使用 VB.NET 以更快的方式搜索巨大的 Excel 表格
4.44/5 (11投票s)
本文介绍了使用 VLOOKUP 搜索大型 Excel 表格的方法,以及如何更改单元格中数据的字体和颜色。它还介绍了如何从内存中释放 Office 对象。
引言
在进行 Excel 自动化时,大家通常会遇到搜索巨大的 Excel 表格的情况。此代码搜索 Excel 表格并从单元格中读取数据,然后以更快的方式将其插入到指定的列中。
背景
我接到一个工作,需要在一个包含超过 4000 条记录的大型 Excel 表格中搜索另一个包含 6000 条记录的表格。手动操作需要 2 天才能完成。所以我选择了 Excel 自动化。如果你在大型 Excel 表格中逐个单元格地搜索数据,在一个列中大约需要 10 秒来搜索数据。如果需要搜索这么多记录,将会花费很长时间。使用 VLookUp,搜索变得非常快。搜索 2000 条记录只需要 1 分钟。
使用代码
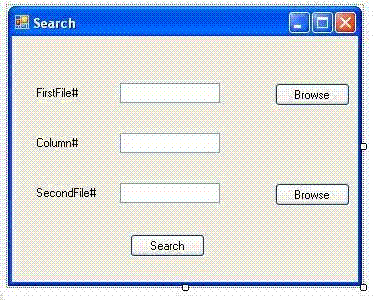
在 FirstFile 文本框中,指定要搜索数据的 Excel 表格。在代码中,我将工作表指定为第 1 个工作表,将列指定为第 1 列。在 SecondFile 文本框中,指定要在其中搜索数据的 Excel 表格。我在演示 zip 文件中添加了 2 个 Excel 表格。
代码在第二个 Excel 表格的第一个工作表的第 1 列中搜索数据,并从第二列的相应行中读取数据,并以二维数组的形式返回。如果不存在数据,VLookUp 将返回“-2146826246”。
使用 VB.NET 自动化 Microsoft Office 程序需要在你的 VB.NET 项目中引用项目库。
在这里,我们正在自动化 Excel,因此我们需要添加对 Microsoft Excel 对象库的引用。
(1) 在 Visual Studio .NET IDE 中,选择“项目” > “添加引用...” 菜单项。接下来,您需要单击顶部的 COM 选项卡,因为 Excel 对象模型是一个组件对象模型 (COM) 库。现在向下滚动,直到找到“Microsoft Excel 11.0 对象库”(取决于您的系统,可能为 10.0、9.0、8.0 甚至 12.0)。
(2) 接下来,单击 [选择] 按钮,然后单击 [确定]。现在已加载对 Excel 对象库的引用。
'For importing office components,we want to use this statement
Imports Microsoft.Office.Core
"<span" class="code-string">"<span" class="code-string">"vb.net">Private Sub btnSearch_Click(ByVal sender As System.Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnSearch.Click
Dim row As Integer
Dim a As String
Dim Value As String
Dim SecondFileRange As String
Dim FirstFileRange As String
Dim lastrow1, lastrow2, lastCol2 As Integer
Dim xlappFirstFile As Excel.Application = Nothing
Dim xlappSecondFile As Excel.Application = Nothing
Dim xlFirstFile_WB1 As Excel.Workbook = Nothing
Dim xlSecondFile_WB2 As Excel.Workbook = Nothing
Dim xlSecondfile_WS2 As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing
Dim xlFirstfile_WS1 As Excel.Worksheet = Nothing
Try
xlappFirstFile = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
xlappSecondFile = CreateObject("Excel.Application")
'Open the first file
xlFirstFile_WB1 = xlappFirstFile.Workbooks.Open(txtbxFirstFile.Text)
xlFirstFile_WB1.Application.Visible = True
xlFirstFile_WB1.Application.WindowState = Excel.XlWindowState.xlMinimized
xlFirstfile_WS1 = xlappFirstFile.Application.Worksheets(1)
lastrow1 = xlFirstfile_WS1.UsedRange.Rows.Count
'Open the second file
xlSecondFile_WB2 = xlappSecondFile.Workbooks.Open(txtbxSecondFile.Text)
xlSecondFile_WB2.Application.Visible = True
xlSecondFile_WB2.Application.WindowState = Excel.XlWindowState.xlMinimized
xlSecondfile_WS2 = xlappSecondFile.Application.Worksheets(1)
lastrow2 = xlSecondfile_WS2.UsedRange.Rows.Count
lastCol2 = xlSecondfile_WS2.UsedRange.Columns.Count
'Calculate the Range in First file to which the searched data is to be inserted
FirstFileRange = Chr(txtbxCol.Text + 64) & "2:" & Chr(txtbxCol.Text + 64) & lastrow2
'Calculate the Range in Second file in which searching is to be done
SecondFileRange = "A2:" & Chr(lastCol2 + 64) & lastrow2
Dim searchvalues(lastrow2, 0) As String
'Search for the data
For row = 2 To lastrow1
a = xlFirstFile_WB1.Worksheets(1).Cells(row, 1).value()
