Mastermind for Windows Mobile
使用 .NET Compact Framework 开发 Mastermind 游戏。
引言
我女儿喜欢玩 Master Mind 游戏。我没时间总是陪她玩,所以我想写一个程序,这样当我不在她身边时,她也可以自己玩这个游戏,用我的 HTC Touch。
在这篇文章中,我将简要描述这个程序的设计。
背景
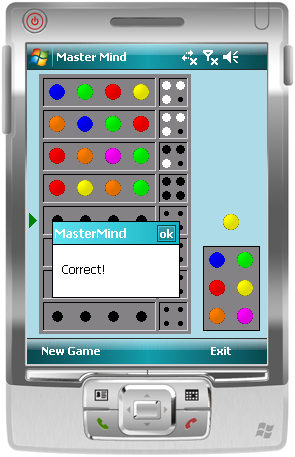
Master Mind 是一款猜密码的棋盘游戏。游戏使用一个解码板、一些六种(或更多)不同颜色的密码钉和一些带有黑白颜色的钥匙钉进行游戏。
两名玩家进行游戏:密码制定者和密码破解者。密码制定者选择一个四颗密码钉的模式,并将它们放在由挡板遮盖的四个孔中,密码破解者看不到。
密码破解者尝试猜测图案,包括顺序和颜色。每次猜测都通过在解码板上放置一行密码钉来完成。放置后,密码制定者通过在猜测行上放置钥匙钉来提供反馈。黑色钥匙钉表示猜测中与答案颜色和位置都正确的密码钉。白色钥匙钉表示猜测中存在颜色正确但位置错误的密码钉。请参考维基百科了解详情。
设计
该程序的设计基本上遵循 MVC 设计模式。模型负责管理游戏状态、已进行的猜测以及答案——密码制定者选择的模式。视图显示游戏状态并提供反馈。控制器处理鼠标事件,更新模型和视图。
模型
Game 类代表一次 Master Mind 游戏会话。Pattern 类可以代表答案和密码破解者进行的猜测。Game 对象保留一个 Pattern 对象作为 Answer,以及多个 Pattern 对象作为 Guesses。当进行新的猜测时,会在 Game 对象上调用 Guess() 方法。
Guess() 方法返回一个 GuessResult 对象,指示猜测的结果。如果猜测与答案完全相同,则 Succeeded 属性返回 true。如果猜测与答案不同且猜测次数已超过限制,则 Failed 属性返回 true。

CodePeg 和 KeyPeg 类继承自抽象类 Peg 并重写了 Draw() 方法。

视图和控制器
GameBox 类负责显示游戏状态、向用户提供视觉反馈以及响应鼠标事件。从某种意义上说,GameBox 在 MVC 模式中充当控制器。GameBox 拥有一组属性,用于定义视图的布局,包括 Board 和 PegBox。Board 是用户放置密码钉和显示猜测结果的地方。PegBox 是用户选择特定颜色密码钉以放置在 Board 上的地方。
为了减少 Board 和 PegBox 类对 GameBox 类的依赖,引入了 IGameBox 接口。Board 和 PegBox 类依赖于 IGameBox 接口,该接口由 GameBox 类实现。

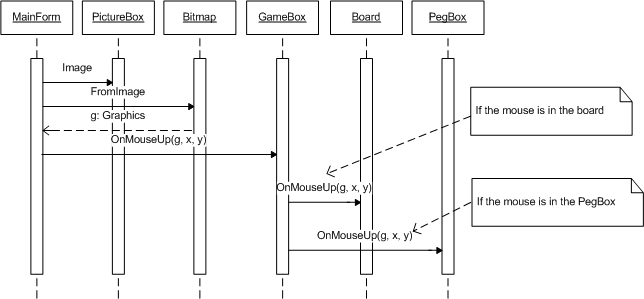
为了避免闪烁,我们不直接绘制在主窗体的客户端区域。相反,我们将 GameBox 绘制在 PictureBox 的图像上,该 PictureBox 覆盖了主窗体的整个客户端区域,由继承自 Form 类的 MainForm 类表示。
如下面的序列图所示,当 MainForm 加载时,会调用 InitializeGameBox() 方法,该方法创建一个 GameBox 类的实例并对其调用 Initialize() 方法。GameBox.Initialize() 方法首先创建 Board 和 PegBox 的一个实例,然后创建与主窗体客户端区域大小相同的位图,从该位图中获取 Graphics 对象,并使用 Graphics 对象作为参数调用 Board 和 PegBox 对象的 Draw() 方法。因此,实际上 Board.Draw() 和 PegBox.Draw() 方法是在位图上绘制图形,然后将该位图设置为 MainForm 中的 PictureBox 对象。
Board.Draw() 方法绘制棋盘、行以及用于放置密码钉和钥匙钉的孔。PegBox.Draw() 方法绘制 6 种不同颜色的密码钉供用户选择。

public void Initialize()
{
// Set the selected color randomly.
