C# .NET 中完整的 TCP 服务器/客户端通信和 RMI 框架 - 实现
4.91/5 (146投票s)
在本文中,我将解释一个开源的轻量级框架(名为 Simple Client Server Library (SCS))的实现,该框架旨在通过简单的 TCP/IP 远程方法调用机制来创建客户端/服务器应用程序。
引言
在本文中,我将解释一个名为 **S**imple **C**lient **S**erver Library (SCS) 的开源轻量级框架的实现,该框架旨在通过简单的远程方法调用机制在TCP/IP上创建客户端/服务器应用程序。这是一个高度可扩展和健壮的框架,完全用C#和.NET Framework 4.0开发(您可以查看本文的 SCS 框架性能部分)。
这是关于 SCS 的第二篇文章,解释了我如何实现它。要了解 SCS 是什么以及如何使用它,请参阅下面的链接中的第一篇文章。第一篇文章中有基于 SCS 的运行示例应用程序。我建议您在阅读本文之前先看一下第一篇文章。
文章大纲
什么是 TCP?
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) 是 TCP/IP 协议套件中的传输层协议(TCP/IP 中另一个常见的传输协议是 UDP (User Datagram Protocol))。它是一个分层协议套件,使用强大的DoD模型。DoD 是一个四层模型,包括链路层、互联网层、传输层和应用层。TCP 和 IP 协议是 TCP/IP 的核心协议(因此得名 TCP/IP)。以下是 TCP 层从上到下的一些常见协议列表:
- 应用层:HTTP, FTP, SMTP...
- 传输层:TCP, UDP...
- 互联网层:IP, ARP, ICMP...
- 链路层:Ethernet, Token Ring...
同样,您所有的 TCP 应用程序(如 SCS 框架)都位于应用层。每一层上都有许多其他协议。
TCP 提供从一台计算机上的程序到另一台计算机上的程序的可靠、有序的字节流传输。TCP 是一个面向连接、异步和双向的通信协议(见下图)。让我们解释一下这些概念:
- 有序的字节流传输:在 TCP 中,应用程序通过字节流进行通信。最小数据传输大小为一字节。第一个发送的字节首先到达目的地(FIFO队列,有序传输)。有两个独立的通信流(双向通信)。应用程序可以随时发送数据,彼此独立(异步通信)。
- 可靠性:TCP 使用序号来标识数据的每个字节。序号标识了从每台计算机发送的字节的顺序,以便在传输过程中可能发生的任何分段、乱序或丢包的情况下,数据都可以按顺序重新构建。因此,如果与远程应用程序的物理连接没有失败,并且您没有收到异常,您的数据几乎可以保证能够送达。即使您的一字节数据未送达(因为错误),在它送达之前,后续字节也不会送达。如果您的数据到达了目的地,您可以确定它没有损坏且没有缺失。

像所有通信协议一样,在 TCP 中,每个应用程序都有一个唯一的地址。该地址由IP地址和 TCP端口组成。
IP 地址(对于 IPv4)是一个由点分隔的四字节数字,例如 85.112.23.219。连接到互联网的所有计算机都有 IP 地址。(如果您通过路由器等连接到互联网,您可能没有公共 IP 地址,但您的路由器有一个,您的计算机有一个本地网络 IP,因此路由器动态使用 NAT 来允许您使用 TCP/IP。但是,远程应用程序可以发送 IP 数据报到您的计算机。)
TCP 端口只是一个数字(2 字节无符号整数,因此 TCP 端口可以是 0 到 65536),它允许 TCP 在同一台计算机上区分您的应用程序与其他应用程序。
我将提到的最后一个 TCP 概念是套接字。套接字是操作系统提供的用于向 TCP/IP 堆栈发送数据和从 TCP/IP 堆栈接收数据的接口。在 .NET 中,套接字由 Socket 对象表示。Socket 对象用于在两个 TCP 端点之间发送/接收数据。一种特殊的套接字是监听套接字。在服务器/客户端架构中,服务器首先打开一个TCP 监听套接字,以允许客户端连接到服务器。与客户端建立通信后,将创建一个专用的套接字对象与该客户端关联,所有与该客户端的通信都将在此新套接字上进行。
为什么选择 TCP?
两个应用程序之间的通信通常称为IPC (Inter-Process Communication)。IPC 有多种方式。TCP/IP 是其中之一。TCP/IP 的优点在于通信的应用程序可以运行在不同的计算机和不同的位置。由于 Internet 也基于 TCP/IP 工作,远程应用程序可以通过互联网进行通信。TCP/IP 完全平台无关,是标准的,并且被所有操作系统(以及许多其他设备)实现。此外,它还可以用于同一台计算机上应用程序的通信。当然,其他技术,如命名管道和共享内存,可以用于两个应用程序的通信,但它们有一个重要的限制,即这两个应用程序必须运行在同一台计算机上(最好是在同一网络上),并且无法通过互联网通信。无论如何,SCS 框架独立于 TCP,并且可以扩展以支持其他 IPC 技术甚至其他通信框架。
构建基于 TCP 的通信框架的阶段有哪些?
在本节中,我将讨论如何制定一个计划来构建基于 TCP 的通信框架以及需要考虑的问题。
基于流的数据传输
从 TCP 的角度来看,从一个应用程序发送到另一个应用程序的所有内容都是流的字节。TCP 不知道它们是图片的字节、文件的字节、字符串还是序列化对象的字节。TCP 也不知道一个数据(例如序列化对象)是否已发送,而我们现在正在发送另一个数据(我指的是消息边界)。
流上的消息传递
从应用程序的角度来看,通过 TCP 流传输的数据是独立的包。我称之为消息。应用程序需要在需要时向另一个应用程序发送消息。此外,应用程序希望在收到远程应用程序的新消息时得到通知(通过某种回调机制)。
因此,我们必须在 TCP 流之上构建一个机制,用于将消息写入流并将消息从流中读取。我们必须提供一种分隔消息的方法。
线协议(消息到流的协议)
将消息写入流和从流中读取消息的方式称为线协议。线协议对正在发送和接收的消息有一些了解。在 .NET 中,如果我们用对象表示消息,我们可以使用序列化从对象构建字节数组。我们可以使用二进制序列化、XML 序列化(然后进行字符串到字节数组编码),或自定义序列化。无论如何,在从消息创建字节数组后,我们可以将其写入TCP 流。此外,我们还可以使用某种反序列化从 TCP 流中重新创建对象。
如果我们创建一个可以在任何其他编程语言或平台上实现的自定义线协议,我们可以构建一个平台无关的系统。但如果我们使用 .NET 二进制序列化,我们的应用程序只能在 .NET 世界中使用。
请求/响应式消息传递
在大多数情况下,一个应用程序向远程应用程序发送消息并等待响应消息。由于 TCP 的异步性质,这是一个重要的实现细节。在这种情况下,我们必须使用多线程工具(如 .NET 中的 ManualResetEvent 类)来阻塞/等待发送线程,直到收到响应,并在收到响应时发出通知。我们还必须提供一种匹配请求和响应消息的方法。最后但同样重要的是,如果远程应用程序在指定时间内未发送响应消息,我们必须提供超时机制。
将消息与类和方法映射
从用户(使用框架构建应用程序)的角度来看,这是基于 TCP 的通信库最重要和独特的特性。可以根据用户的需求、编程语言或平台的能力等偏好选择许多不同的方法。让我们在这里讨论几种方法。
第一种方法是面向消息的通信。在这种方式下,发送方应用程序使用特殊类型的类并通过序列化发送对象(如前所述),接收方应用程序反序列化对象,并进入一个 switch 或 if 语句,根据对象的属性调用方法。消息类可以从基类派生并定义公共方法。甚至,消息对象可以是简单的字符串。应用程序解析此字符串并执行所需的操作。此方法的缺点是库的用户必须定义自己的消息传递逻辑并编写 switch 语句。如果向系统中添加了新的消息类型,许多类、方法或代码块必须进行更改。此外,它不是类型安全的,消息在运行时解析。因此,应用程序可以发送未知消息类型等...
可以通过反射实现消息传递的扩展。由于 .NET 支持反射,我们可以发送一条消息,该消息会导致在远程应用程序上调用方法。假设我们有一个消息类(实际上,它是 SCS 框架中的一个类)
/// <summary>
/// This message is sent to invoke a method of a remote application.
/// </summary>
[Serializable]
internal class ScsRemoteInvokeMessage : ScsMessage
{
/// <summary>
/// Name of the remove service class.
/// </summary>
public string ServiceClassName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Method of remote application to invoke.
/// </summary>
public string MethodName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Parameters of method.
/// </summary>
public object[] Parameters { get; set; }
}
在发送方应用程序中,您可以创建该类的对象,设置适当的类名、方法名和参数列表,对其进行序列化,并通过 TCP 套接字发送。然后,在接收方应用程序中,您可以使用反射技术根据收到的参数找到正确的类,创建该类的实例(或者您可以使用一个已预先创建的对象),并调用正确的方法。通过这种方法,无需修改我们的通信层即可添加新方法。只需像通常一样将新方法添加到您的业务类中即可。如果发送方应用程序发送一条带有新方法名的新消息,您的方法将自动调用,而无需更改任何内容。您还可以向发送方返回另一个包含方法调用返回值的消息。
好了,这样我们就创建了一个良好的接收端通信层。但是,发送方应用程序仍然必须知道类名、方法名、参数... 而且,它还必须为所有方法调用创建消息对象并发送。当然,您可以编写一个代理类,其方法签名与目标类相同。您的应用程序调用此代理类的各种方法,它内部将正确消息发送到远程应用程序,等待响应消息,并返回从远程应用程序接收到的值。这非常好,但您必须为所有新方法或目标应用程序上的方法更改执行此操作。这将是一项繁琐的工作。因此,也许您可以编写一个应用程序,使用反射来完成这个代理类的创建工作。在这种情况下,您必须为目标应用程序服务签名(Web Services 和 WCF Services 就是这样做的)上的所有更改重新创建您的代理类。
SCS 框架提供了一种更好的方法来调用远程应用程序上的方法。它使用 RealProxy 类和反射的动态代理机制。这是 SCS 的关键点之一。将在 SCS 的实现中进行解释。
服务器/客户端架构和多线程

