Android:如何通过 TCP 与 .NET 应用程序通信
4.89/5 (88投票s)
简单的示例,展示了如何在 Android 和 .NET 应用程序之间进行通信。
相关文章
- Android:使用 Protocol Buffers 与 .NET 进行快速通信
- Android 和 .NET 之间的远程过程调用
- Android:如何通过 Websocket 从多个 .NET 应用程序接收通知消息
引言
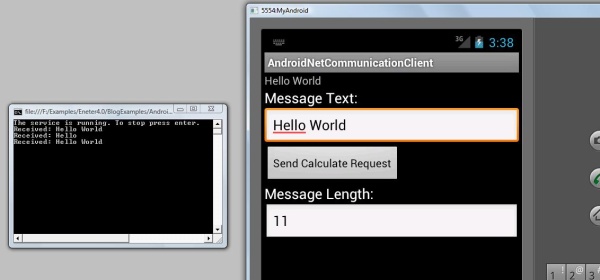
下面的示例实现了一个简单的请求-响应通信,用于 Android 和 .NET 应用程序之间。Android 应用程序是一个简单的客户端,它使用 .NET 应用程序作为服务来计算文本消息的长度。
下面的示例使用了 Eneter Messaging Framework,使得整个通信过程非常简单。(该框架可免费用于非商业用途,可从 http://www.eneter.net 下载。您需要下载 Eneter for .NET 和 Eneter for Android。更多详细技术信息可在 技术信息中找到。)
运行示例
如果您使用 Android Studio
- 下载 Android Studio 示例(包含 Android Studio 的客户端项目和 Visual Studio 的服务项目)。
- 在 Visual Studio 中打开 NetService 解决方案。
- 如果您的 Visual Studio 支持 NuGet 包,那么只需尝试构建解决方案,Eneter 库将自动从 NuGet.org 服务器下载。
如果您的 Visual Studio 不支持 NuGet 包,那么您需要 下载 Eneter Messaging Framework for .NET 并解压缩。然后添加 Eneter 库的引用。(右键单击“References”,然后选择“Add Reference ...”,导航到解压缩 Eneter for .NET 的路径,并选择 .NET 4.0 的库) - 在 Android Studio 中打开 AndroidNetCommunicationClientActivity。
- 下载 Eneter Messaging Framework for Java 并解压缩。
- 将 eneter-messaging-android 库复制到 AndroidNetCommunicationClientActivity\app\libs。
- 右键单击 Eneter 库,然后(从上下文菜单的底部)选择“Add As Library...”
- 从 Visual Studio 启动 NetService。
- 从 Android Studio 启动 Android 客户端。
此外,如果您使用 Android Studio 2.3 或更高版本,则需要关闭“Instant Run”功能。(问题在于此功能会“秘密地”在类中添加名为 $change 的字段,这会导致 XmlSerializer 出现问题。)
- 打开 Settings 或 Preferences 对话框。
- 导航到 Build, Execution, Deployment > Instant Run。
- 取消选中 Enable Instant Run 复选框。
如果您使用 Eclipse
- 下载 Eclipse 示例(包含 Eclipse 的客户端项目和 Visual Studio 的服务项目)。
- 在 Visual Studio 中打开 NetService 解决方案。
- 如果您的 Visual Studio 支持 NuGet 包,那么只需尝试构建解决方案,Eneter 库将自动从 NuGet.org 服务器下载。
如果您的 Visual Studio 不支持 NuGet 包,那么您需要 下载 Eneter Messaging Framework for .NET 并添加 Eneter 库的引用。(右键单击“References”,然后选择“Add Reference ...”,导航到解压缩 Eneter for .NET 的路径,并选择 .NET 4.0 的库) - 在 Eclipse 中打开 AndroidNetCommunicationClient。
- 下载 Eneter Messaging Framework for Java 并解压缩。
- 右键单击 'libs' 并选择 'Import...' -> 'General/File System' -> 'Next'。
- 然后单击“From directory”的“Browser”按钮,并导航到 Eneter 库所在的目录。
- 选中复选框,然后按“Finish”。
- 从 Visual Studio 启动 NetService。
- 从 Android Studio 启动 Android 客户端。
Android 上的 TCP
在 Android 上实现 TCP 通信时,您必须考虑到两个特定问题:
如果未设置权限,则不允许应用程序跨网络通信。要设置 INTERNET 权限,您必须在 AndroidManifest.xml 中添加以下行。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
允许跨网络通信的 AndroidManifest.xml 示例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="net.client"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<application
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<activity
android:name=".AndroidNetCommunicationClientActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
模拟器充当独立设备。因此,IP 地址 127.0.0.1 是该设备的环回地址,不能用于与运行在同一计算机上的其他应用程序进行通信。
取而代之的是,您必须使用计算机的实际 IP 地址,或者模拟器可以使用特殊地址 10.0.2.2,该地址路由到计算机上的 127.0.0.1(环回)。在我的示例中,Android 模拟器使用 10.0.2.2,而 .NET 服务正在监听 127.0.0.1。
- 您必须为您的 Android 应用程序设置 INTERNET 权限!
- Android 模拟器不能设置 127.0.0.1(环回)IP 地址与 .NET 应用程序通信!
Android 客户端应用程序
Android 客户端是一个非常简单的应用程序,允许用户输入一些文本消息,并发送请求给服务以获取文本的长度。当收到响应消息时,必须将其封送到 UI 线程以显示结果。另外,请不要忘记设置 android.permission.INTERNET。
使用 Eneter 框架,整个实现非常简单。
package net.client;
import eneter.messaging.diagnostic.EneterTrace;
import eneter.messaging.endpoints.typedmessages.*;
import eneter.messaging.messagingsystems.messagingsystembase.*;
import eneter.messaging.messagingsystems.tcpmessagingsystem.TcpMessagingSystemFactory;
import eneter.net.system.EventHandler;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.*;
public class AndroidNetCommunicationClientActivity extends Activity
{
// Request message type
// The message must have the same name as declared in the service.
