树迭代器
讨论树迭代器:数据结构和算法的选择。
引言
您可能已经注意到,树是一种二维数据结构,无法像列表那样进行线性访问。要遍历树,您必须按照其顺序和层次结构访问所有节点。这可以通过递归或循环来实现。
面向对象的树遍历方法是构建一个尽可能通用的类来封装遍历算法。一种现代且好的方法是构建一个树迭代器。
本文讨论了树迭代器以及在编写它们时可以采取的不同选择,以考虑性能、可重用性和理解性。
背景
首先,我们假设您熟悉树数据结构。在这种情况下,您知道树是一种分层结构,由链接节点组织而成。它也可以被视为图的一种特殊情况(无环连通图)。每个节点都有一个唯一的父节点和零个或多个子节点。树最底层节点称为叶子节点。
迭代器和 C#
迭代器是一个对象,可以迭代容器数据结构,并以增量方式显示其元素。在面向对象编程中,迭代器模式是一种封装迭代过程内部结构的设计模式。
它广泛用于 C++ STL,在那里它被实现为一个可以通过 ++ 运算符递增的指针。C# 也可以这样做,但 Framework 为我们提供了一种方便的替代方法:foreach 关键字。在这种情况下,迭代器必须实现 IEnumerator 接口。
// Define the data container : a list of strings
StringList mylist = new StringList();
// C++ STL syntax :
ListIterator iterator = new ListIterator(mylist);
while(iterator++) ShowValue(iterator.Value);
// C# enumerator syntax :
foreach(string value in mylist) ShowValue(value);
如您所见,C++ 语法非常自然。您首先定义迭代器,然后在 while 循环中使用它。
但是,C# 语法如何呢?嗯,它并不直接,但让我们看看基本机制。实际上,StringList 类实现了 IEnumerable 接口,并提供了一个名为 GetEnumerator() 的方法,该方法返回列表上的迭代器。因此,在枚举之前,IEnumerable 实例会调用 GetEnumerator() 方法来提供迭代器并在每次循环中递增它。
在 Visual Studio 2005 版本中,Microsoft 引入了一个非常有用的新关键字:yield。如果您不知道这个神奇的关键字,我建议您立即阅读这篇文章。否则,您可能知道它可以节省大量时间,避免您创建 IEnumerator 类。在这种情况下,编译器会为您生成它。阅读这篇关于 yield 关键字的精彩文章。
树结构的 G选择
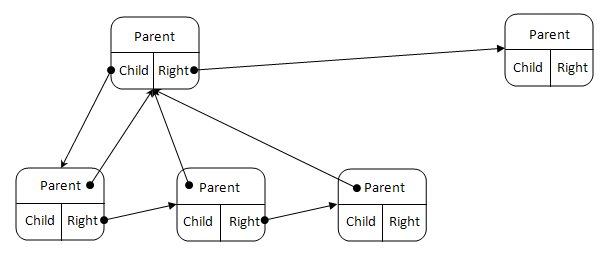
树可以以多种方式表示。由于树是组织好的节点集合,因此自然地将节点视为基础。一个节点可以有零个、一个或多个子节点。第一个想法是将节点列表设置为一个节点。这不是本文选择的方法,因为在子节点较少的情况下(例如二叉树),列表实现并未得到优化。对于更通用和灵活的实现,我更喜欢链表,就像下图所示一样
public interface INode<T>
{
INode<T> Parent { get; set; }
INode<T> Child { get; set; }
INode<T> Right { get; set; }
}
正如您所见,每个节点都有一个父节点、一个右邻居和一个子节点。您还可以注意到
- 如果父节点为
null,则该节点是树的根。 - 如果右侧为
null,则该节点是其父节点的子节点中最右边的节点。 - 如果子节点为
null,则该节点是叶子节点(分支最底部的节点)。
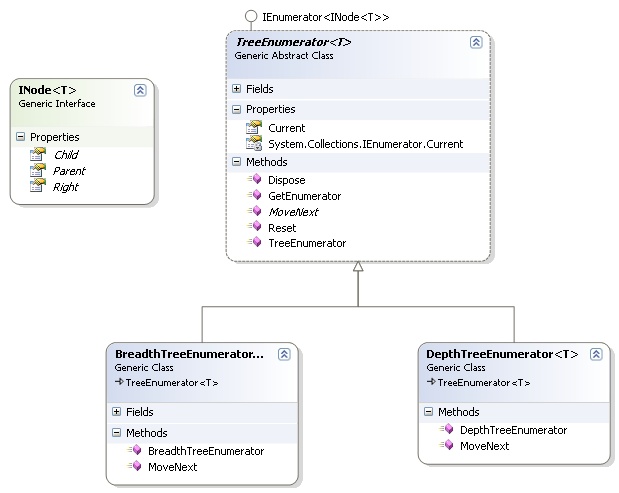
定义通用迭代过程的代码易于编写且直接。请注意,由于它是通用的,该算法实际上什么也不做,必须在继承类中实现。这就是为什么以下类被声明为 abstract
public abstract class TreeEnumerator<T> : IEnumerator<INode<T>>
{
// Contains the original parent tree.
