Mach-O 中的导入函数重定向
4.78/5 (6投票s)
本文涵盖了在 Mac OS X 程序中拦截和重定向对第三方动态链接库的调用。
目录
引言
在上一篇文章中,我们研究了 Mach-O 中函数的动态链接机制。现在让我们开始实践。
我们有一个 Mac OS X 上的程序,它使用了许多第三方动态链接库,而这些库反过来又使用了彼此的函数。
任务如下:我们需要拦截一个库中的某个函数调用到另一个库,并在处理程序中调用原始函数。
测试示例
让我们举一个虚构的例子。假设我们有一个用 C 语言编写的名为“test”的程序(test.c 文件)和一个内容固定、预先编译好的共享库(libtest.c 文件)。该库实现了一个 libtest() 函数。在它们的实现中,程序和库都使用了 C 语言标准库中的 puts() 函数(它随 Mac OS 一起提供,包含在 libSystem.B.dylib 中)。让我们看一下描述情况的示意图

任务是这样的
- 我们需要将
libtest.dylib库对puts()函数的调用替换为主程序(test.c 文件)中实现的hooked_puts()函数的调用。后者可以进一步使用原始的puts()函数。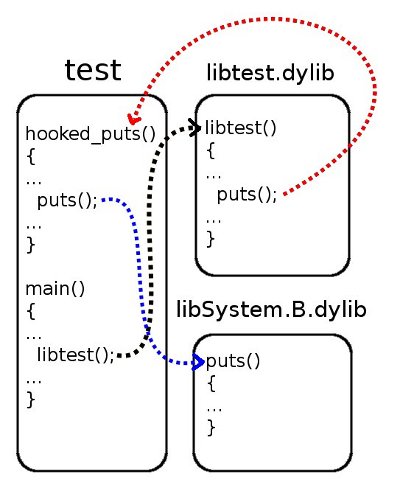
- 我们需要取消所做的更改,即使
libtest()的后续调用导致调用原始的puts()。
不允许更改代码或重新编译库,只能更改主程序。调用重定向本身应该仅针对特定库进行,并且是动态进行的,无需重新启动程序。
重定向算法
让我们用文字描述所有操作,因为即使有大量的注释,代码也可能不够清晰。
- 使用
LC_SYMTAB加载器命令查找符号表和字符串表。 - 从
LC_DYSYMTAB加载器命令中,找出未定义符号子集(iundefsym字段)从符号表的哪个元素开始。 - 在符号表中的未定义符号子集中按名称查找目标符号。
- 记住目标符号相对于符号表的起始索引。
- 使用
LC_DYSYMTAB加载器命令(indirectsymoff字段)查找间接符号表。 - 找出映射导入表(
__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr段的内容;或__IMPORT, __jump_table— 会是其中一个)到间接符号表(reserved1字段)的起始索引。 - 从该索引开始,我们遍历间接符号表,并搜索与目标符号在符号表中的索引对应的项。
- 记住目标符号相对于导入表到间接符号表映射的起始编号。保存的值就是导入表中所需元素的索引。
- 使用
__la_symbol_ptr段(或__jump_table)的偏移字段查找导入表。 - 获得其中目标元素的索引后,重写地址(对于
__la_symbol_ptr)到所需值(或者仅将CALL/JMP指令更改为带有操作数 — 所需函数地址的JMP指令(对于__jump_table))。
我将指出,您应该仅在从文件中加载这些表后,才能处理符号表、字符串表和间接符号表。此外,您应该读取描述导入表的段的内容,并在内存中执行重定向。这是因为符号表和字符串表可能不存在,或者无法显示目标 Mach-O 的实际状态。这是因为动态加载器已经在我们之前工作过,并且成功保存了关于符号的所有必要数据,而无需分配这些表本身。
重定向实现
现在是时候将我们的想法转化为代码了。为了优化所需 Mach-O 元素的搜索,我们将所有操作分为三个阶段。
1. void *mach_hook_init(char const *library_filename, void const *library_address);
基于 Mach-O 文件及其在内存中的表示,此函数返回一个不明确的描述符。此描述符包含导入表、符号表、字符串表以及动态符号表中间接符号映射的偏移量,以及该模块的一些有用索引。描述符如下:
struct mach_hook_handle
{
void const *library_address; //base address of a library in memory
char const *string_table; //buffer to read string_table table
//from file
struct nlist const *symbol_table; //buffer to read symbol table from file
uint32_t const *indirect_table; //buffer to read the indirect symbol
//table in dynamic symbol table from file
uint32_t undefined_symbols_count; //number of undefined symbols in the
//symbol table
uint32_t undefined_symbols_index; //position of undefined symbols in the
//symbol table
uint32_t indirect_symbols_count; //number of indirect symbols in the
//indirect symbol table of DYSYMTAB
uint32_t indirect_symbols_index; //index of the first imported symbol
//in the indirect symbol table of
//DYSYMTAB
uint32_t import_table_offset; //the offset of (__DATA, __la_symbol_ptr)
// or (__IMPORT, __jump_table)
uint32_t jump_table_present; //special flag to show if we work
//with (__IMPORT, __jump_table)
};
2. mach_substitution mach_hook(void const *handle,
char const *function_name, mach_substitution substitution);
此函数使用现有的库描述符、目标符号名称和拦截器的地址,根据上述算法执行重定向。
3. void mach_hook_free(void *handle);
这样,就完成了对 mach_hook_init() 返回的任何描述符的清理。
考虑到这些原型,我们需要重写测试程序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include "mach_hook.h"
#define LIBTEST_PATH "libtest.dylib"
void libtest(); //from libtest.dylib
int hooked_puts(char const *s)
{
puts(s); //calls the original puts() from libSystem.B.dylib,
//because our main executable module called "test" remains intact
return puts("HOOKED!");
}
int main()
{
void *handle = 0; //handle to store hook-related info
mach_substitution original; //original data for restoration
Dl_info info;
if (!dladdr((void const *)libtest, &info)) //gets an address of a
//library which contains libtest() function
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to get the base address of a library!\n",
LIBTEST_PATH);
goto end;
}
handle = mach_hook_init(LIBTEST_PATH, info.dli_fbase);
if (!handle)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Redirection init failed!\n");
goto end;
}
libtest(); //calls puts() from libSystem.B.dylib
puts("-----------------------------");
original = mach_hook(handle, "puts", (mach_substitution)hooked_puts);
if (!original)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Redirection failed!\n");
goto end;
}
libtest(); //calls hooked_puts()
puts("-----------------------------");
original = mach_hook(handle, "puts", original); //restores the original
//relocation
if (!original)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Restoration failed!\n");
goto end;
}
libtest(); //again calls puts() from libSystem.B.dylib
end:
mach_hook_free(handle);
handle = 0; //no effect here, but just a good advice to
//prevent double freeing
return 0;
}
测试开始
我们可以按以下方式进行测试:
user@mac$ arch -i386 ./test
libtest: calls the original puts()
-----------------------------
libtest: calls the original puts()
HOOKED!
-----------------------------
libtest: calls the original puts()
user@mac$ arch -x86_64 ./test
libtest: calls the original puts()
-----------------------------
libtest: calls the original puts()
HOOKED!
-----------------------------
libtest: calls the original puts()
程序的输出表明,最初制定的任务已完全执行。
测试示例的完整实现,包括重定向算法和项目文件,均已附在本文档中。
历史
- 2011 年 4 月 26 日:初始帖子
