集成: 运动学 + 数字图像处理 + 3D 图形
5.00/5 (4投票s)
进一步推广集成理念
1. 引言
本文旨在推广集成理念以及我其他许多文章的理念。这个理念通过以下问题得以说明。我们希望可视化一个具有通过数字图像处理获得的纹理的3D对象。
2. 数据交换架构
2.1 基本接口
文章标题中的所有问题都需要数据交换。数据交换架构有四个基本接口。第一个接口是数据交换的基本单元。
/// <summary> /// Elementary unit of data exchange /// </summary> public interface IMeasure { /// <summary> /// Function which returns unit of data /// </summary> Func<object> Parameter { get; } /// <summary> /// The name of data unit /// </summary> string Name { get; } /// <summary> /// Type of parameter /// </summary> object Type { get; } }
此接口的成员如下表所示。
| N | 成员名称 | 含义 |
| 1 | 参数 |
返回数据单元的函数 |
| 2 | 名称 |
数据单元的名称 |
| 3 | 类型 |
参数类型 |
Parameter函数可以返回任何对象。Name属性使我们能够链接输入参数到输出参数。Type属性包含单元的元信息。此属性不一定是System.Type类型的变量。下表是变量与其“类型”之间的映射。
| N | 变量类型 | Type属性的值 |
| 1 | 字符串 | string s = "" |
| 2 | bool | bool b = false |
| 3 | double | double d = 0 |
| 4 | float | float f = 0 |
| 5 | byte | byte b = 0x0 |
| 6 | sbyte | sbyte s = 0x0 |
| 7 | short | short s = 0 |
| 8 | short | ushort u = 0 |
| 9 | int | int i = 0 |
| 10 | uint | uint u = 0 |
| 11 | long | long l = 0 |
| 12 | ulong | ulong u = 0 |
| 13 | 数组 | ArrayReturnType a = (取决于数组的类型和长度) |
如果基本数据单元是数组,则单元的“类型”是ArrayReturnType变量。ArrayReturnType代码如下。
/// <summary>
/// Return type of array
/// </summary>
public class ArrayReturnType
{
#region Fields
object elementType;
int[] dimension;
bool isObjectType;
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="elementType">Type of element</param>
/// <param name="dimension">Dimension</param>
/// <param name="objectType">The "is object" sign</param>
public ArrayReturnType(object elementType, int[] dimension, bool objectType)
{
this.elementType = elementType;
this.dimension = dimension;
this.isObjectType = objectType;
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is object" sign
/// </summary>
public bool IsObjectType
{
get
{
return isObjectType;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Dimension
/// </summary>
public int[] Dimension
{
get
{
return dimension;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Type of element
/// </summary>
public object ElementType
{
get
{
return elementType;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Overriden Equals
/// </summary>
/// <param name="obj">Compared obje</param>
/// <returns>True if equal</returns>
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (!(obj is ArrayReturnType))
{
return false;
}
ArrayReturnType at = obj as ArrayReturnType;
if (!at.elementType.Equals(elementType))
{
return false;
}
if (at.dimension.Length != dimension.Length)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dimension.Length; i++)
{
if (dimension[i] != at.dimension[i])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Overriden
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Hash code</returns>
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return dimension.Length * dimension[0];
}
/// <summary>
/// Checks equality of imension
/// </summary>
/// <param name="type">Type</param>
/// <returns>True in case of equal dimesion and false otherwise</returns>
public bool HasEqualDimension(ArrayReturnType type)
{
if (type.dimension.Length != dimension.Length)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < dimension.Length; i++)
{
if (dimension[i] != type.dimension[i])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets base type
/// </summary>
/// <param name="o">The object</param>
/// <returns>Object's base type</returns>
static public object GetBaseType(object o)
{
if (o is ArrayReturnType)
{
ArrayReturnType rt = o as ArrayReturnType;
return rt.elementType;
}
return o;
}
}
下表包含变量及其Type属性的示例。
| N | 变量 | Type属性的值 | 注释 |
| 1 | double[] d = new double[3]; | new ArrayReturnType((double)0, new int[]{3}, false); | |
| 2 | object[] o = new object[2]; | new ArrayReturnType((double)0, new int[]{2}, true); | o的每个元素都是double |
| 3 | bool[,] b = new object[2,3]; | new ArrayReturnType(false, new int[]{2, 3}, false); | |
| 4 | string[,,] s = new string[5,2,3]; | new ArrayReturnType("", new int[]{5, 2, 3}, false); |
支持的参数类型集可以扩展。
第二个接口由所有数据提供者实现。
/// <summary> /// Data provider /// </summary> public interface IMeasurements { /// <summary> /// The count of data units /// </summary> int Count { get; } /// <summary> /// Gets number - th unit of data /// </summary> IMeasure this[int number] { get; } /// <summary> /// Updates data /// </summary> void UpdateMeasurements(); /// <summary> /// Shows, weather the object is updated /// </summary> bool IsUpdated { get; set; } }
下表解释了这个接口成员的含义
| N | 成员名称 | 含义 | 注释 |
| 1 | Count | 数据单元的数量 | |
| 2 | this[int number] | 获取第number个数据单元 | |
| 3 | UpdateMeasurements() | 更新数据 | 数据可以按时间更新 |
| 4 | IsUpdated | 显示对象是否已更新 | 此属性用于避免多次更新 |
所有数据消费者都实现以下接口。
/// <summary> /// Consumer of data /// </summary> public interface IDataConsumer { /// <summary> /// Adds data provider /// </summary> /// <param name="measurements">Provider to add</param> void Add(IMeasurements measurements); /// <summary> /// Removes data provider /// </summary> /// <param name="measurements">Provider to remove</param> void Remove(IMeasurements measurements); /// <summary> /// Updates data of data providers /// </summary> void UpdateChildrenData(); /// <summary> /// Count of providers /// </summary> int Count { get; } /// <summary> /// Access to n - th provider /// </summary> IMeasurements this[int number] { get; } /// <summary> /// Resets measurements /// </summary> void Reset(); /// <summary> /// Change Input event /// </summary> event Action OnChangeInput; }
以下接口是辅助的。
/// <summary> /// Collection on named data units /// </summary> public interface IAlias : IAliasBase { /// <summary> /// Names of all data units /// </summary> IList<string> AliasNames { get; } /// <summary> /// Access to data unit by name /// </summary> object this[string name] { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets unit type /// </summary> /// <param name="name">Unit name</param> /// <returns>Type of unit</returns> object GetType(string name); }
