通过概念性语言理解引擎实现真正的自然语言理解
4.97/5 (52投票s)
2010年1月7日
29分钟阅读
70996
3140
介绍一种人工智能技术,该技术能够理解和操作文本中的概念。

引言
人们花费大量时间和精力将思想付诸文字。因此,是时候让技术专注于自动化地检索和处理这些思想,并且在过程中不丢失其原始含义了。为此,需要一种能够从自然语言中重构和操作概念的方法。这种目标无法通过仅限于词语识别或语义块表面关联的狭隘自然语言理解来实现,而是需要一种模拟人脑处理和结果功能的流程。本文揭示了一种通过概念语言理解引擎(CLUE)实现此类处理的新颖方法。
“识别”一词的主要部分是“认知”,牛津词典将其定义为“通过思考、经验和感官获得的知识”。本方法使用封装了大多数与识别的认知方法相关的技术。
沟通是一个涉及以下过程的程序性序列
- “去认知”过程——产生代表要沟通的认知方面的语法流。
- 传输过程——将此语法流放置在介质上。
- 感知过程——感官获取语法流。
- “再认知”过程——重建最初的认知实质,希望它在语法、传输和感知过程中没有丢失。
因为一个完整的语言分析周期,包括自然语言理解,需要将概念恢复到其原始形式,而不损失在“去认知”和“再认知”过程之后可以实现的任何概念操作,因此语言的概念方面不能也不应被忽视。只有当语音分析的概念维度可用时,语言处理的语法方面才会不受限制。也就是说,语法分析将仅限于通信适应介质所需的暂时步骤。只有到那时,我们至今在自然语言理解和处理方面所遭受的限制才会开始消退。
CLUE的价值在于能够从传达的概念中抽象出书面的语法形式——一旦计算出概念,用于沟通的词语就变得无关紧要——同时保持智能响应已识别内容的能力。它进一步将消歧的最终责任转移到概念分析层,而不是像迄今为止通常所做的那样转移到语音和语法层。这使得沟通者不必义务使用预先确定的单词或命令序列,以便被自动化设备成功理解。在一个自动化设备已成为常态的时代,瓶颈已转移到技术无法有效处理人的因素。人们不习惯一套与语法相关的规则,因为与他们天生的概念能力相比,这些规则显得不自然。
背景
本文是一个系列中的第三篇。在第一篇文章《实现一个永不耗尽内存的 std::map 替代品以及生成 ARPA 兼容语言模型来测试该实现的说明》中,介绍了本文代码库中使用的内存管理技术。因此,您会发现在整个代码库中只有一个 delete 调用,并且可以确定上述 C++ 代码没有内存泄漏。在第二篇文章《使用 C++ 构建知识库以及谓词逻辑的强大介绍》中,介绍了谓词逻辑,但未能处理自然语言输入。尽管它还揭示了从知识库进行推理的技术(本文未使用,但可轻松改编),但文章涵盖了本文广泛使用的基本谓词逻辑技术。阅读这两篇文章将帮助您更好地理解本文代码的基础。尽管概念语音识别用于解释语音(声音),但为了简单和演示起见,本文仅限于文本输入。此技术的软件实现可以称为概念语言理解引擎,简称“CLUE”。处理语音识别的方法与此处暴露的类似,但有一些软件工程方面的技巧,以便通过集成本文未讨论的隐马尔可夫模型来包含来自语音的更多偏差。
Using the Code
当前项目在 Visual Studio 2008 下构建。它由大约 10,000 行 C++ 源代码和大约 500 行由 Google V8 处理的 JavaScript 代码组成。
代码的主要组成部分划分如下
- 词典:一个包含 195,443 个单词、222,048 个词性的词典,存储在一个 2.1 MB 的文件中,几乎可以即时返回拼写信息。[IndexStructure.h, StoredPOSNode.h, StoredPOSNode.cpp, DigitalConceptBuilder::BuildDictionary]
- 分词:将自然语言输入流转换为基于词典中包含的内容的词元。[IndexStructure.h, POSList.h, POSList.cpp, POSNode.h, POSNode.cpp, IndexInStream.h, DigitalConceptBuilder::Tokenize]
- 语法分析:从分词阶段后从词典中获得的原子节点(如
NOUN、ADJECTIVE和VERB)外推复杂节点(如SENTENCE)的算法。[SyntaxTransform.txt, POSTransformScript.h, POSTransformScript.cpp, Permutation.h, Permutation.cpp, POSList.h, POSList.cpp, POSNode.h, POSNode.cpp, Parser.h, Parser.cpp, BottomUpParser.h, BottomUpParser.cpp, MultiDimEarleyParser.h, MultiDimEarleyParser.cpp] - 概念分析:基于语法结构构建概念,以及 Google V8(JavaScript 引擎)如何集成到项目中。[Conceptual Analysis/*.js, Conceptual Analysis/Permutation scripts/*.js, Conceptual Analysis/POS scripts/*.js, POSList.h, POSList.cpp, POSNode.h, POSNode.cpp, Predicate.h, Predicate.cpp, JSObjectSupport.h, JSObjectSupport.cpp, POSNode::BuildPredicates]
代码执行
使用本文提供的代码执行将运行SimpleTestCases.txt中指定的测试用例。花括号内的每个块定义了一个要运行的范围,其中 CONTENT 是要分析的自然语言流。
测试用例句子之前的每个变量定义也可以插入花括号范围中以覆盖其值。例如,要仅启用第一个测试用例,可以进行以下更改
...
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# ENABLED
# _______
#
# Possible values: TRUE, FALSE
#
# TRUE: enable the test cases within that scope.
#
# FALSE: disable the test cases within that scope.
ENABLED = FALSE
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
{
ENABLED = TRUE
CONTENT = Is a red car a car?
ID = CAR1
}
...
执行作为本文附带的 zip 文件中提供的测试用例,将产生以下输出。本文的其余部分将揭示用于从这些测试用例的自然语言输入过渡到此处公开的概念和响应所使用的方法、理念和技术。
Evaluating: "Is a red car a car?" (ID:CAR1)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 250 ms
Syntactic: 63 ms
Conceptual: 187 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a red car the car?" (ID:CAR2)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
DETERMINED:TRUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 2 sec (2235 ms)
Syntactic: 31 ms
Conceptual: 2 sec (2204 ms).
Evaluating: "Is the red car a car?" (ID:CAR3)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
DETERMINED:TRUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 203 ms
Syntactic: 31 ms
Conceptual: 172 ms.
Evaluating: "Is the red car red?" (ID:CAR4)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
DETERMINED:TRUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[COLOR:RED]]]
Total time: 219 ms
Syntactic: 31 ms
Conceptual: 188 ms.
Evaluating: "The car is red" (ID:CAR5)
No inquiry to analyze here:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:AFFIRMATION
OBJECT:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
DETERMINED:TRUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]
Total time: 547 ms
Syntactic: 15 ms
Conceptual: 532 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a red car blue?" (ID:CAR6)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[COLOR:BLUE]]]
Total time: 2 sec (2453 ms)
Syntactic: 31 ms
Conceptual: 2 sec (2422 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a red car red?" (ID:CAR7)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[COLOR:RED]]]
Total time: 235 ms
Syntactic: 32 ms
Conceptual: 203 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a car or a boat a car?" (ID:CAR8)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:OR[VALUE1:BOAT
VALUE2:CAR]
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 390 ms
Syntactic: 187 ms
Conceptual: 203 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a car an object that is not a car?" (ID:CAR9)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:AND[VALUE1:PP[QUANTITY:1
TYPE:{DEFINED}]
VALUE2:NOT[VALUE:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3297 ms)
Syntactic: 141 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3156 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a boat an object that is not a car?" (ID:CAR10)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]
VALUE2:AND[VALUE1:PP[QUANTITY:1
TYPE:{DEFINED}]
VALUE2:NOT[VALUE:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]]]
Total time: 328 ms
Syntactic: 78 ms
Conceptual: 250 ms.
Evaluating: "Is an object that is not a car a boat?" (ID:CAR11)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:AND[VALUE1:PP[QUANTITY:1
TYPE:{DEFINED}]
VALUE2:NOT[VALUE:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3500 ms)
Syntactic: 63 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3437 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a car that is not red a car?" (ID:CAR12)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 313 ms
Syntactic: 63 ms
Conceptual: 250 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a car an object that is a car or a boat?" (ID:CAR13)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:OR[VALUE1:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3875 ms)
Syntactic: 125 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3750 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a red car an object that is a car or a boat?" (ID:CAR14)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:OR[VALUE1:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]]
Total time: 4 sec (4563 ms)
Syntactic: 344 ms
Conceptual: 4 sec (4219 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a car that is not red a car?" (ID:CAR15)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 360 ms
Syntactic: 63 ms
Conceptual: 297 ms.
Evaluating: "Is a red car not red?" (ID:CAR16)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[COLOR:!RED]]]
Total time: 1 sec (1844 ms)
Syntactic: 32 ms
Conceptual: 1 sec (1812 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a car a car that is not red?" (ID:CAR17)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3125 ms)
Syntactic: 78 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3047 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a car that is not red a blue car?" (ID:CAR18)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:BLUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 4 sec (4250 ms)
Syntactic: 250 ms
Conceptual: 4 sec (4000 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a red car a car that is not red?" (ID:CAR19)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3547 ms)
Syntactic: 234 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3313 ms).
