带预览功能的图像查看器用户控件
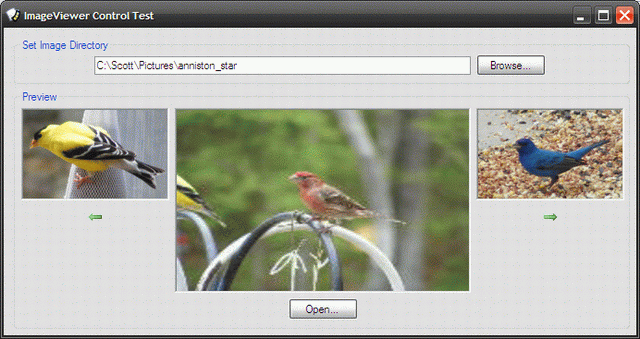
本文讨论了构建一个图片查看器用户控件,该控件可用于显示包含图片文件集合的目录中的图片。
引言
本文讨论了构建一个图片查看器用户控件,该控件可用于显示包含图片文件集合的目录中的图片。该控件会显示当前图片、文件中的上一张和下一张图片。当前图片可以从用户控件中打开到用户计算机上默认的图片应用程序中,这取决于该计算机的文件关联设置。图片缩略图用于提供目录中的上一张、当前和下一张图片。正如演示中所示,该用户控件可以添加到某个应用程序中,您可能需要在其中允许用户在打开图片进行查看或编辑之前进行预览或视觉扫描。

(显示 Microsoft Office Picture Manager)
入门
要开始,请解压包含的项目并使用 Visual Studio 2005 环境打开解决方案。解决方案中包含两个项目。ImageViewer 是第一个项目,它是一个控件库项目,包含一个用户控件。第二个项目是一个测试应用程序,它显示一个用于包含用户控件的单个窗体。
在解决方案资源管理器中,您应该会注意到这些文件
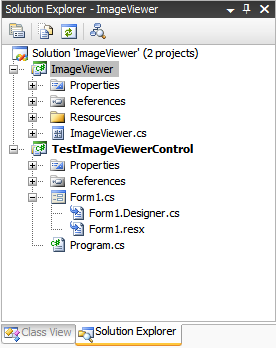
图片查看器用户控件 (ImageViewer.cs)
图片查看器用户控件包含浏览图片文件夹以及查看当前、下一张和上一张图片所需的一切。控件本身包含一个文本框和一个浏览按钮,用于打开文件夹浏览器对话框;当用户导航到所需文件夹并选择它时,文件夹的路径将显示在 textbox 控件中,并且浏览 button 的点击事件处理程序将触发收集所选文件夹中所有图片文件的集合,并开始显示图片。该控件包含三个图片框,用于显示上一张、当前和下一张图片。上一张和下一张图片旁边有两个按钮,用于在图片集合中向后和向前移动。每个图片文件的路径都包含在一个数组列表中,并且使用一个类作用域的整数值来维护该数组列表中的当前位置。
如果您愿意在 IDE 中打开代码视图,您将看到代码文件以以下 using 语句开头;大多数都遵循默认配置,但添加了 System.IO 以支持代码中使用的目录操作。
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.IO;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
在导入语句之后,定义了命名空间和类,并添加了构造函数以及一系列本地成员变量,用于维护文件夹路径、图片文件路径(在数组列表中)、图片列表位置以及图片本身(上一张、当前和下一张)。
namespace ImageViewer
{
/// <summary>
/// A user control used to allow previewing
/// the previous, current and next images in a
/// folder containing image files
/// </summary>
public partial class ImageViewer : UserControl
{
// private member variables
private string mFolder;
private ArrayList mImageList;
private int mImagePosition;
private Image mPreviousImage;
private Image mCurrentImage;
private Image mNextImage;
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public ImageViewer()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
接下来是用户控件的加载事件处理程序;此演示在加载事件中不执行任何操作,但您可以根据需要使用此处理程序设置默认图片文件夹或其他类似内容。
/// <summary>
/// Load Event for User Control
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void UserControl1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// do nothing on load
}
代码的下一部分是浏览 button 的点击事件处理程序。在这部分代码中,处理程序打开文件夹浏览器对话框,用户可以使用该对话框设置图片文件夹的路径。一旦设置了文件夹,处理程序将循环遍历该文件夹并查找所有 BMP、JPEG 和 GIF 文件;找到的任何图片文件的文件路径都将被添加到数组列表中(BMP、GIF 和 JPEG)。一旦数组列表填充了文件路径,点击事件处理程序将通过将列表索引位置设置为零来完成,然后它会调用 SetImages 方法,该方法会将当前、上一张和下一张图片设置到相应的图片框中。代码有注释,应该很容易理解。
/// <summary>
/// Set the image folder location.