以下类链接数据消费者到数据提供者。
/// <summary> /// The link between data provider and data consumer /// </summary> [Serializable()] public class DataLink : ICategoryArrow, ISerializable, IRemovableObject, IDataLinkFactory { #region Fields /// <summary> /// Error message /// </summary> public static readonly string SetProviderBefore = "You should create measurements source before consumer"; /// <summary> /// DataLink checker /// </summary> private static Action<DataLink> checker; /// <summary> /// The source of this arrow /// </summary> private IDataConsumer source; /// <summary> /// The target of this arrow /// </summary> private IMeasurements target; /// <summary> /// Auxiliary field /// </summary> private int a = 0; /// <summary> /// Linked object /// </summary> protected object obj; /// <summary> /// Data link factory /// </summary> private static IDataLinkFactory dataLinkFactory = new DataLink(); #endregion #region Ctor /// <summary> /// Default constructor /// </summary> public DataLink() { } /// <summary> /// Deserialization constructor /// </summary> /// <param name="info">Serialization info</param> /// <param name="context">Streaming context</param> public DataLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { a = (int)info.GetValue("A", typeof(int)); } #endregion #region ISerializable Members /// <summary> /// ISerializable interface implementation /// </summary> /// <param name="info">Serialization info</param> /// <param name="context">Streaming context</param> public void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { } #endregion #region ICategoryArrow Members /// <summary> /// The source of this arrow /// </summary> public ICategoryObject Source { set { if (source != null) { throw new Exception(); } IDataLinkFactory f = this; source = f.GetConsumer(value); } get { return source as ICategoryObject; } } /// <summary> /// The target of this arrow /// </summary> public ICategoryObject Target { get { return target as ICategoryObject; } set { if (target != null) { throw new Exception(); } IDataLinkFactory f = this; bool check = true; IAssociatedObject s = source as IAssociatedObject; if (s.Object != null & value.Object != null) { if (check) { INamedComponent ns = s.Object as INamedComponent; INamedComponent nt = value.Object as INamedComponent; if (nt != null & ns != null) { if (PureDesktopPeer.GetDifference(nt, ns) >= 0) { throw new Exception(SetProviderBefore); } } } target = t; source.Add(target); } if (!check) { return; } try { if (checker != null) { checker(this); } } catch (Exception e) { e.ShowError(10); source.Remove(target); throw e; } } } /// <summary> /// The "is monomorhpism" sign /// </summary> public bool IsMonomorphism { get { return false; } } /// <summary> /// The "is epimorhpism" sign /// </summary> public bool IsEpimorphism { get { return false; } } /// <summary> /// The "is isomorhpism" sign /// </summary> public bool IsIsomorphism { get { return false; } } /// <summary> /// Composes this arrow "f" with next arrow "g" /// </summary> /// <param name="category"> The category of arrow</param> /// <param name="next"> The next arrow "g" </param> /// <returns>Composition "fg" </returns> public ICategoryArrow Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next) { return null; } #endregion #region IAssociatedObject Members /// <summary> /// Associated object /// </summary> public object Object { get { return obj; } set { obj = value; } } #endregion #region IRemovableObject Members /// <summary> /// The post remove operation /// </summary> public void RemoveObject() { if (source == null | target == null) { return; } source.Remove(target); } #endregion #region IDataLinkFactory Members IDataConsumer IDataLinkFactory.GetConsumer(ICategoryObject source) { IAssociatedObject ao = source; object o = ao.Object; if (o is INamedComponent) { IDataConsumer dcl = null; INamedComponent comp = o as INamedComponent; IDesktop desktop = comp.Root.Desktop; desktop.ForEach<DataLink>(delegate(DataLink dl) { if (dcl != null) { return; } object dt = dl.Source; if (dt is IAssociatedObject) { IAssociatedObject aot = dt as IAssociatedObject; if (aot.Object == o) { dcl = dl.source as IDataConsumer; } } }); if (dcl != null) { return dcl; } } IDataConsumer dc = DataConsumerWrapper.Create(source); if (dc == null) { CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException(); } return dc; } IMeasurements IDataLinkFactory.GetMeasurements(ICategoryObject target) { IAssociatedObject ao = target; object o = ao.Object; if (o is INamedComponent) { IMeasurements ml = null; INamedComponent comp = o as INamedComponent; IDesktop d = null; INamedComponent r = comp.Root; if (r != null) { d = r.Desktop; } else { d = comp.Desktop; } if (d != null) { d.ForEach<DataLink>(delegate(DataLink dl) { if (ml != null) { return; } object dt = dl.Target; if (dt is IAssociatedObject) { IAssociatedObject aot = dt as IAssociatedObject; if (aot.Object == o) { ml = dl.Target as IMeasurements; } } }); if (ml != null) { return ml; } } } IMeasurements m = MeasurementsWrapper.Create(target); if (m == null) { CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException(); } return m; } #endregion #region Public Members /// <summary> /// Checker of data link /// </summary> public static Action<DataLink> Checker { set { checker = value; } } /// <summary> /// Data link factory /// </summary> public static IDataLinkFactory DataLinkFactory { get { return dataLinkFactory; } set { dataLinkFactory = value; } } /// <summary> /// Measurements provider /// </summary> public IMeasurements Measurements { get { return target; } } #endregion }
意味着执行以下运算符
consumer.Add(provider); // Consumer adds a provider.
实际上,上述运算符从未显式编写,但它们是由以下图形设计器隐含的。