Evaluating: "Is an object that is not a car a car?" (ID:CAR20)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:AND[VALUE1:PP[QUANTITY:1
TYPE:{DEFINED}]
VALUE2:NOT[VALUE:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 3 sec (3891 ms)
Syntactic: 47 ms
Conceptual: 3 sec (3844 ms).
Evaluating: "Is an object that is a car or a boat a car?" (ID:CAR21)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:OR[VALUE1:BOAT
VALUE2:CAR]
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 781 ms
Syntactic: 141 ms
Conceptual: 640 ms.
Evaluating: "Is an object that is a car or a boat a red car?" (ID:CAR22)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:OR[VALUE1:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 5 sec (5984 ms)
Syntactic: 344 ms
Conceptual: 5 sec (5640 ms).
Evaluating: "Is an object that is a car and a boat a red car?" (ID:CAR23)
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:AND[VALUE1:BOAT
VALUE2:CAR]
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 6 sec (6437 ms)
Syntactic: 734 ms
Conceptual: 5 sec (5703 ms).
Evaluating: "Is a car an object that is a car and a boat?" (ID:CAR24)
NO:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:AND[VALUE1:PP[CLASS:BOAT
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]]
Total time: 4 sec (4313 ms)
Syntactic: 125 ms
Conceptual: 4 sec (4188 ms).
Evaluating: "Is an object that is a car and a boat a car?" (ID:CAR25)
YES:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:AND[VALUE1:BOAT
VALUE2:CAR]
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 797 ms
Syntactic: 156 ms
Conceptual: 641 ms.
Done.
词典
通过 zip 文件提供的词典是一个文件,article_testcases_streams.txt,其部分内容是为了仅提供成功运行测试用例所需的单词和词性而累积的。此特殊步骤是为了节省本文读者的大量下载时间,因为完整词典的大小超过 8 MB。
完整词典可在此 点击下载(2.2 MB)。解压缩下载的文件,并将 streams.txt 放在 DigitalConceptBuilder 目录中,与 article_testcases_streams.txt 同级,以便下次启动程序时加载它。

文本文件 streams.txt 和 article_testcases_streams.txt 是可编辑的。streams.txt 中的内容是多年来从各种来源获得的,其中一些受版权保护,如完整词典 zip 文件中的“Licensing information.txt”文件所述。
使用的格式如下
<spelling - mandatory>:<pronunciation - mandatory>:
<part-of-speech - optional>(<data - optional>)
示例:December:dusembar:DATE(m_12)。
发音是强制性的,但对于本文的目的并不重要。当以后文章的主题涉及语音识别时,它将是必要的。
包含拼写和词性的文本文件被加载到一个三向决策树中,其代码可在 IndexStructure 模板中找到,如文章《实现一个永不耗尽内存的 std::map 替代品以及生成 ARPA 兼容语言模型来测试该实现的说明》中所述。三向决策树的表示可以在此处看到,它包含主键“node”、“do”、“did”、“nesting”、“null”和“void”,如下所示
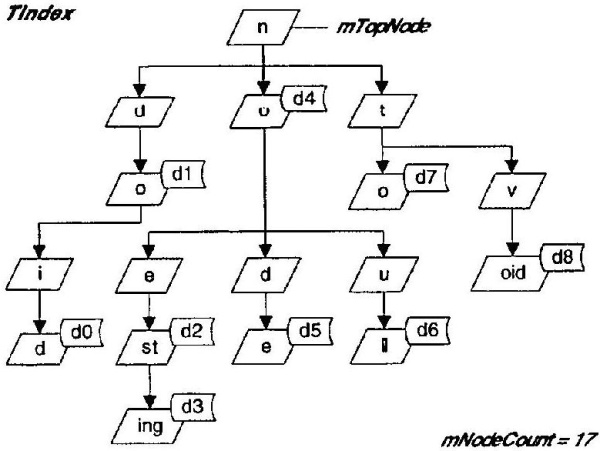
将词典保留在这种结构中,可以在分词时提供最佳性能,同时确保从该过程中生成的词元在词典中具有相应的条目。此外,使用的 IndexStructure 模板可以将数据部分存储在磁盘上,部分存储在内存中,使其成为该目的的合适介质。
分词
分词的目标是创建一个 POSList 对象,该对象保存提供给它的语法流的拼写和相应的词性。
以下是使用 DEFINITIONNEEDED = FALSE、OUTPUTTOKENS = TRUE 并加载了完整词典执行第一个测试用例的部分输出。
Evaluating: "Is a red car a car?" (ID:CAR1)
Tokens before syntactic analysis:
[NOUN & "IS"], from 0, to: 1, bridge: 3, index: 0
[VERB & "IS"], from 0, to: 1, bridge: 3, index: 0
[AUX & "IS"], from 0, to: 1, bridge: 3, index: 0
[NOUN & "A"], from 3, to: 3, bridge: 5, index: 1
[PREPOSITION & "A"], from 3, to: 3, bridge: 5, index: 1
[VERB & "A"], from 3, to: 3, bridge: 5, index: 1
[DEFINITE_ARTICLE & "A"], from 3, to: 3, bridge: 5, index: 1
[ADJECTIVE & "RED"], from 5, to: 7, bridge: 9, index: 2
[NOUN & "RED"], from 5, to: 7, bridge: 9, index: 2
[VERB & "RED"], from 5, to: 7, bridge: 9, index: 2
[PROPER_NOUN & "RED"], from 5, to: 7, bridge: 9, index: 2
[NOUN & "CAR"], from 9, to: 11, bridge: 13, index: 3
[PROPER_NOUN & "CAR"], from 9, to: 11, bridge: 13, index: 3
[NOUN & "A"], from 13, to: 13, bridge: 15, index: 4
[PREPOSITION & "A"], from 13, to: 13, bridge: 15, index: 4
[VERB & "A"], from 13, to: 13, bridge: 15, index: 4
[DEFINITE_ARTICLE & "A"], from 13, to: 13, bridge: 15, index: 4
[NOUN & "CAR"], from 15, to: 17, bridge: 18, index: 5
[PROPER_NOUN & "CAR"], from 15, to: 17, bridge: 18, index: 5
[PUNCTUATION & "?"], from 18, to: 18, bridge: 0, index: 6
分词看似是一项简单的任务,但它自身隐藏着困难。
- 分词必须允许将单词包含在其他单词中(例如,“all”和“all-in-one”)。
- 在分词时,必须处理不包含在词典中的数字的特殊规定。
- 必须考虑到允许的标点符号。
- 除非它是词典条目的一部分,否则不允许的标点符号必须被忽略。
POSList中的词汇列表中的任何单词都必须根据其在流中的位置和词性易于访问,以确保后续处理在性能方面不会受到负面影响。
#ifndef __POSLIST_HH__
#define __POSLIST_HH__
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <string>
using std::vector;
using std::map;
using std::string;
#include "POSNode.h"
#include "shared_auto_ptr.h"
#include "IndexInStream.h"
class POSList;
class POSList
{
public:
// Constructor, pass duplicateDefense
// to true if the POSList should filter out
// apparent duplicates.
POSList(bool duplicateDefense = false);
// AddToPOSList, call to add a POSNode to the list.
virtual POSNode *AddToPOSList(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dNode);
// BrigdgeableNodes, call to acquire all POSNode
// in the POSList object that respect the conditions
// stipulated in dPOSNode at stream index position
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>>
BrigdgeableNodes(int position, shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode);
// GetLowestStartPosition, returns the lowest
// start position from all POSNode in the POSList.
int GetLowestStartPosition();
// GetHighestEndPosition, returns the highest
// end position from all POSNode in the POSList.
int GetHighestEndPosition();
// AccumulateAll, accumulates all POSNode respecting
// the condition stipulated in dPOSNode and sorting
// the resulting vector based on sort,
// all accumulated nodes need to respect the start position fromPos
// (or -1 to ignore) and end position toPos (or -1 to ignore).
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> AccumulateAll(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode,
POSNode::ESortType sort = POSNode::eNoSort,
int fromPos = -1, int toPos = -1);
// Output, outputs the POSNode accumulated into
// the POSList at position pos (or -1 if the position is
// irrelevant).
void Output(int pos = -1);
// Count, returns how many POSNode are accumulated into the POSList.
unsigned long Count();
// Clear, removes all POSNode from the POSList.
virtual void Clear();
// ResetPOSNodeIteration, resets the tracer
// to the first POSNode in the POSList.
void ResetPOSNodeIteration();
// GetPositionInList, returns a copy
// of the tracer for the current position in stream.
virtual IndexInStream<POSNode> *GetPositionInList();
// GetNext, gets the next POSNode from the
// tracer's position, returns true if one is available,
// false otherwise.
