Property Finder - 跨平台 HTML5 移动应用
5.00/5 (44投票s)
本文描述了为 Windows Phone 和 iPhone 开发跨平台 HTML5 应用程序的过程。
目录
- 概述
- 引言
- 工具和框架
- 开发过程
- JavaScript 模式
- 应用程序结构概述
- 模型层
- 视图模型层
- ApplicationViewModel
- App.js
- PropertySearchViewModel
- LocationViewModel 和 GeoLocationViewModel
- SearchResultsViewModel
- 状态持久化
- Property Finder iOS
- 借鉴 jQuery Mobile
- 使用 iScroll 滚动
- 项目结构和构建
- 对用户体验的批判性审视
- Windows Phone
- iPhone
- 结论

概述
本文描述了为搜索英国房产列表而开发的跨平台 HTML5 移动应用。该应用程序使用 JavaScript、Knockout、jQuery-Mobile 的一些元素和 Apache Cordova (PhoneGap) 来封装应用程序,以便将其部署到应用程序商店/市场。我还将演示如何使用 PhoneGap Build 创建应用程序的 iOS 版本,而无需 Mac 电脑。该应用程序利用公开可用的 Nestoria API,该 API 提供多种方法来查询其销售和租赁房产数据库。
以下是 iOS 和 Windows Phone 应用程序运行时的视频
本文将探讨此应用程序的技术细节以及它所提供的整体用户体验。结论表明,通过使用 HTML5,可以在两个移动平台之间共享大量通用代码,但是,HTML5 的使用确实导致了一些用户体验上的妥协。
引言
使用 HTML5 开发跨平台移动应用程序的趋势日益增长。这项技术允许开发人员使用平台无关的 Web 技术编写应用程序,并将其交付给各种智能手机设备。这得益于现代智能手机通常具有功能强大的浏览器,并且对 HTML5 / CSS3 功能有很好的支持。
本文使用 Apache Cordova(以前称为 PhoneGap),这是一个开源框架,它提供了一种将 HTML5 内容(HTML、JavaScript、CSS、图像)打包为适用于 Windows Phone、iOS、BlackBerry 和 Android 的原生可执行文件的机制。Cordova 还为使用 HTML5 技术无法访问的原生手机功能(例如摄像头、加速度计、指南针)提供了 JavaScript 接口。
我最近为 Microsoft MSDN 杂志撰写了一篇文章,其中介绍了创建 Windows Phone Cordova 应用程序的基本步骤。杂志文章中描述的应用程序相当简单。在本文中,我想描述一个更复杂的应用程序“Property Finder”,我去年将其发布到 Windows Phone 市场。从那时起,我使用这个代码库创建了同一个应用程序的 iOS 版本,我也会在本文中进行描述。

您可以通过市场下载适用于 Windows Phone 的 Property Finder。
如果您完全不熟悉 Apache Cordova,您可能需要先阅读我的 MSDN 文章。同样,如果您不熟悉 Knockout(一个非常时髦的 JavaScript MVVM 框架),您可能需要阅读我之前对比Knockout 和 Silverlight的 codeproject 文章。我过去曾撰写过许多与 Windows Phone 和 Cordova 相关的主题,因此本文的许多细节都很简略,其中包含了对博客文章和其他信息来源的引用。
在本文中,我将假定您了解 JavaScript、Cordova 和 Knockout,并专注于应用程序本身!
工具和框架
我将简要总结一下我用于开发此应用程序的工具和框架
JavaScript – 好的,这是一个非常明显的,它是一个 HTML5 应用程序,所以它是用 JavaScript 编写的,这还用说!然而,JavaScript 很少单独使用;有大量的框架和工具供您选择。以下是我为这个特定应用程序选择的框架。
jQuery – 事实上的 JavaScript 开发框架!在这个项目中,我很少使用 jQuery,因为 Knockout 消除了直接访问 DOM 的大部分需求。我使用 jQuery 进行偶尔的选择器来定位 DOM 中的元素,以及我广泛使用的 each() 便利函数。
jQuery-JSONP – 标准 jQuery-JSONP 功能缺少指定超时机制。 jQuery-JSONP 插件是一个紧凑且功能丰富的替代方案,提供了这一急需的功能。
Apache Cordova – 这是一个用于将基于 HTML5 的应用程序打包到原生 shell 中的框架。这允许您像分发原生应用程序一样分发 HTML5 应用程序。Cordova 还提供了一组通用 API,用于使用手机硬件功能,例如位置、持久化等……
JSLint – JavaScript 是一种非常宽容的语言……太宽容了!全局变量和分号插入等语言特性使得编写草率的 JavaScript 代码变得非常容易。 JSLint 强制执行一套规则,以确保您的 JavaScript 更一致、更可读且无错误。如果您编写的 JavaScript 代码不仅仅是最简单的片段,我建议您对其进行 linting!有一个提供 JSLint 支持的 Visual Studio 2010 扩展,我建议您使用。
JavaScript Intellisense – 说实话,Visual Studio 并不是编写 JavaScript 的最佳工具,我个人认为 Eclipse 更胜一筹。然而,在 Visual Studio 中开发确实允许您快速构建和部署 Windows Phone 版本的代码。Visual Studio 通过伪执行您的代码提供 JavaScript Intellisense,这是必需的,因为 JavaScript 是动态的,所以 IDE 无法仅通过静态分析来理解您的代码。为了有效地使用它,您需要确保 IDE 可以发现您的所有文件。因此,我的项目中包含以下文件,它会通知 Visual Studio 我希望包含在 Intellisense 中的所有 JavaScript 文件
/// Ensure that all the files listed below are included, so that VS provides /// Intellisense /// /// <reference path="namespaces.js" /> /// <reference path="model//JSONDataSource.js" /> /// <reference path="model//Location.js" /> /// <reference path="model//Property.js" /> /// <reference path="model//PropertyDataSource.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//AboutViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//ApplicationViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//FavouritesViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//GeolocationViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//LocationViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//PropertySearchViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//PropertyViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="viewModel//SearchResultsViewModel.js" /> /// <reference path="lib//knockout-2.1.0.js" />所有 JavaScript 文件都引用上述“内容”文件,如下所示
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />Firefox 和 Firebug – 您可以使用 Windows Phone 模拟器开发 Cordova 应用程序,但是启动时间和糟糕的 JavaScript 调试工具使得这个过程非常痛苦!因为您应用程序的核心将是纯 JavaScript,所以可以在桌面浏览器中直接运行它。我长期以来一直偏爱带有 Firebug 插件的 Firefox,但最近我开始使用 Chrome 开发工具。有一点是肯定的,它们都比 IE 工具强得多!