TCP 套接字可以在阻塞(同步)或非阻塞(异步)模式下使用。在阻塞模式下,接收和发送数据是阻塞操作,发送方/接收方线程在操作完成之前将被阻塞。尤其是在阻塞接收中,线程会一直等待,直到从远程应用程序发送数据。因此,我们必须利用多线程在等待远程应用程序数据时执行其他操作。这在客户端中不是一个主要问题,因为只使用一个套接字,并且只需要一个额外的线程来监听传入数据。但在服务器端,每个客户端都有一个专用套接字。因此,如果有100 个客户端并发连接,则有100 个套接字用于与客户端通信,在阻塞模式下有100 个线程用于等待来自客户端的传入数据。
阻塞模式易于实现,但由于上述原因不具可扩展性。因此,我们必须使用异步套接字和回调机制以及线程池来处理数据。
SCS 框架的实现
在简要讨论了开发基于 TCP 的服务器/客户端通信框架之后,现在我将解释我如何实现 SCS 框架。SCS 框架包含两个层,如下图所示。

消息传递层
消息传递层负责将消息(对象)发送到远程应用程序和从远程应用程序接收消息。它独立于远程方法调用层,并且可以单独用于构建面向消息的通信应用程序。它还允许您定义自定义线协议(这样您的应用程序就可以与非 .NET 应用程序通信)。消息传递层中的所有类都定义在 Hik.Communication.Scs 命名空间(及其子命名空间)中。
消息
所有发送或接收的消息都实现 IScsMessage 接口。ScsMessage 类实现了它,所有消息类都从 ScsMessage 派生。

ScsMessage 类有两个 string 属性,它们是 SCS 框架的关键属性:MessageId 和 RepliedMessageId。MessageId 是一个唯一的字符串(它是一个自动生成的 GUID),用于区分消息对象。RepliedMessageId 默认为 null。如果此消息是对另一条消息的回复,它将包含原始消息的 MessageId。此属性用于匹配请求消息和回复消息。ScsMessage 不包含任何数据。
ScsTextMessage 可用于发送/接收简单的字符串消息。ScsRawDataMessage 可用于发送/接收字节数组。使用 ScsRawDataMessage,您可以发送/接收图片、文件、序列化的 .NET 对象... 等。PingMessage 没有附加数据,SCS 框架使用它从客户端向服务器发送 Ping 消息,以保持 TCP 连接活跃并检查连接是否活跃。
您还可以编写自己的类,从 ScsMessage(或其子类)派生,以发送/接收您自己的对象。当然,您可以直接实现 IScsMessage 接口而不是从 ScsMessage 类派生。如果您决定发送/接收自定义类的对象,必须将该类标记为 Serializable。此外,最好将消息类定义在一个单独的类库中,并将此库的引用添加到服务器和客户端应用程序中。
线协议
线协议用于序列化和反序列化消息以与远程应用程序通信。SCS 中的所有线协议类都必须实现 IScsWireProtocol 接口。

SCS 从远程应用程序(通过套接字流)接收字节,并将接收到的字节发送到 IScsWireProtocol 的 CreateMessages(...) 方法。线协议可能会使用给定的字节创建零个(如果接收到的字节不足以创建消息)或多个消息。给定的字节数组可能不包含完整的消息,线协议必须将其存储起来以与后续接收到的字节连接。线协议不得阻塞线程。
SCS 调用 GetBytes(...) 来序列化消息以发送到远程应用程序。最后,在需要时调用 Reset() 方法来重置协议的内部状态(例如,在断开/重新连接的情况下)。
客户端直接使用 IScsWireProtocol,而服务器使用 IScsWireProtocolFactory,因为服务器需要为每个客户端创建一个线协议对象。IScsWireProtocolFactory 只有一个方法(CreateWireProtocol),用于创建线协议对象。
正如您在上图所示,目前 SCS 框架中定义的唯一线协议是 BinarySerializationProtocol。它使用 .NET 的 BinaryFormatter 类来序列化/反序列化对象。您可以继承它来更改序列化机制,或者直接实现 IScsWireProtocol 和 IScsWireProtocolFactory 接口来创建自定义线协议(稍后将进行解释)。您可以通过使用自定义协议轻松地与非 .NET 应用程序进行通信。
端点
正如我在(在*什么是 TCP*部分)中提到的,端点用于定义应用程序的地址。在 SCS 中,所有端点类都必须从 ScsEndPoint 抽象类派生。

ScsEndPoint 类定义了两个重要的 internal 抽象方法,用于创建服务器(在此端点上监听传入的客户端连接)和创建客户端(连接到在此端点上监听的服务器)。我稍后会回到这些方法。ScsEndPoint 还定义了一个静态 CreateEndPoint(...) 方法,用于从字符串地址创建端点对象。因此,要为 127.0.0.1 IP 地址和 10048 TCP 端口创建 ScsTcpEndPoint 对象,您可以将 "tcp://127.0.0.1:10048" 字符串传递给 CreateEndPoint(...) 方法。当然,您也可以直接创建 ScsTcpEndPoint 对象。正如您所见,唯一从 ScsEndPoint 派生的类是 ScsTcpEndPoint。它有两个属性:IpAddress 和 TcpPort。
连接监听器
连接监听器用于服务器监听和接受传入的客户端连接。它们为新连接的客户端创建一个通信通道(将在下一节中解释)。

正如您在类图中所见,IConnectionlistener 接口定义了启动/停止监听器的两个方法,以及一个名为 CommunicationChannelConnected 的事件,当新客户端连接到服务器且通信通道成功创建时会触发该事件。唯一的具体连接监听器类是 TcpConnectionListener。下面显示了 TcpConnectionListener 类的一些重要部分。
/// <summary>
/// This class is used to listen and accept incoming TCP
/// connection requests on a TCP port.
/// </summary>
internal class TcpConnectionListener : ConnectionListenerBase
{
/// <summary>
/// The endpoint address of the server to listen incoming connections.
/// </summary>
private readonly ScsTcpEndPoint _endPoint;
/// <summary>
/// Server socket to listen incoming connection requests.
/// </summary>
private TcpListener _listenerSocket;
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new TcpConnectionListener for given endpoint.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endPoint">The endpoint address of the server to listen incoming connections</param>
public TcpConnectionListener(ScsTcpEndPoint endPoint)
{
_endPoint = endPoint;
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts listening incoming connections.
/// </summary>
public override void Start()
{
StartSocket();
_running = true;
_thread = new Thread(DoListenAsThread);
_thread.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts listening socket.
/// </summary>
private void StartSocket()
{
_listenerSocket = new TcpListener(System.Net.IPAddress.Any, _endPoint.TcpPort);
_listenerSocket.Start();
}
TcpConnectionListener 类定义了一个构造函数,该构造函数接受一个 ScsTcpEndPoint 进行监听。在 Start() 方法中,它使用指定端口号的端点创建并启动一个 TcpListener (System.Net.Sockets.TcpListener) 对象,然后启动一个单独的线程来监听和接受新客户端。DoListenAsThread 方法定义如下:
/// <summary>
/// Entrance point of the thread.
/// This method is used by the thread to listen incoming requests.
/// </summary>
private void DoListenAsThread()
{
while (_running)
{
try
{
var clientSocket = _listenerSocket.AcceptSocket();
if (clientSocket.Connected)
{
OnCommunicationChannelConnected(
new TcpCommunicationChannel(clientSocket));
}
}
catch
{
//Disconnect, wait for a while and connect again.
StopSocket();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
if (!_running)
{
return;
}
try
{
StartSocket();
}
catch
{
}
}
}
}
DoListenAsThread 方法调用 TcpListener 对象(_listenerSocket)的 AcceptSocket() 方法。这是一个阻塞方法,因此线程在有新客户端连接到服务器之前将被阻塞。当客户端连接后,它会继续检查套接字是否正确连接,然后使用 OnCommunicationChannelConnected 方法通过 CommunicationChannelConnected 事件。它创建一个新的 TcpCommunicationChannel(将在下一节中考察)对象,并将其作为参数传递给 OnCommunicationChannelConnected 方法(它在 ConnectionListenerBase 类中定义为 protected)。您可以查看 SCS 框架源代码中的 CommunicationChannelEventArgs(用作事件的参数)。
通信通道
您已经看到了服务器端是如何创建通信通道的。同样,客户端也会创建通道来连接到服务器(我们稍后会看到)。在 SCS 中,应用程序之间的所有通信(服务器到客户端和客户端到服务器)都在通信通道上进行。通道对象负责将消息对象发送到远程应用程序,并监听和接收来自远程应用程序的网络传入消息。SCS 中的通信通道层次结构如下图所示。