Random ran = new Random();
CurrentColor = (PegColor)ran.Next(0, NumOfCodeColors);
// Create the Board
{
int boardWidth =
BoxBorderWidth * 2 +
RowHeight * 5 +
CellBorderWidth;
int boardHeight =
BoxBorderWidth * 2 +
RowHeight * MaxGuesses +
CellBorderWidth * (MaxGuesses - 1);
int yMargin = (TotalHeight - boardHeight) / 2;
int xMargin = LeftMargin + yMargin;
Rectangle rcBoard = new Rectangle(xMargin, yMargin,
boardWidth, boardHeight);
m_board = new Board(this, rcBoard);
}
// Create the code peg box.
{
int width = RowHeight * 2;
int height = RowHeight * NumOfCodeColors / 2;
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle
(
TotalWidth - width - RightMargin,
TotalHeight - height - RightMargin,
width,
height
);
m_pegBox = new PegBox(this, rect);
}
DrawBitmap();
}
private void DrawBitmap()
{
Bitmap = new Bitmap(TotalWidth, TotalHeight);
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(Bitmap))
{
Draw(g);
}
}
public void Draw(Graphics g)
{
var rc = new Rectangle(0, 0, TotalWidth, TotalHeight);
using (SolidBrush bgBrush = new SolidBrush(BackgroundColor))
{
g.FillRectangle(bgBrush, rc);
}
m_board.Draw(g);
m_pegBox.Draw(g);
}
当用户点击 PictureBox 时,会触发 MouseUp 事件。pbGameBox_MouseUp() 方法从 PictureBox 的图像中获取 Graphics 对象,并将其与鼠标位置一起传递给 GameBox 对象上的 OnMouseUp() 方法。请注意,从 PictureBox 控件的位图中获取的 Graphics 对象被传递给 GameBox.OnMouseUp() 方法,以便 GameBox 对象能够更新屏幕。
private void pbGameBox_MouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
Status status = Status.Continue;
using (Graphics g = Graphics.FromImage(pbGameBox.Image))
{
/* let the GameBox object handles the event and draw the image
* of the pictuer box.
*/
status = m_gameBox.OnMouseUp(g, e.X, e.Y);
}
// redraw the picture box to reflect of changes in the image.
pbGameBox.Refresh();
// Check the status of the guess just made.
switch (status)
{
case Status.Succeeded:
MessageBox.Show("Correct!", "MasterMind");
break;
case Status.Failed:
{
Pattern answer = m_gameBox.Game.Answer;
MessageBox.Show(string.Format(
"The correct answer is: {0} {1} {2} {3}",
answer.GetAt(0), answer.GetAt(1), answer.GetAt(2),
answer.GetAt(3)),
"MasterMind");
}
break;
}
}
GameBox.OnMouseUp() 方法根据鼠标位置调用 Board 对象或 PegBox 对象上的 OnMouseUp() 方法。
public Status OnMouseUp(Graphics g, int x, int y)
{
if (m_board.Rectangle.Contains(x, y))
{
// The user tapped on the board.
return m_board.OnMouseUp(g, x, y);
}
else if (m_pegBox.Rectangle.Contains(x, y))
{
// The user tapped on the code peg box to select the current color.
m_pegBox.OnMouseUp(g, x, y);
}
return Status.Continue;
}
如果鼠标在当前猜测行的区域内,则 Board.OnMouseUp() 方法检查并将当前选中的密码钉放置在最近的孔中。如果当前猜测已完成,则显示猜测结果并返回游戏状态。
public Status OnMouseUp(Graphics g, int x, int y)
{
var rowRect = GetCurrentRowRect();
if (rowRect.Contains(x, y))
{
// The user tapped in the current row.