注意:此应用程序和文章是针对 Cordova 1.9 编写的。当前发布版本是 2.0,但是,最新版本中存在一些 Windows Phone 错误,无法解决。
开发过程
开发 Cordova 应用程序时,您可以将 HTML、JavaScript 和 CSS 文件添加到 www 文件夹中,只要将它们的“生成操作”标记为“内容”,它们就会包含在您的项目中,并在应用程序执行时通过浏览器控件访问。Cordova API 在 PhoneGap 网站上进行了文档说明,我在这里将不再详细描述。需要注意的一点是,在调用任何其他 API 方法之前,您必须等待 deviceready 事件。如果您检查由 Visual Studio Cordova 应用程序模板生成的 index.html 文件,您会看到它在设备准备就绪之前会等待,然后才更新 UI
<script type="text/javascript">
document.addEventListener("deviceready",onDeviceReady,false);
// once the device ready event fires, you can safely do your thing! -jm
function onDeviceReady()
{
document.getElementById("welcomeMsg").innerHTML += "PhoneGap is ready! version=" + window.device.phonegap;
console.log("onDeviceReady. You should see this message in Visual Studio's output window.");
}
</script> 您可以通过修改 HTML / JavaScript、编译并部署到模拟器或设备来开发应用程序,但是有更快的方法。由于您的 Cordova 应用程序只是一个 HTML / JavaScript 应用程序,您可以直接在桌面浏览器中运行它。但是,您必须提供您使用的任何 Cordova API 的模拟实现。例如,要运行由 Visual Studio 模板创建的应用程序,您可以模拟 Cordova 添加到“window”的“device”对象,然后调用 onDeviceReady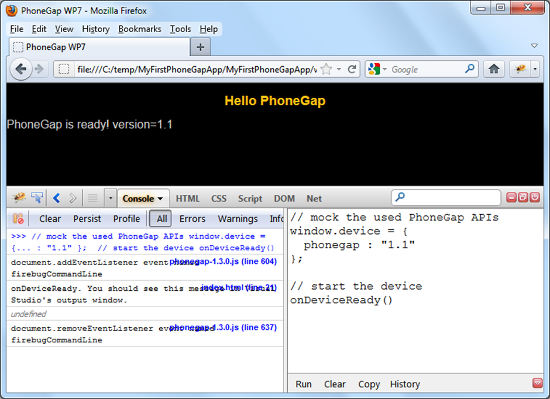
您通常会发现自己使用 Cordova API 的一小部分,因此基于桌面浏览器的测试成为一种可行且快速周转的选择。对于我稍后描述的 Property Finder 应用程序,绝大多数开发都是针对 FireFox 和 FireBug 完成的。
如果您下载 Property Finder 源代码并在浏览器中查看 index.html 文件,您会发现应用程序立即启动。这得益于以下一小段 JavaScript 代码
$(document).ready(function () {
if (window.device) {
document.addEventListener("deviceready", initializeViewModel, false);
} else {
// if there is no 'device' immediately create the view mdoels.
initializeViewModel();
}
}); 如果 Cordova 创建的 `window.device` 不存在,则代码正在桌面浏览器中运行,因此我们立即创建视图模型并启动应用程序。否则,我们等待 `deviceready` 事件,然后启动应用程序。JavaScript 模式
在深入了解应用程序本身的细节之前,我想谈谈我使用的一些 JavaScript 设计模式。Knockout 视图模型
在使用 Knockout 示例时,您经常会看到几种不同的创建视图模型的方法,第一种是使用对象字面量var viewModel = {
firstname : ko.observable("Bob")
};
ko.applyBindings(viewModel ); 第二种是为您的视图模型定义一个构造函数,并使用 new 操作符调用此函数来创建实例var ViewModel = function() {
this.firstname = ko.observable("Bob");
};
ko.applyBindings(new ViewModel ()); 我更喜欢第二种方法,因为它允许您创建相同“类型”视图模型的多个实例。命名空间
JavaScript 没有内置的命名空间或打包机制。作为替代,可以使用对象将代码组织到命名空间中。在 Property Finder 应用程序中,我定义了三个用作命名空间的对象var View = View || {};
var Model = Model || {};
var ViewModel = ViewModel || {}; 上面使用的逻辑或运算符等同于 C# 的空合并运算符 (??)。然后将视图模型构造函数定义为这些对象的属性
ViewModel.PropertyViewModel = function () {
// ...view model code goes here
} 然后通过它们的“命名空间”访问这些构造函数var viewModel = new ViewModel.PropertyViewModel();
面向对象的 JavaScript
在 C# 中,面向对象的构造如“class”和“interface”是语言的一等特性。JavaScript 是一种更简单、更灵活的语言,缺乏这些构造。但这并不意味着 JavaScript 不能用于编写面向对象的应用程序。您当然可以用 JavaScript 编写面向对象的应用程序,但是您需要做出选择。有许多不同的模式可以用来定义您的类、它们的方法和变量。值得注意的是,JavaScript 接口实际上没有很好的模式,但是,定义相同函数(即方法)的对象可以互换,因此接口变得不必要。
有两种流行的类定义模式。第一种是使用原型
function Book(title) {
this.title = title;
}
Book.prototype.getTitle = function () {
return this.title;
};
var myBook = new Book('War and Peace');
alert(myBook.getTitle()); // outputs 'War and Peace'
使用原型来定义对象的方法是面向对象编程中流行的 JavaScript 模式。但是,它不允许信息隐藏,即私有方法和变量。
function Book(title) {
this.title = title;
this.getTitle = function () {
return this.title;
};
}
var myBook = new Book('War and Peace');
alert(myBook.getTitle()); // outputs 'War and Peace'
在这里,`getTitle` 方法是在构造函数中添加到 Book 对象的,而不是通过原型。
这种方法的一个优点是它允许通过闭包进行信息隐藏,因为 `getTitle` 函数即使在返回后仍然可以访问构造函数中定义的所有变量。
以下是一个简单示例,说明如何使用闭包创建私有变量和方法(尽管严格来说,在这种上下文中它们实际上是函数!)
function Book(title) {
// this variable is private
var count = 0;
// this method is private
function incrementCount() {
count++;
}
this.title = title;
this.getTitle = function () {
incrementCount();
return this.title + " : " + count;
};
}
var myBook = new Book('War and Peace');
alert(myBook.getTitle()); // outputs 'War and Peace : 1'
alert(myBook.getTitle()); // outputs 'War and Peace : 2'
Douglas Crockford 在他的网站上更详细地描述了这种模式。
在 Property Finder 中,我使用了“闭包”方法,这更多是出于个人偏好。我发现它更容易阅读,而且内存使用和性能对于这个应用程序来说并不是很大的问题。
应用程序结构概述
下图提供了通用应用程序结构的概述。在创建此图表时涉及了一定程度的解释——接口用于两种不同的类可以互换并用于相同目的的地方

让我们深入了解每一层的细节……
模型层
从模型层来看,`PropertyDataSource` 为应用程序的其余部分提供了查询 Nestoria API 的接口。这通过几个简单的方法公开,一个通过纯文本搜索字符串(例如“London”)进行查询,另一个通过地理位置(纬度和经度)进行查询。在内部,此类使用 `JSONDataSource`,它封装了执行实际 Web 请求的逻辑,其源代码如下所示
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, Model */
Model.JSONDataSource = function () {
/// <summary>
/// A service that allows property searches, returning the results in JSON format. This service
/// uses the Nestoria APIs.
