VB.NET 应用框架中的全局 Try-Catch
在仍然使用 .NET 应用框架的情况下实现全局 Try-Catch 块。
引言
本示例演示如何使用 .NET 应用框架设置全局 try-catch 块。示例代码为 VB.NET,但也可以轻松转换为 C#。
背景
由于我不是一个完美的程序员,有时会出现异常从我手中溜走,导致出现未处理的异常,通常会导致应用程序非常不优雅地崩溃。本示例展示了如何设置全局 try-catch 块,以便更优雅地处理崩溃,以及如何设计一个与您的主应用程序匹配的表单,提供其他信息,以及一个简单的“复制文本”按钮,将文本放置到剪贴板中,以便用户将其通过电子邮件发送给技术支持。您可以进一步改进,将按钮更改为“发送报告”,自动通过电子邮件发送文本或其他类似操作。
通常,当发生未处理的异常时,用户会截取屏幕截图并将其转发给技术支持,然后技术支持将其转发给我,就像下面显示的那样。虽然这些信息对于追踪异常发生的位置可能非常有价值,但由于它只是一个屏幕截图,我无法读取所有文本。为了解决这个问题,我创建了一个简单的表单,可以对其进行样式设置以匹配我的主应用程序,并显示来自 .Net 未处理异常的信息以及其他一些信息。

有类似的方法可以在不使用 .NET 应用框架的情况下执行全局 try-catch,但那样就无法使用 .NET 应用框架的额外功能,例如“创建单实例应用程序”。
使用代码
请确保在项目属性 -> 应用程序设置中选中“启用应用程序框架”。
在同一页面上,单击“查看应用程序事件”按钮
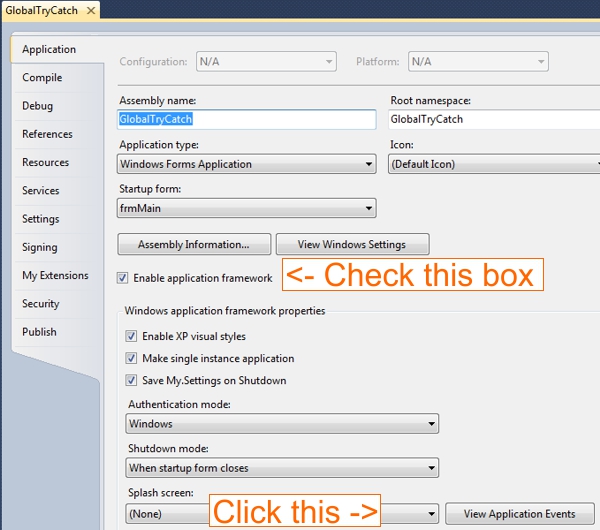
这将打开 / 生成 ApplicationEvents.vb 文件。
在 ApplicationEvents.vb 代码中,添加以下内容
Partial Friend Class MyApplication
'One of the global exceptions we are catching is not thread safe,
'so we need to make it thread safe first.
Private Delegate Sub SafeApplicationThreadException(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As Threading.ThreadExceptionEventArgs)
Private Sub ShowDebugOutput(ByVal ex As Exception)
'Display the output form
Dim frmD As New frmDebug()
frmD.rtfError.AppendText(ex.ToString())
frmD.ShowDialog()
'Perform application cleanup
'TODO: Add your application cleanup code here.
'Exit the application - Or try to recover from the exception:
Environment.Exit(0)
End Sub
Private Sub MyApplication_Startup(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As Microsoft.VisualBasic.ApplicationServices.StartupEventArgs) Handles Me.Startup
'There are three places to catch all global unhandled exceptions:
'AppDomain.CurrentDomain.UnhandledException event.
'System.Windows.Forms.Application.ThreadException event.
'MyApplication.UnhandledException event.
AddHandler AppDomain.CurrentDomain.UnhandledException, AddressOf AppDomain_UnhandledException
AddHandler System.Windows.Forms.Application.ThreadException, AddressOf app_ThreadException
End Sub
Private Sub app_ThreadException(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As Threading.ThreadExceptionEventArgs)
'This is not thread safe, so make it thread safe.
