2D 多边形碰撞检测
4.77/5 (52投票s)
一篇关于多边形碰撞检测的文章。 可用于实现 2D 游戏中精灵之间的碰撞。 该算法还可以扩展到 3D。

引言
本文介绍如何检测两个移动的(2D)多边形之间的碰撞。 这不是第一个关于该主题的教程,但是,网络上的教程对于一个相对简单的问题来说往往过于复杂。 我能找到的源代码也有太多的缩写,我看不懂,或者充满了 C 优化。 所以在这里,我将尽量保持简单。 在任何情况下,应该可以将此处提供的函数直接包含到您的 C# 项目中。 该技术可用于检测精灵之间的碰撞,作为像素完美碰撞的替代方法,后者通常太慢。
背景
为了检测两个多边形是否相交,我们使用分离轴定理。 这个想法是找到一条分离两个多边形的线 - 如果存在这样一条线,则多边形不相交(图 1)。 这个定理的实现相对简单,可以总结为以下伪代码
- 对于两个多边形的每一条边
- 找到垂直于当前边的轴。
- 将两个多边形投影到该轴上。
- 如果这些投影不重叠,则多边形不相交(退出循环)。
通过添加一个额外的步骤,可以很容易地扩展到处理移动的多边形。 在检查当前投影没有重叠之后,将多边形的相对速度投影到轴上。 通过将速度投影添加到第一个多边形,来扩展第一个多边形的投影(图 2)。 这将为您提供多边形在运动期间跨越的间隔。 从那里,您可以使用用于静态多边形的技术:如果多边形 A 和 B 的投影不重叠,则多边形不会发生碰撞。(注意:但是,请记住,如果间隔确实重叠,这并不一定意味着多边形会碰撞。 我们需要对所有边进行测试才能知道这一点。)
一旦我们发现多边形将要碰撞,我们计算将多边形推开所需的平移量。 投影重叠最小的轴将是发生碰撞的轴。 我们将沿该轴推动第一个多边形。 然后,平移量将简单地是在该轴上的重叠量(图 3)。
就是这样! 现在,每次发生碰撞时,第一个多边形都会很好地沿着另一个多边形的表面滑动。

图 1: 多边形在轴上的投影。
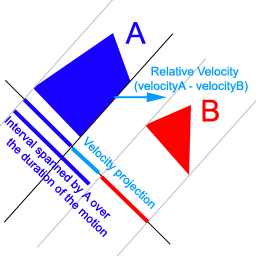
图 2: 移动多边形的投影。
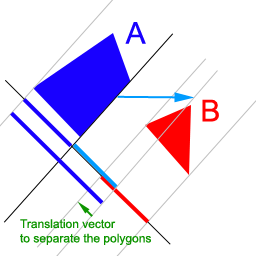
图 3: 找到最小的间隔重叠,然后计算将多边形推开所需的平移量。
使用代码
PolygonCollision() 函数执行以上所有操作,并返回一个 PolygonCollisionResult 结构,其中包含处理碰撞所需的所有必要信息
// Structure that stores the results of the PolygonCollision function
public struct PolygonCollisionResult {
// Are the polygons going to intersect forward in time?
public bool WillIntersect;
// Are the polygons currently intersecting?
public bool Intersect;
// The translation to apply to the first polygon to push the polygons apart.
public Vector MinimumTranslationVector;
}
PolygonCollision 函数使用了两个辅助函数。 第一个用于将多边形投影到轴上
// Calculate the projection of a polygon on an axis
// and returns it as a [min, max] interval
public void ProjectPolygon(Vector axis, Polygon polygon,
ref float min, ref float max) {
// To project a point on an axis use the dot product
float dotProduct = axis.DotProduct(polygon.Points[0]);
min = dotProduct;
max = dotProduct;
for (int i = 0; i < polygon.Points.Count; i++) {
dotProduct = polygon.Points[i].DotProduct(axis);
if (d < min) {
min = dotProduct;
} else {
if (dotProduct> max) {
max = dotProduct;
}
}
}
}
第二个返回两个给定投影之间的有符号距离
// Calculate the distance between [minA, maxA] and [minB, maxB]
// The distance will be negative if the intervals overlap
public float IntervalDistance(float minA, float maxA, float minB, float maxB) {
if (minA < minB) {
return minB - maxA;
} else {
return minA - maxB;
}
}
最后,这是主函数
// Check if polygon A is going to collide with polygon B.