/// </summary>
// ----- private functions
function ajaxRequest(uri, params, callback, errorCallback) {
/// <summary>
/// Performs a JSON request via the jQuery-JSONP library
/// http://code.google.com/p/jquery-jsonp/
/// </summary>
$.jsonp({
dataType: "jsonp",
data: params,
url: uri,
timeout: 5000,
success: function (result) {
callback(result);
},
error: function (jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
errorCallback("datasource error [" + textStatus + "] [" + errorThrown + "]");
}
});
}
// ----- public functions
this.findProperties = function (location, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
/// <summary>
/// Finds properties based on a location string
/// </summary>
var query = "http://api.nestoria.co.uk/api",
params = {
country: "uk",
pretty: "1",
action: "search_listings",
encoding: "json",
listing_type: "buy",
page: pageNumber,
place_name: location,
callback: "_jqjsp"
};
ajaxRequest(query, params, callback, errorCallback);
};
this.findPropertiesByCoordinate = function (latitude, longitude, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
/// <summary>
/// Finds properties based on lat / long values
/// </summary>
var query = "http://api.nestoria.co.uk/api",
params = {
country: "uk",
pretty: "1",
action: "search_listings",
encoding: "json",
listing_type: "buy",
page: pageNumber,
centre_point: latitude + "," + longitude,
callback: "_jqjsp"
};
ajaxRequest(query, params, callback, errorCallback);
};
};
将向 Nestoria API 发送请求的代码与解析响应的代码分离,使我们能够轻松地注入测试数据。上面的类可以替换为以下代码,它会等待 1 秒钟然后返回一个“预设”响应
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, Model, setTimeout */
Model.JSONFileDataSource = function () {
/// <summary>
/// A test version of JSONDataSource, which returns 'canned' responses.
/// </summary>
this.findProperties = function (location, pageNumber, callback) {
function fetchData() {
$.ajax({
dataType: "json",
url: location.trim() === "" ? "model/AmbiguousSearchResults.json" : "model/SearchResults.json",
success: function (result) {
callback(result);
}
});
}
setTimeout(fetchData, 1000);
};
};
这对于针对 Web 服务进行测试非常有用,因为您无法直接控制返回的响应。如您所见,上面的代码返回了几种不同类型的响应,以允许更彻底的测试。
`ProperyDataSource` 类接收 `JSONDataSource` 提供的 JSON 响应,并将其解析为更适合 Property Finder 应用程序的格式。它还处理各种响应代码并返回适当的响应
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, Property, Location, setTimeout, Model */
Model.PropertySearchResponseCode =
{
propertiesFound : 1,
ambiguousLocation : 2,
unknownLocation : 3
};
Model.PropertyDataSource = function (config) {
/// <summary>
/// A service that allows property searches, returning the results as JavaScript objects. This class
/// wraps a JSON datasource to create a more structured response that is de-coupled from the specifics
/// of the Nestoria APIs.
/// </summary>
// ----- private variables
// A source of JSON data.
var jsonDataSource = config.dataSource;
// ----- private functions
function parseResponse(result) {
/// <summary>
/// Parses the JSON response into an array of Property instances or
/// Location instances.
/// </summary>
var properties = [],
locations = [],
responseCode = result.response.application_response_code,
property, location, response;
if (responseCode === "100" || /* one unambiguous location */
responseCode === "101" || /* best guess location */
responseCode === "110" /* large location, 1000 matches max */) {
$.each(result.response.listings, function (index, value) {
property = new Model.Property({
guid: value.guid,
title: value.title,
price: value.price_formatted.substr(0, value.price_formatted.lastIndexOf(" ")),
bedrooms: value.bedroom_number,
bathrooms: value.bathroom_number,
propertyType: value.property_type,
thumbnailUrl: value.img_url,
summary: value.summary
});
properties.push(property);
});
response = new Model.PropertyDataSourceResponse({
responseCode: Model.PropertySearchResponseCode.propertiesFound,
data: properties,
totalResults: result.response.total_results,
pageNumber: result.response.page
});
} else if (responseCode === "200" || /* ambiguous location */
responseCode === "202"/* mis-spelled location */) {
$.each(result.response.locations, function (index, value) {
location = new Model.Location({
longTitle: value.long_title,
placeName: value.place_name,
title: value.title
});
locations.push(location);
});
response = new Model.PropertyDataSourceResponse({
responseCode: Model.PropertySearchResponseCode.ambiguousLocation,
data: locations
});
} else {
/*
201 - unkown location
210 - coordinate error
*/
response = new Model.PropertyDataSourceResponse({
responseCode: Model.PropertySearchResponseCode.unknownLocation
});
}
return response;
}
// ----- public functions
this.findProperties = function (location, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
jsonDataSource.findProperties(location, pageNumber, function (results) {
callback(parseResponse(results));
}, errorCallback);
};
this.findPropertiesByCoordinate = function (latitude, longitude, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
jsonDataSource.findPropertiesByCoordinate(latitude, longitude, pageNumber, function (results) {
callback(parseResponse(results));
}, errorCallback);
};
};
上面的代码突出显示了我做的一个有趣的架构决策;返回的各种模型对象,Location,`Property`,`PropertyDataSourceResponse`,都是使用构造函数创建的。以创建 Location 的代码为例
location = new Model.Location({
longTitle: value.long_title,
placeName: value.place_name,
title: value.title
});
由于这些是模型对象,它们没有任何方法或任何功能,除了作为数据载体。上面的代码可以修改为使用字面量语法创建等效对象
location = {
longTitle: value.long_title,
placeName: value.place_name,
title: value.title
};
使用以上代码,应用程序仍能正常工作。那么我为什么要费力创建这些模型对象呢?下面显示的 `Location` 对象说明了原因
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, Model */
Model.Location = function (config) {
/// <summary>
/// A model that represents a location. This is composed of a human readable display string and a
/// placename, which is the string sent to Nestoria in order to perform a search.