Value = xlappSecondFile.VLookup(a, xlSecondfile_WS2.Range(SecondFileRange), 1, False)
If Value <> "-2146826246" Then
searchvalues(row - 2, 0) = xlappSecondFile.VLookup(a, xlSecondfile_WS2._
_Range(SecondFileRange),2, False)
End If
'End If
Next
'Insert the values into the col:2 of first excel file
xlFirstfile_WS1.Range(FirstFileRange).Value = searchvalues
'Change the font and size
xlFirstfile_WS1.Range(FirstFileRange).Font.Color = ColorTranslator.ToOle(Color.Blue)
xlFirstfile_WS1.Range(FirstFileRange).Font.Name = "Verdana"
xlFirstfile_WS1.Range(FirstFileRange).Font.Size = 8
Catch ex As Exception
MsgBox(ex.ToString)
Finally
Me.Close()
GC.Collect()
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers()
GC.Collect()
GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers()
ReleaseObject(xlFirstfile_WS1)
xlFirstFile_WB1.Close(SaveChanges:=True)
ReleaseObject(xlFirstFile_WB1)
ReleaseObject(xlSecondfile_WS2)
xlSecondFile_WB2.Close(SaveChanges:=False)
ReleaseObject(xlSecondFile_WB2)
xlappFirstFile.Quit()
ReleaseObject(xlappFirstFile)
xlappSecondFile.Quit()
ReleaseObject(xlappSecondFile)
End Try
End Sub
当您从 Microsoft Visual Basic .NET 自动化 Microsoft Office 应用程序时,调用 Quit 方法时,Office 应用程序不会退出。
这些步骤用于释放 COM 对象。
1. 调用 System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject 减少 RCW 的引用计数。
2. 要释放对变量的引用,请将变量设置为 Nothing 或 Null。
3. 使用 Office 应用程序对象的 Quit 方法告诉服务器关闭。
4. 在释放最后一个对象后,调用 GC.Collect() 方法和 GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers() 方法。
步骤 4 用于,因为运行时对 RCW 执行垃圾回收,GC.Collect() 方法强制垃圾回收器运行,并可能释放 RCW 仍然拥有的任何引用。
GC.Collect() 和 GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers() 被调用两次,因为每个 COM 对象的运行时可调用包装器 ("RCW") 都有一个终结器,用于执行从 .NET 释放 COM 对象的实际工作。并且具有终结器(在本例中为 RCW)的 .NET 对象需要第二轮垃圾回收才能完全从内存中删除。
"<span" class="code-string">"<span" class="code-string">"vb.net">'Subroutine to release objects. Private Sub ReleaseObject(ByVal ob As Object) Try System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.ReleaseComObject(ob) Catch Finally ob = Nothing GC.Collect() GC.WaitForPendingFinalizers() End Try End Sub
关注点
在编写代码时,我遇到了两种情况。第一种情况是我想将列转换为范围字符串。这里我使用 chr() 将十进制转换为 ascii。'A' 的 ascii 码是 65。所以我将列号加上 64。
"<span" class="code-string">"<span" class="code-string">"vb.net">FirstFileRange = Chr(txtbxCol.Text + 64) & "2:" & Chr(txtbxCol.Text + 64) & lastrow2
第二种情况是 Excel.Worksheet.Range.Value。它接受数组。如果我们使用一维数组,它将用单个值替换范围内的每个单元格。在这里,我们只想替换一列。所以我声明了一个二维数组作为一维数组,维度为 lastrow1 X 0。如果要替换 2 列,则需要将维度更改为 lastrow1 X 1。
"<span" class="code-string">"<span" class="code-string">"vb.net">Dim searchvalues(lastrow2, 0) As String 'Search for the data For row = 2 To lastrow1 a = xlFirstFile_WB1.Worksheets(1).Cells(row, 1).value() Value = xlappSecondFile.VLookup(a, xlSecondfile_WS2.Range(SecondFileRange), 1, False) If Value <> "-2146826246" Then searchvalues(row - 2, 0) = xlappSecondFile.VLookup(a, xlSecondfile_WS2._ _Range(SecondFileRange), 2, False) End If Next 'Insert the values into the col:2 of first excel file xlFirstfile_WS1.Range(FirstFileRange).Value = searchvalues
历史
原始文章提交时间:2007 年 11 月 27 日