所有通信通道都必须实现 ICommunicationChannel 接口或继承自 CommunicationChannelBase 抽象类。CommunicationChannelBase 实现 ICommunicationChannel 并为具体的通信通道类提供了一个良好的模板。
正如您所见,ICommunicationChannel 接口扩展了 IMessenger 接口。IMessenger 接口表示一个可以发送和接收消息的对象。SendMessage(...) 方法定义了向远程应用程序发送消息的方法。当从通信的远程应用程序接收到新消息时,会触发 MessageReceived 事件(因此,消息是通过事件接收的),并且在消息成功发送时触发 MessageSent 事件。IMessenger 还定义了 WireProtocol 属性,可用于更改线协议(如前所述)。其他属性不言自明。
ICommunicationChannel 继承了 IMessenger 并增加了一些功能。它定义了一个名为 CommunicationState 的属性,用于了解通道是否已连接到远程应用程序。定义了 RemoteEndPoint 以获取远程应用程序的地址(对于 TCP,它是一个 ScsTcpEndPoint 对象)。它还定义了 Start() 和 Disconnect() 方法来启动/停止通信。最后,它定义了当通道断开连接时会触发的 Disconnected 事件。
SCS 中唯一的具体通信通道类是 TcpCommunicationChannel。它继承自 CommunicationChannelBase。我将检查这个类,看看通信通道是如何使用 TCP 实现的。它只定义了一个构造函数,并接收一个 Socket (System.Net.Sockects.Socket) 对象。
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new TcpCommunicationChannel object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="clientSocket">A connected Socket object that is
/// used to communicate over network</param>
public TcpCommunicationChannel(Socket clientSocket)
{
_clientSocket = clientSocket;
_clientSocket.NoDelay = true;
var ipEndPoint = (IPEndPoint)_clientSocket.RemoteEndPoint;
_remoteEndPoint = new ScsTcpEndPoint(ipEndPoint.Address.ToString(), ipEndPoint.Port);
_buffer = new byte[ReceiveBufferSize];
_syncLock = new object();
}
正如您在通信监听器部分看到的,这个构造函数是由 TcpConnectionListener 类在新客户端连接到服务器时使用的。NoDelay = true 用于禁用Nagle算法(因为它限制了 SCS 消息发送的速度,并且不需要,因为 SCS 会一次性将整个消息写入套接字)。创建了一个 ScsTcpEndPoint 对象作为远程端点。它还创建了一个缓冲区来异步接收消息。
/// <summary>
/// Starts the thread to receive messages from socket.
/// </summary>
protected override void StartInternal()
{
_running = true;
_clientSocket.BeginReceive(_buffer, 0, _buffer.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), null);
}
StartInternal 方法由基类调用,以启动从远程应用程序接收消息。由于我们使用异步套接字方法,我们调用非阻塞的 BeginReceive 方法,提供一个缓冲区(用于获取接收到的字节)和一个回调方法,在从远程应用程序接收到任何字节时调用该方法。
/// <summary>
/// This method is used as callback method in _clientSocket's BeginReceive method.
/// It reveives bytes from socker.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ar">Asyncronous call result</param>
private void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar)
{
if(!_running)
{
return;
}
try
{
//Get received bytes count
var bytesRead = _clientSocket.EndReceive(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0)
{
LastReceivedMessageTime = DateTime.Now;
//Copy received bytes to a new byte array
var receivedBytes = new byte[bytesRead];
Array.Copy(_buffer, 0, receivedBytes, 0, bytesRead);
//Read messages according to current wire protocol
var messages = WireProtocol.CreateMessages(receivedBytes);
//Raise MessageReceived event for all received messages
foreach (var message in messages)
{
OnMessageReceived(message);
}
}
//Read more bytes if still running
if (_running)
{
_clientSocket.BeginReceive(_buffer, 0, _buffer.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), null);
}
}
catch
{
Disconnect();
}
}
在 ReceiveCallBack 方法中,使用套接字的EndReceive方法完成接收操作。接收到的字节被交给当前的线协议来创建消息。如果线协议成功创建了任何消息,就会通过基类的 OnMessageReceived 方法为每条消息触发一个 MessageReceived 事件。最后,再次调用套接字的非阻塞 BeginRecieve 方法来接收套接字上接下来的传入字节(请注意,这是一种递归调用,因为回调方法与调用方法相同)。
现在,让我们看看消息是如何发送的。ICommunicationChannel.SendMessage(IScsMessage message) 方法由 CommunicationChannelBase 类实现,它调用其子类 TcpCommunicationChannel 的 SendMessageInternal 方法。
/// <summary>
/// Sends a message to the remote application.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">Message to be sent</param>
protected override void SendMessageInternal(IScsMessage message)
{
//Send message
var totalSent = 0;
lock (_syncLock)
{
//Create a byte array from message according to current protocol
var messageBytes = WireProtocol.GetBytes(message);
//Send all bytes to the remote application
while (totalSent < messageBytes.Length)
{
var sent = _clientSocket.Send(messageBytes, totalSent, messageBytes.Length - totalSent, SocketFlags.None);
if (sent <= 0)
{
throw new CommunicationException("Message could not be sent via TCP socket. Only " +
totalSent + " bytes of " + messageBytes.Length + " bytes are sent.");
}
totalSent += sent;
}
LastSentMessageTime = DateTime.Now;
OnMessageSent(message);
}
}
它使用 WireProtocol 对象将消息(IScsMessage)对象序列化为字节数组,并使用 Socket 对象(_clientSocket)将其发送到远程应用程序。消息发送在一个 lock 语句中完成。因此,如果多个线程想发送消息,一次只有一个线程可以发送,其他线程将等待。
客户端
我们已经看到了通信通道是如何创建的(在服务器端通过连接监听器创建),以及通信通道是如何发送和接收消息的。现在我将检查 SCS 客户端对象,这些对象用于连接到服务器并与其通信。客户端的主要接口是 IScsClient。

IScsClient 接口继承了 IMessenger 和 IConnectableClient,并且不定义任何其他成员。我们之前已经考察了 IMesenger(在*通信通道*部分)。IConnectableClient 用于控制客户端与服务器的连接。它看起来像 ICommunicationChannel 接口,但实现和目的略有不同。它定义了 Connect() 方法来连接到服务器(而不是通道的 Start() 方法),以及 Disconnect() 方法来关闭连接。它定义了两个重要的事件:Connected 和 Disconnected。它们可用于监视客户端的连接状态。ConnectTimeout 用于设置连接到服务器时的超时值。最后,它定义了 CommunicationState 属性来检查连接的当前状态(与通道相同)。
ScsClientBase 抽象类为实现 IScsClient 提供了一个良好的模板。几乎所有的实现都在这个类中完成。因此,我将首先考察 ScsClientBase 类。我们来看这里有两个属性:
/// <summary>
/// Gets/sets wire protocol that is used while reading and writing messages.
/// </summary>
public IScsWireProtocol WireProtocol
{
get { return _wireProtocol; }
set
{
if (CommunicationState == CommunicationStates.Connected)
{
throw new ApplicationException("Wire protocol can not " +
"be changed while connected to server.");
}
_wireProtocol = value;
}
}
private IScsWireProtocol _wireProtocol;
/// <summary>
/// Gets the communication state of the Client.
/// </summary>
public CommunicationStates CommunicationState
{
get
{
return _communicationChannel != null
? _communicationChannel.CommunicationState
: CommunicationStates.Disconnected;
}
}
正如您所见,WireProtocol 只能在未连接到服务器时更改。CommunicationState 直接获取底层通道对象的 CommunicationState。LastReceivedMessageTime、LastSentMessageTime 属性以及 SendMessage(...) 和 Disconnect() 方法也直接映射到底层通道对象。ScsClientBase 的构造函数如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// The communication channel that is used by client to send and receive messages.
/// </summary>
protected ICommunicationChannel _communicationChannel;
/// <summary>
/// This timer is used to send PingMessage messages to server periodically.
/// </summary>
private readonly Timer _pingTimer;
/// <summary>
/// Constructor.
/// </summary>
protected ScsClientBase()
{
_pingTimer = new Timer(30000);
_pingTimer.Elapsed += PingTimer_Elapsed;
ConnectTimeout = DefaultConnectionAttemptTimeout;
WireProtocol = WireProtocolManager.GetDefaultWireProtocol();
}
在构造函数中,我们创建了一个 Timer(该计时器由 SCS 框架定义),用于向服务器发送周期性的 PingMessage 对象(如果通信线路在 last minute空闲)。我们还获取了默认线协议(BinarySerializationProtocol)的引用。如果用户未设置 WireProtocol,则使用默认协议。现在,让我们看看客户端如何连接到服务器(Connect() 方法是如何实现的)。
/// <summary>
/// Connects to server.
/// </summary>
public void Connect()
{
WireProtocol.Reset();
_communicationChannel = CreateCommunicationChannel();
_communicationChannel.WireProtocol = _wireProtocol;
_communicationChannel.Disconnected += CommunicationChannel_Disconnected;
_communicationChannel.MessageReceived += CommunicationChannel_MessageReceived;
_communicationChannel.MessageSent += CommunicationChannel_MessageSent;
_communicationChannel.Start();
_pingTimer.Start();
OnConnected();
}
我们首先重置线协议。如果用户重新连接到服务器(断开并使用同一个对象重新连接),则需要这样做。然后我们创建一个通信通道。这很关键,因为我们必须根据当前的传输层协议(TCP 是默认的)来创建合适的通信通道。我们通过将 CreateCommunicationChannel() 方法定义为 abstract 来实现这一点。因此,它将由派生类(由 ScsTcpClient 类)实现。然后我们设置通道的 WireProtocol,注册通道的事件并启动它。最后,我们启动ping 计时器并触发 Connected 事件。我将在这里考察的 ScsClientBase 的最后一个方法是 _pingTimer 对象的 Elapsed 事件处理程序。我们发送一个Ping消息,以防在 last minute 没有通信,如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// Handles Elapsed event of _pingTimer to send PingMessage messages to server.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event arguments</param>
private void PingTimer_Elapsed(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (CommunicationState != CommunicationStates.Connected)
{
return;
}
try
{
var lastMinute = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(-1);
if (_communicationChannel.LastReceivedMessageTime > lastMinute ||
_communicationChannel.LastSentMessageTime > lastMinute)
{
return;
}
_communicationChannel.SendMessage(new PingMessage());
}
catch
{
}
}
正如本节开头的图所示,唯一实现 IScsClient 的具体客户端类是 ScsTcpClient。它继承自 ScsClientBase 并重写了 CreateCommunicationChannel() 方法,如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// Creates a communication channel using ServerIpAddress and ServerPort.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Ready communication channel to communicate</returns>
protected override ICommunicationChannel CreateCommunicationChannel()
{
return new TcpCommunicationChannel(
TcpHelper.ConnectToServer(
new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(_serverEndPoint.IpAddress), _serverEndPoint.TcpPort),
ConnectTimeout
));
}
它创建一个 .NET Socket (System.Net.Sockets.Socket) 对象,并使用该套接字创建一个 TcpCommunicationChannel 对象。您可以在源代码中看到 TcpHelper.ConnectToServer(...) 方法。它只是创建一个 Socket 对象并连接到服务器。如果无法在指定时间内(ConnectTimeout)连接到服务器,则会抛出异常。
我们已经了解了 TCP 客户端(ScsTcpClient)是如何工作的。现在,让我们看看 SCS 框架的用户是如何创建它的。
/// <summary>
/// This class is used to create SCS Clients to connect to a SCS server.
/// </summary>
public static class ScsClientFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new client to connect to a server using an end point.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endpoint">End point of the server to connect it</param>
/// <returns>Created TCP client</returns>
public static IScsClient CreateClient(ScsEndPoint endpoint)
{
return endpoint.CreateClient();
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new client to connect to a server using an end point.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endpointAddress">End point address of the server to connect it</param>
/// <returns>Created TCP client</returns>
public static IScsClient CreateClient(string endpointAddress)
{
return CreateClient(ScsEndPoint.CreateEndPoint(endpointAddress));
}
}
ScsClientFactory.CreateClient(...) 方法之一用于创建客户端。它获取一个端点(ScsEndPoint)对象并返回一个客户端(IScsClient)对象。正如您所见,它只是调用端点的 CreateClient() 方法。因此,我们不会进入 switch 或 if 语句,因为每个端点对象都知道将使用端点创建哪种类型的客户端。因此,如果添加了新协议,则无需更改 ScsClientFactory。如果 endPoint 参数是 ScsTcpEndPoint(默认为唯一的端点),则在 ScsTcpEndPoint.CreateClient() 方法中创建 ScsTcpClient 对象,如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// Creates a Scs Client that uses this end point to connect to server.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Scs Client</returns>
internal override IScsClient CreateClient()
{
return new ScsTcpClient(this);
}
此外,用户还可以传递一个字符串地址(例如,本地主机上 10048 TCP 端口的tcp://127.0.0.1:10048)而不是端点。使用ScsEndPoint.CreateEndPoint静态方法可以从字符串创建端点。
最后,用户可以轻松创建一个基于 TCP 的 SCS 客户端对象,连接到服务器,发送/接收消息,然后关闭连接,如下所示:
using System;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Client;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.EndPoints.Tcp;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.Messages;
namespace ClientApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
//Create a client object to connect a server on 127.0.0.1 (local) IP and listens 10085 TCP port
var client = ScsClientFactory.CreateClient(new ScsTcpEndPoint("127.0.0.1", 10085));
//Register to MessageReceived event to receive messages from server.
client.MessageReceived += Client_MessageReceived;
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to connect to the server...");
Console.ReadLine(); //Wait user to press enter
client.Connect(); //Connect to the server
Console.Write("Write some message to be sent to server: ");
var messageText = Console.ReadLine(); //Get a message from user
//Send message to the server
client.SendMessage(new ScsTextMessage(messageText));
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to disconnect from server...");
Console.ReadLine(); //Wait user to press enter
client.Disconnect(); //Close connection to server
}
static void Client_MessageReceived(object sender, MessageEventArgs e)
{
//Client only accepts text messages
var message = e.Message as ScsTextMessage;
if (message == null)
{
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Server sent a message: " + message.Text);
}
}
}
为了演示,客户端只发送/接收 ScsTextMessage 对象,但可以发送从 ScsMessage 派生的任何类型的对象(或实现 IScsMessage),如前所述。此应用程序的服务器端将在服务器端部分末尾显示。您可以在下载文件中的Samples\SimpleMessaging文件夹中找到源代码。
服务器端
我们已经了解了 SCS 客户端的几乎所有内容。在本节中,我将考察SCS 消息传递层的服务器端是如何实现的。服务器端的主要接口是 IScsServer。与 SCS 框架中的其他继承模型一样,有一个名为 ScsServerBase 的模板抽象实现。ScsServerBase 实现 IScsServer 中的通用成员,并为具体的服务器类提供了一个良好的基础。唯一的具体服务器类是 ScsTcpServer 类。