///
/// e.g. longTitle='Albury, Guildford', placename = 'albury_guildford'
/// </summary>
// this display name
this.longTitle = config.longTitle;
// the query name
this.placeName = config.placeName;
};
模型对象并没有为应用程序的功能增加任何东西,但是,它们使代码更具可读性,为文档提供了一个位置,并提供了一种指定正在传递的对象的“形状”的方式。
请注意,`config` 对象允许更简洁和可读地构建模型对象。
这是一个使用 `config` 构造函数的快速示例
location = new Model.Location({
longTitle: value.long_title,
placeName: value.place_name,
title: value.title
});
没有的情况下是这样
location = new Model.Location();
location.longTitle = value.long_title;
location.placeName = value.place_name;
location.title = value.title;
总之,模型层非常简单,为 Nestoria API 提供了一个轻薄的包装器。
视图模型层
Property Finder 应用程序使用了我在最近的 MSDN 杂志文章中概述的相同模式,所以我在这里会轻描淡写。MSDN 文章使用了一个更简单的 Twitter 搜索应用程序示例,使其更容易理解
ApplicationViewModel
应用程序有一个 `ApplicationViewModel` 的单例实例,它管理应用程序的返回栈。这个视图模型包含一个视图模型实例数组,UI 会为最顶层的视图模型渲染(并使用 Knockout 进行数据绑定)。
当返回栈中有多个视图模型时,会处理 Cordova 硬件返回按钮事件,以捕获返回按钮按压(否则会退出应用程序,毕竟它是一个单一的 Silverlight 页面!)并从栈中移除最顶层的视图模型。
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, ViewModel, ko, window, propertySearchViewModel, hydrateObject */
ViewModel.ApplicationViewModel = function () {
/// <summary>
/// The view model that manages the view model back-stack
/// </summary>
// ----- public fields
// the back stack that represents the applications current state
this.viewModelBackStack = ko.observableArray();
// A boolean dependant observable that is true if this application
// needs to handle the back button, and false otherwise.
this.backButtonRequired = ko.computed(function () {
return this.viewModelBackStack().length > 1;
}, this);
// Gets the view model that is top of the back-stack.
this.currentViewModel = ko.computed (function () {
return this.viewModelBackStack()[this.viewModelBackStack().length - 1];
}, this);
// ----- public functions
this.navigateTo = function (viewModel) {
/// <summary>
/// Navigates to the given view model by placing it on the top of the back-stack.
/// </summary>
this.viewModelBackStack.push(viewModel);
};
this.back = function () {
/// <summary>
/// Navigates backwards.
/// </summary>
this.viewModelBackStack.pop();
};
};
app.js
Property Finder 的结构类似于经典的 Silverlight / WPF MVVM 模式,包含用于视图模型、模型对象等的文件夹……

`app.js` 文件是应用程序的入口点,它创建 `ApplicationViewModel` 和 `PropertySearchViewModel`(应用程序的第一个页面)的实例,然后将此视图模型推入应用程序返回堆栈。
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, PropertyDataSource, PropertySearchViewModel, Location, PropertyViewModel,
hydrateObject, ko, Model, ViewModel, window, localStorage, document, console*/
// globals
var application,
propertySearchViewModel = null,
propertyDataSource = new Model.PropertyDataSource({
dataSource: new Model.JSONDataSource()
});
function onBackButton() {
application.back();
}
function initializeViewModel() {
// create the view model
application = new ViewModel.ApplicationViewModel();
// subscribe to changes in the current view model, creating
// the required view
application.currentViewModel.subscribe(function (viewModel) {
if (viewModel !== undefined) {
$("#app").empty();
$("#" + viewModel.template).tmpl("").appendTo("#app");
wireUpUI();
ko.applyBindings(viewModel);
// disable scrolling if the current content does not require it
var disableScroll = $(".content").hasClass("noScroll");
notifyNativeCode("scrollDisabled:" + disableScroll);
}
});
// handle back button
application.backButtonRequired.subscribe(function (backButtonRequired) {
if (backButtonRequired) {
document.addEventListener("backbutton", onBackButton, false);
} else {
document.removeEventListener("backbutton", onBackButton, false);
}
});
// create the top-level view model
propertySearchViewModel = new ViewModel.PropertySearchViewModel();
application.navigateTo(propertySearchViewModel);
}
$(document).ready(function () {
if (window.device) {
document.addEventListener("deviceready", initializeViewModel, false);
} else {
// if there is no 'device' immediately create the view mdoels.
initializeViewModel();
}
});<span style="white-space: normal; ">
</span>
你可以看到,上面的代码使用了 `ApplicationViewModel.backButtonRequired` 属性,这是一个计算观察量,它在 true / false 之间切换状态,具体取决于应用程序是否需要处理后退按钮。
我喜欢将 `app.js` 大致等同于 Silverlight 应用程序实例;它处理应用程序和页面生命周期。
PropertySearchViewModel
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, ViewModel, ko, propertyDataSource, Model, navigator, application */
ViewModel.PropertySearchViewModel = function () {
/// <summary>
/// The 'top level' property search view model.
/// </summary>
// ----- private fields
var synchroniseSearchStrings = true,
that = this;
// ----- framework fields
this.template = "propertySearchView";
// ----- public fields
this.searchDisplayString = ko.observable("");
this.userMessage = ko.observable();
this.searchLocation = undefined;
this.isSearchEnabled = ko.observable(true);
// ...
}<span style="white-space: normal; ">
</span> <span style="white-space: normal; ">
</span>
每个视图模型的 template 属性用于标识渲染其 UI 的 jQuery 模板名称。`PropertySearchViewModel` 的模板如下所示
<script id="propertySearchView" type="text/x-jquery-tmpl">
<div class="content noScroll">
<h2>Property Finder UK</h2>
<p>Use the form below to search for houses to buy. You can search by place-name,
postcode, or click 'My location', to search in your current location!</p>
<div class="searchForm">
<input type="text" data-bind="value: searchDisplayString,
enable: isSearchEnabled,
valueUpdate:'afterkeydown'"/>
<button type="submit" data-bind="enable: isSearchEnabled,
click: executeSearch">Go</button>
<button data-bind="enable: isSearchEnabled,
click: searchMyLocation">My location</button>
</div>
<div class="loading" data-bind="visible: isSearchEnabled() == false">
Searching...
</div>
<p class="userMessage" data-bind="text:userMessage"/>
<div data-bind="visible: locations().length > 0">
<div>Please select a location below:</div>
<ul class="locationList" data-bind='template: { name: "locationTemplate",
foreach: locations }'/>
</div>
<div data-bind="visible: recentSearches().length > 0 && locations().length === 0">
<div data-bind="visible: isSearchEnabled">
<div>Recent searches:</div>
<ul class="locationList" data-bind='template: { name: "locationTemplate",
foreach: recentSearches }'/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="appBar">
<div class="more"><div class="pip"/><div class="pip"/><div class="pip"/></div>
<div class="icons">
<div class="icon" data-bind="click: viewFavourites">
<img src="img/favourites.png"/>
<div class="iconText">favourites</div>
</div>
<div class="icon" data-bind="click: viewAbout">
<img src="img/about.png"/>
<div class="iconText">about</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</script>
从上图可以看出,这是非常直接的 Knockout 内容。有几点值得注意……
`content` div 也带有 `noScroll` 类,`app.js` 中的页面生命周期代码会检测此类的存在。如果找到,则向原生 Silverlight 代码发送消息,告知它应禁用原生 WebBrowser 控件的滚动。这与我之前写的一篇关于如何在 Windows Phone WebBrowser 中抑制捏合缩放和滚动以提供更好的 HTML5 应用程序用户体验的博客文章有关。
在此模板的底部有一个用于创建应用程序栏的 div。项目 CSS 创建了一个 Metro 风格的 UI,如下所示

app.js 中有少量代码,它为应用程序栏添加了各种事件处理程序,以使其具有显示/隐藏行为
// wire up event handlers for various UI elements
function wireUpUI() {
$(".appBar .more").click(function () {
var appBar = $(".appBar");
if (appBar.css("height") !== "80px") {
appBar.animate({ height: 80 }, { duration: 300});
}
});
$(".appBar").click(function () {
var appBar = $(".appBar");
if (appBar.css("height") === "80px") {
appBar.animate({ height: 63 }, { duration: 300});
}
});
}

Property Finder 使用一个简单的 CSS 文件来实现上面看到的 Metro 样式。您可能想知道为什么我没有使用最近发布的 jQuery-Mobile Metro 来实现相同的结果,并且工作量更少。不幸的是,jQuery-Mobile 不仅仅是 CSS,它为 DOM 添加了大量的额外结构,并且有自己的页面生命周期。让 jQuery Mobile 与 Knockout 良好配合并不好玩,经过我自己的努力,我会避免尝试这样做!
