图像的仿射变换
C# .NET CF 的图像变换
下载 Windows Mobile 的示例应用程序(源代码)- 97.79 KB

介绍
这是我的第一篇 CodeProject 文章,希望您喜欢。进入正题
不幸的是,与 .NET framework 相比,CF 不支持在图像上进行此类操作。
因此,这个类库实现了图像的仿射变换,例如平移、旋转、缩放、倾斜。算法效率不高,但是很简单。此代码不应用于实时转换,在这种情况下,您需要更高效的东西,一些将 GPU 应用于工作的东西,而不仅仅是可怜的、孤独的 CPU ;>(例如 DirectX API)
算法
Transforms.ImageTransform(Bitmap dst, Bitmap src, Matrix matTrans, Interpolate sampler)
- 使用定义的插值方法,使用变换矩阵将源图像像素放置到目标图像上。怎么做?
首先,我们需要找到定义的反向变换。为什么?
如果您使用定义的矩阵转换源位图的像素并将它们放在目标位图上,则输出图像可能存在“孔洞”。想象一下最简单的 2 倍缩放变换
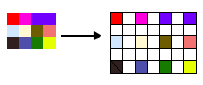
解决该问题的方法是沿相反方向转换。只需遍历所有目标位图的像素,使用逆矩阵转换它们的坐标,以了解像素应该去源位图的哪个位置,另一方面,我们知道源像素应该去目标位图的哪个位置。现在我们必须使用某种插值方法用源像素的颜色填充目标像素。 如果转换后的像素没有去源位图,则目标像素可以保持不变或填充定义的背景颜色。
如何处理源像素的浮点坐标?(插值问题)。
我实现了两种方法:
- 最近邻插值 - 我们只是将坐标四舍五入到最接近的整数
unsafe public static void NearestNeigbour(Pixel* dstPixel, Pixel* src, Vector2 vec, int srcStrideInPixels) { int tx, ty; tx = Convert.ToInt32(vec.x); // Note: Convert.ToInt32 rounds float numbers! ty = Convert.ToInt32(vec.y); // Note: Convert.ToInt32 rounds float numbers! *dstPixel= src[ty * srcStrideInPixels + tx]; }
- 双线性插值 - 我们将具有整数坐标的 4 个相邻像素的颜色相加(在浮点坐标上使用 floor、ceiling 操作),并使用以下方式计算的适当权重
(1.0f - 变换像素和相邻像素之间的 X 维度距离)*(1.0f - Y 维度距离)
如果您仔细查看下图...
假设转换后的像素 P 具有坐标 (4.25f, 11.3f),则像素
P0 的坐标为 (4, 11),其权重为 (1.0f -0.25f) * (1.0f - 0.3f)
P1 的坐标为 (5, 11),其权重为 (1.0f -0.75f) * (1.0f - 0.3f)
P2 的坐标为 (4, 12),其权重为 (1.0f -0.25f) * (1.0f - 0.7f)
P3 的坐标为 (5, 12),其权重为 (1.0f -0.75f) * (1.0f - 0.7f)
显然,相邻像素越接近变换后的像素,它在最终颜色中就越重要。
unsafe
public static void BilinearInterpolation(Pixel* dstPixel, Pixel* src, Vector2 vec, int srcStrideInPixels)
{
Pixel result;
int tx, ty;
float f1, f2;
tx = (int)vec.x; // Note: this is just a truncation of float numbers
ty = (int)vec.y; // Note: this is just a truncation of float numbers
f1 = vec.x - (float)tx;
f2 = vec.y - (float)ty;
src = src + ty * srcStrideInPixels + tx;
Pixel upperLeft = *src;
Pixel upperRight = src[1];
Pixel bottomLeft = src[srcStrideInPixels];
Pixel bottomRight = src[srcStrideInPixels + 1];
result.A = 0;
result.R = (Byte)((float)upperLeft.R * (1.0f - f1) * (1.0f - f2) + (float)upperRight.R * f1 * (1.0f - f2) +
(float)bottomLeft.R * (1.0f - f1) * f2 + (float)bottomRight.R * f1 * f2);
result.G = (Byte)((float)upperLeft.G * (1.0f - f1) * (1.0f - f2) + (float)upperRight.G * f1 * (1.0f - f2) +
(float)bottomLeft.G * (1.0f - f1) * f2 + (float)bottomRight.G * f1 * f2);
result.B = (Byte)((float)upperLeft.B * (1.0f - f1) * (1.0f - f2) + (float)upperRight.B * f1 * (1.0f - f2) +
(float)bottomLeft.B * (1.0f - f1) * f2 + (float)bottomRight.B * f1 * f2);
*dstPixel = result;
}
效率
正如您所看到的,算法的效率取决于目标图像的大小以及您选择的插值方法。
有什么改进吗?
所有数学运算都可以仅用整数运算代替。 如您所知,对整数进行运算比对浮点数进行运算快得多。 但是我们失去了数学运算的精度。 要获得整数的精度,只需乘以某个大数(最好是 2 的幂并进行位移运算),然后进行所需的运算,最后除以相同的数字(建议使用位移运算)。
位图是像素的有序集合。 使用该事实,您可以创建增量算法。
使用代码
using ImageTransforms;
Bitmap buffer = new Bitmap(128,128);
Bitmap srcBuffer = new Bitmap(bmpArrows); //load image for transformations
Matrix matRot = new Matrix();
Matrix matTrans1 = new Matrix();
Matrix matTrans0 = new Matrix();
matTrans0.Translation(-(float)(srcBuffer.Width) / 2.0f, -(float)(srcBuffer.Height) / 2.0f);
matRot.Rotation(angle);
matTrans1.Translation((float)(buffer.Width) / 2.0f, (float)(buffer.Height) / 2.0f);
unsafe
{
Transforms.ImageTransform(buffer, srcBuffer, matTrans1 * (matRot * matTrans0), ImageTransforms.Transforms.NearestNeigbour);
}
//now buffer contains our transformed image