If MainForm.InvokeRequired Then
' Invoke back to the main thread
MainForm.Invoke(New SafeApplicationThreadException(AddressOf app_ThreadException), _
New Object() {sender, e})
Else
ShowDebugOutput(e.Exception)
End If
End Sub
Private Sub AppDomain_UnhandledException(ByVal sender As Object, _
ByVal e As UnhandledExceptionEventArgs)
ShowDebugOutput(DirectCast(e.ExceptionObject, Exception))
End Sub
Private Sub MyApplication_UnhandledException(sender As Object, _
e As Microsoft.VisualBasic.ApplicationServices.UnhandledExceptionEventArgs) _
Handles Me.UnhandledException
ShowDebugOutput(e.Exception)
End Sub
End Class
可选
如果您想要与上述屏幕截图类似的结果,则代码如下
Public Sub New()
On Error Resume Next
' This call is required by the designer.
InitializeComponent()
' Add any initialization after the InitializeComponent() call.
rtfError.AppendText("Product Name: " & My.Application.Info.ProductName & vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("Product Version: " & My.Application.Info.Version.ToString() & vbNewLine)
Dim asms As New List(Of Assembly)
For Each asm As Assembly In My.Application.Info.LoadedAssemblies
asms.Add(asm)
Next asm
'Assemblies are listed in the order they are loaded - I prefer them alphabetical.
'But if the order in which assemblies are being loaded is important, then don't do the sort.
Dim asmc As New AsmComparer()
asms.Sort(asmc)
rtfError.AppendText(vbNewLine)
For Each asm As Assembly In asms
'Many of the assemblies are core .Net assemblies. I do not care about them.
'If you do, comemnt out this next line:
If IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(asm.Location).ToUpper() <> _
My.Application.Info.DirectoryPath.ToUpper() Then Continue For
'Included in this list is the executable path - which is meaningless.
'Have to cast to Upper (or lower), because one of the paths returns as .EXE,
'and the other .exe
If asm.Location.ToUpper() = Application.ExecutablePath.ToUpper() Then Continue For
rtfError.AppendText("Loaded Assembly: " & asm.ToString() & vbNewLine)
Next asm
rtfError.AppendText(vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("OS Name: " & My.Computer.Info.OSFullName & vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("OS Version: " & My.Computer.Info.OSVersion & vbNewLine)
''IMPORTANT: This next line is .Net 4.0 only.
'' If you need to know if it is a 64 bit OS or not, you will need to use
'' a different method for any .Net older than 4.0
rtfError.AppendText("OS Platform: " & IIf(Environment.Is64BitOperatingSystem, _
"x64", "x86") & vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("Physical Memory: " & _
FormatBytes(My.Computer.Info.AvailablePhysicalMemory) & " / " & _
FormatBytes(My.Computer.Info.TotalPhysicalMemory) & _
" (Free / Total)" & vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("Virtual Memory: " & _
FormatBytes(My.Computer.Info.AvailableVirtualMemory) & " / " & _
FormatBytes(My.Computer.Info.TotalVirtualMemory) & _
" (Free / Total)" & vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText(vbNewLine)
rtfError.AppendText("Error Output:" & vbNewLine)
End Sub
Private Function FormatBytes(ByVal bytes As Long) As String
If bytes < 1000 Then
Return CStr(bytes) & "B"
ElseIf bytes < 1000000 Then
Return FormatNumber(bytes / 1024, 2) & "KB"
ElseIf bytes < 1000000000 Then
Return FormatNumber(bytes / 1048576, 2) & "MB"
Else
Return FormatNumber(bytes / 1073741824, 2) & "GB"
End If
End FunctionPrivate Sub btnCopy_Click(sender As System.Object, e As System.EventArgs) Handles btnCopy.Click
My.Computer.Clipboard.Clear()
My.Computer.Clipboard.SetText(rtfError.Text, TextDataFormat.Text)
My.Computer.Clipboard.SetText(rtfError.Rtf, TextDataFormat.Rtf)
End Sub
Public Class AsmComparer
Implements IComparer(Of Assembly)
Public Function Compare(x As System.Reflection.Assembly, y As System.Reflection.Assembly) _
As Integer _
Implements System.Collections.Generic.IComparer(Of System.Reflection.Assembly).Compare
Return String.Compare(x.ToString(), y.ToString())
End Function
End Class
历史
2012/11/19 - 更新为使用正确的 ApplicationEvents.vb 文件,而不是 Application.Designer.vb 文件。(感谢 Zac Greve 指出这一点!)
2018/7/27 - 更新源代码下载,包含一个具有类似代码的 C# 项目。