LocationViewModel 和 GeoLocationViewModel
Nestoria API 允许您通过纯文本搜索字符串或地理位置进行搜索。Property Finder 拥有代表每种搜索类型的视图模型。
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, ViewModel, propertyDataSource, ko*/
ViewModel.GeolocationViewModel = function () {
/// <summary>
/// The view model that backs the a search based on geolocation
/// </summary>
// ----- public fields
this.lat = undefined;
this.lon = undefined;
this.displayString = undefined;
// ----- public functions
this.initialise = function (lat, lon) {
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the state of this view model.
/// </summary>
this.lat = lat;
this.lon = lon;
this.displayString = lat.toFixed(2) + ", " + lon.toFixed(2);
};
this.executeSearch = function (pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
/// <summary>
/// Executes a search by the geolocation represented by this view model for the given page
/// </summary>
propertyDataSource.findPropertiesByCoordinate(this.lat, this.lon, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback);
};
};
一个用于基于文本的搜索
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global $, propertyDataSource, ViewModel, ko*/
ViewModel.LocationViewModel = function () {
/// <summary>
/// The view model that backs the a search based on a location string
/// </summary>
// ----- public fields
// the string used to search the Nestoria APIs
this.searchString = undefined;
// this string displayed to the end-user
this.displayString = undefined;
// ----- framework functions
this.initialise = function (searchString) {
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the state of this view model.
/// </summary>
this.searchString = searchString;
this.displayString = searchString;
};
this.initialiseDisambiguated = function (location) {
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the state of this view model via a location that has a 'display name' which is shown to the
/// user, which differs from the name used to search the Nestoria APIs
/// </summary>
this.searchString = location.placeName;
this.displayString = location.longTitle;
};
this.executeSearch = function (pageNumber, callback, errorCallback) {
/// <summary>
/// Executes a search by the search string represented by this view model for the given page
/// </summary>
propertyDataSource.findProperties(this.searchString, pageNumber, callback, errorCallback);
};
};
每个视图模型都有自己的 `executeSearch` 方法,该方法使用前面描述的 `PropertyDataSource` 来执行所需的搜索。将执行搜索的责任交给代表每种搜索类型的对象,消除了对讨厌的“基于类型”的切换来调用所需搜索方法的需要。
这些如何使用的一个例子是当用户点击“我的位置”按钮时,该按钮由 `PropertySearchViewModel` 处理。在这里,`navigation.geolocation` 对象(属于 HTML5 地理位置规范的一部分)用于查找当前位置,然后创建 `GeolocationViewModel` 的实例并执行搜索。
this.searchMyLocation = function () {
/// <summary>
/// Performs a search based on the current geolocation
/// </summary>
// check that the use of location is enabled.
if (this.locationEnabled() === false) {
that.userMessage("The use of location is currently disabled. Please enable via the 'about' page.");
return;
}
function successCallback(result) {
var location = new ViewModel.GeolocationViewModel();
location.initialise(result.coords.latitude, result.coords.longitude);
synchroniseSearchStrings = false;
that.searchLocation = location;
that.searchDisplayString(location.displayString);
synchroniseSearchStrings = true;
that.executeSearch();
}
function errorCallback() {
that.userMessage("Unable to detect current location. Please ensure location is turned on in your phone settings and try again.");
}
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(successCallback, errorCallback);
};<span style="white-space: normal; ">
</span>
this.executeSearch = function () {
/// <summary>
/// Executes a search based on the current search string
/// </summary>
that.userMessage("");
that.isSearchEnabled(false);
function errorCallback(error) {
/// <summary>
/// A callback that is invoked if the search fails, in order to report the failure to the end user
/// </summary>
that.userMessage("An error occurred while searching. Please check your network connection and try again.");
that.isSearchEnabled(true);
}
function successCallback(results) {
/// <summary>
/// A callback that is invoked if the search succeeds
/// </summary>
if (results.responseCode === Model.PropertySearchResponseCode.propertiesFound) {
if (results.totalResults === null) {
that.userMessage("There were no properties found for the given location.");
} else {
// if properties were found, navigate to the search results view model
that.searchLocation.totalResults = results.totalResults;
that.updateRecentSearches();
var viewModel = new ViewModel.SearchResultsViewModel();
viewModel.initialize(that.searchLocation, results);
application.navigateTo(viewModel);
}
} else if (results.responseCode === Model.PropertySearchResponseCode.ambiguousLocation) {
// if the location was ambiguous, display the list of options
that.locations.removeAll();
$.each(results.data, function () {
var viewModel = new ViewModel.LocationViewModel();
viewModel.initialiseDisambiguated(this);
that.locations.push(viewModel);
});
} else {
that.userMessage("The location given was not recognised.");
}
that.isSearchEnabled(true);
}
this.searchLocation.executeSearch(1, successCallback, errorCallback);
};
如果您想知道为什么我在“this”和“that”之间切换,您可能需要了解 JavaScript 如何处理“this”关键字,它与 C# 不同!通常的做法是在对象内部将“this”分配给“that”或“self”变量,以便在上下文改变时保持对包含对象的引用。
SearchResultsViewModel
搜索成功执行后,应用程序导航到 `SearchResultsViewModel`
/*global $, ViewModel, ko, propertyDataSource */
ViewModel.SearchResultsViewModel = function () {
var that = this;
// framework fields
this.template = "searchResultsView";
// ----- public properties
this.isLoading = ko.observable(false);
this.totalResults = undefined;
this.pageNumber = ko.observable(1);
this.searchLocation = undefined;
this.properties = ko.observableArray();
// ----- public functions
this.initialize = function (searchLocation, results) {
$.each(results.data, function () {
var viewModel = new ViewModel.PropertyViewModel();
viewModel.initialize(this);
that.properties.push(viewModel);
});
that.searchLocation = searchLocation;
that.totalResults = results.totalResults;
};
this.loadMore = function() {
this.pageNumber(this.pageNumber()+1);
this.isLoading(true);
this.searchLocation.executeSearch(this.pageNumber(), function (results) {
that.isLoading(false);
$.each(results.data, function () {
var viewModel = new ViewModel.PropertyViewModel();
viewModel.initialize(this);
that.properties.push(viewModel);
});
that.pageNumber(that.pageNumber() + 1);
});
};
};
这是一个简单的视图模型,使用下面给出的模板呈现 `PropertyViewModel` 实例的集合
<script id="searchResultsView" type="text/x-jquery-tmpl">
<div class="content">
<div>
<div class="summary">
Search results for
<span class="searchString" data-bind="text: searchLocation.displayString"/>
, showing
<span data-bind="text: properties().length"/> of
<span data-bind="text: totalResults"/> matching properties
</div>
<ul class="propertyList" data-bind='template: { name: "propertyThumbnailView", foreach: properties }'/>
<table style="width:100%">
<tr><td>
<div class="summary">
<span data-bind="text: properties().length"/> of
<span data-bind="text: totalResults"/>
</div>
</td><td style="text-align:right">
<button data-bind="click: loadMore,
enable: isLoading() == false,
visible: properties().length!==totalResults">
Load more ...
