协同过滤 - 如何构建推荐系统
4.78/5 (12投票s)
使用 C# 和皮尔逊相关系数实现推荐系统的概述。
引言
是否曾经浏览亚马逊并注意到“购买此商品的顾客也购买了这些商品”列表,或者在 Netflix 上选择了一部电影后,会推荐类似的电影? 发现用户的浏览习惯和选择趋势的能力已成为许多面向客户的网站的必备功能。 协同过滤是实现这些功能的魔力。 在本文中,我们将探讨推荐系统的一种流行实现、它的工作原理以及如何将其集成到您的项目中。
背景
我们将用来查找数据趋势的算法称为皮尔逊相关系数。 选择它的原因很简单 - 它可以有效地处理和平衡未归一化的数据。 例如,普通用户给出的电影评论往往比评论家的更中立。 代码示例将用 .NET 3.5 SP1 编写,我们将使用 LINQ 遍历数据集的各个部分。 这些示例将编写为控制台应用程序,以保持代码片段的简单性并使整体概念更容易掌握。
使用代码
首先,我们需要数据结构来保存每个产品的推荐。
public class Recommendation
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Rating { get; set; }
}
为了简单起见,我们将产品保存在字典中,产品名称作为键,而 List<Recommendation> 作为值。
Dictionary<string, List<Recommendation>> productRecommendations =
new Dictionary<string, List<Recommendation>>();
在实际系统中,数据将存在于数据库中,但在本示例中,我们将数据硬编码到字典中。
List<Recommendation> list = new List<Recommendation>();
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Wile E Coyote", Rating = 4.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Bugs Bunny", Rating = 2.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Elmer Fudd", Rating = 5.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Foghorn Leghorn", Rating = 2.0 });
productRecommendations.Add("ACME Industrial Rocket Pack", list);
list = new List<Recommendation>();
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Wile E Coyote", Rating = 5.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Bugs Bunny", Rating = 3.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Elmer Fudd", Rating = 1.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Foghorn Leghorn", Rating = 3.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Daffy Duck", Rating = 1.0 });
productRecommendations.Add("ACME Super Sling Shot", list);
list = new List<Recommendation>();
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Wile E Coyote", Rating = 1.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Bugs Bunny", Rating = 3.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Elmer Fudd", Rating = 5.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Foghorn Leghorn", Rating = 4.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Daffy Duck", Rating = 4.0 });
productRecommendations.Add("ACME X-Large Catapult", list);
list = new List<Recommendation>();
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Bugs Bunny", Rating = 3.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Elmer Fudd", Rating = 4.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Foghorn Leghorn", Rating = 5.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Daffy Duck", Rating = 2.5 });
productRecommendations.Add("ACME Super Glue", list);
list = new List<Recommendation>();
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Wile E Coyote", Rating = 4.5 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Bugs Bunny", Rating = 5.0 });
list.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = "Foghorn Leghorn", Rating = 3.0 });
productRecommendations.Add("ACME Jet Powered Roller Skates", list);
在这里,我们有一系列产品,每个产品都有一系列评论。 每个评论都有一个从 1 到 5 的值,描述了他们对产品的喜爱程度。 此值可以基于您尝试分析的内容。 例如,您可以使用值 1 来表示购买了特定产品的用户(0 表示未购买产品的用户)。 只要我们有一种将数据转换为数值的方法,就可以分析数据。
推荐产品是通过能够找到产品之间的相似性来实现的。 为此,我们使用皮尔逊相关系数。 相关系数衡量两组数据在一条直线上拟合的程度。 皮尔逊分数一个有趣的方面是它可以纠正等级膨胀。 也就是说,如果一个产品的得分始终高于另一个产品,那么仍然可能存在完美的相关性——如果评级之间的差异是一致的。
此算法的代码
- 首先找到评论过这两种产品的评论者。 然后
- 计算两种产品的评分的总和和平方和,以及
- 计算产品的评论总和。 最后,
- 它使用这些结果来计算皮尔逊相关系数,如下面的代码所示
List<Recommendation> shared_items = new List<Recommendation>();
// collect a list of products have have reviews in common
foreach (var item in productRecommendations[product1])
{
if (productRecommendations[product2].Where(x => x.Name == item.Name).Count() != 0)
{
shared_items.Add(item);
}
}
if (shared_items.Count == 0)
{
// they have nothing in common exit with a zero
return 0;
}
// sum up all the preferences
double product1_review_sum = 0.00f;
foreach (Recommendation item in shared_items)
{
product1_review_sum += productRecommendations[product1].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating;
}
double product2_review_sum = 0.00f;
foreach (Recommendation item in shared_items)
{
product2_review_sum += productRecommendations[product2].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating;
}
// sum up the squares
double product1_rating = 0f;
double product2_rating = 0f;
foreach (Recommendation item in shared_items)
{
product1_rating += Math.Pow(productRecommendations[product1].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating, 2);
product2_rating += Math.Pow(productRecommendations[product2].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating, 2);
}
//sum up the products
double critics_sum = 0f;
foreach (Recommendation item in shared_items)
{
critics_sum += productRecommendations[product1].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating *
productRecommendations[product2].Where(
x => x.Name == item.Name).FirstOrDefault().Rating;
}
//calculate pearson score
double num = critics_sum - (product1_review_sum *
product2_review_sum / shared_items.Count);
double density = (double)Math.Sqrt((product1_rating -
Math.Pow(product1_review_sum, 2) / shared_items.Count) *
((product2_rating - Math.Pow(product2_review_sum, 2) / shared_items.Count)));
if (density == 0)
return 0;
return num / density;
该算法将返回一个介于 -1 和 1 之间的值,其中 1 表示两个产品具有完全相同的评级。 需要注意的一点是,该算法仅比较两个产品,因此要计算整个目录的分数,我们必须遍历每个产品,计算分数
// grab of list of products that *excludes* the item we're searching for
var sortedList = productRecommendations.Where(x => x.Key != name);
sortedList.OrderByDescending(x => x.Key);
List<Recommendation> recommendations = new List<Recommendation>();
// go through the list and calculate the Pearson score for each product
foreach (var entry in sortedList)
{
recommendations.Add(new Recommendation() { Name = entry.Key,
Rating = CalculatePearsonCorrelation(name, entry.Key) });
}
return recommendations;
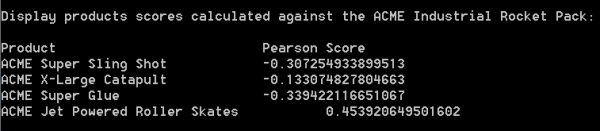
从给定的分数可以看出,正在查看工业火箭包的用户也会对一双喷气动力溜冰鞋感兴趣。
历史
- v1.0:初始版本。