virtual bool GetNext(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> &dPOSNode);
protected:
virtual string GetLineOutput(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dNode);
IndexInStream<POSNode> m_position;
int m_lowestStart;
int m_highestEnd;
bool m_duplicateDefense;
map<string, int> m_uniqueEntries;
int m_count;
};
#endif
为了拥有一个快速检索机制,POSList 类使用了 m_position 成员,它是一个 IndexInStream<POSNode> 实例。IndexInStream 模板在某些情况下被使用,当需要基于流中的位置和 POSEntry 类型快速检索对象(在我们的例子中是 POSNode)时。IndexInStream 模板的实现如下
#ifndef __INDEXSINSTREAM_H__
#define __INDEXSINSTREAM_H__
#include <map>
#include <vector>
using std::map;
using std::vector;
#include "POSEntry.h"
template <class T> class IndexInStreamPosition
{
public:
IndexInStreamPosition();
void Add(shared_auto_ptr<T> dContent, POSEntry dPosEntry);
typedef typename map<int, vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>>>
container_map_vector_type;
typedef typename
container_map_vector_type::iterator iterator_map_vector_type;
container_map_vector_type m_content;
};
template <class T> IndexInStreamPosition<T>::IndexInStreamPosition() {}
template <class T> void IndexInStreamPosition<T>::Add(
shared_auto_ptr<T> dContent, POSEntry dPosEntry)
{
m_content[dPosEntry.GetValue()].push_back(dContent);
}
template <class T> class IndexInStream
{
public:
IndexInStream();
void Reset();
void Clear();
void Add(shared_auto_ptr<T> dObject, int position, POSEntry dPos);
bool GetNext(shared_auto_ptr<T> &dPOSNode);
vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>> ObjectsAtPosition(int position,
POSEntry dPOSEntry, int *wildcardPosition = NULL);
protected:
typedef typename map<int,
shared_auto_ptr<IndexInStreamPosition<T>>>
container_map_index_type;
typedef typename
container_map_index_type::iterator iterator_map_index_type;
typedef typename map<int,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>>> container_map_vector_type;
typedef typename container_map_vector_type::iterator
iterator_map_vector_type;
container_map_index_type m_allSameEventPOSList;
iterator_map_index_type m_iterator1;
iterator_map_vector_type m_iterator2;
int m_posVectorEntryIndex;
};
template <class T> IndexInStream<T>::IndexInStream(): m_posVectorEntryIndex(-1)
{
Reset();
m_allSameEventPOSList.clear();
}
template <class T> void IndexInStream<T>::Clear()
{
Reset();
}
template <class T> vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>>
IndexInStream<T>::ObjectsAtPosition(int position,
POSEntry dPOSEntry, int *wildcardPosition)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>> dReturn;
if (m_allSameEventPOSList.find(position) != m_allSameEventPOSList.end())
{
if (m_allSameEventPOSList[position]->m_content.find(dPOSEntry.GetValue()) !=
m_allSameEventPOSList[position]->m_content.end())
{
dReturn =
m_allSameEventPOSList[position]->m_content[dPOSEntry.GetValue()];
}
}
if (wildcardPosition != NULL)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<T>> temp =
ObjectsAtPosition(*wildcardPosition, dPOSEntry);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < temp.size(); i++)
{
dReturn.push_back(temp[i]);
}
}
return dReturn;
}
template <class T> bool IndexInStream<T>::GetNext(shared_auto_ptr<T> &dObject)
{
while (m_iterator1 != m_allSameEventPOSList.end())
{
while ((m_posVectorEntryIndex != -1) &&
(m_iterator2 != m_iterator1->second.get()->m_content.end()))
{
if (m_posVectorEntryIndex < (int)m_iterator2->second.size())
{
dObject = m_iterator2->second[m_posVectorEntryIndex];
m_posVectorEntryIndex++;
return true;
}
else
{
m_iterator2++;
m_posVectorEntryIndex = 0;
}
}
m_iterator1++;
m_posVectorEntryIndex = 0;
if (m_iterator1 != m_allSameEventPOSList.end())
{
m_iterator2 = m_iterator1->second.get()->m_content.begin();
}
else
{
m_posVectorEntryIndex = -1;
}
}
Reset();
return false;
}
template <class T> void IndexInStream<T>::Add(
shared_auto_ptr<T> dObject, int position, POSEntry dPos)
{
if (m_allSameEventPOSList.find(position) == m_allSameEventPOSList.end())
{
m_allSameEventPOSList[position] =
shared_auto_ptr<IndexInStreamPosition<T>>(
new IndexInStreamPosition<T>());
}
m_allSameEventPOSList[position]->Add(dObject, dPos);
}
template <class T> void IndexInStream<T>::Reset()
{
m_iterator1 = m_allSameEventPOSList.begin();
m_posVectorEntryIndex = 0;
if (m_iterator1 != m_allSameEventPOSList.end())
{
m_iterator2 = m_iterator1->second.get()->m_content.begin();
}
else
{
m_posVectorEntryIndex = -1;
}
}
#endif
使用实现的 POSList 类,分词实现如下
shared_auto_ptr<POSList> DigitalConceptBuilder::Tokenize(string dContent,
string posNumbers,
string posPunctuation,
string punctuationAllowed,
bool definitionNeeded)
{
struct TokenizationPath
{
TokenizationPath(
shared_auto_ptr<IndexStructureNodePosition<StoredPOSNode>> dPosition,
unsigned int dStartIndex): m_position(dPosition), m_startIndex(dStartIndex) {}
shared_auto_ptr<IndexStructureNodePosition<StoredPOSNode>> m_position;
unsigned int m_startIndex;
};
unsigned int dWordIndex = 0;
shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dReturn = shared_auto_ptr<POSList>(new POSList(true));
string dNumberBuffer;
vector<TokenizationPath> activePaths;
vector<POSNode*> floatingBridges;
int latestBridge = -1;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i <= dContent.length(); i++)
{
bool isAllowedPunctuation = false;
string dCharStr = "";
if (i < dContent.length())
{
dCharStr += dContent.c_str()[i];
if ((posPunctuation.length()) &&
(punctuationAllowed.find(dCharStr) != string.npos))
{
isAllowedPunctuation = true;
latestBridge = i;
}
}
activePaths.push_back(TokenizationPath(
shared_auto_ptr<IndexStructureNodePosition<StoredPOSNode>>(
new IndexStructureNodePosition<StoredPOSNode>(
m_POS_Dictionary.GetTopNode())), i));
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < activePaths.size(); j++)
{
if ((activePaths[j].m_position.get() != NULL) &&
(activePaths[j].m_position->get() != NULL) &&
(activePaths[j].m_position->get()->m_data != NULL))
{
if ((i == dContent.length()) || (IsDelimitor(dContent.c_str()[i])))
{
string dKey = activePaths[j].m_position->GetNode()->GetKey();
if ((i < dKey.length()) ||
(IsDelimitor(dContent.c_str()[i - dKey.length() - 1])))
{
StoredPOSNode *dPOS = activePaths[j].m_position->get();
for (int k = 0; k < kMAXPOSALLOWED; k++)
{
if (dPOS->m_pos[k] != -1)
{
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> candidate =
POSNode::Construct("["+POSEntry::StatGetDescriptor(
dPOS->m_pos[k]) + " & \"" + dKey + "\"]", NULL,
activePaths[j].m_startIndex, i-1, 0,
(dPOS->m_data[k] != -1)?m_data[dPOS->m_data[k]]:"");
if (PassedDefinitionRequirement(candidate, definitionNeeded))
{
POSNode *dNewNode = dReturn->AddToPOSList(candidate);
if (dNewNode != NULL)
{
floatingBridges.push_back(dNewNode);
}
latestBridge = activePaths[j].m_startIndex;
}
}
}
}
}
}
if ((latestBridge != -1) && (((i < dContent.length()) &&
(!IsDelimitor(dContent.c_str()[i]))) ||
(i == dContent.length()) || (isAllowedPunctuation)))
{
bool atLeastOneAdded = false;
for (int l = (floatingBridges.size() - 1); l >= 0; l--)
{
if ((floatingBridges[l]->GetBridgePosition() == 0) &&
(floatingBridges[l]->GetStartPosition() != latestBridge))
{
atLeastOneAdded = true;
floatingBridges[l]->SetWordIndex(dWordIndex);
floatingBridges[l]->SetBridgePosition(latestBridge);
floatingBridges.erase(floatingBridges.begin() + l);
}
}
if (atLeastOneAdded)
{
dWordIndex++;
}
if (isAllowedPunctuation)
{
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> candidate =
POSNode::Construct("[" + posPunctuation + " & \"" +
dCharStr + "\"]", NULL, i, i, 0);
if (PassedDefinitionRequirement(candidate, definitionNeeded))
{
POSNode *dNewNode = dReturn->AddToPOSList(candidate);
if (dNewNode != NULL)
{
floatingBridges.push_back(dNewNode);
}
latestBridge = i;
}
}
else
{
latestBridge = -1;
}
}
if (i == dContent.length())
{
break;
}
shared_auto_ptr<IndexStructureNodePosition<StoredPOSNode>>
dNewPosition = m_POS_Dictionary.ForwardNodeOneChar(
activePaths[j].m_position, toupper(dContent.c_str()[i]));
if (dNewPosition.get() != NULL)
{
activePaths[j].m_position = dNewPosition;
}
else
{
activePaths[j].m_position->Clear();
}
}
if ((posNumbers.length() > 0) && ((dContent.c_str()[i] >= '0') &&
(dContent.c_str()[i] <= '9') ||
((dContent.c_str()[i] == '.') && (dContent.length() > 0))))
{
if ((i == 0) || (dNumberBuffer.length() > 0) ||
(IsDelimitor(dContent.c_str()[i-1])))
{
dNumberBuffer += dContent.c_str()[i];
}
}
else if (dNumberBuffer.length() > 0)
{
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> candidate =
POSNode::Construct("["+posNumbers + " & \"" +
dNumberBuffer + "\"]", NULL, i - dNumberBuffer.length(), i - 1, 0);
if (PassedDefinitionRequirement(candidate, definitionNeeded))
{
POSNode *dNewNode = dReturn->AddToPOSList(candidate);
if (dNewNode != NULL)
{
floatingBridges.push_back(dNewNode);
}
latestBridge = i - dNumberBuffer.length();
dNumberBuffer = "";
}
}
for (int j = (activePaths.size() - 1); j >= 0; j--)
{
if ((activePaths[j].m_position.get() == NULL) ||
(activePaths[j].m_position->GetNode().get() == NULL))
{
activePaths.erase(activePaths.begin() + j);
}
}
}
for (int l = (floatingBridges.size() - 1); l >= 0; l--)
{
floatingBridges[l]->SetWordIndex(dWordIndex);
}
return dReturn;
}
语法分析
语法分析的目的是从 POSList 中传入的原子节点生成复杂节点,并识别目标复杂节点以提供给概念分析过程。在 CLUE 中,语法分析不是最终的消歧器;相反,概念分析过程与语法分析过程协同工作,根据含义和语法完整性确定哪个概念优于其他概念。因此,语法分析过程不需要完全消歧,这意味着语法分析会产生大量的语法结构,这些结构之后需要由概念分析进行消歧。在语法分析之前,存在很多歧义,因为该过程只持有一个 POSNode 的列表,每个列表都有关联的词性;在语法分析之后,歧义减少,因为目标词性已被识别并与其对应的单词序列和词性相关联,以构建它们。语法分析也有助于为概念分析提供语法信息,供其在谓词计算中使用。正如本文后面所揭示的,谓词生成器脚本由主要与语法相关的代码组成,从语法流过渡到概念在很大程度上依赖于语法分析期间产生的语法信息。
存储在SyntaxTransform.txt中的语法转换脚本是语法分析的核心。该文件的内容包含用于从词典中发现的复杂节点和原子节点的配置构建复杂节点的排序决策。语法转换脚本由一种专为节点排列而设计的语言组成,代码行数约为 50 行。
仔细查看SyntaxTransform.txt的前三行代码,有助于理解该语言。
ADJECTIVE PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 1: ([ADVERB])[ADJECTIVE] -> ADJECTIVE_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
ADJECTIVE PHRASE ENUMERATION: [ADJECTIVE_PHRASE]([CONJUNCTION])
[ADJECTIVE_PHRASE] -> ADJECTIVE_PHRASE
# Verbs
MAXRECURSIVITY:1
COMPLEX VERB CONSTRUCTION: [VERB & "is" | "was" | "will" | "have" |
"has" | "to" | "will be" | "have been" |
"has been" | "to be" | "will have been" |
"be" | "would" | "could" | "should"]([ADVERB])[VERB] -> VERB
上面的代码片段为了避免滚动而进行了换行。.