IScsServer 定义了 WireProtocolFactory,允许用户更改消息传递协议(由于服务器为每个客户端创建一个线协议对象,因此使用工厂类而不是直接使用 WireProtocol)。它定义了一种排序列表,名为 Clients,用于存储当前连接到服务器的客户端(使用 ThreadSafeSortedList 来存储客户端以确保线程安全,因为它可能被多个线程修改)。此集合的键是 ClientId(一个唯一的长数字),值为指向客户端对象(IScsServerClient)的引用,用于与客户端通信(稍后将考察)。服务器类定义了 ClientConnected 和 ClientDisonnected 事件。使用这些事件,我们可以在客户端成功连接到服务器和断开连接时得到通知。我们可以在 事件处理程序中使用 ServerClientEventArgs 事件参数来获取连接/断开连接的客户端的引用。
作为开始考察服务器端的,让我们看看 ScsServerBase 的一些重要方法。
/// <summary>
/// Starts server.
/// </summary>
public virtual void Start()
{
_connectionListener = CreateConnectionListener();
_connectionListener.CommunicationChannelConnected +=
ConnectionListener_CommunicationChannelConnected;
_connectionListener.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// Stops server.
/// </summary>
public virtual void Stop()
{
if (_connectionListener != null)
{
_connectionListener.Stop();
}
foreach (var client in Clients.GetAllItems())
{
client.Disconnect();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// This method is implemented by derived classes to create
/// appropriate connection listener to listen incoming connection requets.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
protected abstract IConnectionListener CreateConnectionListener();
/// <summary>
/// Handles CommunicationChannelConnected event of _connectionListener object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event arguments</param>
private void ConnectionListener_CommunicationChannelConnected(object sender,
CommunicationChannelEventArgs e)
{
var client = new ScsServerClient(e.Channel)
{
ClientId = ScsServerManager.GetClientId(),
WireProtocol = WireProtocolFactory.CreateWireProtocol()
};
client.Disconnected += Client_Disconnected;
Clients[client.ClientId] = client;
OnClientConnected(client);
e.Channel.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// Handles Disconnected events of all connected clients.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event arguments</param>
private void Client_Disconnected(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
var client = (IScsServerClient) sender;
Clients.Remove(client.ClientId);
OnClientDisconnected(client);
}
ScsServerBase 类主要负责管理客户端。在 Start() 方法中,它使用抽象的 CreateConnectionListener() 方法创建一个连接监听器(IConnectionListener)。ScsTcpServer 实现此方法以创建 ScsTcpConnectionListener 对象(请参阅源代码中的 ScsTcpServer 类)。然后它注册 CommunicationChannelConnected 事件并启动连接监听器。Stop() 方法仅停止连接监听器并断开所有活动客户端的连接。
CommunicationChannelConnected 事件处理程序(ConnectionListener_CommunicationChannelConnected 方法)使用新通道创建一个新的 ScsServerClient 对象,注册其 Disconnect 事件以在客户端连接失败时收到通知,将其添加到 Clients 集合,并启动与新客户端的通信。最后,Client_Disconnected 事件处理程序方法用于从 Clients 集合中删除已断开连接的客户端。请注意,新客户端的 ClientId 属性是在使用 ScsServerManager.GetClientId() 创建对象时设置的。此方法定义如下。它使用 Interlocked (System.Threading.Interlocked) 类以线程安全的方式增加 _lastClientId。
internal static class ScsServerManager
{
/// <summary>
/// Used to set an auto incremential unique identifier to clients.
/// </summary>
private static long _lastClientId;
/// <summary>
/// Gets an unique number to be used as idenfitier of a client.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static long GetClientId()
{
return Interlocked.Increment(ref _lastClientId);
}
}
正如您所见,在服务器端,客户端由 IScsServerClient 接口表示。该接口用于从服务器与客户端通信。

