C# 中它是如何工作的? - 第二部分
4.81/5 (41投票s)
在 C# 编程语言中,throw、rethrow 和 Enumerable 类的 where、select 子句如何工作。
目录
- 引言
- 它是如何工作的?
- throw an exceptionObject
- Enumerable 的 Where 和 Select
- 限制
- 历史
- 参考
源代码和演示
引言
在《C# 如何工作?》一文的第一部分中,我讨论了 C# 中的 var、自动属性以及事件的 += 和 -=。在本文中,我将讨论异常的抛出及其工作原理和内部机制,以及 C# 中 Enumerable 类的 where 和 select 子句的内部工作机制。
它是如何工作的?
在接下来的讨论中,我们将了解 throw 语句以及 Enumerable 类的 where、select 的内部工作机制。
throw an exceptionObject
异常是任何应用程序的常见场景之一。因此, proper exception management is one of the important tasks in application development. In here, I would like to discuss about throw statement in C#, how does throw anExceptionObject; or just throw works. I wrote a small program which will help me to explain the details. The task of this program is simple, it will raise an exception and throw it,
namespace TestHarnessPart2
{
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Person person = new Person();
}
catch (Exception exceptionObject)
{
throw;
}
}
}
public class Person
{
public Person()
{
throw new Exception("Exception from Person.");
}
}
}
上面的代码捕获了异常,并且在不传递任何显式异常对象的情况下将其抛出。我创建了上述代码的另一个版本作为示例,
namespace TestHarnessPart2
{
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Person person = new Person();
}
catch (Exception exceptionObject)
{
throw exceptionObject;
}
}
}
public class Person
{
public Person()
{
throw new Exception("Exception from Person.");
}
}
}
上面的代码将创建一个 Person 对象,如果在创建过程中发生任何异常,它将捕获该异常,并在 catch 块中抛出捕获的异常,即 throw exceptionObject;。现在,如果我们查看上述代码的堆栈跟踪,我们将发现差异。第一个版本的代码的堆栈跟踪如下:
图:代码第一个版本的堆栈跟踪。
以及第二个版本的代码的堆栈跟踪:
图:代码第二个版本的堆栈跟踪
从上面两张图片中,我们可以看到堆栈跟踪的详细信息不同。现在的问题是,这是如何发生的?为了得到答案,我们将借助 ILDasm 程序,从 bin 文件夹中获取 TestHarnessPart2 的 exe 文件并将其放入 ILDasm 程序中。对于代码的第一个版本,我们将看到如下内容:
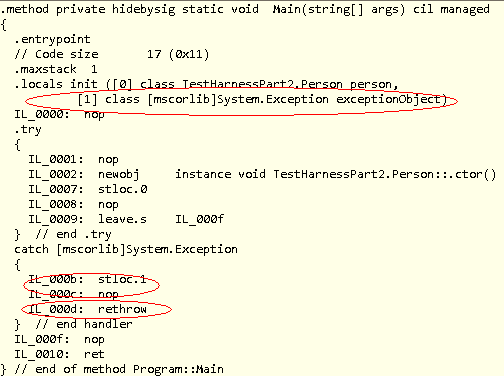
图:在 catch 块中使用 just throw 的 IL 代码。
从上面的图片中,我们可以看到 exceptionObject 被定义为本地变量,使用 .locals init [1],但在 catch 块中,编译器将 throw 语句更改为
catch [mscorlib]System.Exception
{
IL_000b: stloc.1
IL_000c: nop
IL_000d: rethrow
} // end handler
rethrow,这意味着编译器不会改变异常对象的原始堆栈跟踪,而是重新抛出存在的堆栈跟踪。而如果我们查看下面第二版本上述 C# 代码的图片:

图:在 catch 块中使用 just throw exceptionObject 的 IL 代码。
我们也可以看到 exceptionObject 被定义为本地变量,使用与第一个版本相同的代码,例如 .locals init [1]。但是,在 catch 块中,它所做的与上面代码的第一个版本完全不同。在 catch 块中,编译器加载位置 1 (ldloc.1),也就是 exceptionObject
catch [mscorlib]System.Exception
{
IL_000b: stloc.1
IL_000c: nop
IL_000d: ldloc.1
IL_000e: throw
} // end handler
并抛出它。结果是,这个 exceptionObject 将不会保留之前抛出的所有堆栈跟踪,除了当前状态的堆栈跟踪。现在,最后一块拼图是,throw 和 rethrow 语句到底做了什么?从 ECMA C# 和 Common Language Infrastructure Standards 检索到的 **Partition III CIL.doc** 中,我们可以看到 throw 和 rethrow 到底做了什么:
| IL 指令 | 描述 |
throw |
Throw an exception. The throw instruction throws the exception object (type O) on the stack and empties the stack. So in relation to the second version of the code block it will be,[1] class [mscorlib]System.Exception
exceptionObject
|
| rethrow | Rethrow the current exception. The rethrow instruction is only permitted within the body of a catch handler. It throws the same exception that was caught by this handler. A rethrow does not change the stack trace in the object. |
因此,很清楚 throw exceptionObject 会覆盖堆栈跟踪,而 just throw 语句则不会覆盖堆栈跟踪。
Enumerable 的 Where 和 Select
在我们开始讨论 Where 和 Select 之前,先快速看一下 where 和 select 子句的签名:

图:Where 子句的签名

图:Select 子句的签名
Where 和 Select 是 .Net 中 Enumerable 类的两个扩展方法。后面的章节将讨论 Where 和 Select 的内部工作原理。在继续之前,先简单介绍一下 .Net 中的 Func。根据 MSDN,*我们可以使用此委托来表示可以作为参数传递而无需显式声明自定义委托的方法。被封装的方法必须与此委托定义的签名相匹配*。Func 的一个简单示例如下:
namespace TestHarnessPart2
{
using System;
public class ExampleOfFunc
{
public int TestFunc(string dataToCheck, Func<string,> getLength)
{
return getLength(dataToCheck);
}
}
}
并测试上面的代码:
private static void TestFuncExample()
{
ExampleOfFunc exampleOfFunc = new ExampleOfFunc();
Console.WriteLine(exampleOfFunc.TestFunc("Example of Func", (dataToTest) => dataToTest.Length));
}
所以从上面的代码可以看出,TestFunc 方法接受一个 Func 作为参数,并通过 return getLength(dataToCheck); 来执行它。调用者实际上为 Func 参数传递了一个匿名方法块。在对 where 和 select 的整个讨论过程中,我们都会发现这个概念被用在了很多地方。
在继续之前,我想展示一段用于解释 where 和 select 语句的代码:
namespace TestHarnessPart2
{
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
class WhereSelect
{
List<string> bookList = new List<string>() { "Einstein: His Life and Universe", "Ideas And Opinions", "The World As I See It " };
public IEnumerable<string> GetBookListWhichLengthIsGreaterThan(int lengthOfTheBookName)
{
//return bookList.Where(book => book.Length == lengthOfTheBookName).Select(book => book);
return bookList.Where(book =>
{
var currentBook = book;
return book.Length > lengthOfTheBookName;
}).Select(book =>
{
var currentBook = book;
return book;
});
}
}
}
上面的代码并没有做什么,而是检查 booklist 是否有书名长度大于给定长度(lengthOfTheBookName)的书。现在我们将尝试找出 Where 和 Select 子句的一些内部工作机制。where 和 select 子句定义在 Enumerable 类中,where 子句的内部如下:

图:Where 内部
从上面的图片中,我们看到 Where 方法调用了另一个内部私有类 WhereListIterator
private class WhereListIterator<tsource> : Enumerable.Iterator<tsource>
{
public override bool MoveNext()
{
// most of the code has been removed for simplicity
while (this.enumerator.MoveNext())
{
TSource current = this.enumerator.Current;
if (this.predicate(current))
{
base.current = current;
return true;
}
}
}
}
从上面的代码中,我们可以看到 this.predicate(current)) 这行代码实际上正在执行 Func 或匿名方法块,在这种情况下是

图:Select 内部
同样,从上面的图片中,我们可以看到有一个 selector,它实际上是

图:WhereSelect 测试的输出
Where 和 Select 子句使用这两个方法来执行操作。再做一点调查来找出原因。现在我们需要 .Net Reflector 和 ILDasm 的帮助。首先从 bin 文件夹中获取 TestHarnessPart2.exe 并将其放入 .Net Reflector 中,然后我们会发现以下有趣的内容,一个类 <>c__DisplayClass3 及其详细信息:
[CompilerGenerated]
private sealed class <>c__DisplayClass3
{
// Fields
public int lengthOfTheBookName;
// Methods
public bool <GetBookListWhichLengthIsGreaterThan><getbooklistwhichlengthisgreaterthan>b__0(string book)
{
string currentBook = book;
return (book.Length > this.lengthOfTheBookName);
}
}
从类中,我们可以看到一个名为
{
var currentBook = book;
return book.Length > lengthOfTheBookName;
}
还有一个方法(在 <>c__DisplayClass3 类之外),名为
[CompilerGenerated]
private static string <GetbookListWhichLengthIsGreaterThan><getbooklistwhichlengthisgreaterthan>b__1(string book)
{
string CS$<>8__locals4 = book;
return book;
}
它实际上包含了我们为 select 子句定义的语句,如下所示:
{
var currentBook = book;
return book;
}
现在为了证明上述内容,我们将查看从 ILDasm 检索到的 IL 代码(同样从 bin 文件夹中获取 TestHarnessPart2.exe 并将其放入 ILDasm 程序中),用于上述 C# 代码:
图:GetBookListWhichLengthIsGreaterThan 方法的 IL 代码
从上图可以看出,where 子句使用了 <>c__DisplayClass3 类的
局限性
- 没有讨论查询表达式和 Lambda 表达式。
历史
- 版本 1
参考
- Expert C# 5.0: with the .NET 4.5 Framework
- C# in Depth, Second Edition, Jon Skeet
- CLR Via C#, Third Edition, Jeffrey Richter
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/netframework/aa569283.aspx