protected INode<T> _Tree = null;
// Contains the current node.
protected INode<T> _Current = null;
// Constructor.
// The parameter tree is the main tree.
public TreeEnumerator(INode<T> tree) {
_Tree = tree;
}
// Get the explicit current node.
public INode<T> Current { get { return _Current; } }
// Get the implicit current node.
object System.Collections.IEnumerator.Current {
get { return _Current; }
}
// Increment the iterator and moves the current node to the next one
public abstract bool MoveNext();
// Dispose the object.
public void Dispose() {
}
// Reset the iterator.
public void Reset() {
_Current = null;
}
// Get the underlying enumerator.
public virtual TreeEnumerator<T> GetEnumerator() {
return this;
}
}
树遍历算法及其实现
树遍历有两种类型:深度优先和广度优先算法。第一个算法可以使用递归轻松编写,而后者需要 FIFO 结构来存储已访问过的节点。有关树遍历的更多信息,请参阅 此处。
为了实现迭代器,使用递归方法是不可行的。传统 while 循环得到了优先考虑。这里我仅展示深度遍历算法。广度算法可以在文件部分下载(包含完整的 Visual Studio 解决方案)。
public class DepthTreeEnumerator<t> : TreeEnumerator<t>
{
public DepthTreeEnumerator(INode<t> tree)
: base(tree) { }
public override bool MoveNext() {
if (_Current == null) _Current = _Tree;
else if (_Current.Child != null) _Current = _Current.Child;
else if (_Current.Right != null) _Current = _Current.Right;
else {
// The current node has no more child node
INode node = _Current;
do {
if (node.Parent == null) return false;
node = node.Parent;
} while (node.Right == null);
_Current = node.Right;
}
return true;
}
}
性能比较
这是我用来比较经典实现和 yield 方法实现的 C# 代码。
class Program
{
// The entry point of the program.
static void Main(string[] args) {
// Build the node.
Node tree = new Node(1);
tree.Child = new Node(2);
tree.Child.Right = new Node(5);
tree.Child.Child = new Node(3);
tree.Child.Child.Right = new Node(4);
tree.Child.Right.Child = new Node(6);
tree.Child.Right.Child.Right = new Node(7);
int imax = 100;
double[] ratios = new double[imax];
ulong iter = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < imax; i++)
ratios[i] = TestPerformance(tree, iter);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
foreach(double value in ratios)
sb.Append(value.ToString()+";");
string copy = sb.ToString();
}
// Define a yield return method iteration.
public static IEnumerable<Node> MoveNext(Node root) {
yield return root;
if (root.Child != null)
foreach (Node node in MoveNext((Node)root.Child))
yield return node;
if (root.Right != null)
foreach (Node node in MoveNext((Node)root.Right))
yield return node;
}
public static double TestPerformance(Node tree, ulong iter) {
DateTime start;
// Classic method test
start = DateTime.Now;
for (ulong i = 0; i < iter; i++) {
DepthTreeEnumerator<int> enumerator;
enumerator = new DepthTreeEnumerator<int>(tree);
foreach (Node node in enumerator) {}
long ticks1 = ((TimeSpan)(DateTime.Now - start)).Ticks;
}
// Yield return method test
start = DateTime.Now;
for (ulong i = 0; i < iter; i++) {
foreach (Node node in MoveNext(tree)) { }