第一行排列了 ([ADVERB])[ADJECTIVE] 的所有可能性,并创建一个作为词性的结果节点,即 ADJECTIVE_PHRASE。例如,像“more red”这样的词元会产生一个 ADJECTIVE_PHRASE,因为“more”是 ADVERB,“red”是 ADJECTIVE。但由于 ADVERB 节点位于括号内,因此被识别为可选。因此,词元“blue”也产生一个 ADJECTIVE_PHRASE 节点。
下一行 [ADJECTIVE_PHRASE]([CONJUNCTION])[ADJECTIVE_PHRASE],它接收 ADJECTIVE_PHRASE 节点序列,可以选择由 CONJUNCTION 节点分隔,并将它们组合成一个新的 ADJECTIVE_PHRASE 节点。这种脚本行是递归的,因为它转换成构成其排序一部分的词性。为此,为了将计算限制在合理的解析级别,我们可能希望限制递归,就像在前一行中所做的那样:MAXRECURSIVITY:2。这基本上表明只允许在此转换行上进行两次成功传递。这意味着像“more blue and less green”这样的词元可以成功转换,而像“red, some green and grey”这样的词元则无法成功转换,因为这种情况需要至少 3 级的递归。请注意,递归限制仅在执行自下而上解析时相关,而在多维 Earley 解析时则不相关。稍后将进一步讨论这一点...
下一行 [VERB & "is" | "was" | "will" | "have" | "has" | "to" | "will be" | "have been" | "has been" | "to be" | "will have been" | "be" | "would" | "could" | "should"]([ADVERB])[VERB],具有类似的规则,但还规定了关于第一个节点拼写的一些条件。双引号之间的部分是拼写条件,其中至少一个必须成功才能匹配节点。从该行代码来看,对于词元序列“could never see”会发生成功的转换,但对于词元序列“see always ear”则会失败。
这是完整的脚本。它包含了大部分英语语言,尽管如果更复杂的测试用例未能按预期转换,可能需要进行微调。
# NOTES ON THE SYNTAX OF THE SCRIPTING LANGUAGE
# - BEFORE THE ':' CHARACTER ON A LINE IS THE LINE NAME
# - A NODE BETWEEN PARENTHESIS IS INTERPREATED AS BEING OPTIONAL
# - CONTENT BETWEEN QUOTES RELATES TO SPELLING
# - SPELLINGS THAT BEGIN WITH A '*' CHARACTER ARE INTERPREATED
#- AS A 'START WITH' STRING MATCH
# - ON THE RIGHT SIDE OF THE CHARACTERS '->'
# - IS THE DEFINITION OF THE NEW ENTITY (AFFECTATION)
# SCRIPT
# Adjective phrase construction
ADJECTIVE PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 1: ([ADVERB])[ADJECTIVE] -> ADJECTIVE_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
ADJECTIVE PHRASE ENUMERATION: [ADJECTIVE_PHRASE]([CONJUNCTION])
[ADJECTIVE_PHRASE] -> ADJECTIVE_PHRASE
# Verbs
MAXRECURSIVITY:1
COMPLEX VERB CONSTRUCTION: [VERB & "is" | "was" | "will" | "have" |
"has" | "to" | "will be" | "have been" |
"has been" | "to be" | "will have been" |
"be" | "would" | "could" |
"should"]([ADVERB])[VERB] -> VERB
# Noun phrase construction
GERUNDIVE ING: [VERB & "*ing"] -> GERUNDIVE_VERB
GERUNDIVE ED: [VERB & "*ed"] -> GERUNDIVE_VERB
PLAIN NOUN PHRASE CONSTRUCTION: ([DEFINITE_ARTICLE | INDEFINITE_ARTICLE])
([ORDINAL_NUMBER])([CARDINAL_NUMBER])
([ADJECTIVE_PHRASE])[NOUN | PLURAL |
PROPER_NOUN | TIME |
DATE | PRONOUN] -> NOUN_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
NOUN PHRASE ENUMERATION: [NOUN_PHRASE]([CONJUNCTION])[NOUN_PHRASE] -> NOUN_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:1
# Preposition phrase construction
PREPOSITION PHRASE CONSTRUCTION: [PREPOSITION][NOUN_PHRASE] -> PREPOSITION_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
PREPOSITION PHRASE ENUMERATION: [PREPOSITION_PHRASE]([CONJUNCTION])
[PREPOSITION_PHRASE] -> PREPOSITION_PHRASE
# Verb phrase construction
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 1: [VERB]([ADVERB])[NOUN_PHRASE]
([PREPOSITION_PHRASE]) -> VERB_PHRASE
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 2: [VERB][PREPOSITION_PHRASE] -> VERB_PHRASE
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 3: [ADJECTIVE_PHRASE][PREPOSITION][VERB] -> VERB_PHRASE
# Noun phrase construction while considering gerundive
GERUNDIVE PHRASE CONSTRUCTION: [GERUNDIVE_VERB]([NOUN_PHRASE])
([VERB_PHRASE])([ADVERB]) -> GERUNDIVE_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
NOUN PHRASE CONST WITH GERUNDIVE: [NOUN_PHRASE][GERUNDIVE_PHRASE]
([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE])([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE]) -> NOUN_PHRASE
PREPOSITION PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 3: [PREPOSITION][GERUNDIVE_PHRASE] -> PREPOSITION_PHRASE
# Noun phrase construction while considering restrictive relative clauses
RESTRICTIVE RELATIVE CLAUSE: [WH_PRONOUN & "who" | "where" | "when" |
"which"][VERB_PHRASE] -> REL_CLAUSE
RESTRICTIVE RELATIVE CLAUSE 2: [PRONOUN & "that"][VERB_PHRASE] -> REL_CLAUSE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
NOUN PHRASE WITH REL_CLAUSE: [NOUN_PHRASE][REL_CLAUSE] -> NOUN_PHRASE
# Make sure the restrictive relative clauses built are part of the verb phrases
VERB PHRASE WITH REL_CLAUSE: [VERB_PHRASE][REL_CLAUSE] -> VERB_PHRASE
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 4: [VERB][NOUN_PHRASE][REL_CLAUSE]
([PREPOSITION_PHRASE]) -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
WH_PRONOUN CONSTRUCTION ENUMERATION: [WH_PRONOUN][CONJUNCTION][WH_PRONOUN] -> WH_PRONOUN
# Make sure the gerundive built are part of the verb phrases
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 5: [VERB][NOUN_PHRASE][GERUNDIVE_PHRASE]
([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE])([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE])
([PREPOSITION_PHRASE]) -> VERB_PHRASE
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 6: [VERB][NOUN_PHRASE][ADJECTIVE_PHRASE] -> VERB_PHRASE
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 7: ([VERB])[NOUN_PHRASE][VERB] -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 8: [VERB_PHRASE][NOUN_PHRASE][GERUNDIVE_PHRASE]
([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE])([GERUNDIVE_PHRASE])
([PREPOSITION_PHRASE]) -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 9: [VERB_PHRASE]([NOUN_PHRASE])
[ADJECTIVE_PHRASE] -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 10: [WH_PRONOUN][VERB_PHRASE] -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 11: [VERB_PHRASE][NOUN_PHRASE](
[PREPOSITION_PHRASE |
GERUNDIVE_PHRASE]) -> VERB_PHRASE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
VERB PHRASE CONSTRUCTION 12: [VERB_PHRASE][PREPOSITION_PHRASE] -> VERB_PHRASE
# WH-Phrases construction
WH_NP CONSTRUCTION 1: [WH_PRONOUN][NOUN_PHRASE] -> WH_NP
WH_NP CONSTRUCTION 2: [WH_PRONOUN][ADJECTIVE]([ADVERB]) -> WH_NP
WH_NP CONSTRUCTION 3: [WH_PRONOUN][ADVERB][ADJECTIVE] -> WH_NP
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
WH_NP CONSTRUCTION 4: [WH_NP][CONJUNCTION][WH_NP | WH_PRONOUN] -> WH_NP
# Sentence construction
SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION QUESTION 1: [VERB & "is" | "was" | "were"]
[NOUN_PHRASE][NOUN_PHRASE](
[PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION QUESTION 2: [VERB & "is" | "was" | "were"]
[VERB_PHRASE][VERB_PHRASE](
[PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 1: [VERB_PHRASE]([PREPOSITION & "at" | "in" | "of" |
"on" | "for" | "into" | "from"])
([PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 2: ([AUX])[NOUN_PHRASE][VERB_PHRASE | VERB](
[PREPOSITION & "at" | "in" | "of" |
"on" | "for"])([ADVERB])([PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
WH_NP SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 1: [WH_NP][VERB_PHRASE]([PREPOSITION & "at" |
"in" | "of" | "on" | "for" | "into" |
"from"])([PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
WH_NP SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 2: [WH_NP]([AUX])[NOUN_PHRASE][VERB_PHRASE | VERB](
[PREPOSITION & "at" | "in" | "of" | "on" | "for"])
([ADVERB])([PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
WH_NP SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 3: [NOUN_PHRASE | VERB_PHRASE]([PREPOSITION &
"at" | "in" | "of" | "on" | "for" | "into" |
"from"])[WH_NP]([PUNCTUATION & "?"]) -> SENTENCE
MAXRECURSIVITY:2
SENTENCE CONSTRUCTION 4: [SENTENCE]([CONJUNCTION])[SENTENCE] -> SENTENCE
上面的代码片段为了避免滚动而进行了换行。.