PutCodePeg(g, rowRect, x);
if (m_gameBox.CurrentGuess.IsComplete)
{
/* The current guess is completed. Check if the guess is
* or if the user has failed to get the correct answer within
* the limit.
*/
GuessResult r = m_gameBox.Game.Guess(m_gameBox.CurrentGuess);
DrawGuessResult(g, r, y);
DrawRowIndicator(g);
m_gameBox.CurrentGuess.Clear();
if (r.Failed)
{
return Status.Failed;
}
else if (r.Succeeded)
{
return Status.Succeeded;
}
}
}
return Status.Continue;
}
PegBox.OnMouseUp() 方法获取并绘制选定的颜色。
public void OnMouseUp(Graphics g, int x, int y)
{
x -= Rectangle.Left;
y -= Rectangle.Top;
int i = y / m_gameBox.RowHeight; // row
int j = x / m_gameBox.RowHeight; // column
m_gameBox.CurrentColor = m_gameBox.Game.PegColors[i * 2 + j];
DrawCurrentColor(g);
}
一些其他代码
Pattern 类中有两个方法值得一提:Generate() 和 Compare()。Generate() 方法随机生成一个模式。在当前实现中,生成的模式中的 4 种颜色必须是唯一的。m_random 成员变量在构造函数中初始化。
public void Generate(int colors)
{
var usedColors = new Dictionary<int, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int n = -1;
// Make sure the pattern has 4 unique colors.
do
{
n = m_random.Next(0, colors - 1);
} while (usedColors.ContainsKey(n));
usedColors[n] = n;
m_pegs[i] = m_pegColors[n];
}
}
Compare() 方法将给定的模式与答案进行比较。它首先检查有多少密码钉的颜色和位置都正确,然后检查有多少密码钉的颜色正确但位置错误。black 变量表示应标记为黑钥匙钉的密码钉。blackWhite 变量表示应标记为黑钥匙钉或白钥匙钉的密码钉。
public GuessResult Compare(Pattern pegs)
{
int blackCount = 0;
int whiteCount = 0;
bool[] black = new bool[4] { false, false, false, false };
/* Find all code pegs in the two patterns that have the same
* color and position.
*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (m_pegs[i] == pegs.GetAt(i))
{
blackCount++;
black[i] = true;
}
}
if (blackCount < 4)
{
/* Find all remaining code pegs in the two patterns that have
* the same color.
*/
bool[] blackWhite = new bool[4];
black.CopyTo(blackWhite, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
if (!black[j])
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
if (!blackWhite[k] && m_pegs[j] == pegs.GetAt(k))
{
whiteCount++;
blackWhite[k] = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
return new GuessResult(blackCount, whiteCount);
}
单元测试
创建了一个名为 TestMasterMind 的单元测试项目,用于单元测试可进行单元测试的类。目前,只有 Pattern 和 Game 类进行了单元测试。
例如,GameTester.TestSucceeded() 测试方法进行两次猜测,并检查第二次猜测的结果是否为 Succeded。
[TestMethod]
public void TestSucceeded()
{
m_game.NewGame();
m_game.Answer.SetAt(0, PegColor.Green);
m_game.Answer.SetAt(1, PegColor.Magenta);
m_game.Answer.SetAt(2, PegColor.Orange);
m_game.Answer.SetAt(3, PegColor.Red);
Pattern p = new Pattern();
p.SetAt(0, PegColor.Orange);
p.SetAt(1, PegColor.Blue);
p.SetAt(2, PegColor.Green);
p.SetAt(3, PegColor.Yellow);
GuessResult r = m_game.Guess(p);
Assert.AreEqual(false, r.Succeeded);
Assert.AreEqual(false, r.Failed);
p.SetAt(0, PegColor.Green);
p.SetAt(1, PegColor.Magenta);
p.SetAt(2, PegColor.Orange);
p.SetAt(3, PegColor.Red);
r = m_game.Guess(p);
Assert.AreEqual(true, r.Succeeded);
Assert.AreEqual(false, r.Failed);
}
请注意,由于 TestMasterMind 项目依赖于 MasterMind 项目(一个智能设备项目),因此当您运行单元测试时,系统会要求您将 MasterMind 程序部署到模拟器,这有点令人恼火。
关注点
在 PictureBox 控件的位图中绘制图形有助于避免闪烁。
尽管这个程序非常小,但定义可进行单元测试的域类有助于实现松散耦合的设计并缩短开发过程。
