WordCloud - 词频的方形树图
4.85/5 (12投票s)
2007年8月10日
4分钟阅读
85343
2281
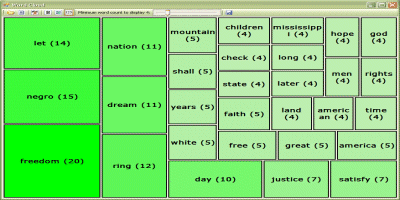
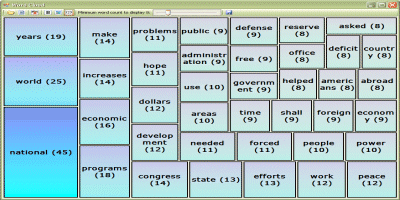
一个词频的方形树图。
引言
WordCloud 是一个可视化表示,展示给定词集中一个词被使用的次数,或者说它的频率。它通过以下步骤实现:读取纯文本、过滤“停用词”、计算词语使用的次数,并将结果显示在一个方形树图中。(在上面的图片中,节点越大、颜色越饱和,表示使用频率越高。)
背景
我非常欣赏并受到 Chirag Mehta 的 酷炫的基于 Web 的标签云生成器(统计美国总统演讲) 的启发。于是我尝试用 .NET 实现一个简化版本。
我最多算是一个业余爱好者,对这个示例中使用的技术也只是略知一二,所以我参考了许多我读过的文章来创建 WordCloud。
方形树图
- 显示由 Microsoft 的 TreemapGenerator 处理,它是数据可视化组件套件的一部分。虽然真正的树图同时利用了层级和比例属性,但 WordCloud 只使用比例属性来显示词频。
- 维基百科上的 树图概述 是理解其起源的好地方。
- Jonathan Hodgson 在 CodeProject 上的 方形树图文章 对这个主题进行了深入的探讨。
- WordCloud 执行的功能与 标签云 基本相同。
- Newsmap - 一个令人印象深刻的基于 Flash 的 Google 新闻方形树图。
- 互联网标签网站 del.icio.us 最受欢迎的树图。
词干提取
- WordCloud 使用 Porter 词干提取算法 来移除(或缩减)具有共同词源的词。
停用词
- 停用词 用于在处理前过滤掉常用词。
代码
要构建 WordCloud,你需要获取最新版本的 Microsoft 数据可视化组件,并更新 WordCloud 的项目引用以包含 `TreemapGenerator`。你可以在 \VisualizationComponents\Treemap\Latest\Components\TreemapGenerator.dll 中找到此引用。注意:WordCloud 需要 .NET Framework 2.0 或更高版本才能构建和运行。
TreemapPanel.cs
TreemapPanel 负责节点渲染。节点被预处理成一个 `ArrayList` 集合,然后添加到 `TreemapGenerator` 中。对象数据以 `NodeInfo` 的形式存储在每个节点中。
// Treemap drawing engine in TreemapPanel.cs
protected TreemapGenerator m_oTreemapGenerator;
...
public void PopulateTreeMap(Hashtable wordsHash, Hashtable stemmedWordsHash)
{
AssertValid();
ArrayList nodes = new ArrayList();
ArrayList aKeys = new ArrayList(stemmedWordsHash.Keys);
aKeys.Sort();
foreach (string key in aKeys)
{
//build each node element
int count = (int)stemmedWordsHash[key];
string name = (string)wordsHash[key];
//show count in node?
if(m_bShowWordCount)
name += String.Format(" ({0})", count);
NodeInfo nodeinfo = new NodeInfo(name, count);
nodes.Add(nodeinfo);
}
m_nodes = nodes;
RepopulateTreeMap();
}
...
private void RepopulateTreeMap()
{
if(m_nodes.Count == 0)
return;
Nodes TreemapGeneratorNodes;
//reset treemap
m_TreemapGenerator.Clear();
TreemapGeneratorNodes = m_TreemapGenerator.Nodes;
foreach(NodeInfo n in m_nodes)
{
//does this node have enough to display?
if(n.Count >= m_nDisplayCount)
{
//Create node with basic default size and color
Node oWordNode = new Node(n.Name, n.Count * 50.0f, 0F);
//set object data
oWordNode.Tag = n;
//add category to tree
TreemapGeneratorNodes.Add(oWordNode);
//used later for determining node color
if (n.Count > m_nLargestCount)
m_nLargestCount = n.Count;
else if (n.Count < m_nSmallestCount)
m_nSmallestCount = n.Count;
}
}
}
绘制节点
树图使用自定义的节点绘制方法,该方法在 OnPaint 中调用。
// We want to do owner drawing, so handle the DrawItem event.
m_TreemapGenerator.DrawItem +=
new TreemapGenerator.TreemapDrawItemEventHandler(DrawItem);
...
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)
{
AssertValid();
// Save the Graphics object so it can be accessed by OnDrawItem().
m_Graphics = e.Graphics;
// Tell the TreemapGenerator to draw the treemap using owner-
// implemented code. This causes the DrawItem event to get fired for
// each node in the treemap.
m_TreemapGenerator.Draw(this.ClientRectangle);
// All DrawItem events have been fired. Make sure the Graphics object
// doesn't get used again.
m_Graphics = null;
}
节点渲染在 `DrawItem()` 方法中处理。在该方法中,我们提取 `NodeInfo` 对象,获取名称和计数,根据计数设置颜色和文本大小,然后绘制节点。最终的节点结果是:计数越大,文本越大,颜色越饱和。
private void DrawItem(Object sender, TreemapDrawItemEventArgs e)
{
AssertValid();
Node oNode = e.Node;
float fontSize = m_FontSize;
int count = 0;
// Retrieve the NodeInfo object from the node's tag.