</button>
</td></tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</script>
呈现每个单独属性的模板定义如下
<script id="propertyThumbnailView" type="text/x-jquery-tmpl">
<li class="property"
data-bind="click: select">
<div class="thumbnailContainer">
<img data-bind="attr: { src: thumbnailUrl }" class="thumbnail fade-in"/>
</div>
<ul class="propertyDetails">
<li class="price">£<span data-bind="text: price"/></li>
<li class="propertyType"><span data-bind="text: bedrooms"/> bed <span data-bind="text: propertyType"/></li>
<li class="title" data-bind="text: title"></li>
</ul>
</li>
</script>
如果还有更多数据页面,列表末尾会显示一个“加载更多…”按钮

状态持久化
希望前面的部分足以让您了解 Property Finder 应用程序的结构和功能。我没有详尽地描述应用程序的所有功能,例如最近搜索、收藏夹等……但是,这些都遵循类似的模式。
我希望进一步详细说明的一个领域是状态持久化。在 `app.js` 中,属性更改处理程序被添加到我们希望在应用程序会话之间持久化的所有视图模型属性中
// handle changes in persistent state
propertySearchViewModel.favourites.subscribe(persistentStateChanged);
propertySearchViewModel.recentSearches.subscribe(persistentStateChanged);
propertySearchViewModel.locationEnabled.subscribe(persistentStateChanged);
当状态改变时,这些各种对象的 JSON 表示形式会保存到本地存储中
// save app state to persistent storage
function persistentStateChanged() {
var state = {
recentSearches : propertySearchViewModel.recentSearches,
favourites: propertySearchViewModel.favourites,
locationEnabled : propertySearchViewModel.locationEnabled
},
jsonState = ko.toJSON(state);
localStorage.setItem("state", jsonState);
}
Cordova 在这里施展了它的魔力,用它自己的等效对象替换了 `localStorage` 对象,该等效对象提供了一个平台特定的状态保存机制,即对于 Windows Phone,它通过 Silverlight API 使用隔离存储。
当应用程序重新启动时,我们会检查是否有任何以前保存的状态并重新加载它
function initializeViewModel() {
// create the view model
application = new ViewModel.ApplicationViewModel();
// ...
// create the top-level view model
propertySearchViewModel = new ViewModel.PropertySearchViewModel();
application.navigateTo(propertySearchViewModel);
// load application state
try {
var state = localStorage.getItem("state");
console.log("loading state:" + state);
if (typeof (state) === 'string') {
setState(state);
}
} catch (err) {
}
// ...
}
// restore saved state
function setState(jsonState) {
var state = $.parseJSON(jsonState);
if (!state) {
return;
}
if (state.favourites) {
$.each(state.favourites, function () {
propertySearchViewModel.favourites.push(hydrateObject(this));
});
}
if (state.recentSearches) {
$.each(state.recentSearches, function () {
propertySearchViewModel.recentSearches.push(hydrateObject(this));
});
}
if (state.locationEnabled !== undefined) {
propertySearchViewModel.locationEnabled(state.locationEnabled);
}
}
保存的应用程序状态是 JSON 格式的,因此我们可以轻松地重新创建我们的视图模型对象,例如使用 `ko.fromJSON` 实用函数。但是,这将提供看起来像我们的视图模型但缺少我们在其构造函数中添加到这些对象的方法的对象。
因此,我创建了一个实用函数 `hydrateObject`,它递归地重建视图模型,每个视图模型都由 `factoryName` 属性标识其构造函数
/// <reference path="..//intellisense.js" />
/*global ko, $, window */
function hydrateObject(state) {
/// <summary>
/// Takes a JSON representation of view model state and creates view model instances
/// via their constructor function as indicated by the 'factoryName' property.