链接箭头对应于Data链接对象。源(图表)(或目标(公式))对象是实现IDataConsumer(或IMeasurements)接口的对象。链接箭头的图形设置意味着执行下一个运算符
consumer.Add(provider); // Consumer adds a provider
删除箭头意味着执行下一个运算符
consumer.Remove(provider); // Consumer removes a provider
2.2 示例
以下示例展示了数据交换。

此示例包含三个对象和三个Data链接箭头。下表包含对象类型。
| N | 对象 | 类型 | 实现的接口 |
| 1 | 公式 | VectorFormulaConsumer | IDataConsumer, IMeasurements, IAlias |
| 2 | 微分方程 | DifferentialEquationSolver | IDataConsumer, IMeasurements, IAlias |
| 3 | 图表 | DataConsumer | IDataConsumer |
VectorFormulaConsumer和DifferentialEquationSolver同时实现了IDataConsumer和IMeasurements接口。因此,这些对象都可以是Data链接箭头的源和目标。但DataConsumer对象只能是源。Formula对象具有以下属性

变量a和b已被标记。这意味着这些变量对应于IAlias接口。以下代码片段解释了这种情况。
VectorFormulaConsumer formula = ...;
IAlias alias = formula;
IList<string> names = alias.AliasNames; // names[0] = "a", names[1] = "b";
double a = (double)alias["a"]; // a = 1;
double b = (double)alias["b"]; // b = 2;
object ta = alias.GetType("a"); // ta = (double)0;
object tb = alias.GetType("b"); // tb = (double)0;
t变量对应于虚拟时间。
Differential equation对象具有以下属性

此对象执行以下常微分方程系统的求解

Chart对象指示时间依赖性。其属性是清晰的。

3. 运动学架构
3.1 主要思想
参考系是运动学中的基本概念。本文提出的架构使用相对参考系,这些参考系具有森林结构。这种结构的示例如下图所示

存在一个零参考系。森林的所有根节点都对应于这个参考系。其他框架(节点)的6D位置相对于其父级的6D位置是相对的。这意味着框架1.1.2的6D位置相对于框架1.1的6D位置是相对的。这种架构使我们能够轻松模拟许多不同的有用情况。例如,我们可以在飞机(空间)上安装一组虚拟摄像头。还可以轻松可视化直升机旋翼(慢动作)、带可变后掠翼的飞机或推力矢量控制的复杂运动。
3.2 基本类和接口
以下两个接口分别对应3D位置和3D方向
/// <summary> /// 3D Position /// </summary> public interface IPosition { /// <summary> /// Absolute position coordinates /// </summary> double[] Position { get; } /// <summary> /// Parent frame /// </summary> IReferenceFrame Parent { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Position parameters /// </summary> object Parameters { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Updates itself /// </summary> void Update(); }
/// <summary> /// Object with orientation /// </summary> public interface IOrientation { /// <summary> /// Orientation quaternion /// </summary> double[] Quaternion { get; } /// <summary> /// Orientation matrix /// </summary> double[,] Matrix { get; } }
ReferenceFrame类实现了IPosition和IOrientation。其代码非常长,包含在源文件中。以下接口提供了相对运动范例。
/// <summary> /// Reference frame holder /// </summary> public interface IReferenceFrame : IPosition { /// <summary> /// Own frame /// </summary> ReferenceFrame Own { get; } /// <summary> /// Children objects /// </summary> List<IPosition> Children { get; } }
IReferenceFrame接口的Parent属性是父参考系。点的运动相对于父参考系是相对的。IReferenceFrame的Children属性是子点集合。以下类将子项链接到父项。
/// <summary> /// Link of relative frame /// </summary> [Serializable()] public class ReferenceFrameArrow : CategoryArrow, ISerializable, IRemovableObject { #region Fields IPosition source; IReferenceFrame target; #endregion #region Constructors /// <summary> /// Default constructor /// </summary> public ReferenceFrameArrow() { } /// <summary> /// Deserialization constructor /// </summary> /// <param name="info">Serialization info</param> /// <param name="context">Streaming context</param> protected ReferenceFrameArrow(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { } #endregion #region ISerializable Members void ISerializable.GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { } #endregion #region ICategoryArrow Members /// <summary> /// The source of this arrow /// </summary> public override ICategoryObject Source { get { return source as ICategoryObject; } set { IPosition position = value.GetSource<IPosition>(); if (position.Parent != null) { throw new CategoryException("Root", this); } source = position; } } /// <summary> /// The target of this arrow /// </summary> public override ICategoryObject Target { get { return target as ICategoryObject; } set { IReferenceFrame rf = value.GetTarget<IReferenceFrame>(); IAssociatedObject sa = source as IAssociatedObject; IAssociatedObject ta = value as IAssociatedObject; INamedComponent ns = sa.Object as INamedComponent; INamedComponent nt = ta.Object as INamedComponent; target = rf; source.Parent = target; target.Children.Add(source); } } #endregion #region IRemovableObject Members void IRemovableObject.RemoveObject() { source.Parent = null; if (target != null) { target.Children.Remove(source); } } #endregion #region Specific Members /// <summary> /// Preparation operation /// </summary> /// <param name="collection">Desktop</param> /// <returns>List of position objects</returns> static public List<IPosition> Prepare(IComponentCollection collection) { List<IPosition> frames = new List<IPosition>(); if (collection == null) { return frames; } IEnumerable<object> c = collection.AllComponents; foreach (object o in c) { if (!(o is IObjectLabel)) { continue; } IObjectLabel lab = o as IObjectLabel; ICategoryObject co = lab.Object; if (!(co is IReferenceFrame)) { if (co is IPosition) { IPosition p = co as IPosition; if (p.Parent == null) { frames.Add(p); } } continue; } IReferenceFrame f = co as IReferenceFrame; if (f.Parent != null) { continue; } prepare(f, frames); } return frames; } /// <summary> /// Updates frames /// </summary> /// <param name="frames">List of frames</param> public static void Update(List<IPosition> frames) { foreach (IPosition frame in frames) { frame.Update(); } } private static void prepare(IReferenceFrame frame, List<IPosition> frames) { List<IPosition> children = frame.Children; frames.Add(frame); foreach (IPosition p in children) { if (frames.Contains(p)) { continue; } if (p is IReferenceFrame) { IReferenceFrame f = p as IReferenceFrame; prepare(f, frames); } else { frames.Add(p); } } } #endregion }
此箭头的源是IPoint对象,目标是IReferenceFrame对象。设置ReferenceFrameArrow箭头
IPosition position = ...;
IReferenceFrame frame = ...;
ReferenceFrameArrow link = new ReferenceFrameArrow();
link.Source = position as ICategoryObject;
link.Target = position as ICategoryObject;
意味着执行以下运算符
position.Parent = frame;
frame.Children.Add(position); .
所有箭头的设置都由图形设计器提供。