// Also, if the message is the inner class, then it must be static.
public static class MyRequest
{
public String Text;
}
// Response message type
// The message must have the same name as declared in the service.
// Also, if the message is the inner class, then it must be static.
public static class MyResponse
{
public int Length;
}
// UI controls
private Handler myRefresh = new Handler();
private EditText myMessageTextEditText;
private EditText myResponseEditText;
private Button mySendRequestBtn;
// Sender sending MyRequest and as a response receiving MyResponse.
private IDuplexTypedMessageSender<MyResponse, MyRequest> mySender;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
// Get UI widgets.
myMessageTextEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.messageTextEditText);
myResponseEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.messageLengthEditText);
mySendRequestBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.sendRequestBtn);
// Subscribe to handle the button click.
mySendRequestBtn.setOnClickListener(myOnSendRequestClickHandler);
// Open the connection in another thread.
// Note: From Android 3.1 (Honeycomb) or higher
// it is not possible to open TCP connection
// from the main thread.
Thread anOpenConnectionThread = new Thread(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
try
{
openConnection();
}
catch (Exception err)
{
EneterTrace.error("Open connection failed.", err);
}
}
});
anOpenConnectionThread.start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
// Stop listening to response messages.
mySender.detachDuplexOutputChannel();
super.onDestroy();
}
private void openConnection() throws Exception
{
// Create sender sending MyRequest and as a response receiving MyResponse
IDuplexTypedMessagesFactory aSenderFactory =
new DuplexTypedMessagesFactory();
mySender = aSenderFactory.createDuplexTypedMessageSender(MyResponse.class, MyRequest.class);
// Subscribe to receive response messages.
mySender.responseReceived().subscribe(myOnResponseHandler);
// Create TCP messaging for the communication.
// Note: 10.0.2.2 is a special alias to the loopback (127.0.0.1)
// on the development machine
IMessagingSystemFactory aMessaging = new TcpMessagingSystemFactory();
IDuplexOutputChannel anOutputChannel =
aMessaging.createDuplexOutputChannel("tcp://10.0.2.2:8060/");
// Attach the output channel to the sender and be able to send
// messages and receive responses.
mySender.attachDuplexOutputChannel(anOutputChannel);
}
private void onSendRequest(View v)
{
// Create the request message.
MyRequest aRequestMsg = new MyRequest();
aRequestMsg.Text = myMessageTextEditText.getText().toString();
// Send the request message.
try
{
mySender.sendRequestMessage(aRequestMsg);
}
catch (Exception err)
{
EneterTrace.error("Sending the message failed.", err);
}
}
private void onResponseReceived(Object sender, final TypedResponseReceivedEventArgs<MyResponse> e)
{
// Display the result - returned number of characters.
// Note: Marshal displaying to the correct UI thread.
myRefresh.post(new Runnable()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
myResponseEditText.setText(Integer.toString(e.getResponseMessage().Length));
}
});
}
private EventHandler<TypedResponseReceivedEventArgs<MyResponse>> myOnResponseHandler
= new EventHandler<TypedResponseReceivedEventArgs<MyResponse>>()
{
@Override
public void onEvent(Object sender,
TypedResponseReceivedEventArgs<MyResponse> e)
{
onResponseReceived(sender, e);
}
};
private OnClickListener myOnSendRequestClickHandler = new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
onSendRequest(v);
}
};
}
.NET 服务应用程序
该 .NET 服务是一个简单的控制台应用程序,监听 TCP 并接收计算给定文本长度的请求。
服务的实现非常简单。
using System;
using Eneter.Messaging.EndPoints.TypedMessages;
using Eneter.Messaging.MessagingSystems.MessagingSystemBase;
using Eneter.Messaging.MessagingSystems.TcpMessagingSystem;
namespace ServiceExample
{
// Request message type
public class MyRequest
{
public string Text { get; set; }
}
// Response message type
public class MyResponse
{
public int Length { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
private static IDuplexTypedMessageReceiver<MyResponse, MyRequest> myReceiver;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create message receiver receiving 'MyRequest' and receiving 'MyResponse'.
IDuplexTypedMessagesFactory aReceiverFactory = new DuplexTypedMessagesFactory();
myReceiver = aReceiverFactory.CreateDuplexTypedMessageReceiver<MyResponse, MyRequest>();
// Subscribe to handle messages.
myReceiver.MessageReceived += OnMessageReceived;
// Create TCP messaging.
IMessagingSystemFactory aMessaging = new TcpMessagingSystemFactory();
IDuplexInputChannel anInputChannel =
aMessaging.CreateDuplexInputChannel("tcp://127.0.0.1:8060/");
// Attach the input channel and start to listen to messages.
myReceiver.AttachDuplexInputChannel(anInputChannel);
Console.WriteLine("The service is running. To stop press enter.");
Console.ReadLine();
// Detach the input channel and stop listening.
// It releases the thread listening to messages.
myReceiver.DetachDuplexInputChannel();
}
// It is called when a message is received.
private static void OnMessageReceived(object sender,
TypedRequestReceivedEventArgs<MyRequest> e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Received: " + e.RequestMessage.Text);
// Create the response message.
MyResponse aResponse = new MyResponse();
aResponse.Length = e.RequestMessage.Text.Length;
// Send the response message back to the client.
myReceiver.SendResponseMessage(e.ResponseReceiverId, aResponse);
}
}
}
这是应用程序通信的示例。