///
/// Store all of the image file names into the
/// Image List (mImageList) and then load the
/// initial images
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnBrowse_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Label the folder browser dialog
this.folderBrowserDialog1.Description =
"Select the image directory.";
// disable create folder feature of folder browser
this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowNewFolderButton = false;
// display the folder browser
DialogResult result = folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog();
if (result == DialogResult.OK)
{
// on okay, set the image folder to the
// folder browser's selected path
mFolder = folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(mFolder))
{
txtImageDirectory.Text = mFolder;
}
}
else
{
// exit if the user cancels
return;
}
// initialize the image arraylist
mImageList = new ArrayList();
// loop through the image directory
// and find all of the image files;
// add the found files to the image
// list - add other image types if
// necessary
DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(mFolder);
foreach (FileInfo f in dir.GetFiles("*.*"))
{
switch (f.Extension.ToUpper())
{
case ".JPG":
mImageList.Add(f.FullName);
break;
case ".BMP":
mImageList.Add(f.FullName);
break;
case ".GIF":
mImageList.Add(f.FullName);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
// set the starting position to 0
// and call the set images method
// to load the pictures
mImagePosition = 0;
SetImages();
}
下一段代码是 SetImages 函数;此函数用于为每个图片框(上一张、当前和下一张图片)设置图片。此代码会创建存储在图片数组列表中的文件路径的缩略图,然后将图片框设置为显示缩略图而不是完整图片。代码的编写方式是,在达到用于存储实际图片文件路径的数组列表的极限时,会做出不同的响应;在极限处,上一张或下一张图片将被清空。
此外,代码会在设置图片框后清除图片,并且每次调用函数时都会调用垃圾回收进行清理。我发现如果没有垃圾回收,当一次性扫描大量图片时,控件会抛出内存不足异常。同样,这段代码也有注释,应该很容易理解。
/// <summary>
/// This function is used to set the previous,
/// current, and next images into the
/// correct picture boxes
/// </summary>
private void SetImages()
{
// clear any existing images
// memory will be an issue if
// cycling through a large
// number of images
mPreviousImage = null;
mNextImage = null;
mCurrentImage = null;
// set the previous image
if (mImagePosition > 0)
{
try
{
// set delegate
Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort prevCallback =
new Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort(ThumbnailCallback);
// get the previous image
Bitmap prevBmp =
new Bitmap(mImageList[mImagePosition - 1].
ToString());
// thumbnail the image to the size
// of the picture box
mPreviousImage =
prevBmp.GetThumbnailImage(160, 100,
prevCallback, IntPtr.Zero);
// set the picture box image
picPreviousImage.Image = mPreviousImage;
// clear everything out
prevBmp = null;
prevCallback = null;
mPreviousImage = null;
}
catch
{
//stall if it hangs, the user can retry
}
}
else
{
// at the limit; clear the
// image
picPreviousImage.Image = null;
}
// set current image
if (mImagePosition < mImageList.Count)
{
try
{
// set delegate
Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort currentCallback =
new Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort(ThumbnailCallback);
// get the current image
Bitmap currentBmp =
new Bitmap(mImageList[mImagePosition].ToString());
// thumbnail the image to the size
// of the picture box
mCurrentImage =
currentBmp.GetThumbnailImage(320, 200,
currentCallback, IntPtr.Zero);
// set the picture box image
picCurrentImage.Image = mCurrentImage;
// clear everything out
currentBmp = null;
mCurrentImage = null;
currentCallback = null;
}
catch
{
//stall if it hangs, the user can retry
}
}
// set next image
if (mImagePosition < mImageList.Count-1)
{
try
{
// set delegate
Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort nextCallback =
new Image.GetThumbnailImageAbort(ThumbnailCallback);
// get the next image
Bitmap nextBmp =
new Bitmap(mImageList[mImagePosition + 1]
.ToString());
// thumbnail the image to the size
// of the picture box
mNextImage =
nextBmp.GetThumbnailImage(160, 100, nextCallback,
IntPtr.Zero);
// set the picture box image
picNextImage.Image = mNextImage;
// clear everything out
nextBmp = null;
nextCallback = null;
mNextImage = null;
}
catch
{
//stall if it hangs, the user can retry
}
}
else
{
// at the limit; clear the
// image
picNextImage.Image = null;
}
// call for garbage collection
GC.Collect();
}
下一段代码是在生成缩略图时会调用的代码,如果缩略图尝试被中止;这是生成缩略图的方法所必需的。
/// <summary>
/// Thumbnail image abort target
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool ThumbnailCallback()
{
return false;
}
上一张图片按钮的点击事件处理程序接下来;它用于更新数组列表中的图片位置,并在更新索引位置时重新调用 SetImages 方法。
/// <summary>
/// Set the image position and reset all of
/// the images when the previous image
/// button is clicked
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnPreviousImage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (mImagePosition >= 0 && picPreviousImage.Image != null)
{
mImagePosition--;
SetImages();
}
}
下一张图片按钮的点击事件处理程序接下来;它用于更新数组列表中的图片位置,并在更新索引位置时重新调用 SetImages 方法。
/// <summary>
/// Set the image position and reset all
/// of the images when the next image
/// button is clicked
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnNextImage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (mImagePosition <= (mImageList.Count - 2))
{
mImagePosition++;
SetImages();
}
}
最后一个方法用于根据计算机的文件关联将当前图片打开到默认的图片查看应用程序中。此方法仅调用进程启动函数并将当前图片文件的路径传递给它。
/// <summary>
/// Open the current image using the default
/// program per the user's file associations
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void btnOpenImage_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(mImageList[mImagePosition].ToString());
}
文本窗体 (Form1.cs)
测试应用程序中包含的测试窗体包含一个 Image Viewer 用户控件的实例;窗体本身没有任何特定代码,因此此处无需报告。测试应用程序被设置为启动项目,并在执行时,测试窗体打开并显示用户控件。
摘要
此解决方案提供了一个用户控件,可用于提供一个用户界面,该界面在应用程序用户需要浏览图片文件时可能很有用。该用户控件提供了浏览包含图片的文件夹所需的控件,以及预览当前选择的、上一张和下一张图片的手段。通过该控件,最终用户可以浏览文件夹中包含的所有图片文件,并且如果需要,可以将图片打开到新的应用程序中。
历史
- 2008年6月3日:初始版本