这张图中有三个链接,分别是L1、L2和L3,类型为ReferenceFrameArrow,以及四个对象
| N | 名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 | Parent |
| 1 | 基准参考系 | RigidReferenceFrame |
IPosition, IReferenceFrame | null |
| 2 | 参考系 1 | ReferenceFrameData |
IPosition, IReferenceFrame, IDataConsumer | 基准参考系 |
| 3 | 参考系 2 | ReferenceFrameData |
IPosition, IReferenceFrame, IDataConsumer | 参考系 1 |
| 4 | 相机参考系 | RigidReferenceFrame |
IPosition, IReferenceFrame | 参考系 2 |
| 5 | 相机 | WpfCamera |
IPosition | 相机参考系 |
由于基准参考系的父节点为null,因此该参考系的运动被视为相对于零参考系的运动。RigidReferenceFrame类对应于具有恒定相对坐标和方向的参考系。ReferenceFrameData类对应于运动参考系。此类实现了IDataConsumer接口,以实现数据交换的互操作性。
3.3 与数据交换的互操作性
ReferenceFrameData实现了IDataConsumer接口。它使用外部数据作为相对运动的参数。下图展示了ReferenceFrameData的应用

Motion Parameters对象以如下方式计算运动参数

此对象作为IMeasurements通过Data链接链接到作为IDataConsumer的Motion Frame。Motion Frame对象使用Motion Parameters的输出数据。
| N | Motion Frame的运动参数 | Motion Parameters的输出参数 |
| 1 | 相对x坐标 | Formula_3 |
| 2 | 相对y坐标 | Formula_4 |
| 3 | 相对z坐标 | Formula_4 |
| 4 | 相对方向四元数的Q0分量 | Formula_1 |
| 5 | 相对方向四元数的Q1分量 | Formula_2 |
| 6 | 相对方向四元数的Q2分量 | Formula_4 |
| 7 | 相对方向四元数的Q3分量 | Formula_4 |
此外,除了IDataConsumer,运动学架构还包含实现IMeasurements接口的RelativeMeasurements。上述Relative对象的类型是RelativeMeasurements。Relative和参考系之间的R1、R2箭头表示Relative提供了Motion Frame相对于Base frame的运动参数。由于Relative实现了IMeasurements接口,它可以与IDataConsumer通过Data链接连接。