IScsServerClient 接口也扩展了 IMessenger。它由 ScsServerClient 类实现。IScsServerClient 没有基于传输层的实现(如 ScsTcpServerClient),因为 ScsServerClient 使用 ICommunicationChannel 与客户端通信(因此,它是协议无关的)。ScsServerClient 的构造函数和一些方法如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// Unique identifier for this client in server.
/// </summary>
public long ClientId { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// The communication channel that is used by client to send and receive messages.
/// </summary>
protected ICommunicationChannel _communicationChannel;
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new ScsClient object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="communicationChannel">The communication channel
/// that is used by client to send and receive messages</param>
public ScsServerClient(ICommunicationChannel communicationChannel)
{
_communicationChannel = communicationChannel;
_communicationChannel.MessageReceived += CommunicationChannel_MessageReceived;
_communicationChannel.MessageSent += CommunicationChannel_MessageSent;
_communicationChannel.Disconnected += CommunicationChannel_Disconnected;
}
/// <summary>
/// Disconnects from client and closes underlying communication channel.
/// </summary>
public void Disconnect()
{
_communicationChannel.Disconnect();
}
/// <summary>
/// Sends a message to the client.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">Message to be sent</param>
public void SendMessage(IScsMessage message)
{
_communicationChannel.SendMessage(message);
}
如前所述,ScsServerClient 使用通信通道与客户端通信,并将其作为构造函数的参数。它注册通信通道的事件,以便能够触发这些事件,因为它实现了 IMessenger 和 IScsServerClient,并且它们定义了 MessageReceived 和 Disconnected 事件。ClientId 是服务器在创建 ScsServerClient 时设置的一个唯一编号(如前所述)。
SCS 框架的用户使用 ScsServerFactory 类来创建服务器对象。
/// <summary>
/// This class is used to create SCS servers.
/// </summary>
public static class ScsServerFactory
{
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new SCS Server using an EndPoint.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endPoint">Endpoint that represents address of the server</param>
/// <returns>Created TCP server</returns>
public static IScsServer CreateServer(ScsEndPoint endPoint)
{
return endPoint.CreateServer();
}
}
与创建客户端对象非常相似,我们获取一个端点对象(用于监听传入的客户端连接请求),并使用该端点来创建服务器。因此,服务器对象是根据端点创建的(请注意,此方法是 internal,用户不能直接使用)。由于所有端点(实际上只有一个)都知道要创建哪种类型的服务器,因此服务器对象会成功创建。让我们看看 ScsTcpEndPoint 类中 CreateServer() 方法的 TCP 实现。
/// <summary>
/// Creates a Scs Server that uses this
/// end point to listen incoming connections.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Scs Server</returns>
internal override IScsServer CreateServer()
{
return new ScsTcpServer(this);
}
最后,让我们看一个简单的服务器应用程序,它监听客户端连接,从客户端获取文本消息,并为消息发送响应。这完成了我们在客户端部分构建的示例应用程序。
using System;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.EndPoints.Tcp;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.Messages;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Server;
namespace ServerApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
//Create a server that listens 10085 TCP port for incoming connections
var server = ScsServerFactory.CreateServer(new ScsTcpEndPoint(10085));
//Register events of the server to be informed about clients
server.ClientConnected += Server_ClientConnected;
server.ClientDisconnected += Server_ClientDisconnected;
server.Start(); //Start the server
Console.WriteLine("Server is started successfully. Press enter to stop...");
Console.ReadLine(); //Wait user to press enter
server.Stop(); //Stop the server
}
static void Server_ClientConnected(object sender, ServerClientEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("A new client is connected. Client Id = " + e.Client.ClientId);
//Register to MessageReceived event to receive messages from new client
e.Client.MessageReceived += Client_MessageReceived;
}
static void Server_ClientDisconnected(object sender, ServerClientEventArgs e)
{
Console.WriteLine("A client is disconnected! Client Id = " + e.Client.ClientId);
}
static void Client_MessageReceived(object sender, MessageEventArgs e)
{
var message = e.Message as ScsTextMessage; //Server only accepts text messages
if (message == null)
{
return;
}
//Get a reference to the client
var client = (IScsServerClient)sender;
Console.WriteLine("Client sent a message: " + message.Text +
" (Cliend Id = " + client.ClientId + ")");
//Send reply message to the client
client.SendMessage(
new ScsTextMessage(
"Hello client. I got your message (" + message.Text + ")",
message.MessageId //Set first message's id as replied message id
));
}
}
}
如果您运行服务器和客户端应用程序并从客户端向服务器发送消息,您将看到如下屏幕:

您可以在下载文件中的Samples\SimpleMessaging文件夹中找到源代码。
远程方法调用层
正如我之前提到的,SCS 框架允许用户调用远程方法。我已经详细解释了消息传递层。远程方法调用层负责将方法调用转换为消息并通过消息传递层发送。它还从消息传递层接收消息,并调用应用程序的服务方法。消息传递层中的所有类都定义在 Hik.Communication.ScsServices 命名空间(及其子命名空间)中。我建议您查看第一个文章中的聊天系统,以了解 RMI 层的使用方式。
请求/响应式消息传递
方法调用是一种请求/响应操作。请求包括方法的名称和参数,响应是方法的结果值(即使方法返回类型为 void,该方法也可以抛出异常,该异常可被视为响应/输出)。SCS 的消息传递层是异步的(由于 TCP 的性质)。这意味着服务器和客户端可以独立地发送/接收消息。因此,我们必须构建一个机制来发送方法调用请求并等待方法调用的结果。
请求/响应式消息传递是通过 RequestReplyMessenger 类在 SCS 中实现的。它实际上是任何 IMessenger 的一个装饰器。RequestReplyMessenger 的类图如下所示:

RequestReplyMessenger 是一个泛型类,它接受一个实现 IMessenger 的类作为其泛型参数。RequestReplyMessenger 也实现 IMessenger(如上面的类图所示)。它用以下功能装饰一个 IMessenger 对象:
SendMessageAndWaitForReply(...)方法:使用此方法,我们可以向远程应用程序发送消息并获取回复消息。它会阻塞调用线程,直到收到响应或发生超时。如果在指定时间内未收到响应,则会抛出异常。它使用 IScsMessage.RepliedMessageId 属性来匹配消息。- 传入消息的排队处理:
RequestReplyMessenger通过FIFO(先进先出)队列处理消息。如果发送方应用程序生成消息的速度快于接收方的处理速度,则消息将被排队。
首先,我们必须看看 RequestReplyMessenger 是如何创建和使用的。假设您已经创建了一个 SCS 客户端,并希望使用 RequestReplyMessenger 通过该客户端发送请求/响应式消息。我将重写我们在客户端部分构建的应用程序。
using System;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Client;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.EndPoints.Tcp;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.Messages;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.Messengers;
namespace RequestReplyStyleClient
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to connect to the server...");
Console.ReadLine(); //Wait user to press enter
//Create a client object to connect a server on 127.0.0.1 (local) IP and listens 10085 TCP port
using (var client = ScsClientFactory.CreateClient(new ScsTcpEndPoint("127.0.0.1", 10085)))
{
//Create a RequestReplyMessenger that uses the client as internal messenger.
using (var requestReplyMessenger = new RequestReplyMessenger<IScsClient>(client))
{
requestReplyMessenger.Start(); //Start request/reply messenger
client.Connect(); //Connect to the server
Console.Write("Write some message to be sent to server: ");
var messageText = Console.ReadLine(); //Get a message from user
//Send user message to the server and get response
var response = requestReplyMessenger.SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(new ScsTextMessage(messageText));
Console.WriteLine("Response to message: " + ((ScsTextMessage) response).Text);
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to disconnect from server...");
Console.ReadLine(); //Wait user to press enter
}
}
}
}
}
正如您所见,我们创建了一个 RequestReplyMessenger<IScsClient> 对象。泛型参数是 IScsClient,因为我们使用这种类型的对象与服务器通信(请记住 IScsClient 继承自 IMessenger)。然后我们调用 Start() 方法(它会在内部启动消息处理队列,我们稍后会看到)。关键一行是我们调用 SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(...) 方法。它返回一个 IScsMessage 对象。该对象是服务器为我们的出站消息发送的响应消息。最后,我们必须调用 Stop RequestReplyMessenger(以停止内部消息队列)。由于它是IDisposible的,因此在使用语句中进行处理时会自动停止。现在,让我们考察 RequestReplyMessenger 类的实现。
由于 RequestReplyMessenger 可以由多个线程使用,因此它必须阻塞每个线程,存储消息上下文(如发送的消息 ID),并与接收到的消息进行匹配。因此,它必须存储一些关于请求的信息,直到收到响应(或发生超时)。它使用 WaitingMessage 类对象来完成这项任务。
/// <summary>
/// This class is used to store messaging context for a request message
/// until response is received.
/// </summary>
private sealed class WaitingMessage
{
/// <summary>
/// Response message for request message (null if response
/// is not received yet).
/// </summary>
public IScsMessage ResponseMessage { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// ManualResetEvent to block thread until response is received.
/// </summary>
public ManualResetEvent WaitEvent { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// State of the request message.
/// </summary>
public WaitingMessageStates State { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new WaitingMessage object.
/// </summary>
public WaitingMessage()
{
WaitEvent = new ManualResetEvent(false);
State = WaitingMessageStates.WaitingForResponse;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// This enum is used to store the state of a waiting message.
/// </summary>
private enum WaitingMessageStates
{
/// <summary>
/// Still waiting for response.
/// </summary>
WaitingForResponse,
/// <summary>
/// Message sending is cancelled.
/// </summary>
Cancelled,
/// <summary>
/// Response is properly received.
/// </summary>
ResponseReceived
}
WaitingMessage 对象在收到响应之前存储在 _waitingMessages 集合中。
/// <summary>
/// This messages are waiting for a response.
/// Key: MessageID of waiting request message.
/// Value: A WaitingMessage instance.
/// </summary>
private readonly SortedList<string, WaitingMessage> _waitingMessages;
现在,让我们看看我是如何实现 SendMessageAndWaitForReply(...) 方法的。
/// <summary>
/// Sends a message and waits a response for that message.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="message">message to send</param>
/// <param name="timeoutMilliseconds">Timeout duration as milliseconds.</param>
/// <returns>Response message</returns>
public IScsMessage SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(IScsMessage message,
int timeoutMilliseconds)
{
//Create a waiting message record and add to list
var waitingMessage = new WaitingMessage();
lock (_waitingMessages)
{
_waitingMessages[message.MessageId] = waitingMessage;
}
try
{
//Send message
Messenger.SendMessage(message);
//Wait for response
waitingMessage.WaitEvent.WaitOne(timeoutMilliseconds);
//Check for exceptions
switch (waitingMessage.State)
{
case WaitingMessageStates.WaitingForResponse:
throw new Exception("Timeout occured. Can not received response.");
case WaitingMessageStates.Cancelled:
throw new Exception("Disconnected before response received.");
}
//return response message
return waitingMessage.ResponseMessage;
}
finally
{
//Remove message from waiting messages
lock (_waitingMessages)
{
if (_waitingMessages.ContainsKey(message.MessageId))
{
_waitingMessages.Remove(message.MessageId);
}
}
}
}
首先,我们创建一个 WaitingMessage 对象,并以发送消息的 MessageId 作为键将其存储在 _waitingMessages SortedList 集合中(我们对集合进行操作是在 lock 语句中进行的,以确保线程安全)。然后,我们使用底层的 Messenger 对象(如您之前所见,它作为参数传递给构造函数)发送消息。我们必须等待直到收到响应消息。因此,我们调用 ManualResetEvent (System.Threading.ManualResetEvent) 类的 WaitOne(...) 方法。它会阻塞调用线程,直到另一个线程调用同一个 ManualResetEvent 对象的 Set() 方法或发生超时。无论如何,调用线程将继续运行,并检查 WaitingMessage 对象的当前 State。如果它仍然处于 WaitForResponse 状态,则表示发生了超时。如果它处于 Canceled 状态,则表示 RequestReplyMessenger 在收到响应之前已停止;否则(即状态为 ResponseReceived),响应消息将作为 SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(...) 方法的返回值返回。最后,我们必须从 _waitingMessages 集合中删除 WaitingMessage 对象,因为它不再被等待。
现在,让我们考察 WaitingMessage 对象的 State 是如何改变的。第一种情况是成功接收到响应消息。为此,我们必须注册底层 IMessenger 对象的 MessageReceived 事件。MessageReceived 的事件处理程序如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// Handles MessageReceived event of Messenger object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event arguments</param>
private void Messenger_MessageReceived(object sender, MessageEventArgs e)
{
//Check if there is a waiting thread for this message
//(in SendMessageAndWaitForResponse method)
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.Message.RepliedMessageId))
{
WaitingMessage waitingMessage = null;
lock (_waitingMessages)
{
if (_waitingMessages.ContainsKey(e.Message.RepliedMessageId))
{
waitingMessage = _waitingMessages[e.Message.RepliedMessageId];
}
}
//If there is a thread waiting for this response message, pulse it
if (waitingMessage != null)
{
waitingMessage.ResponseMessage = e.Message;
waitingMessage.State = WaitingMessageStates.ResponseReceived;
waitingMessage.WaitEvent.Set();
return;
}
}
_incomingMessageProcessor.EnqueueMessage(e.Message);
}
此方法首先检查接收到的消息是否是响应消息(如果其 RepliedMessageId 为空,则它不是响应消息)。如果是,则检查 _waitingMessages 集合中是否有消息正在等待此响应。如果此条件也为真,则将消息的状态设置为 ResponseReceived,将 ResponseMessage 设置为新的传入消息,最后调用 ManualResetEvent 对象(WaitEvent)的 Set() 方法来通知等待线程继续。如果所有条件都为假,并且消息是普通的传入消息,则将其添加到 _incomingMessageProcessor 中进行处理(请参阅源代码中此队列中的消息处理)。对于非回复消息,将调用 MessageReceived 事件。
改变 WaitingMessage 状态的第二种也是最后一种方法是 RequestReplyMessenger 的 Stop() 方法。它定义如下:
/// <summary>
/// Stops the messenger.
/// Cancels all waiting threads in SendMessageAndWaitForResponse
/// method and stops message queue.
/// SendMessageAndWaitForResponse method throws exception
/// if there is a thread that is waiting for response message.
/// </summary>
public void Stop()
{
_incomingMessageProcessor.Stop();
//Pulse waiting threads for incoming messages,
//since underlying messenger is disconnected
//and can not receive messages anymore.
lock (_waitingMessages)
{
foreach (var waitingMessage in _waitingMessages.Values)
{
waitingMessage.State = WaitingMessageStates.Cancelled;
waitingMessage.WaitEvent.Set();
}
_waitingMessages.Clear();
}
}
如果 RequestReplyMessenger 已停止,它会将所有等待消息的状态设置为 Canceled,并通过调用 ManualResetEvent 的 Set() 方法通知等待线程继续。
通过考察 Stop 方法,我完成了对请求/响应式消息传递的解释。这是 SCS 框架的关键点之一。
远程方法调用消息
到目前为止,我们已经构建了一个强大的消息传递基础结构。现在是时候看看方法调用如何被翻译成消息,反之亦然。远程方法调用层定义了两个新消息类。它们是 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 和 ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage。

ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 存储方法调用信息,例如方法的名称(MethodName)、拥有该方法的类(ServiceClassName)以及调用远程应用程序上的方法时使用的所有参数(Parameters)。ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage 存储方法调用的返回值(ReturnValue)(如果未发生异常),或者在远程方法中抛出异常时存储异常对象(RemoteException)。由于这两个类都继承自 ScsMessage,因此它们具有 MessageId 和 RepliedMessageId 属性,这些属性用于匹配请求(ScsRemoteInvokeMessage)和响应(ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage)消息。
服务合同及其使用
服务合同是 SCS 框架的另一个关键点。服务合同是一个接口,用于定义服务器上可被客户端远程调用的方法。您还可以创建一个服务合同来定义服务器上可被客户端远程调用的方法(您可以认为 SCS 框架中的服务合同对应于 WCF 中的合同)。
在进一步深入 SCS 远程方法调用层的实现之前,我想用一个非常简单的应用程序来演示此层的用法。如果您阅读了第一个文章,可以跳到下一节。如果您想查看此层(用于服务器到客户端方法调用)的完整用法,请参阅第一篇文章。在此简单应用程序中,我将使用一个计算器服务和一个使用该服务进行计算的客户端。
首先,我们定义一个服务合同接口,如下所示:
/// <summary>
/// This interface defines methods of calculator
/// service that can be called by clients.
/// </summary>
[ScsService]
public interface ICalculatorService
{
int Add(int number1, int number2);
double Divide(double number1, double number2);
}
服务合同非常清晰。这是一个普通的 C# 接口,除了 ScsService 属性。让我们看看一个实现此合同的服务应用程序。完整的服务器端代码如下所示:
using System;
using CalculatorCommonLib;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.EndPoints.Tcp;
using Hik.Communication.ScsServices.Service;
namespace CalculatorServer
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Create a service application that runs on 10083 TCP port
var serviceApplication =
ScsServiceBuilder.CreateService(new ScsTcpEndPoint(10083));
//Create a CalculatorService and add it to service application
serviceApplication.AddService<ICalculatorService,
CalculatorService>(new CalculatorService());
//Start service application
serviceApplication.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Calculator service is started. Press enter to stop...");
Console.ReadLine();
//Stop service application
serviceApplication.Stop();
}
}
public class CalculatorService : ScsService, ICalculatorService
{
public int Add(int number1, int number2)
{
return number1 + number2;
}
public double Divide(double number1, double number2)
{
if(number2 == 0.0)
{
throw new DivideByZeroException("number2 can not be zero!");
}
return number1 / number2;
}
}
}
CalculatorService 类实现了 ICalculatorService。它必须继承自 ScsService 类。在控制台应用程序的 Main 方法中,我们首先创建一个在 10083 TCP 端口上运行的服务应用程序。然后我们创建一个 CalculatorService 对象,并使用 AddService(...) 将其添加到服务应用程序。此方法是泛型的,接受服务合同接口类型和服务实现类型。然后我们使用 Start() 方法启动服务。正如您所见,创建 SCS 服务应用程序非常简单明了。现在,让我们编写一个使用此服务的客户端应用程序:
using System;
using CalculatorCommonLib;
using Hik.Communication.Scs.Communication.EndPoints.Tcp;
using Hik.Communication.ScsServices.Client;
namespace CalculatorClient
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to connect " +
"to server and call methods...");
Console.ReadLine();
//Create a client that can call methods of Calculator
//Service that is running on local computer and 10083 TCP port
//Since IScsServiceClient is IDisposible,
//it closes connection at the end of the using block
using (var client =
ScsServiceClientBuilder.CreateClient<ICalculatorService>(
new ScsTcpEndPoint("127.0.0.1", 10083)))
{
//Connect to the server
client.Connect();
//Call a remote method of server
var division = client.ServiceProxy.Divide(42, 3);
Console.WriteLine("Result: " + division);
}
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to stop client application");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
正如您所见,我们正在使用客户端对象(IScsServiceClient)的 ServiceProxy 属性来远程调用服务方法。这是一个动态代理。我们没有生成代理类。当您将 Web 服务或 WCF 服务添加到应用程序时,Visual Studio 会自动生成一个代理类(或者您可以使用控制台实用程序wsdl.exe来处理 Web 服务,使用scvutil.exe来处理 WCF 服务)。当服务合同或 Web 服务定义发生更改时,您必须更新/重新生成代理代码。在 SCS 服务中,它是完全动态的。您无需生成代理类。
动态代理
代理,在其最一般的形式中,是一个充当其他事物接口的类。代理类实现与真实类相同的接口。用户可以调用代理对象的方法,而不是直接调用真实对象的相同方法。代理对象可以在调用真实对象的方法之前/之后执行一些操作,它可以调用多个方法或执行任何它想要的操作。
我们在*将消息与类和方法映射*部分讨论了如何实现代理类。当用户调用服务方法时,我们必须获取服务合同接口名称、方法名称和参数列表,使用这些参数创建一个 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 对象,发送消息,并使用 RequestReplyMessenger 类获取响应(一个 ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage 对象),然后将方法结果返回给用户。让我们看看我们是如何动态实现的。
.NET Framework 允许通过继承 RealProxy (System.Runtime.Remoting.Proxies.RealProxy) 类来创建动态透明代理类。它有一个名为 GetTransparentProxy() 的方法,该方法返回一个透明代理对象。您可以将此对象转换为任何接口。尽管该对象不是实现已转换接口的类的实例,但它不会抛出异常!它是 .NET Framework 中最有趣的类之一。那么,当您通过接口调用对象的方法时会发生什么?当然,它没有实现(因为同一个 TransparentProxy 对象可以转换为任何接口)。因此,您必须重写 RealProxy.Invoke 方法来决定在方法调用时做什么。在 Invoke 方法中,您可以获取用户调用的方法名以及作为参数传递给方法的参数列表。无论用户调用哪个方法,您都必须在同一个 Invoke 方法中处理所有方法调用。
SCS 框架使用 RemoteInvokeProxy 类(继承自 RealProxy)来动态地将方法调用转换为消息。它定义如下:
/// <summary>
/// This class is used to generate a dynamic proxy to invoke remote methods.
/// It translates method invocations to messaging.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TProxy">Type of the proxy class/interface</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TMessenger">Type of the messenger object
/// that is used to send/receive messages</typeparam>
internal class RemoteInvokeProxy<TProxy, TMessenger> :
RealProxy where TMessenger : IMessenger
{
/// <summary>
/// Messenger object that is used to send/receive messages.
/// </summary>
private readonly RequestReplyMessenger<TMessenger> _clientMessenger;
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new RemoteInvokeProxy object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="clientMessenger">Messenger object
/// that is used to send/receive messages</param>
public RemoteInvokeProxy(RequestReplyMessenger<TMessenger> clientMessenger)
: base(typeof(TProxy))
{
_clientMessenger = clientMessenger;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overrides message calls and translates
/// them to messages to remote application.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg">Method invoke message (from RealProxy base class)</param>
/// <returns>Method invoke return message (to RealProxy base class)</returns>
public override IMessage Invoke(IMessage msg)
{
var message = msg as IMethodCallMessage;
if (message == null)
{
return null;
}
var requestMessage = new ScsRemoteInvokeMessage
{
ServiceClassName = typeof (TProxy).Name,
MethodName = message.MethodName,
Parameters = message.InArgs
};
var responseMessage =
_clientMessenger.SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(requestMessage)
as ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage;
if (responseMessage == null)
{
return null;
}
return responseMessage.RemoteException != null
? new ReturnMessage(responseMessage.RemoteException, message)
: new ReturnMessage(responseMessage.ReturnValue,
null, 0, message.LogicalCallContext,
message);
}
}
RemoteInvokeProxy 是一个泛型类。第一个泛型参数(TProxy)是服务合同接口的类型,第二个(TMessenger)是消息者对象的类型(这是使用 RequestReplyMessenger 所必需的)。它接收一个 RequestReplyMessenger 对象,该对象用于向远程应用程序发送消息并获取响应。唯一的方法是重写 RealProxy.Invoke() 方法。不要被 IMessage、IMethodCallMessage... 接口所混淆。它们是 .NET Framework 的一部分,与 SCS 无关。
在 Invoke 方法中,我们创建一个新的 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 对象。ServiceClassName 是服务合同接口类型的名称。MethodName 和 Parameters 使用 Invoke 方法的输入参数设置(此输入参数提供了关于方法调用的所有信息)。然后,我们使用 RequestReplyMessenger.SendMessageAndWaitForResponse(...) 方法发送消息并接收响应。最后,我们使用响应消息向方法调用提供返回值。Invoke 方法的实现主要与 RealProxy 类相关。我们将在后续章节中看到如何创建和使用 RemoteInvokeProxy。
使用反射调用方法
将用户方法调用转换为消息并发送消息是远程方法调用的第一部分。第二部分是根据接收到的 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 对象在远程应用程序中调用适当的方法,并将方法调用的结果作为 ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage 对象发送。这可以通过使用 .NET Framework 中的反射机制轻松实现。
有两种不同的方法调用实现。一种实现在服务器端,另一种实现在客户端。它们具有截然不同的方法来确定如何找到要调用其方法的适当对象,但调用方法的部分几乎相同。我在这里将考察客户端(请记住,服务器可以远程调用客户端方法;例如,请参阅第一个文章中的聊天系统)。因此,让我们看看当消息从服务器端接收到客户端时会发生什么。
/// <summary>
/// Handles MessageReceived event of messenger.
/// It gets messages from server and invokes appropriate method.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event arguments</param>
private void RequestReplyMessenger_MessageReceived(object sender,
MessageEventArgs e)
{
//Cast message to ScsRemoteInvokeMessage and check it
var invokeMessage = e.Message as ScsRemoteInvokeMessage;
if (invokeMessage == null)
{
return;
}
//Check client object.
if(_clientObject == null)
{
SendInvokeResponse(invokeMessage, null,
new ScsRemoteException("Client does not wait for " +
"method invocations by server."));
return;
}
//Invoke method
object returnValue;
try
{
var type = _clientObject.GetType();
var method = type.GetMethod(invokeMessage.MethodName);
returnValue =
method.Invoke(_clientObject, invokeMessage.Parameters);
}
catch (TargetInvocationException ex)
{
var innerEx = ex.InnerException;
SendInvokeResponse(invokeMessage, null,
new ScsRemoteException(innerEx.Message, innerEx));
return;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SendInvokeResponse(invokeMessage, null,
new ScsRemoteException(ex.Message, ex));
return;
}
//Send return value
SendInvokeResponse(invokeMessage, returnValue, null);
}
我们使用 MessageReceived 事件来接收来自服务器的传入消息。由于系统是基于远程方法调用的,我们只接受 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 消息(否则,我们在事件处理程序方法中立即返回)。我们正在检查用户是否提供了一个对象来处理来自服务器的方法调用(我们在本文的计算器客户端示例中没有这样做,但您可以查看第一个文章以获取此方法的示例)。我们使用反射调用适当的方法,获取返回值,最后发送一条消息给服务器作为对方法调用的响应。SendInvokeResponse(...) 方法使用给定的参数创建一个 ScsRemoteInvokeReturnMessage 对象,并将其发送给服务器(请参阅源代码)。我们知道服务器端如何处理该消息(来自上面的*动态代理*部分)。如果方法调用抛出异常,我们也会将此异常发送给服务器。
我们已经完成了对 SCS 框架中消息传递层之上的远程方法调用机制的考察。在接下来的章节中,我们将看到客户端和服务器端是如何使用这些 RMI 技术实现的。
客户端
我们在前面的章节中已经看到了客户端的大部分内容。此外,我们还创建了一个示例应用程序来查看 SCS 服务客户端的用法。现在,我们将考察 SCS 中的客户端类。服务客户端是通过使用 ScsServiceClientBuilder.CreateClient(...) 静态方法创建的,正如我们之前看到的。此方法定义如下:
/// <summary>
/// Creates a client to connect to a SCS service.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">Type of service interface for remote method call</typeparam>
/// <param name="endpoint">EndPoint address of the server</param>
/// <param name="clientObject">Client-side object that
/// handles remote method calls from server to client.
/// May be null if client has no methods to be invoked by server</param>
/// <returns>Created client object to connect to the server</returns>
public static IScsServiceClient<T> CreateClient<T>(ScsEndPoint endpoint,
object clientObject = null) where T : class
{
return new ScsServiceClient<T>(endpoint.CreateClient(), clientObject);
}
它返回一个 IScsServiceClient 接口,该接口由 ScsServiceClient 类实现。类图如下所示:
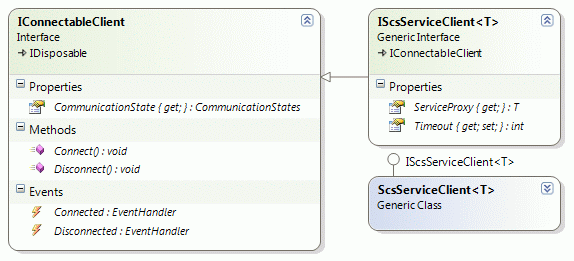
IScsServiceClient 接口扩展了 IConnectableClient。IConnectableClient 接口之前已解释过。IScsServiceClient 只添加了两个属性:ServiceProxy 属性是一个动态透明代理,用于调用服务器的远程方法。它是一个泛型成员,T 参数是服务合同的类型(该类型传递给 ScsServiceClientBuilder.CreateClient() 泛型方法)。Timeout 用于设置远程方法调用的超时值。接口的所有成员都由 ScsServiceClient 类实现。其构造函数如下所示:
/// <summary>>
/// Creates a new ScsServiceClient object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="client">Underlying IScsClient object
/// to communicate with server</param>
/// <param name="clientObject">The client object that
/// is used to call method invokes in client side.
/// May be null if client has no methods to be invoked by server.</param>
public ScsServiceClient(IScsClient client, object clientObject)
{
_client = client;
_clientObject = clientObject;
_client.Connected += Client_Connected;
_client.Disconnected += Client_Disconnected;
_requestReplyMessenger = new RequestReplyMessenger<IScsClient>(client);
_requestReplyMessenger.MessageReceived +=
RequestReplyMessenger_MessageReceived;
_realProxy = new RemoteInvokeProxy<T, IScsClient>(_requestReplyMessenger);
ServiceProxy = (T)_realProxy.GetTransparentProxy();
}
正如您在 ScsServiceClientBuilder.CreateClient() 方法中已经看到的那样,ScsServiceClient 获取一个 IScsClient 对象(正如之前在消息传递层部分所解释的,这是用于发送消息到服务器和从服务器接收消息的主要接口)。在构造函数中,我们创建了一个 RequestReplyMessenger 对象以请求/回复的方式发送/接收消息。最后但同样重要的是,我们创建了一个 RemoteInvokeProxy 对象并调用其 GetTransparentProxy() 方法来创建一个用于调用服务器远程方法的对象。正如您所见,我们正在将其转换为 T(服务契约的类型)。尽管 T 在 SCS 框架的编译时是未知的,并且它可以是任何接口,但通过 RealProxy 的特殊行为将其转换为 T 没有问题。我们已经研究了如何通过客户端到服务器进行方法调用,因此对客户端的检查到此结束。
服务器端
正如您之前所见,服务应用程序是通过使用下面定义的 ScsServiceBuilder.CreateService(...) 静态方法创建的。
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new SCS Service application using an EndPoint.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="endPoint">EndPoint that represents address of the service</param>
/// <returns>Created SCS service application</returns>
public static IScsServiceApplication CreateService(ScsEndPoint endPoint)
{
return new ScsServiceApplication(ScsServerFactory.CreateServer(endPoint));
}
CreateService(...) 方法获取一个端点并返回一个 IScsServiceApplication 接口。类图如下所示。