语法转换脚本的一个目标是创建 [SENTENCE] 复杂节点。句子是特殊的,因为它们应该封装一个完整的思想流,之后可以由谓词表示。尽管其他复杂节点也可以计算谓词,但只有 [SENTENCE] 词性才能可靠地完全封装到谓词中。但这并不意味着 [SENTENCE] 词性必然是自给自足的。例如,考虑以下两个 [SENTENCE]:“I saw Edith yesterday. She is feeling great.” 第二个 [SENTENCE] 中的知识对象“she”指代第一个 [SENTENCE] 中的知识对象“Edith”。就本示例项目而言,尽管可以这样做,但我们不会在不同的 [SENTENCE] 节点之间保持上下文。
排列语法转换脚本
语法分析器首先做的事情之一是创建一个无决策的语法转换脚本版本。也就是说,它会在 POSDictionary_flat.txt 中创建一个在功能上等同于 SyntaxTransform.txt 的版本,该版本不包含任何决策节点(SyntaxTransform.txt 中括号内的节点,或节点内用管道字符分隔的不同拼写条件)。由本文附加的可下载可执行文件生成的 POSDictionary_flat.txt 的内容可以通过点击此处访问。为了做到这一点,它在 POSTransformScript::ManageSyntacticDecisions 中执行两个独立的步骤,其中参数 decisionFile 是保存语法转换脚本名称的字符串。
void POSTransformScript::ManageSyntacticDecisions(string decisionFile,
string dFlatFileName)
{
FlattenDecisions(decisionFile, "temp.txt");
FlattenDecisionNodes("temp.txt", dFlatFileName);
}
在第一步(进入 POSTransformScript::FlattenDecisions)中,读取文件的每一行,并将括号中的每个元素从括号中移除并放入一行,并在另一行中忽略。由于括号内的元素是可选的,因此只有两种可能性——它包含或不包含。
void POSTransformScript::FlattenDecisions(string dDecisionFileName,
string dFlattenDecisionFileName)
{
fstream dOutputStream;
dOutputStream.open(dFlattenDecisionFileName.c_str(),
ios::out | ios::binary | ios::trunc);
ifstream dInputStream(dDecisionFileName.c_str(), ios::in | ios::binary);
dInputStream.unsetf(ios::skipws);
string dBuffer;
char dChar;
while (dInputStream >> dChar)
{
switch (dChar)
{
case '\n':
case '\r':
if (dBuffer.find("#") != string::npos)
{
dBuffer = SubstringUpTo(dBuffer, "#");
}
if (dBuffer.length() > 0)
{
unsigned int i;
vector<string> *matches;
Permutation perms(dBuffer);
matches = perms.GetResult();
for (i = 0; i < matches->size(); i++)
{
dOutputStream.write(
matches->at(i).c_str(), matches->at(i).length());
dOutputStream.write("\r\n", strlen("\r\n"));
}
}
dBuffer = "";
break;
default:
dBuffer += dChar;
}
}
dInputStream.close();
dOutputStream.close();
}
为了帮助计算单行所有可能的排列,使用了 Permutation 类。由于一行可能有多个排列,因此使用递归的 Permutation::FillResult 方法是执行这些计算的最佳方法。
void Permutation::FillResult()
{
m_result.clear();
vector<string> matches;
if (PatternMatch(m_value, "(*)", &matches, true))
{
string tmpString = m_value;
size_t pos = tmpString.find("(" + matches[0] + ")");
if (SearchAndReplace(tmpString, "(" + matches[0] +
")", "", 1, true) == 1)
{
Permutation otherPerms(tmpString);
vector<string> *otherMatches = otherPerms.GetResult();
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < otherMatches->size(); i++)
{
// We push the value with
// the potential value out and then in...
m_result.push_back(otherMatches->at(i));
m_result.push_back(m_value.substr(0, pos) +
matches[0] + otherMatches->at(i).substr(pos));
}
}
}
else
{
m_result.push_back(m_value);
}
}
在处理完括号内的内容的第一步之后,就需要处理原子节点中的决策。带有决策的原子节点就像 [DEFINITE_ARTICLE | INDEFINITE_ARTICLE],其中词性是选择;或者 [WH_PRONOUN & "who" | "where" | "when" | "which"],其中拼写约束也是选择。大部分逻辑都在 POSTransformScript::FlattenOneDecisionNodes 中,它本身严重依赖 POSNode::Construct 进行解析。
vector<string> POSTransformScript::FlattenOneDecisionNodes(string dLine)
{
vector<string> dReturn;
vector<string> matches;
if (PatternMatch(dLine, "[*]", &matches, true) > 0)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr> possibilities;
POSNode::Construct("[" + matches[i] + "]", &possibilities);
if (possibilities.size() > 1)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < possibilities.size(); j++)
{
string dLineCopy = dLine;
SearchAndReplace(dLineCopy, "[" + matches[i] + "]",
possibilities[j].get()->GetNodeDesc(), 1);
vector<string> dNewLineCopies = FlattenOneDecisionNodes(dLineCopy);
for (unsigned int k = 0; k < dNewLineCopies.size(); k++)
{
dReturn.push_back(dNewLineCopies[k]);
}
}
break;
}
}
}
if (dReturn.size() == 0)
{
dReturn.push_back(dLine);
}
return dReturn;
}
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> POSNode::Construct(string dNodeDesc,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *allPOSNodes,
unsigned int dStartPosition,
unsigned int dEndPosition,
unsigned int dBridgePosition,
string data)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> tmpVector;
if (allPOSNodes == NULL)
{
allPOSNodes = &tmpVector;
}
vector<string> matches;
vector<string> spellings;
vector<POSEntry> dPOS;
string dLeftPart = "";
if (PatternMatch(dNodeDesc, "[* & *]", &matches, false) == 2)
{
dLeftPart = matches[0];
string dRightPart = matches[1];
if (PatternMatch(dRightPart, "\"*\"", &matches, true, "|") > 0)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
spellings.push_back(matches[i]);
}
}
}
else
{
matches.clear();
if (PatternMatch(dNodeDesc, "[*]", &matches, false) == 1)
{
dLeftPart = matches[0];
}
else
{
throw new exception("Formatting error");
}
}
while (dLeftPart.length())
{
matches.clear();
if (PatternMatch(dLeftPart, "* | *", &matches, false) == 2)
{
dPOS.push_back(POSEntry(matches[0]));
dLeftPart = matches[1];
}
else
{
dPOS.push_back(POSEntry(dLeftPart));
dLeftPart = "";
}
}
if ((spellings.size() > 0) && (dPOS.size() > 0))
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < dPOS.size(); i++)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < spellings.size(); j++)
{
allPOSNodes->push_back(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>(
new POSNode(dPOS[i], spellings[j], dStartPosition,
dEndPosition, dBridgePosition, data)));
}
}
}
else if (dPOS.size() > 0)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < dPOS.size(); i++)
{
allPOSNodes->push_back(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>(
new POSNode(dPOS[i], "", dStartPosition,
dEndPosition, dBridgePosition, data)));
}
}
if (allPOSNodes->size() > 0)
{
return shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>(allPOSNodes->at(0));
}
else
{
return NULL;
}
}
加载无决策的语法转换脚本
只有在生成了 POSDictionary_flat.txt 后,才会创建一个 POSTransformScript 对象,并通过调用 POSTransformScript::BuildFromFile 方法将 POSDictionary_flat.txt 的内容加载到其中。参考下面的类定义,我们可以看到它相当简单。POSTransformScript 基本上由一个 POSTransformScriptLine 的向量组成。
#ifndef __POSTRANSFORM_H__
#define __POSTRANSFORM_H__
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include "POSNode.h"
#include "POSList.h"
#include "shared_auto_ptr.h"
#include "StoredScriptLine.h"
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::stack;
class POSTransformScriptLine
{
public:
friend class POSTransformScript;
int GetLineNumber() const;
int GetRecursivity() const;
string GetLineName() const;
string ReconstructLine() const;
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> GetTransform() const;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> GetSequence() const;
bool MustRecurse() const;
protected:
POSTransformScriptLine(string lineName,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dSequence,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dTransform,
int recursivity,
string originalLine,
int lineNumber);
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> m_sequence;
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> m_transform;
string m_lineName;
string m_originalLineContent;
int m_recursivity;
int m_lineNumber;
bool m_mustRecurse;
};
class POSTransformScript
{
public:
friend class POSTransformLine;
POSTransformScript();
void BuildFromFile(string dFileName);
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>> *GetLines();
string GetDecisionTrees(string dTreesType);
void KeepDecisionTrees(string dTreesType, string dValue);
bool IsDerivedPOS(POSEntry dPOSEntry) const;
static void ManageSyntacticDecisions(string decisionFile,
string dFlatFileName);
private:
static void FlattenDecisions(string dDecisionFileName,
string dFlattenDecisionFileName);
static void FlattenDecisionNodes(string dDecisionFileName,
string dFlattenDecisionFileName);
static vector<string> FlattenOneDecisionNodes(string dLine);
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>> m_lines;
vector<bool> m_derived;
map<string, string> m_decisionTrees;
};
#endif
解析词元
一旦语法转换脚本被保存在内存中的一个对象中,词元解析就是下一步需要进行的。它将原子词性转换为复杂词性,而这些复杂词性正是之后与概念分析处理相关的词性。由于解析主题在实现算法方面存在巨大差异,因此首选抽象接口。
#ifndef __PARSER_H__
#define __PARSER_H__
#include "shared_auto_ptr.h"
#include "POSTransformScript.h"
class Parser
{
public:
Parser(shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScript> dScript);
virtual ~Parser();
virtual void ParseList(shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dList) = 0;
protected:
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScript> m_script;
};
#endif
Parser 抽象类保存了对 POSTransformScript 对象的引用,该对象包含有关可以发生的转换的详细信息。ParseList 方法负责执行参数 dList 中词元的实际转换。
自下而上解析器:一个简单的解析器实现
自下而上解析(也称为移入-归约解析)是一种用于解析句子的策略,它试图构建一个解析树,从叶节点开始,向“自下而上”的根节点工作。它的优点是算法简单,通常易于实现,缺点是计算速度慢,因为在到达根节点之前需要构建所有节点。
#include "BottomUpParser.h"
#include "CalculationContext.h"
#include "POSTransformScript.h"
#include "StringUtils.h"
#include "DigitalConceptBuilder.h"
#include "DebugDefinitions.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
#endif
BottomUpParser::BottomUpParser(
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScript> dScript): Parser(dScript) {}
BottomUpParser::~BottomUpParser() {}
void BottomUpParser::ParseList(shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dList)
{
string dLastOutput = "";
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < m_script->GetLines()->size(); i++)
{
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->SyntacticAnalysisTrace())
{
if (i == 0)
{
originalprintf("\nBottom-up Syntactic trace:\n\n");
}
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dLastOutput.length(); j++)
{
originalprintf("\b");
originalprintf(" ");
originalprintf("\b");
}
dLastOutput = FormattedString(
"%d of %d. line \"%s\" (%lu so far)",
i+1, m_script->GetLines()->size(),
m_script->GetLines()->at(i)->GetLineName().c_str(),
dList->Count());
originalprintf(dLastOutput.c_str());
}
BottomUpLineParse(dList, m_script->GetLines()->at(i));
}
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dLastOutput.length(); j++)
{
originalprintf("\b");
originalprintf(" ");
originalprintf("\b");
}
}
int BottomUpParser::BottomUpLineParse(shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dList,
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> dLine,
int fromIndex,
int atPosition,
int lowestPos,
string cummulatedString,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *cummulatedNodes)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> childNodes;
if (cummulatedNodes == NULL)
{
cummulatedNodes = &childNodes;
}
int dTransformCount = 0;
if (fromIndex == -1)
{
fromIndex = 0;
}
int fromPosition = atPosition;
int toPosition = atPosition;
if (atPosition == -1)
{
fromPosition = dList->GetLowestStartPosition();
toPosition = dList->GetHighestEndPosition();
}
for (int i = 0; i < dLine->GetRecursivity(); i++)
{
dTransformCount = 0;
for (int pos = fromPosition; pos <= toPosition; pos++)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> > dNodes =
dList->BrigdgeableNodes(pos, dLine->GetSequence()[fromIndex]);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dNodes.size(); j++)
{
if (fromIndex == (dLine->GetSequence().size() - 1))
{
dTransformCount++;
string dSpelling = cummulatedString + " " +
dNodes[j]->GetSpelling();
RemovePadding(dSpelling, ' ');
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dNewNode(new POSNode(
dLine->GetTransform()->GetPOSEntry(), dSpelling,
(lowestPos == -1)?pos:lowestPos, dNodes[j]->GetEndPosition(),
dNodes[j]->GetBridgePosition()));
dNewNode->SetConstructionLine(dLine->GetLineName());
for (unsigned int k = 0; k < cummulatedNodes->size(); k++)
{
cummulatedNodes->at(k)->SetParent(dNewNode);
}
dNodes[j]->SetParent(dNewNode);
dList->AddToPOSList(dNewNode);
}
else
{
if (dNodes[j]->GetBridgePosition() != 0)
{
int sizeBefore = cummulatedNodes->size();
cummulatedNodes->push_back(dNodes[j]);
dTransformCount += BottomUpLineParse(dList, dLine,
fromIndex+1, dNodes[j]->GetBridgePosition(),
(lowestPos == -1)?pos:lowestPos, cummulatedString +
" " + dNodes[j]->GetSpelling(), cummulatedNodes);
while ((int)cummulatedNodes->size() > sizeBefore)
{
cummulatedNodes->erase(cummulatedNodes->begin() +
cummulatedNodes->size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
}
if ((dTransformCount == 0) || (!dLine->MustRecurse()))
{
break;
}
}
return dTransformCount;
}
多维 Earley 解析器:一种更有效的解析方法
Earley 解析器本质上是一个生成器,它使用给定的序列产生式来构建最左边的推导。解析功能之所以出现,是因为生成器会跟踪所有在一定程度上与输入一致的可能推导。随着输入的越来越多,可能推导的集合(每个推导对应一个解析)可以随着新选择的引入而扩展,或者随着消歧的解决而收缩。通常,Earley 解析器不处理歧义输入,因为它需要一维词元序列。但在我们的例子中,存在歧义,因为每个单词可能生成多个具有不同词性的词元。这就是为什么该算法被改编并命名为多维 Earley 解析器的原因。
#include "MultiDimEarleyParser.h"
#include "CalculationContext.h"
#include "POSTransformScript.h"
#include "StringUtils.h"
#include "DigitalConceptBuilder.h"
#include "DebugDefinitions.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
#endif
class ScriptMultiDimEarleyInfo
{
public:
map<int, vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>>>
m_startPOSLines;
};
class UnfinishedTranformLine
{
public:
UnfinishedTranformLine();
UnfinishedTranformLine(
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> dTransformLine);
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> m_transformLine;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> m_cummulatedNodes;
};
map<uintptr_t, ScriptMultiDimEarleyInfo>
MultiDimEarleyParser::m_scriptsExtraInfo;
MultiDimEarleyParser::MultiDimEarleyParser(
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScript> dScript): Parser(dScript) {}
MultiDimEarleyParser::~MultiDimEarleyParser() {}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::ParseList(shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dList)
{
m_listParsed = dList;
MultiDimEarleyParser::BuildDecisionsTree(m_script);
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode;
m_derivedNodesLookup.Clear();
m_derivedNodesProduced.Clear();
m_targetNodesProduced.Clear();
// For each word in the list, we try to forward
// in its corresponding decision tree...
// At this point, we care only about the starting node
// (the one for which a sequence is started
// with). Hence, we know as a fact that we
// are dealing with nodes that are not derived from a
// construct - the nodes are the ones indirectly
// obtained from a dictionary entry.