此处,Chart对象指示相对的x、y和z坐标。
4. 数字图像处理架构
4.1 主要接口和类
粗略地说,数字图像处理是从一个图像获取另一个图像。因此,架构包含图像的提供者和消费者。以下接口是图像提供者。
/// <summary> /// Provider of image /// </summary> public interface IBitmapProvider { /// <summary> /// Bitmap /// </summary> Bitmap Bitmap { get; } }
以下接口是图像的消费者。
/// <summary> /// Consumer of image /// </summary> public interface IBitmapConsumer { /// <summary> /// Procesess image /// </summary> void Process(); /// <summary> /// Providers /// </summary> IEnumerable<IBitmapProvider> Providers { get; } /// <summary> /// Adds a provider /// </summary> /// <param name="provider">The provider</param> void Add(IBitmapProvider provider); /// <summary> /// Removes a provider /// </summary> /// <param name="provider">The provider</param> void Remove(IBitmapProvider provider); }
以下类是IBitmapProvider和IBitmapConsumer之间的链接。
/// <summary> /// Link between bitmap consumer and bitmap provider /// </summary> [Serializable()] public class BitmapConsumerLink : ICategoryArrow, IRemovableObject, ISerializable { #region Fields /// <summary> /// Error message /// </summary> static public readonly string ProviderExists = "Bitmap provider already exists"; /// <summary> /// Error message /// </summary> public static readonly string SetProviderBefore = "You should create bitmap provider before consumer"; /// <summary> /// Associated object /// </summary> private object obj; /// <summary> /// Auxiliary variable /// </summary> private int a = 0; /// <summary> /// Source /// </summary> private IBitmapConsumer source; /// <summary> /// Target /// </summary> private IBitmapProvider target; #endregion #region Constructors public BitmapConsumerLink() { } public BitmapConsumerLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { info.GetValue("A", typeof(int)); } #endregion #region ICategoryArrow Members public ICategoryObject Source { get { return source as ICategoryObject; } set { source = value.GetObject<IBitmapConsumer>(); } } public ICategoryObject Target { get { return target as ICategoryObject; } set { target = value.GetObject<IBitmapProvider>(); source.Add(target); } } public bool IsMonomorphism { get { return false; } } public bool IsEpimorphism { get { return false; } } public bool IsIsomorphism { get { return false; } } public ICategoryArrow Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next) { return null; } #endregion #region IAssociatedObject Members public object Object { get { return obj; } set { obj = value; } } #endregion #region IRemovableObject Members public void RemoveObject() { if (source != null & target != null) { source.Remove(target); } } #endregion #region ISerializable Members public void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context) { } #endregion #region Specific Members /// <summary> /// Updates consumer /// </summary> /// <param name="consumer">Consumer</param> public static void Update(IBitmapConsumer consumer) { IEnumerable<IBitmapProvider> providers = consumer.Providers; foreach (IBitmapProvider provider in providers) { if (provider is IBitmapConsumer) { IBitmapConsumer c = provider as IBitmapConsumer; Update(c); } } consumer.Process(); } /// <summary> /// Gets provider for consumer /// </summary> /// <param name="provider">Provider</param> /// <param name="consumer">Consumer</param> /// <param name="mutipleProviders">The multiple providers flag</param> /// <returns>The provider</returns> public static IBitmapProvider GetProvider(IBitmapProvider provider, IBitmapConsumer consumer, bool mutipleProviders) { if (provider == null) { return null; } ICategoryObject t = provider as ICategoryObject; ICategoryObject s = consumer as ICategoryObject; if (s.Object != null & t.Object != null) { INamedComponent ns = s.Object as INamedComponent; INamedComponent nt = t.Object as INamedComponent; if (nt != null & ns != null) { if (nt.Desktop == ns.Desktop) { if (nt.Ord >= ns.Ord) { throw new Exception(SetProviderBefore); } } else { if (nt.Root.Ord >= ns.Root.Ord) { throw new Exception(SetProviderBefore); } } } } return provider; } #endregion }
设置BitmapConsumer链接箭头
IBitmapProvider provider = ...;
IBitmapConsumer consumer = ...;
BitmapConsumerLink link = new BitmapConsumerLink();
link.Source = provider as ICategoryObject;
link.Target = consumer as ICategoryObject;
意味着执行以下运算符
consumer.Add(provider);。然而,上述操作是由图形设计器执行的。
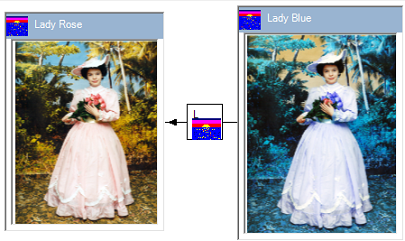
这里,Lady Rose和Lady Blue分别是IBitmapProvider和IBitmapConsumer。这些对象由BitmapConsumer链接链接。
4.2 与数据交换的互操作性
4.2.1 单张位图处理
数字图像处理具有实现IDataConsumer和/或IMeasurements接口的类。让我们考虑一个局部数字滤波示例。

| N | 对象名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 |
| 1 | 地球 | SourceBitmap | IBitmapProvider |
| 2 | 处理结果 | BitmapTransformer | IBitmapProvider, IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer |
| 3 | 公式 | VectorFormulaConsumer | IMeasurements, IAlias |
Result of processing对象作为IBitmapConsumer通过BitmapConsumer链接连接到作为IBitmapProvider的Earth。Result of processing对象作为IDataConsumer通过Data链接连接到作为IMeasurements的Formulae。任何SourceBitmap类的对象都只是将图像存储在内存中。此类的主要成员如下所示。
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Bitmap
/// </summary>
protected Bitmap bitmap;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public SourceBitmap()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public SourceBitmap(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
try
{
bitmap = (Bitmap)info.GetValue("Bitmap", typeof(Bitmap));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ShowError(100);
}
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
/// <summary>
/// ISerializable interface implementation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public override void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.AddValue("Bitmap", bitmap);
}
#region IBitmapProvider Members
/// <summary>
/// Bitmap
/// </summary>
Bitmap IBitmapProvider.Bitmap
{
get
{
return bitmap;
}
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Sets bitmap
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bitmap"></param>
public void SetBitmap(Bitmap bitmap)
{
this.bitmap = bitmap;
}
// Other members ...
SourceBitmap的业务逻辑非常清晰。此类具有一个Bitmap类型的字段。用户可以设置此字段的值吗?此字段已序列化,并用作IBitmapProvider接口的Bitmap。Formulae对象具有以下属性。

此公式根据源位图的颜色计算颜色。参数r、g和b分别对应源位图的红色、绿色和蓝色。如果所有颜色的值都超过阈值(a),则公式返回x。否则,它返回y。Result of processing对象具有以下属性。