/// </summary>
// if state is a primitive type, rather than an object - no
// need to hydrate;
if (!(state instanceof Object)) {
return state;
}
var property, unwrapped, propertyValue,
// create the required view model instance
viewModel = new window["ViewModel"][state.factoryName]();
// iterate over each state property
for (property in state) {
if (property === "template" ||
property === "factoryName" ||
property === undefined) {
continue;
}
propertyValue = state[property];
// if the view model property is a function - it might be a KO observable
if (viewModel[property] instanceof Function) {
// check if this is a KO observable
unwrapped = ko.utils.unwrapObservable(viewModel[property]);
// if after unwrapping we do not get the same object back, then
// this is an observable
if (viewModel[property] !== unwrapped) {
// check if this is an array observable
if (unwrapped instanceof Array) {
$.each(propertyValue, function () {
viewModel[property].push(hydrateObject(this));
});
} else {
// otherwise set the value via the observable setter
viewModel[property](propertyValue);
}
}
} else {
viewModel[property] = hydrateObject(propertyValue);
}
}
return viewModel;
}
Property Finder iOS
由于 Property Finder 是使用平台无关的 HTML5 编写的,因此它可以直接在 iPhone 上运行。然而,由于我决定使用 Windows Phone Metro 风格,它在苹果设备上看起来会非常奇怪!相反,我希望为这两个操作系统的用户提供适合他们设备的使用体验;Windows Phone 使用 Metro 风格,iOS 使用经典的“苹果”主题。
所有的应用程序逻辑都使用 Knockout 视图模型编写,因此与 UI 层完全分离。这意味着应该可以通过简单地更改模板和样式表,将 Metro UI 替换为 iOS 等效的 UI。
借鉴 jQuery Mobile
不幸的是,正如我之前提到的,Knockout 和 jQuery Mobile 并不兼容!所以我使用了 jQuery Mobile 的 CSS 而没有使用它们的 JavaScript 代码。这带来的副作用是我的 HTML 模板复杂得多。
<button type="submit" data-bind="enable: isSearchEnabled, click: executeSearch">Go</button>
现在变成了这个怪物
<div class="ui-btn ui-btn-inline ui-btn-corner-all ui-shadow ui-btn-up-c">
<span class="ui-btn-inner ui-btn-corner-all">
<span class="ui-btn-text">Go</span>
</span>
<input class="ui-btn-hidden" type="button" value="Go"
data-bind="enable: isSearchEnabled,
click: executeSearch"/>
</div>
需要额外的 HTML 元素才能支持 jQuery Mobile CSS(如果 HTML / CSS 有 Silverlight 模板的等效功能就好了!)。
通过这种稍微冗长的方法,我能够创建利用 jQuery Mobile CSS 的 HTML 模板,从而生成看起来与原生应用程序非常相似的 iOS 屏幕
使用 iScroll 滚动
iPhone 应用程序的“标准”布局是顶部有一个固定的标题栏,下面是可滚动的内容。不幸的是,iOS 浏览器(iOS5 之前)缺少实现这种页面布局所需的一些 CSS 结构。有关这些问题的概述,请参阅 jQuery Mobile 关于 touchOverflow 的页面。
为了创建一个带有固定标题和滚动内容的页面,人们会采取一些相当复杂的 JavaScript 和 CSS,手动处理触摸事件,偏移内容,计算惯性等等……一个封装了所有所需复杂代码的流行脚本是 iScroll。您可以在这里看到它的实际演示。为了渲染一个可滚动的房产列表,我将 iScroll 集成到 Property Finder 的 iOS 版本中。
在 `app.js` 中需要一些额外的代码来处理属性列表的更改并更新 iScroll 实例,使其知道其内容已更改。除此之外,集成相当简单
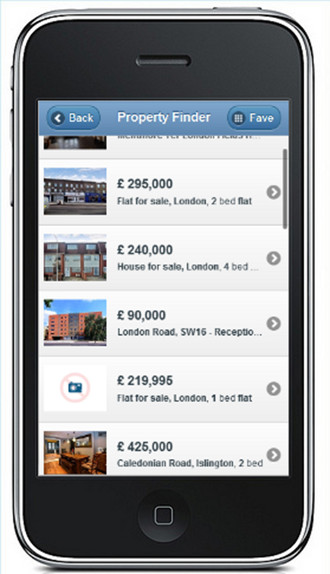
同样,列表布局使用 jQuery Mobile CSS 和手工制作的 HTML 来匹配。
iPhone 缺少硬件返回按钮,因此在上面的屏幕截图中,标题栏中包含了返回按钮。
iScroll 还有一些非常好的额外功能,例如下拉刷新。我能够将此功能集成到 PropertyFinder 中,作为 Windows Phone 版本中“加载更多…”按钮的替代方案

处理此问题的代码有点凌乱,因为它超出了优雅的 Knockout 视图模型驱动代码的范围
function wireUpUI($view) {
// fade in images as they appear
fadeImages();
var $iScroll = $view.find(".iScrollWrapper"),
$pullUpEl = $view.find(".pullUp"),
$pullUpLabel, pullUpEl, pullUpOffset;
// pull-to-refresh, taken from this iScroll demo:
// http://cubiq.org/dropbox/iscroll4/examples/pull-to-refresh/
if ($iScroll.length > 0) {
if ($pullUpEl.length > 0) {
pullUpEl = $pullUpEl.get(0);
pullUpOffset = $pullUpEl.attr('offsetHeight');
$pullUpLabel = $pullUpEl.find(".pullUpLabel");
myScroll = new iScroll($iScroll.get(0), {
useTransition: true,
onRefresh: function () {
if ($pullUpEl.hasClass('loading')) {
$pullUpEl.removeClass();
$pullUpLabel.html('Pull up to load more...');
}
},
onScrollMove: function () {
if (this.y < (this.maxScrollY - 5) && !$pullUpEl.hasClass('flip')) {
$pullUpEl.addClass('flip');
$pullUpLabel.html('Release to refresh...');
this.maxScrollY = this.maxScrollY;
} else if (this.y > (this.maxScrollY + 5) && $pullUpEl.hasClass('flip')) {
$pullUpEl.removeClass("flip");
$pullUpLabel.html('Pull up to load more...');
this.maxScrollY = pullUpOffset;
}
},
onScrollEnd: function () {
if ($pullUpEl.hasClass('flip')) {
$pullUpEl.addClass("loading");
$pullUpLabel.html('Loading...');
pullUpAction();
}
}
});
} else {
myScroll = new iScroll($iScroll.get(0), {
useTransition: true
});
}
}
}
应该可以创建一个具有良好绑定支持的 iScroll 版本,Knockout 框架非常容易扩展以添加自定义绑定……但这将是另一天的工作!
`fadeImages` 函数为图像缩略图添加了一个酷炫的小效果,使它们在加载时逐渐淡入。这是通过 CSS3 opacity transition 实现的
img.ui-li-thumb
{
-webkit-transition: opacity 1s ease-in-out;
-moz-transition: opacity 1s ease-in-out;
-webkit-backface-visibility: hidden;
opacity: 0;
}
img.shown
{
opacity: 1;
}
当图像加载时,通过添加 `shown` 类来触发
function fadeImages() {
$("img.ui-li-thumb:not(.shown)").bind("load", function () {
$(this).addClass("shown");
});
}
项目结构和构建
除了上面详述的界面更改之外,所有核心应用程序功能,包括地理位置和状态持久化,在 iOS 上都保持不变。为了方便 iOS 版本的开发,我创建了一个简单的批处理文件,将 Windows Phone 项目中的共享代码复制到我的 iOS 文件夹中
copy ..\HTML5PropertySearch\www\viewModel\*.js viewModel /Y copy ..\HTML5PropertySearch\www\model\*.js model /Y copy ..\HTML5PropertySearch\www\lib\*.js lib /Y
iOS 版本不是用 Visual Studio 构建的,所以我不能使用 VS 文件引用!
