3>You are seeing this ${pageInfo} because...</h3>
<p>You are logged in as ${userInfo}</p>
上面的 JSP 模板代码没有什么不寻常之处,只有两行,每行都有一个占位符,可以替换为实际值。
在同一个模板中,上面更复杂的部分是一个简单的菜单。菜单项是根据用户角色显示的。只有拥有正确角色的用户才能看到菜单项。在上图中,有两个可用项目。
- Staff Access:如果您单击此链接,您将看到与上面屏幕截图相同的页面。
- User Access:如果您单击此链接,您将看到只有普通用户角色才能访问的页面。
限制这些链接的方法是使用 Spring Security 标签(这就是为什么我在 Maven Pom 中放入 Spring Security taglib)。这是仅允许管理员用户查看链接的方法。
<sec:authorize access="hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')">
<li><a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/secure/adminPage">Admin Access</a></li>
</sec:authorize>
关于页面模板,您能做的就这么多。接下来,我将向您展示登录页面。
登录页面
当应用程序运行时,并且用户尝试访问 SecuredPageController 类中定义的受保护页面时,用户将看到登录页面。这是其屏幕截图。

与普通页面(无论它是受保护的还是公共的)不同,登录页面最有可能显示的方式是当 Spring Security 触发它时,例如当用户尝试访问受保护页面而未登录时。它的工作方式是每个请求都通过 HTTP 过滤器,在此示例项目中,唯一的过滤器是安全过滤器。当检测到未经授权的请求时,将不返回用户所需的页面,而是返回登录页面。用户使用该页面来验证和授权自己,然后 SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler 对象会将所需的页面返回给用户。
登录页面的 HTML 代码如下所示:
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Login Page</title>
<link href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet">
<link href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/css/index.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="row top-margin">
<div class="col-xs-offset-1 col-xs-10 col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-8 col-md-offset-3 col-md-6">
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="panel-body">
<form id="login_form"
action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login" method="post">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">User Name:</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="username"
name="username" placeholder="User Name...">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="username">Password:</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control"
id="password" name="password" placeholder="Password...">
</div>
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName}" value="${_csrf.token}" />
<div class="form-group">
<button class="btn btn-primary form-control" type="submit">Login</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/jquery/js/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript"
src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/assets/bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
登录页面非常简单。有两个输入字段;一个用于输入用户名;另一个用于输入密码。输入字段的名称必须是“username”和“password”。Spring Security 的表单身份验证会期望这些输入参数。
一个重要的事情是 Spring Security 使用 CSRF 进行验证。当登录表单在服务器端创建时,CSRF 令牌值将作为隐藏输入添加。当表单发布到后端服务器时,Spring Security 将验证此隐藏输入值。这就像一次秘密握手,一旦验证通过,用户名和密码就会传递给我的 UserAuthenticationService 对象进行身份验证和授权。
CSRF 不是必需的,但默认是启用的。如果您想关闭它,可以在 WebAppSecurityConfig 类中进行设置。
测试应用程序
至此,我已经涵盖了这个示例应用程序所有最重要的方面。现在是时候进行测试了。下载示例应用程序并解压缩后,第一步是重命名项目 zip 文件中的所有 *.sj 文件为 *.js。在 resources/static 文件夹及其子文件夹中搜索所有这些文件。所有 *.sj 文件都在那里。
要构建应用程序,请转到项目文件已解压缩的文件夹。您应该在其中看到 pom.xml。从此文件夹路径打开 cmd.exe 或终端窗口。运行以下命令。
mvn clean install
构建将成功。接下来,您可以使用同一文件夹位置的以下命令来运行已打包的 WAR 文件。
java -jar target\boot-war-1.0.0.war
运行将成功,并将等待用户交互。您应该在命令行提示符中看到以下输出。
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.0.5.RELEASE)
2018-10-31 22:24:34.092 INFO 9784 --- [ main] org.hanbo.boot.app.App:
Starting App v1.0.0 on U3DTEST-PC with PID 9784
(C:\Users\u3dadmin\workspace-mars8\SpringBootAuth\target\boot-war-1.0.0.war
started by u3dadmin in C:\Users\u3dadmin\workspace-mars8\SpringBootAuth)
2018-10-31 22:24:34.128 INFO 9784 --- [ main] org.hanbo.boot.app.App:
No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
...
<Skipped a lot of lines>
...
2018-10-31 22:24:57.076 INFO 9784 --- [ main] org.hanbo.boot.app.App:
Started App in 27.075 seconds (JVM running for 30.198)
现在,是时候测试应用程序了。首先,尝试默认的 index 页面。
https://:8080/
登录页面将首先出现。

如前所述,您可以使用三种不同的用户凭据来测试此应用程序。
- 用户名:
admin;密码:admin12345 - 用户名:
staff1;密码:staff12345 - 用户名:
user1;密码:user12345
无论您使用哪一个登录,您都将看到受保护的 index 页面,如下所示。

上面的屏幕截图显示已登录的用户是 staff 用户。此用户有两个关联的角色。简单的标题只显示两个链接。如果用户以管理员身份登录,标题中将有三个链接,页面上将显示三个角色,如下所示。
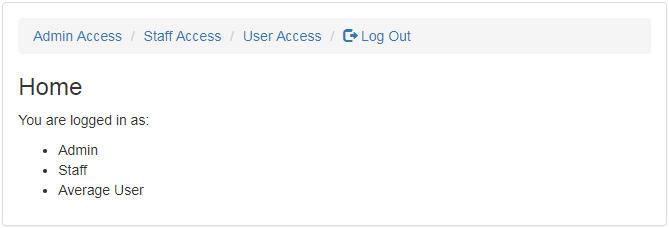
如果用户以普通用户身份登录,index 页面将如下所示。

尝试标题中列出的链接。这些链接仅对具有特定用户角色的用户可用。例如,“Staff Access”链接仅对具有 staff 角色的用户可见。当用户单击它时,它将显示此内容。

现在,如果只有普通用户角色的用户尝试访问此页面,您将看到“Access Denied”页面。尝试此场景的唯一方法是首先以普通用户身份登录。然后导航到此 URL。
https://:8080/secure/staffPage
然后,您将看到以下页面。

您可能想做的最后一个测试是尝试使用随机密码的用户进行登录,这将导致显示登录错误页面,如下所示。

关于这个示例应用程序,以上就是全部内容。
关注点
本文扩展了我之前关于 Spring Boot 的文章。然而,内容实际上并没有什么新东西。我很久以前发表了另一篇关于 Spring MVC 与 Spring Security 和 Spring 的集成文章。如果您在此文章中遇到困难,请使用这篇其他文章作为参考。网上也有很多参考资料可以帮助您摆脱困境。
我确实修复了 HTTP 安全过滤器配置的问题。在我之前关于 Spring Security 的文章中,配置不正确。因此,示例应用程序无法正常工作。这次,我正确地完成了配置。我之所以能够正确配置,是因为我没有在此示例应用程序中包含 RESTFul API 控制器。对于 RESTFul API,Spring Security 配置有所不同。也许我会写另一篇关于这个的文章。
总的来说,使用 Spring Boot 设计这样一个示例应用程序比使用 Spring MVC、Spring Security 并打包为 WAR 归档以部署到应用程序容器要简单得多。运行它也更简单。整个 WAR 归档作为 JAR 可执行文件运行。我喜欢这个教程。会有更多关于 Spring Boot 和 Web 应用程序开发的文章。希望您喜欢阅读本教程。谢谢。
历史
- 2018/10/29 - 初稿