这些属性具有以下含义。对象扫描提供者对象(Earth)的位图并检测像素的颜色。它将这些对象设置为Formulae的别名。然后,它计算Formulae并将Formula_1设置为结果位图的红色、绿色和蓝色。源位图和转换结果如下所示。


此算法是检测积雪的最简单粗糙算法。该算法的C#解释如下。
//============ Formulae ==============
VectorFormulaConsumer formulae = ...; // Formulae object
IMeasurements measurements = formulae;
IMeasure m = measurements[0]; // Formula_1
IAlias alias = formulae; // Formulae object as IAlias
// =========================================
// =========== Source bitmap ===============
SourceBitmap sb = ...;
IBitmapProvider provider = sb;
Bitmap source = provider.Bitmap;
//===========================================
// ============ Target bitmap ===============
Bitmap target = // Size of tagtet is equal to source one
new Bitmap(source.Width, source.Height);
for (int x = 0; x < source.Width; x++) // x = coordinate of bitmap
{
for (int y = 0; y < source.Height; y++) // y - coordinate of bitmap
{
Color colorSource = source.GetPixel(x, y); // Color of source pixel
double r = (double)colorSource.R / 256; // Scaling
double g = (double)colorSource.G / 256;
double b = (double)colorSource.B / 256;
alias["r"] = r; // Setting of aliases
alias["g"] = g;
alias["b"] = b;
measurements.UpdateMeasurements(); // Calculates all formulae
double cd = (double)m.Parameter(); // Formula_1
int cdi = (int)(cd * 256); // Inverse scaling
Color colorTarget =
Color.FromArgb(cdi, cdi, cdi); // Target color
target.SetPixel(x, y, colorTarget); // Sets pixel to target bitmap
}
}
请注意,目标颜色可能与“Lady Blue”示例中所示的不同。上面的代码片段未包含在我的代码中,它只是对算法的清晰解释。有关此主题的更多信息,您可以在我的文章“数字图像处理”中找到。
4.2.2 双张位图处理
几项任务需要同时处理多个图像。例如,云动力学指示需要比较两个或多个图像。下图展示了两个图像的比较

这张图有以下对象
| N | 对象名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 | 注释 |
| 1 | Picture 1 | SourceBitmap | IBitmapProvider | 第一个源图像 |
| 2 | Picture 2 | SourceBitmap | IBitmapProvider | 第二个源图像 |
| 3 | P 1 | BitmapColorTable | IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer, IMeasurements | 适配器对象 |
| 4 | P 2 | BitmapColorTable | IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer, IMeasurements | 适配器对象 |
| 5 | 输入 | VectorFormulaConsumer | IMeasurements, IAlias | 数字图像处理计算器 |
| 6 | 结果 | VectorFormulaConsumer | IMeasurements, IAlias | 数字图像处理计算器 |
| 7 | Compare | BitmapTransformer | IBitmapProvider, IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer | 数字图像处理结果 |
Compare对象作为IBitmapConsumer通过BitmapConsumer链接连接到作为IBitmapProvider的Picture 2。这意味着P 2为Compare提供位图。根据BitmapTransformer的实现,这意味着Compare的位图大小与Picture 2的位图大小相同。Compare具有以下属性。

这些属性具有以下含义。Compare对象扫描其自身的位图并将别名参数设置为像素坐标的值。然后,它将Formula_1的值设置为图像的红色、绿色和蓝色。以下代码阐明了此算法。
VectorFormulaConsumer Input = ...; // The "Input" object
VectorFormulaConsumer Result = ...; // The "Result" object
IAlias alias = Input; // "Input" as IAlias
IMeasurements measurements = // "Result" as IMeasurements
Result;
IMeasure Formula_1 = measurements[0]; // "Formula_1"
Bitmap Compare = ...; // Bitmap of "Compare object"
for (int x = 0; x < Compare.Width; x++) // x = coordinate of bitmap
{
for (int y = 0; y < Compare.Height; y++) // y - coordinate of bitmap
{
alias["x"] = (double)x; // Setting parameters
alias["y"] = (double)y;
measurements.UpdateMeasurements(); // Calculation
int color = // Color
(int)((double)Formula_1.Parameter() * 256);
Color c = Color.FromArgb(color, color, color);
Compare.SetPixel(x, y, c); // Sets pixel color
}
}
P 1和P 2都是BitmapColorTable类型的对象。该类型作为IDataConsumer消耗像素坐标,并作为IMeasurements提供RGB颜色参数。下图

意味着P 1返回Picture 1位图像素的RGB参数。像素的坐标x(或y)等于Input的Formula_1(或Formula_2)。Input的属性如下所示。

因此,Input作为IAlias的参数x(或y)等于同一对象的作为IMeasurements的Formula_1(或Formula_2)。因此,P 1和P 2的输入参数是Compare位图的像素坐标。Result的属性如下所示。

此对象的参数x(或y)是P 1(或P 2)的Red参数,即Picture 1(或Picture 2)像素的红色分量。Result的Formula_1与Picture 1和Picture 2的红色分量之间的差异成正比。
5. 3D图形架构
5.1 主要接口和类
3D图形的主要接口是IVisible和IVisibleConsumer
/// <summary> /// Object linked to position /// </summary> public interface IPositionObject { /// <summary> /// Linked position /// </summary> IPosition Position { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// Visible 3D object /// </summary> public interface IVisible : IPositionObject { } /// <summary> /// Consumer of visible 3D object /// </summary> public interface IVisibleConsumer { /// <summary> /// Adds visible object to consumer /// </summary> /// <param name="visible">Visible object to add</param> void Add(IVisible visible); /// <summary> /// Removes visible object from consumer /// </summary> /// <param name="visible">Visible object to remove</param> void Remove(IVisible visible); /// <summary> /// Post operation /// </summary> /// <param name="visible">Visible object</param> void Post(IVisible visible); }
类VisibleConsumer链接链接IVisibleConsumer到IVisible。设置VisibleConsumer链接箭头
IVisible visible = ...;
IVisibleConsumer consumer = ...;
ICategoryArrow link = new VisibleConsumerLink();
link.Source = consumer as ICategoryObject;
link.Target = visible as ICategoryObject;
意味着执行以下运算符
consumer.Add(visible);
移除VisibleConsumer链接会遵循以下操作
#region IRemovableObject Members
/// <summary>
/// Removing of VisibleConsumerLink
/// </summary>
void IRemovableObject.RemoveObject()
{
source.Remove(target);
}
#endregion
下图展示了这些接口的示例。

