Kruskal 算法
4.84/5 (43投票s)
在 C# 中实现 Kruskal 算法

引言
根据 维基百科:“Kruskal 算法是 算法 在 图论 中的一种,用于寻找一个 最小生成树 给一个 连通加权图。这意味着它找到一个 边 的子集,形成一棵包含每个 顶点 的树,其中树中所有边的总权重最小化。如果图不是连通的,那么它会找到一个最小生成森林(每个 连通分量 的最小生成树)。Kruskal 算法是 贪心算法 的一个例子。”
简而言之,Kruskal 算法用于以尽可能低的成本连接图中的所有节点。
示例
一家有线电视公司正在在新社区铺设电缆。一家网吧正在通过网络连接所有电脑。
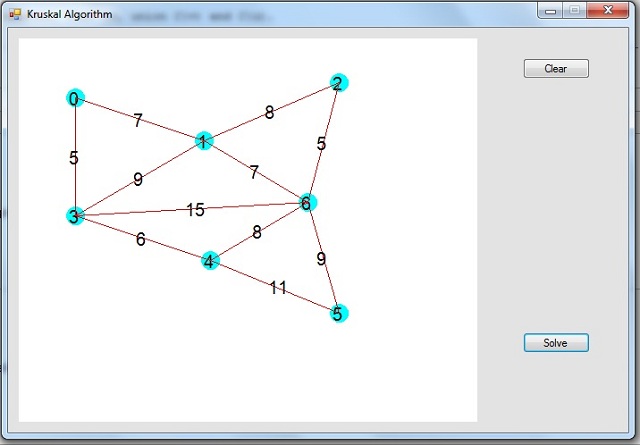
使用演示
点击任意位置绘制顶点。按住 ctrl 并选择两个顶点以创建一条 边。会弹出一个窗口来输入边的成本。完成绘制图后,点击 求解。
高层设计

低层设计

Using the Code
IList<Edge> Solve(IList<Edge> graph, out int totalCost);
如何使用 GDI 形成图不在此讨论范围内,因为它与主题无关。
类
通常,我们的图由两个组件组成,即 顶点 和连接这些顶点的 边。
每个 边 标记有一个值或权重,即连接两个顶点的 成本。
顶点
持有
- 顶点 名称(必须在图中是唯一的)及其 绘制点
- 秩 和 根(稍后会讲到)
using System;
using System.Drawing;
namespace Kruskal
{
public class Vertex
{
#region Members
private int name;
#endregion
#region Public Properties
public int Name
{
get
{
return name;
}
}
public int Rank { get; set; }
public Vertex Root { get; set; }
public Point Position { get; set; }
#endregion
#region Constructor
public Vertex(int name, Point position)
{
this.name = name;
this.Rank = 0;
this.Root = this;
this.Position = position;
}
#endregion
#region Methods
internal Vertex GetRoot()
{
if (this.Root != this)// am I my own parent ? (am i the root ?)
{
this.Root = this.Root.GetRoot();// No? then get my parent
}
return this.Root;
}
internal static void Join(Vertex root1, Vertex root2)
{
if (root2.Rank < root1.Rank)//is the rank of Root2 less than that of Root1 ?
{
root2.Root = root1;//yes! then Root1 is the parent of Root2 (since it has the higher rank)
}
else //rank of Root2 is greater than or equal to that of Root1
{
root1.Root = root2;//make Root2 the parent
if (root1.Rank == root2.Rank)//both ranks are equal ?
{
root2.Rank++;//increment Root2, we need to reach a single root for the whole tree
}
}
}
#endregion
}
}
Edge
持有两个 顶点、它们之间的连接 成本 以及 成本绘制点。
请注意,它实现了 IComparable,稍后我们需要它来按 成本 对 边 进行排序。
using System;
using System.Drawing;
namespace Kruskal
{
public class Edge : IComparable
{
#region Members
private Vertex v1, v2;
private int cost;
private Point stringPosition;
#endregion
#region Public Properties
public Vertex V1
{
get
{
return v1;
}
}
public Vertex V2
{
get
{
return v2;
}
}
public int Cost
{
get
{
return cost;
}
}
public Point StringPosition
{
get
{
return stringPosition;
}
}
#endregion
#region Constructor
public Edge(Vertex v1, Vertex v2, int cost, Point stringPosition)
{
this.v1 = v1;
this.v2 = v2;
this.cost = cost;
this.stringPosition = stringPosition;
}
#endregion
#region IComparable Members
public int CompareTo(object obj)
{
Edge e = (Edge)obj;
return this.cost.CompareTo(e.cost);
}
#endregion
}
}
算法实现
排序边
使用 快速排序,根据 成本 按升序对 边 进行排序。
创建集合
最初,每个 顶点 都是它自己的根,并且秩为零。
public Vertex(int name, Point position)
{
this.name = name;
this.Rank = 0;
this.Root = this;
this.Position = position;
}
为什么要这样做?
我们需要它来确保在添加我们的 顶点 时,我们不会形成一个 环路。
考虑这个例子

边 BD 没有被考虑,因为 B,D 已经通过 B,A,D 连接。
因此,对于我们检查的每个 边,我们必须检查它的两个 顶点 属于 不同的集合(树)。
如何确定两个顶点是否在不同的集合中?
使用递归函数 GetRoot()。
internal Vertex GetRoot()
{
if (this.Root != this)// am I my own parent ? (am i the root ?)
{
this.Root = this.Root.GetRoot();// No? then get my parent
}
return this.Root;
}
如果根确实不同(每个 顶点 都在不同的集合中),则 Join() 这两个 顶点。
internal static void Join(Vertex root1, Vertex root2)
{
if (root2.Rank < root1.Rank)//is the rank of Root2 less than that of Root1 ?
{
root2.Root = root1;//yes! then Root1 is the parent of Root2 (since it has the higher rank)
}
else //rank of Root2 is greater than or equal to that of Root1
{
root1.Root = root2;//make Root2 the parent
if (root1.Rank == root2.Rank)//both ranks are equal ?
{
root2.Rank++;//increment Root2, we need to reach a single root for the whole tree
}
}
}
结论
希望我能提供一个清晰的解释。