IScsServiceApplication 接口定义了用户可以用于管理服务器端的方法和事件。它由 ScsServiceApplication 类实现。该类的构造函数如下所示。
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new ScsServiceApplication object.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="scsServer">Underlying IScsServer object
/// to accept and manage client connections</param>
internal ScsServiceApplication(IScsServer scsServer)
{
if (scsServer == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("scsServer");
}
_scsServer = scsServer;
_scsServer.ClientConnected += ScsServer_ClientConnected;
_scsServer.ClientDisconnected += ScsServer_ClientDisconnected;
_serviceObjects = new ThreadSafeSortedList<string, ServiceObject>();
_serviceClients = new ThreadSafeSortedList<long, IScsServiceClient>();
}
它将 IScsServer 对象作为唯一的参数。该对象(正如我们在消息传递层中看到的)是用于与客户端交互和管理它们的。在构造函数中创建了两个集合。第一个集合用于存储托管的服务。在 SCS 服务应用程序中,您可以在同一端点上同时运行多个服务。第二个集合用于存储当前连接的客户端。
在创建 ScsServiceApplication 后,用户调用 AddService(...) 方法来添加一个由该服务应用程序托管的服务。
/// <summary>
/// Adds a service object to this service application.
/// Only single service object can be added for a service interface type.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TServiceInterface">Service interface type</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="TServiceClass">Service class type.
/// Must be delivered from ScsService and must implement TServiceInterface.</typeparam>
/// <param name="service">An instance of TServiceClass.</param>
public void AddService<TServiceInterface, TServiceClass>(TServiceClass service)
where TServiceClass : ScsService, TServiceInterface
where TServiceInterface : class
{
if (service == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("service");
}
var type = typeof(TServiceInterface);
if(_serviceObjects[type.Name] != null)
{
throw new Exception("Service '" + type.Name + "' is already added.");
}
_serviceObjects[type.Name] = new ServiceObject(type, service);
}
AddService(...) 方法有两个泛型参数。第一个是客户端使用的服务契约接口。第二个是该接口的实现类。正如您在 AddService 方法实现中所看到的,每个服务契约接口只能添加一个对象。
在服务器端,客户端由 IScsServiceClient 接口表示,并由 ScsServiceClient 类实现(这与客户端的 IScsServiceClient 接口不同)。类图如下所示。