上图中的对象和箭头具有以下类型
| N | 对象名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 | 注释 |
| 1 | 相机 | WpfCamera | IVisibleConsumer | PerspectiveCamera的包装器 |
| 2 | Globe | WpfShape | IVisible | Visual的包装器 |
| 3 | 链接 | VisibleConsumer链接 | ICategoryArrow | 链接IVisibleConsumer与IVisible对象 |
以上示例表示Camera消耗Globe,而“消耗”意味着可视化。
5.2 架构的通用性
此架构操作的接口与WPF无关。因此,此软件可以适应其他3D图形技术,例如OpenGL。我已经在我之前的文章“时间机器”中描述了此软件与不同3D技术的兼容性。
5.3 与运动学的互操作性
3D接口的任何对象都与参考系相关联。下一个示例包含一个具有纹理的3D对象(Cube)和四个虚拟摄像头(Perspective Camera、X - camera、Y - camera和Z - camera)。

立方体通过L 1链接到移动参考系Frame 3,摄像头链接到固定参考系。因此,摄像头从不同的3D点指示Cube的运动。
5.4 WPF实现3D图形的特点。
WPF实现使用XAML文件和纹理文件。

以下代码是XAML文件的内容
<ModelVisual3D xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation">
<ModelVisual3D.Children>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<AmbientLight Color="#333333" />
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<DirectionalLight Color="#FFFFFF" Direction="-0.612372,-0.5,-0.612372" />
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<DirectionalLight Color="#FFFFFF" Direction="0.612372,-0.5,-0.612372" />
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="leaves_closeup.png" TileMode="None" ViewportUnits="Absolute" Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5"
Normals="-1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 "
TextureCoordinates="0,1 0,0 1,0 1,0 1,1 0,1 "
Positions="-0.5,0.5,-0.5 -0.5,-0.5,-0.5 -0.5,-0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,0.5 -0.5,0.5,0.5 -0.5,0.5,-0.5 " />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="rocks.png" TileMode="None" ViewportUnits="Absolute" Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5"
Normals="0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 "
TextureCoordinates="0,0 1,0 1,1 1,1 0,1 0,0 "
Positions="-0.5,-0.5,0.5 0.5,-0.5,0.5 0.5,0.5,0.5 0.5,0.5,0.5 -0.5,0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,0.5 " />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource= "branches.png" TileMode="None" ViewportUnits="Absolute" Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5"
Normals="0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 0,0,1 "
TextureCoordinates="1,0 1,1 0,1 0,1 0,0 1,0 "
Positions="0.5,-0.5,-0.5 0.5,0.5,-0.5 0.5,0.5,0.5 0.5,0.5,0.5 0.5,-0.5,0.5 0.5,-0.5,-0.5 " />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="berries.jpg" TileMode="None" ViewportUnits="Absolute" Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5"
Normals="1,0,0 1,0,0 1,0,0 1,0,0 1,0,0 1,0,0 "
TextureCoordinates="1,0 1,1 0,1 0,1 0,0 1,0 "
Positions="-0.5,-0.5,-0.5 -0.5,0.5,-0.5 0.5,0.5,-0.5 0.5,0.5,-0.5 0.5,-0.5,-0.5 -0.5,-0.5,-0.5 " />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="Waterlilies.png" ViewportUnits="Absolute"
Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5 6,7,8 9,10,11"
Normals="0,-1,0 0,-1,0 0,-1,0 0,-1,0 0,-1,0 0,-1,0 0,1,0 0,1,0 0,1,0 0,1,0 0,1,0 0,1,0 "
TextureCoordinates="0,0 1,0 1,1 1,1 0,1 0,0 1,1 0,1 0,0 0,0 1,0 1,1 "
Positions="-0.5,-0.5,-0.5 -0.5,0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,0.5 0.5,-0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,-0.5 -0.5,0.5,-0.5
0.5,0.5,-0.5 -0.5,0.5,-0.5 -0.5,0.5,0.5 -0.5,0.5,0.5 0.5,0.5,0.5 0.5,0.5,-0.5 " />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
<ModelVisual3D >
<ModelVisual3D.Content>
<GeometryModel3D>
<GeometryModel3D.Material>
<MaterialGroup>
<DiffuseMaterial>
<DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="Sunset.jpg" ViewportUnits="Absolute"
Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
</DiffuseMaterial.Brush>
</DiffuseMaterial>
<SpecularMaterial SpecularPower="85.3333">
<SpecularMaterial.Brush>
<SolidColorBrush Color="#FFFFFF" Opacity="1.000000"/>
</SpecularMaterial.Brush>
</SpecularMaterial>
</MaterialGroup>
</GeometryModel3D.Material>
<GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
<MeshGeometry3D
TriangleIndices="0,1,2 3,4,5 6,7,8 9,10,11"
Normals="-1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 -1,0,0 "
TextureCoordinates="1,0 1,1 0,1 0,1 0,0 1,0 "
Positions="-0.5,-0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,-0.5 0.5,-0.5,-0.5 0.5,-0.5,-0.5 0.5,-0.5,0.5 -0.5,-0.5,0.5" />
</GeometryModel3D.Geometry>
</GeometryModel3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Content>
</ModelVisual3D>
</ModelVisual3D.Children>
<ModelVisual3D.Transform>
<Transform3DGroup >
<Transform3DGroup.Children>
<RotateTransform3D>
<RotateTransform3D.Rotation>
<AxisAngleRotation3D Angle="0" Axis="0 1 0" />
</RotateTransform3D.Rotation>
</RotateTransform3D>
<RotateTransform3D>
<RotateTransform3D.Rotation>
<AxisAngleRotation3D Angle="0" Axis="1 0 0" />
</RotateTransform3D.Rotation>
</RotateTransform3D>
<TranslateTransform3D OffsetX="0" OffsetY="0" OffsetZ="0" />
</Transform3DGroup.Children>
</Transform3DGroup>
</ModelVisual3D.Transform>
</ModelVisual3D>
此内容包含对纹理文件的引用,例如
<ImageBrush Stretch="UniformToFill" ImageSource="berries.jpg" TileMode="None" ViewportUnits="Absolute" Viewport="0 0 1 1" AlignmentX="Left" AlignmentY="Top" Opacity="1.000000" />
WpfShape类是这些对象的包装器,它序列化XAML文件和纹理文件的内容。
info.AddValue("Xaml", xaml);
info.AddValue("Textures", textures, typeof(Dictionary<string, byte[]>));
以下代码解释了如何获得textures字典。
string[] files = new string[] // File names
{
"berries.jpg",
"branches.png",
"leaves_closeup.png",
"rocks.png",
"Sunset.jpg",
"Waterlilies.png"
};
foreach (string fileName in files)
{
using (Stream stream = File.OpenRead(fileName))
{
byte[] bytes = new byte[stream.Length];
stream.Read(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); // Reads file
textures[fileName] = bytes; // Fills texture dictionary
}
}
6. 数字图像处理 + 3D图形
6.1 主要思想
数字图像处理和3D图形之间的互操作性是通过用数字图像处理结果替换纹理图像来实现的。以下代码代表了互操作类的核心功能。
/// <summary> /// 3D object with digital image processing interoperability /// </summary> [Serializable()] public class MotionImageFigure : WpfShape, IBitmapConsumer, IPostSetArrow { #region Fields /// <summary> /// Textures - Names of providers /// </summary> Dictionary<string, string> dTextures = new Dictionary<string, string>(); /// <summary> /// Textures - Bitmap poviders /// </summary> Dictionary<string, IBitmapProvider> providers = new Dictionary<string, IBitmapProvider>(); /// <summary> /// Post method /// </summary> protected virtual void Post() { foreach (string textureName in dTextures.Keys) // Textures cycle { string providerName = dTextures[textureName]; // Name of provider if (providers.ContainsKey(providerName)) { IBitmapProvider p = providers[providerName]; // Bitmap provider Bitmap bmp = p.Bitmap; // Bitmap of provider paths.Remove(textureName); using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream()) { bmp.Save(stream, System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageFormat.Bmp); // Saving bitmap to bypes textures[textureName] = stream.GetBuffer(); // Replace texture by bitmap } } } }
上面的Post()方法实现了纹理图像的替换为数字图像处理图像。
6.2 基础示例
下图展示了MotionImageFigure的用法。