if (oNode.Tag is NodeInfo)
{
//get word count
NodeInfo oInfo = (NodeInfo)oNode.Tag;
count = oInfo.Count;
//if we're using text scaling, increment font size
if(m_bUseTextScaling)
fontSize += oInfo.Count;
}
else
{
//should never get here
Debug.WriteLine("DrawItem: Skipping node - bad");
return;
}
//set color alpha based on frequency
Color newStartColor = GetColor(count, m_startColor);
Color newEndColor = GetColor(count, m_endColor);
//set gradient colors and gamma
LinearGradientBrush nodeBrush = new LinearGradientBrush(e.Bounds,
newStartColor, newEndColor, LinearGradientMode.Vertical);
nodeBrush.GammaCorrection = true;
m_Graphics.FillRectangle(nodeBrush, e.Bounds);
// Create font and align in the center
Font newfont = new Font(m_FontName, fontSize, m_FontStyle);
StringFormat sf = new StringFormat();
sf.Alignment = StringAlignment.Center;
sf.LineAlignment = StringAlignment.Center;
//draw the text
m_Graphics.DrawString(e.Node.Text, newfont, new SolidBrush(m_FontColor),
e.Bounds, sf);
// Draw a black border around each node
Pen blackPen = new Pen(Color.Black, 2);
m_Graphics.DrawRectangle(blackPen, e.Bounds);
//clean up
nodeBrush.Dispose();
newfont.Dispose();
blackPen.Dispose();
}
文本“整理”
主窗体中的一个工作线程方法 `DoWordProcessing()` 处理词集合文档。词干提取也在该方法中进行,用于剥离词的后缀。
private void DoWordProcessing(object obj)
{
//unpack array
object[] objArray = (object[])obj;
IProgressCallback callback = (IProgressCallback)objArray[0];
StringBuilder sbRawText = (StringBuilder)objArray[1];
ArrayList arrStopWords = (ArrayList)objArray[2];
try
{
//Build a hash of words and thier frequency
Hashtable wordsHash = new Hashtable();
Hashtable stemmedWordsHash = new Hashtable();
PorterStemmer ps = new PorterStemmer();
//construct our document from the input text
Document doc = new Document(sbRawText.ToString());
callback.Begin(0, doc.Words.Count);
for (int i = 0; i < doc.Words.Count; ++i)
{
//cancel button clicked?
if (callback.IsAborting)
{
callback.End();
return;
}
//update progress dialog
callback.SetText(String.Format("Reading word: {0}", i));
callback.StepTo(i);
//Don't do numbers
if (!IsNumeric(doc.Words[i]))
{
// normalize each word to lowercase
string key = doc.Words[i].ToLower();
//check stop words list
if (!arrStopWords.Contains(key))
{
//set our stemming term
ps.stemTerm(key);
//get the stem word
string stemmedKey = ps.getTerm();
//either add to hash or increment frequency
if (!stemmedWordsHash.Contains(stemmedKey))
{
//add new word
stemmedWordsHash.Add(stemmedKey, 1);
wordsHash.Add(stemmedKey, key);
}
else
{
//increment word count
stemmedWordsHash[stemmedKey] =
(int)stemmedWordsHash[stemmedKey] + 1;
}
}
}
}
//now let the treemap load the information
this.TreePanel.PopulateTreeMap(wordsHash, stemmedWordsHash);
}
catch (System.Threading.ThreadAbortException)
{
// noop
}
catch (System.Threading.ThreadInterruptedException)
{
// noop
}
finally
{
if (callback != null)
{
callback.End();
}
}
}
演示应用程序
控件
工具栏按钮说明(从左到右依次)
- 打开文本文件:打开一个文本文件文档进行可视化
- 输入文本:在此对话框中粘贴其他文档的文本进行可视化(最大 128k,但可根据需要更改)
- 停用词:一个对话框,允许你修改停用词集**

- 字体:一个对话框,允许你设置显示字体
- 节点颜色:一个对话框,允许你设置节点显示的渐变颜色

- 缩放文本:切换以根据计数缩放文本
- 显示计数:切换以显示/隐藏节点中的词频**
- 最小词频滑块:根据词频动态控制显示多少个节点
- 另存为图像:将树图保存为 gif 图像
**注意:** 文档文本不会保留在内存中;它只会被解析,作为节点添加到树图中,然后丢弃。因此,“显示计数”和“停用词”功能仅在打开/输入文本之前有用;它不会动态显示/隐藏节点计数或应用停用词。
输入数据
我尝试了各种文档大小,从 400 到 6000 字不等——主要是总统演讲等。在项目中,我包含了两个文本文件:*mlk.txt* 和 *kennedy.txt*。它们分别是马丁·路德·金于 1963 年 8 月 28 日在华盛顿游行上的“我有一个梦想”演讲,以及前美国总统约翰·F·肯尼迪 1961 年的国情咨文——分别为 1,588 和 5,184 字。
另一个需要注意的问题是停用词。我添加了一组默认的停用词,这些停用词是用户可配置的,并且极大地影响了词语解析。提供的 430 个停用词相当标准,涵盖了大量停用词,但又不至于过于激进。
结论
虽然这个示例非常基础,未经优化,非基于 Web,充其量只能算入门级(与其他标签/词云生成器相比),但它或许可以为对这个想法感兴趣的人提供一个起点。它也可以作为使用 Microsoft 数据可视化组件套件中 TreemapGenerator 的一个基本示例。
鸣谢
Tony Capone 在 Google Groups 帖子 中提供的 TreemapGenerator 代码
Matthew Adams 的 进度对话框
Leif Azzopardi 对 Porter 的 Porter 词干提取算法的移植