}
long ticks2 = ((TimeSpan)(DateTime.Now - start)).Ticks;
return (double)ticks2 / (double)ticks1;
}
}
结果是,经典方法比 yield return 方法快 5 倍!因此,很明显,通过添加简单的测试,可以证明 yield 关键字不适用于此类工作。
示例应用程序
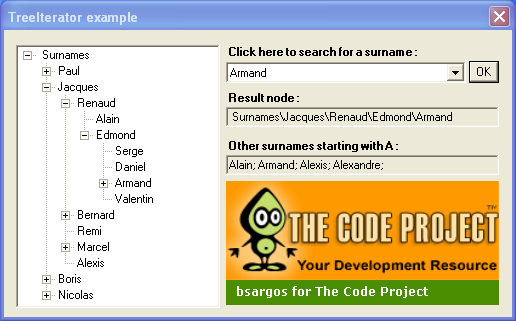
理论讨论没有具体应用是难以理解的。这就是为什么我在这篇文章中添加了一个树迭代器的示例应用程序,对于 C# 开发人员来说在“真实生活”中很有用。该应用程序显示了一个带有许多节点的 TreeView ,每个节点显示一个法国姓氏。
要测试应用程序,请下载上面的文件,解压缩并构建解决方案。运行 TreeIterator.Example 项目(默认选定)。
然后,在出现的对话框中,从组合框建议的姓氏中选择一个。单击“确定”。最后,三件事同时发生:
- 与您选择的姓氏匹配的节点可见。
- 第一个(只读)
TextBox显示所选节点到根的路径。 - 所有以所选姓氏的第一个字母开头的姓氏都列在最下面的
TextBox中。
应用程序运行良好。但要欣赏迭代器的应用,我们需要检查代码。在此项目中,有两个主要文件:
- SurnameTreeNode.cs
- MainForm.cs
那么,它是如何工作的呢?这并不难。请记住,我们已经定义了一个为我们完成所有遍历的树迭代器。但是这个迭代器是为处理任何 INode 结构而设计的。因此,为了完成任务,我们需要创建一个新类(我们将称之为 SurnameNode),该类派生自 INode。这个类将在 TreeView 节点和迭代器之间建立联系。我们唯一需要做的就是定义 SurnameNode 对象的属性。
// Get or set the parent of the Node.
public INode<TreeNode> Parent {
get { return _Node == null ? null : new SurnameTreeNode(_Node.Parent); }
set { throw new NotImplementedException();
}
// Get or set the leftmost child of the Node.
public INode<TreeNode> Child
{
get {
if (_Node == null || _Node.Nodes == null) return null;
if(_Node.Nodes.Count <= 0) return null;
return new SurnameTreeNode(_Node.Nodes[0]);
}
set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
}
// Get or set the right neighbour of the Node.
public INode<TreeNode> Right
{
get {
if (_Node == null || _Node.Parent == null) return null;
if(_Node.Parent.Nodes.Count <= _Node.Index + 1) return null;
var node = _Node.Parent.Nodes[_Node.Index + 1];
return new SurnameTreeNode(node );
}
set { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
}
好的。现在,如果我们想在 foreach 循环中使用我们的迭代器,我们必须用 yield return 循环来延迟其遍历。
// Returns an enumeration of the tree nodes, with a depth traversal.
private IEnumerable<TreeNode> Enumerate() {
// Instantiate the iterator
DepthTreeEnumerator<TreeNode> enumerator = null;
enumerator = new DepthTreeEnumerator<TreeNode>(
new SurnameTreeNode(this.treeView1.Nodes[0])
);
// Defer the traversal of the tree
foreach (SurnameTreeNode node in enumerator) yield return node.Node;
}
此方法必须这样使用:
IEnumerable nodes = Enumerate();
最后一件事是编写搜索方法。这就是迭代器力量的体现。我们现在可以像处理列表一样线性地处理节点,然后应用 LINQ 方法扩展。这非常简单!
第一个用途是按姓氏顺序获取树的所有姓氏。以下是执行此操作的代码:
// Fill the combo box with all the surnames the tree contains.
IQueryable<string> items;
items = Enumerate().OrderBy(node=>node.Text).Select(node=>node.Text);
this.comboBox1.Items.AddRange(items.ToArray());
然后,我们可以搜索匹配特定名称的节点。
string name = "Boris"
TreeNode resultnode = Enumerate().Single(node => node.Text == name);
或者我们可以找到所有以指定字母开头的姓氏。
string letter = "B"
var nodes = Enumerate().Where(node=>node.Text.StartsWith(letter)));
List<string> names = nodes.Select(node=>node.Text).ToList();
关注点
在本文中,我们看到了一种简单、通用且高效的树遍历方法,以及两种不同的算法。我们还看到,实现基于 yield return 的算法会产生较差的性能。然后,我们可以将我们的库应用于日常开发问题,并证明迭代器与 LINQ 结合使用时,在搜索无序树中的元素时会非常强大。
历史
- 2009 年 3 月 20 日:初始发布