// The last parameter is the *relative* velocity
// of the polygons (i.e. velocityA - velocityB)
public PolygonCollisionResult PolygonCollision(Polygon polygonA,
Polygon polygonB, Vector velocity) {
PolygonCollisionResult result = new PolygonCollisionResult();
result.Intersect = true;
result.WillIntersect = true;
int edgeCountA = polygonA.Edges.Count;
int edgeCountB = polygonB.Edges.Count;
float minIntervalDistance = float.PositiveInfinity;
Vector translationAxis = new Vector();
Vector edge;
// Loop through all the edges of both polygons
for (int edgeIndex = 0; edgeIndex < edgeCountA + edgeCountB; edgeIndex++) {
if (edgeIndex < edgeCountA) {
edge = polygonA.Edges[edgeIndex];
} else {
edge = polygonB.Edges[edgeIndex - edgeCountA];
}
// ===== 1. Find if the polygons are currently intersecting =====
// Find the axis perpendicular to the current edge
Vector axis = new Vector(-edge.Y, edge.X);
axis.Normalize();
// Find the projection of the polygon on the current axis
float minA = 0; float minB = 0; float maxA = 0; float maxB = 0;
ProjectPolygon(axis, polygonA, ref minA, ref maxA);
ProjectPolygon(axis, polygonB, ref minB, ref maxB);
// Check if the polygon projections are currentlty intersecting
if (IntervalDistance(minA, maxA, minB, maxB) > 0)\
result.Intersect = false;
// ===== 2. Now find if the polygons *will* intersect =====
// Project the velocity on the current axis
float velocityProjection = axis.DotProduct(velocity);
// Get the projection of polygon A during the movement
if (velocityProjection < 0) {
minA += velocityProjection;
} else {
maxA += velocityProjection;
}
// Do the same test as above for the new projection
float intervalDistance = IntervalDistance(minA, maxA, minB, maxB);
if (intervalDistance > 0) result.WillIntersect = false;
// If the polygons are not intersecting and won't intersect, exit the loop
if (!result.Intersect && !result.WillIntersect) break;
// Check if the current interval distance is the minimum one. If so store
// the interval distance and the current distance.
// This will be used to calculate the minimum translation vector
intervalDistance = Math.Abs(intervalDistance);
if (intervalDistance < minIntervalDistance) {
minIntervalDistance = intervalDistance;
translationAxis = axis;
Vector d = polygonA.Center - polygonB.Center;
if (d.DotProduct(translationAxis) < 0)
translationAxis = -translationAxis;
}
}
// The minimum translation vector
// can be used to push the polygons appart.
if (result.WillIntersect)
result.MinimumTranslationVector =
translationAxis * minIntervalDistance;
return result;
}
该函数可以这样使用
Vector polygonATranslation = new Vector();
PolygonCollisionResult r = PolygonCollision(polygonA, polygonB, velocity);
if (r.WillIntersect) {
// Move the polygon by its velocity, then move
// the polygons appart using the Minimum Translation Vector
polygonATranslation = velocity + r.MinimumTranslationVector;
} else {
// Just move the polygon by its velocity
polygonATranslation = velocity;
}
polygonA.Offset(polygonATranslation);
参考
历史
- 2006 年 9 月 13 日:第一个版本。
- 2006 年 9 月 14 日:小的更改,并添加了参考部分。