Cube对象的类型是MotionImageFigure。此对象具有从以下图形文件中获得的纹理
- berries.jpg
- branches.png
- leaves_closeup.pn
- rocks.png
- Sunset.jpg
- Waterlilies.png
其中一些纹理可以被替换,例如。

此处,纹理替换方式如下。
| N | 纹理文件 | 替换提供者的名称 |
| 1 | rocks.png | Compare |
| 2 | branches.png | 处理结果 |
6.3 高级示例
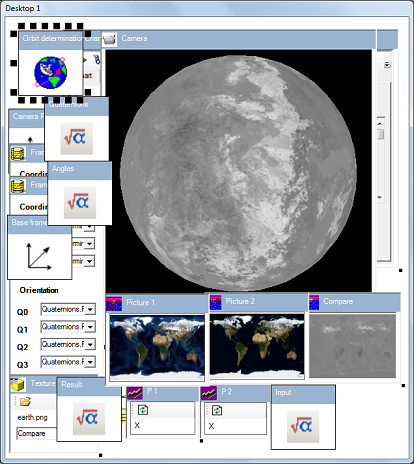
在我关于“人造卫星轨道确定”的文章中,我们考虑了一个复杂的工程任务。最近,该任务通过3D动画和音频得到了扩展(参见“理论与实践?”)。虚拟人造卫星产生以下动画图。

上述3D动画使用了以下文件。

现在我们想用数字图像处理结果替换earth.png纹理。结果如下。


6.3.1 安装这些示例
6.3.1.1 安装容器
将Containers.zip目录解压到Aviation.exe文件所在的目录。
4.2.7.4 启动动画
启动Aviation.exe。
打开OrbitImage.cfa或OrbitTwoImage.cfa。
单击以下Animation button
关注点
撰写本文激起了我的回忆。在我年轻的时候,我曾处理过非常糟糕的文件。很久以后,我开始处理美国公司的文件。这些文件涉及不同领域。然而,这些文件很清晰,因为它们有统一的风格。之后,我试图统一我自己的文档风格。