IScsServiceClient 中的关键方法是 GetClientProxy() 方法。此方法是泛型的,用于获取一个动态透明代理对象的引用,该对象用于从服务器端调用客户端方法。IScsServiceClient 还定义了 RemoteEndPoint,可用于获取客户端应用程序的端点地址(TCP 服务器的IP 地址和TCP 端口)。
所有基于 SCS 框架构建的服务都必须继承自 ScsService 类(正如您在示例应用程序中所见)。ScsService 类只有一个公共属性:CurrentClient。此属性用于获取调用服务方法的客户端的引用。此属性是线程安全的。因此,即使两个客户端并发调用同一方法,您也可以通过 CurrentClient 属性获取正确的客户端对象。让我们检查一下 ScsService 类,看看它是如何实现的。
using System;
namespace Hik.Communication.ScsServices.Service
{
/// <summary>
/// Base class for all services that is serviced by IScsServiceApplication.
/// </summary>
public abstract class ScsService
{
/// <summary>
/// The current client for a thread that called service method.
/// </summary>
[ThreadStatic]
private static IScsServiceClient _currentClient;
/// <summary>
/// Gets the current client which called this service method.
/// </summary>
protected internal IScsServiceClient CurrentClient
{
get
{
if (_currentClient == null)
{
throw new Exception("Client channel can not be obtained. CurrentClient property must be called by the thread which runs the service method.");
}
return _currentClient;
}
internal set
{
_currentClient = value;
}
}
}
}
CurrentClient 用于获取调用服务方法的当前客户端。它在方法中使用以获取客户端对象的引用。请注意,_currentClient 是 ThreadStatic 的,因此它是线程安全的,即使多个客户端并发调用同一服务方法,它也能获取正确的客户端对象。Setter 是 internal 的,用于在调用服务方法之前和之后由 SCS 系统设置客户端对象。此操作的相关部分如下所示。
...
var serviceObject = _serviceObjects[invokeMessage.ServiceClassName];
if (serviceObject == null)
{
SendInvokeResponse(requestReplyMessenger, invokeMessage, null,
new ScsRemoteException("There is no service with name '" +
invokeMessage.ServiceClassName + "'"));
return;
}
//Invoke method
try
{
object returnValue;
//Set client to service, so user service can get client
//in service method using CurrentClient property
serviceObject.Service.CurrentClient = client;
try
{
returnValue = serviceObject.InvokeMethod(invokeMessage.MethodName,
invokeMessage.Parameters);
}
finally
{
//Set CurrentClient as null since method call completed
serviceObject.Service.CurrentClient = null;
}
//Send method invocation return value to the client
SendInvokeResponse(requestReplyMessenger, invokeMessage, returnValue, null);
...
请记住,传入的消息是 ScsRemoteInvokeMessage 对象(由客户端发送)。首先,我们使用消息的 ServiceClassName 属性找到将处理此方法调用的服务对象(不同客户端可以使用不同的服务)。然后,我们设置 ScsService.CurrentClient 属性,使用反射和消息中给定的参数调用请求的方法。最后,我们重置 ScsService.CurrentClient 属性。因此,用户可以在方法调用期间通过使用 CurrentClientt 属性来获取客户端对象。
用户可以通过调用 IScsServiceClient.GetClientProxy() 方法获取一个用于调用客户端远程方法的透明代理对象。此方法创建一个 RemoteInvokeProxy 并调用 GetTransparentProxy() 方法来创建客户端的动态透明代理。
/// <summary>
/// Gets the client proxy interface that provides calling client methods remotely.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">Type of client interface</typeparam>
/// <returns>Client interface</returns>
public T GetClientProxy<T>() where T : class
{
_realProxy = new RemoteInvokeProxy<T, IScsServerClient>(_requestReplyMessenger);
return (T)_realProxy.GetTransparentProxy();
}
有关使用服务器到客户端方法调用的示例应用程序,请参阅第一篇文章中的聊天系统。
SCS 框架的性能
在这里,我将展示 SCS 框架的一些性能结果。我在自己的PC上进行了测试。所有通信都发生在同一台计算机上运行的应用程序之间。您可以下载下载文件中的所有测试应用程序。
测试平台:Intel Core2 Duo 3.00GHz CPU,4GB RAM,Windows 7 64 位。
速度

正如您所见,使用默认序列化大约进行了5500次远程方法调用。消息传递速度要快得多。每秒将34,742条消息从一个应用程序发送到另一个应用程序。当我使用自定义线协议时,每秒可以发送62,410条消息。
可伸缩性
在我的测试中,最多有15,000 个并发客户端连接到 SCS 服务。通常,Windows 将打开的连接数限制在约 5,000 个。我添加了一个 Windows注册表值以允许更多连接。为此,请打开HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters注册表项,并添加一个DWord值MaxUserPort。MaxUserPort 的默认值为5,000。您可以将其更改为最多65,534。您可能需要重新启动计算机才能生效。此外,您可以在此处找到一些其他参数来增加 TCP 连接:http://smallvoid.com/article/winnt-tcpip-max-limit.html
即使有15,000 个客户端并发连接并与服务通信,总线程数也大约为50-60,并且一个客户端可以在1 毫秒或更短的时间内获得方法调用的响应。
最后的几句话
通过本文,我完成了对 SCS 框架的检查。在第一篇文章中,我重点关注了框架的使用。我检查了两个不同的示例应用程序:一个电话簿和一个 IRC 聊天系统。聊天系统尤其展示了框架的强大功能。在本文中,我讨论了如何构建一个基于 TCP/IP 的框架,该框架允许用户像 Web/WCF 服务一样简单地调用远程方法,同时它是面向连接的。然后我解释了框架的几乎所有构造。它是一个稳定、健壮且可伸缩的框架。如果您发现错误,请告知我。
更改/更新
- 2011 年 6 月 13 日(v1.1.0.1)
- BugFix:Ping 消息不应由消息传递层引发。
- 2011 年 5 月 30 日(v1.1.0.0)
- 新增功能
- ClientDisconnected 事件已添加到 IScsServiceApplication 和 IScsServer 类。
- MessageSent 事件已添加到 IMessenger 接口。
- 添加了 SynchronizedMessenger 类以同步接收消息。
- 更改/改进
- 更改了后台线程机制以提供更可伸缩的框架。使用TPL Tasks和Async sockets代替直接使用线程和阻塞套接字(添加了SequentialItemProcessor类)。
- 添加了 IScsWireProtocolFactory 接口,并将 IScsServer.WireProtocol 更改为 IScsServer.WireProtocolFactory。此外,IScsWireProtocol 已完全更改。
- BinarySerializationProtocol 类已设为 public,以允许用户覆盖序列化方法。
- 代码已完全重写,部分代码已重构并注释。
- Bugfix
- 修复了 Timer 中一个潜在的小错误。
- 文章
- 本文已根据框架中的更改完全更新。
- 新增功能
- 2011 年 5 月 11 日(v1.0.2.0)
- 向 server side 添加了
RemoteEndPoint属性以获取客户端的地址。 - 下载文件已修订。
- 2011 年 4 月 10 日(v1.0.1.0)
- 向
IConnectableClient添加了ConnectTimeout属性,以提供一种在连接到服务器时设置超时值的方法。