为了将应用程序部署到 iPhone,它需要经过 Cordova 封装并打包为 IPA 文件。这可以在 Mac 电脑上使用 Xcode 完成,但还有一种更简单的替代方案。
您可以通过 PhoneGap Build 服务在线构建您的 Cordova 应用程序。对于 Property Finder,应用程序资产附带此 XML 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<widget xmlns = "http://www.w3.org/ns/widgets"
xmlns:gap = "http://phonegap.com/ns/1.0"
id = "uk.co.scottlogic.propertyfinder"
version = "1.0.0">
<name>Property Finder</name>
<description>
A HTML5 property finder application
</description>
<author href="http://www.scottlogic.co.uk/blog/colin/"
email="ceberhardt@scottlogic.co.uk">
Colin Eberhardt
</author>
<gap:platforms>
<gap:platform name="android" minVersion="2.1" />
<gap:platform name="webos" />
<gap:platform name="symbian.wrt" />
<gap:platform name="blackberry" project="widgets"/>
</gap:platforms>
<icon src="ApplicationIcon.png" gap:role="default" />
<gap:splash src="SplashScreenImage.png"/>
<preference name="orientation" value="portrait" />
<preference name="webviewbounce" value="false" />
<feature name="http://api.phonegap.com/1.0/geolocation"/>
<feature name="http://api.phonegap.com/1.0/network"/>
</widget><span style="white-space: normal; ">
</span>
上传代码和此配置文件后,Build 服务会为各种设备构建您的代码。以下是在线门户的样子

正如您所看到的,我已经将此服务用于许多项目。我的朋友 Chris Price 还创建了一个有用的 Maven 插件,可以自动将您的代码发送到 PhoneGap Build,从而实现持续集成。
对用户体验的批判性审视
本文中的静态图像与它们的本地对应物几乎没有区别。然而,当您真正将它们交到最终用户手中时,他们会开始发现一些迹象,表明这些是非本地应用程序!
Windows Phone
- 文本选择 – 由于 PhoneGap 视图是 HTML,用户可以选中页面上的任何文本。对于 WebKit 浏览器(iOS、Android),您可以使用 CSS user-select:none 属性禁用此功能。IE 不支持此功能,这很可惜,因为它改善了基于 HTML 的应用程序的用户体验。
- 抑制双指缩放 – 我上面描述的禁用双指缩放和点击缩放的解决方案效果很好,但是,它依赖于 `WebBrowser` 控件的内部视觉树。因此,当我与 Cordova 团队的 Jesse Macfeyden 讨论时,我建议不要将其包含在 Windows Phone Cordova 框架中。`WebBrowser` 控件的未来版本可能具有不同的视觉树,会破坏此功能。真正需要的是更好地支持 user-scalable:no meta 属性。Android 和 iOS 在这方面做得更好!
- 灰色链接高亮 – 从 HTML5 应用程序开发者的角度来看,IE9 移动浏览器最大的问题可能是它以灰色高亮显示链接或任何带有 JavaScript 点击事件处理程序的元素。如果您试图创建一个具有原生外观和感觉的应用程序,这会完全破坏体验。尝试在您的 Windows Phone 浏览器上查看 jQuery Mobile 演示。它几乎是像素完美的 iOS UI,但只要您点击链接,就会立即明显地看出这是一个网页。

这种情况在整个应用程序中都会发生,当他们搜索按钮、应用程序栏按钮、磁贴等,无处不在!关于最后一个问题,我已经在 StackOverflow 上发帖,但尚未找到满意的解决方案。
iPhone
Property Finder iPhone 界面比 Windows Phone 版本表现得稍好。没有立即明显的 UI 缺陷将其识别为 HTML5 应用程序。然而,仍然有一些迹象。最明显的区别可能是页面过渡。对于原生 iOS 应用程序,从一个屏幕到下一个屏幕的过渡是微妙而复杂的,涉及至少五个不同的元素。
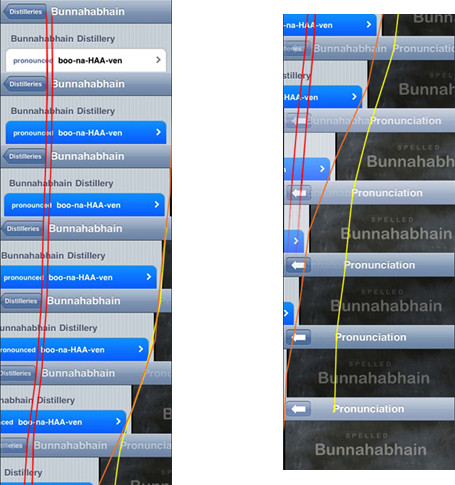
基于 HTML5 的应用程序通常以单个滑动块的形式从一个屏幕过渡到下一个屏幕。
结论
选择使用 HTML5 实现移动应用程序的主要原因是跨多个平台共享代码,从而无需创建多个原生等效项。那么 iOS 和 Windows Phone Property Finder 之间共享了多少代码呢?
以代码行数为指标,43% 的代码在跨平台之间共享

这听起来并不那么令人印象深刻!然而,值得注意的是,这是针对整个代码库而言的,其中包括 JavaScript、CSS 和 HTML。在开发工作量方面,编写 CSS 和 HTML 通常比编写 JavaScript 所需的时间少得多。
如果只关注 JavaScript,重用情况就好多了
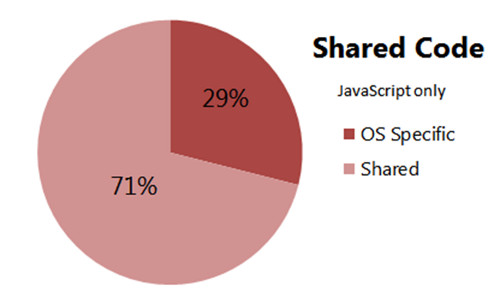
代码共享量不高的另一个原因是,我决定创建一个模仿这两个平台原生外观和感觉的应用程序。几乎所有平台特定的代码都是这个决定造成的。
以下是我发现的简要总结,以易于理解的要点形式呈现
- HTML5 是一种可行的跨平台移动应用开发技术。 Windows Phone 和 iOS 版本都提供了所需的最终用户功能。
- HTML5 确实允许您跨平台共享代码。 所有核心业务逻辑都在两个平台之间共享。这是跨平台方法的一个关键优势,您只需编写和测试一次逻辑。
- HTML5 是一条妥协之路。 尽管这两个应用程序在各自的平台上看起来都很“自然”,但很容易发现它们不是原生应用程序。Windows Phone 版本有一些明显的 UI 怪癖,确实会影响用户体验。就个人而言,我目前不会选择 HTML5 进行 Windows Phone 开发,也许 Windows Phone 8 会解决这些问题?对于 iOS,差异更微妙,但仍然很明显。
- 匹配原生外观和感觉代价高昂。 匹配原生 iOS UI 确实花费了相当多的时间。虽然有一些框架可以提供帮助,例如 jQuery Mobile,但这些框架通常不适用于更复杂的应用程序,您会发现自己与框架作斗争。
- 如果您想要优质体验,请选择原生! 我认为不可能创建出能够与原生等效应用程序的“优质”体验相媲美的 HTML5 应用程序。如果您不想妥协……原生是您唯一的选择。
我给所有考虑创建基于 HTML5 的跨平台移动应用程序的人的建议是,忽略 iOS 风格、忽略 Windows Phone Metro 和 Android Roboto,创建您自己的应用程序风格,可以在所有平台之间共享。创建单一一致的 UI 风格将显著降低您的开发成本。最后,了解您将不得不做出的妥协。
我希望您喜欢这篇文章……我的下一篇文章已经在进行中,我将探讨使用 Xamarin / MonoTouch 作为 HTML5 的替代方案。
您可以下载本文的完整源代码,或在github 上下载/fork 代码库。