// Provided that a sentence (for example) could start
// with a word that is not necessarily the first one,
// we do not have to scan from left to right
// as it is typically done in the Earley algorithm.
dList->GetPositionInList()->Reset();
while (dList->GetPositionInList()->GetNext(dPOSNode))
{
NodeDecisionProcessing(dPOSNode);
ProcessAgainstUnfinishedLines(dPOSNode);
}
while ((m_delayedSuccessCondition.size() > 0) &&
(m_targetNodesProduced.Count() <
(unsigned long)DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetMaxSyntaxPermutations()))
{
SuccessNodeCondition(
m_delayedSuccessCondition.front().m_partialLine,
m_delayedSuccessCondition.front().m_POSNode);
m_delayedSuccessCondition.pop();
}
// We add the targeted nodes acquired through
// this parsing in the list before returning...
m_targetNodesProduced.GetPositionInList()->Reset();
while (m_targetNodesProduced.GetPositionInList()->GetNext(dPOSNode))
{
dList->AddToPOSList(dPOSNode);
}
// We add all the nodes acquired through
// this parsing in the list before returning...
m_derivedNodesProduced.GetPositionInList()->Reset();
while (m_derivedNodesProduced.GetPositionInList()->GetNext(dPOSNode))
{
dList->AddToPOSList(dPOSNode);
}
m_decisionTrees.clear();
m_derivedNodesLookup.Clear();
m_targetNodesProduced.Clear();
Trace("");
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::SuccessNodeCondition(
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine> dPartialLine,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode)
{
if (m_targetNodesProduced.Count() >=
(unsigned long)DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetMaxSyntaxPermutations())
{
return;
}
dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.push_back(dPOSNode);
if (dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.size() ==
dPartialLine->m_transformLine->GetSequence().size())
{
// We have a transform that is done
// since the last node condition was reached.
// Let's create our new node...
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode(new POSNode(
dPartialLine->m_transformLine->GetTransform()->GetPOSEntry()));
dPOSNode->SetConstructionLine(
dPartialLine->m_transformLine->GetLineName());
unsigned int i;
for (i = 0; i < dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.size(); i++)
{
dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes[i]->SetParent(dPOSNode);
}
dPOSNode->UpdateFromChildValues();
ProcessAgainstUnfinishedLines(dPOSNode);
// We add the node to the derived nodes list
// so that future processing may catch it...
m_derivedNodesProduced.AddToPOSList(dPOSNode);
// We invoke NodeDecisionProcessing so that the decisions
// tree associated with the node may be traversed...
NodeDecisionProcessing(dPOSNode);
// Finally, if the node is a POS that is our targeted POS, we flag it...
if ((dPOSNode->GetEndPosition() - dPOSNode->GetStartPosition() >=
(unsigned int)(m_listParsed->GetHighestEndPosition() -
m_listParsed->GetLowestStartPosition() - 1)) &&
(DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetTargetPOS().GetValue() ==
dPOSNode->GetPOSEntry().GetValue()))
{
m_targetNodesProduced.AddToPOSList(dPOSNode);
}
}
else if (dPOSNode->GetBridgePosition() > dPOSNode->GetEndPosition())
{
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine> usePartialLine = dPartialLine;
// We still need to acquire more nodes to complete this transform line.
if (m_script->IsDerivedPOS(
dPartialLine->m_transformLine->GetSequence().at(
dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.size())->GetPOSEntry()))
{
// Regardless if we have a node that matches or not,
// we need to keep that state in memory in the event that
// the transform happens later.
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine>
dPartialLineCopy(new UnfinishedTranformLine());
*dPartialLineCopy.get() = *dPartialLine.get();
m_derivedNodesLookup.Add(dPartialLineCopy, dPOSNode->GetBridgePosition(),
dPartialLine->m_transformLine->GetSequence().at(
dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.size())->GetPOSEntry());
usePartialLine = dPartialLineCopy;
}
// We try to go forward and bridge to other existing nodes
// (without moving in the decision tree)...
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dTestNode =
usePartialLine->m_transformLine->GetSequence()
[usePartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes.size()];
BridgeableNodesProcessing(dPOSNode->GetBridgePosition(),
dTestNode, &usePartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes,
usePartialLine->m_transformLine);
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::ProcessAgainstUnfinishedLines(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode)
{
// Let's pay attention to states
// that were kept into m_derivedNodesLookup...
// We look for unfinished lines that require
// the same part-of-speech as the one we just produced.
vector<shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine>> dUnfinishedLines =
m_derivedNodesLookup.ObjectsAtPosition(dPOSNode->GetStartPosition(),
dPOSNode->GetPOSEntry(), NULL);
for (unsigned long i = 0; i < dUnfinishedLines.size(); i++)
{
if (dPOSNode->Compare(*dUnfinishedLines[i]->
m_transformLine->GetSequence()[dUnfinishedLines[i]->
m_cummulatedNodes.size()].get()) == 0)
{
// If the required node matches the new node,
// we have a success condition for the node check.
// The path is copied since other derived nodes may
// get produced later on to generate other entries.
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine>
dPartialLineCopy(new UnfinishedTranformLine());
*dPartialLineCopy.get() = *dUnfinishedLines[i].get();
m_delayedSuccessCondition.push(
DelayedSuccessCondition(dPartialLineCopy, dPOSNode));
}
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::BridgeableNodesProcessing(unsigned int dPosition,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dTestNode,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *resolvedNodes,
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> scriptLine)
{
if (m_script->IsDerivedPOS(dTestNode->GetPOSEntry()))
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dNodes =
m_derivedNodesProduced.BrigdgeableNodes(dPosition, dTestNode);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dNodes.size(); j++)
{
OneNodeCompareInDecisionTree(dNodes[j], scriptLine, resolvedNodes);
}
}
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dNodes =
m_listParsed->BrigdgeableNodes(dPosition, dTestNode);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dNodes.size(); j++)
{
OneNodeCompareInDecisionTree(dNodes[j], scriptLine, resolvedNodes);
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::NodeDecisionProcessing(unsigned int dPosition,
IndexStructureNode<StoredScriptLine> *fromNode,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *resolvedNodes)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>> *options =
SetUpForNodeProcessing(resolvedNodes->at(0)->GetPOSEntry());
if (options != NULL)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < options->size(); i++)
{
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> dAssociatedLine = options->at(i);
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dTestNode =
dAssociatedLine->GetSequence()[resolvedNodes->size()];
BridgeableNodesProcessing(dPosition, dTestNode,
resolvedNodes, options->at(i));
}
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::OneNodeCompareInDecisionTree(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode,
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> scriptLine,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *resolvedNodes)
{
// Since we are at the starting point in the decision tree,
// we always compare the first node with the
// one passed in parameter here. The result from
// the compare may not always result in a success since
// the spelling condition from the node in the tree
// may be incompatible with the spelling of the node
// passed in parameter.
unsigned int node2Compare = 0;
if (resolvedNodes != NULL)
{
node2Compare = resolvedNodes->size();
}
if (dPOSNode->Compare(*scriptLine->GetSequence()[node2Compare].get()) == 0)
{
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine>
dPartialLine(new UnfinishedTranformLine(scriptLine));
// The caller may have invoked this method
// as a result of the resolution of a derived node.
if (resolvedNodes != NULL)
{
dPartialLine->m_cummulatedNodes = *resolvedNodes;
SuccessNodeCondition(dPartialLine, dPOSNode);
}
else
{
m_delayedSuccessCondition.push(
DelayedSuccessCondition(dPartialLine, dPOSNode));
}
}
}
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>>
*MultiDimEarleyParser::SetUpForNodeProcessing(POSEntry dPOSEntryTree)
{
if (m_scriptsExtraInfo.find((uintptr_t)m_script.get()) != m_scriptsExtraInfo.end())
{
if (m_scriptsExtraInfo[(uintptr_t)m_script.get()].m_startPOSLines.find(
dPOSEntryTree.GetValue()) !=
m_scriptsExtraInfo[(unsigned long)m_script.get()].m_startPOSLines.end())
{
return &m_scriptsExtraInfo[
(uintptr_t)m_script.get()].m_startPOSLines[dPOSEntryTree.GetValue()];
}
}
return NULL;
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::NodeDecisionProcessing(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode,
IndexStructureNode<StoredScriptLine> *fromNode,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *resolvedNodes)
{
Trace(FormattedString("NodeDecisionProcessing for node %s",
dPOSNode->GetNodeDesc().c_str()));
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine>> *options =
SetUpForNodeProcessing(dPOSNode->GetPOSEntry());
if (options != NULL)
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < options->size(); i++)
{
OneNodeCompareInDecisionTree(dPOSNode,
options->at(i), resolvedNodes);
}
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::BuildDecisionsTree(
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScript> dScript)
{
if (m_scriptsExtraInfo.find((uintptr_t)dScript.get()) ==
m_scriptsExtraInfo.end())
{
fstream dOutputStream;
dOutputStream.open("LineNumbers.txt",
ios::out | ios::binary | ios::trunc);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < dScript->GetLines()->size(); i++)
{
string sequence;
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <
dScript->GetLines()->at(i)->GetSequence().size(); j++)
{
sequence +=
dScript->GetLines()->at(i)->GetSequence().at(j)->GetNodeDesc();
}
dOutputStream << FormattedString("%d. %s: %s -> %s\r\n", i,
dScript->GetLines()->at(i)->GetLineName().c_str(), sequence.c_str(),
dScript->GetLines()->at(i)->GetTransform()->GetNodeDesc().c_str()).c_str();
m_scriptsExtraInfo[(uintptr_t)dScript.get()].m_startPOSLines[
dScript->GetLines()->at(i)->GetSequence().at(0)->
GetPOSEntry().GetValue()].push_back(dScript->GetLines()->at(i));
}
dOutputStream.close();
}
}
void MultiDimEarleyParser::Trace(string dTraceString)
{
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::GetCurCalculationContext()->SyntacticAnalysisTrace())
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < m_lastTraceOutput.length(); j++)
{
originalprintf("\b");
originalprintf(" ");
originalprintf("\b");
}
if (dTraceString.length() > 0)
{
originalprintf(dTraceString.c_str());
}
m_lastTraceOutput = dTraceString;
}
}
UnfinishedTranformLine::UnfinishedTranformLine() {}
UnfinishedTranformLine::UnfinishedTranformLine(
shared_auto_ptr<POSTransformScriptLine> dTransformLine):
m_transformLine(dTransformLine) {}
DelayedSuccessCondition::DelayedSuccessCondition(
shared_auto_ptr<UnfinishedTranformLine> dPartialLine,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode):
m_partialLine(dPartialLine), m_POSNode(dPOSNode) {}
概念分析
语法分析从原子节点输入计算出复杂节点,但它向算法提供了一组模糊的结果。
以下内容取自SimpleTestCases.txt。MAXSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS 和 MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS 是确定概念表示中计算了多少语法排列的两个关键变量。
...
# MAXSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS
# _____________________
#
# Possible values: Numeric value
#
# The maximal amount of TARGETPOS that syntactic analysis should
# produce.
MAXSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS = 200
#-------------------------------------------------------------------
# MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS
# _____________________
#
# Possible values: Numeric value
#
# The maximal amount of TARGETPOS that conceptual analysis should
# analyze. From the MAXSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS sequences of TARGETPOS that
# are sorted, only the fist MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS will be analyzed.
MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS = 20
...
在 SimpleTestCases.txt 未经修改的默认条件下,但将 OUTPUTSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS 设置为 TRUE,则针对第 18 个测试用例生成以下输出
Evaluating: "Is a car that is not red a blue car?" (ID:CAR18)
CAR18:1. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] {ADJECTIVE_PHRASE:
BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:2. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:3. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE:
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:4. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:5. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } }
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:6. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:7. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX] {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } IS[VERB] }
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: NOT[ADVERB] RED[ADJECTIVE] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:8. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } }
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:9. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE:
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:10. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } } {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:11. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE:
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:12. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:13. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] }
CAR[NOUN] } } } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:14. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:15. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] }
CAR[NOUN] } } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:16. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:17. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } IS[VERB] }
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: NOT[ADVERB] RED[ADJECTIVE] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:18. {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:19. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } IS[VERB] }
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: NOT[ADVERB] RED[ADJECTIVE] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
CAR18:20. {SENTENCE: IS[AUX]
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } } {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
MAYBE:
DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT
MOOD:INTEROGATIVE
OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS
VALUE1:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:!RED
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]
VALUE2:PP[CLASS:CAR
COLOR:BLUE
QUANTITY:1
TYPE:VEHICLE
WHEELCOUNT:4]]]
Total time: 13 sec (13125 ms)
Syntactic: 937 ms
Conceptual: 12 sec (12188 ms).
上面的代码片段为了避免滚动而进行了换行。.
我们可以看到总共计算了 20 个语法排列——这是 MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS 中指定的值。这限制了提供给概念分析器的语法排列数量。通过对同一测试用例进行改编以探索总共生成了多少语法排列,对 SimpleTestCases.txt 进行了如下更改
...
{
ENABLED = TRUE
OUTPUTSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS = TRUE
MAXSYNTAXPERMUTATIONS = 2000000
MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS = 2000000
CONTENT = Is a car that is not red a blue car?
ID = CAR18
}
...
计算结果生成了 350 个语法排列,而不是原来的 20 个。计算也花费了四分钟,而不是原来的 13 秒,因为它探索了更多的语法排列;然而,它产生了相同的响应。因此,限制计算概念的语法排列数量很重要。如果希望将语法排列的数量限制在 MAXCONCEPTUALANALYSIS,则需要一个标准来确定保留哪些语法排列,排除哪些。
解决这个关键问题的一部分在于人类的认知反射。也就是说,对于两个等效的可能性,人类更喜欢简单的那个。人脑宁愿分析简单的语法结构而不是复杂的结构。但是,究竟如何确定语法结构的简单性呢?根据经验,最小化构成语法排列的节点数量可以很好地识别最简单的语法结构。
让我们仔细看看生成的语法排列,并根据这个知识比较其中的一些。
CAR18:1. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE:
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] }
{REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN]
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE]
{ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
...
CAR18:91. {SENTENCE: {SENTENCE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: THAT[PRONOUN] } } } {SENTENCE:
{VERB_PHRASE: {VERB_PHRASE:
{VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB]
{NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] BLUE[NOUN] } }
{NOUN_PHRASE: CAR[NOUN] } } ?[PUNCTUATION] } }
上面的代码片段为了避免滚动而进行了换行。.
第一个语法排列有 8 个复杂节点,而第 91 个语法排列有 13 个复杂节点。第一个语法排列中有一个 SENTENCE 节点,而第 91 个有三个 SENTENCE 节点。可以肯定地说,分析第 91 种类型语法排列的人类大脑比分析第一种类型语法排列更难形成概念!
因此,作为计算第一个语法排列的一个不变规则,CLUE 的一个假设是,由最少节点组成的语法排列更受青睐。在代码中,这体现为 POSNode 对象在 POSList 中的一种形式。
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> POSList::AccumulateAll(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dPOSNode,
POSNode::ESortType sort, int fromPos, int toPos)
{
if (fromPos == -1)
{
fromPos = GetLowestStartPosition();
}
if (toPos == -1)
{
toPos = GetHighestEndPosition();
}
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dReturn;
for (int i = fromPos; i <= toPos; i++)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dPOSFound =
BrigdgeableNodes(i, dPOSNode);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < dPOSFound.size(); j++)
{
dPOSFound[j]->SetSortRequirement(sort);
dReturn.push_back(dPOSFound[j]);
}
}
if (sort != POSNode::eNoSort)
{
std::sort(dReturn.begin( ), dReturn.end( ), POSNode::CompareNodes);
}
return dReturn;
}
为了识别最简单的语法排列,但具有输入流的最大跨度,请使用 eSortLargestToSmallestNode 排序标准。
bool POSNode::CompareNodes(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> elem1,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> elem2)
{
if ((elem1->GetEndPosition() - elem1->GetStartPosition()) ==
(elem2->GetEndPosition() - elem2->GetStartPosition()))
{
return elem1->ChildNodeCount() < elem2->ChildNodeCount();
}
switch (elem1->m_sortRequirement)
{
case eSortLargestToSmallestNode:
if ((elem1->GetEndPosition() - elem1->GetStartPosition()) ==
(elem2->GetEndPosition() - elem2->GetStartPosition()))
{
elem1->UpdateNodesCount();
elem2->UpdateNodesCount();
return (elem1->m_totalNodesUnder < elem2->m_totalNodesUnder);
}
else
{
return (elem1->GetEndPosition() - elem1->GetStartPosition()) >
(elem2->GetEndPosition() - elem2->GetStartPosition());
}
break;
case eSortSmallestToLargestNode:
if ((elem1->GetEndPosition() - elem1->GetStartPosition()) ==
(elem2->GetEndPosition() - elem2->GetStartPosition()))
{
elem1->UpdateNodesCount();
elem2->UpdateNodesCount();
return (elem1->m_totalNodesUnder < elem2->m_totalNodesUnder);
}
else
{
return (elem1->GetEndPosition() - elem1->GetStartPosition()) <
(elem2->GetEndPosition() - elem2->GetStartPosition());
}
break;
}
return true;
}
POSNode 中的 BuildPredicates 方法
谓词究竟是如何从语法排列中构造出来的?答案的开头在于 POSNode::BuildPredicates 方法,该方法包含了大部分概念分析逻辑。
语法分析会产生大量的目标词性的 POSNode 对象。每个 POSNode 对象由 m_children 向量中的 [0..N] 个 POSNode 对象组成。例如,语法分析计算出的第一个 SENTENCE 是一个 POSNode 对象
CAR18:1. {SENTENCE: IS[VERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] CAR[NOUN] } {REL_CLAUSE: THAT[PRONOUN] {VERB_PHRASE: IS[VERB] NOT[ADVERB] {NOUN_PHRASE: RED[NOUN] } } } } {NOUN_PHRASE: A[DEFINITE_ARTICLE] {ADJECTIVE_PHRASE: BLUE[ADJECTIVE] } CAR[NOUN] } ?[PUNCTUATION] }
#ifndef __POSNODE_H__
#define __POSNODE_H__
#include "shared_auto_ptr.h"
#include "JSObjectSupport.h"
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "POSEntry.h"
#include "Predicate.h"
using std::string;
using std::vector;
class POSNode: public JSObjectSupport<POSNode>
{
public:
enum ESortType
{
eNoSort = 0,
eSortLargestToSmallestNode = 1,
eSortSmallestToLargestNode = 2
};
enum EDirection
{
eSibling = 0,
eSiblingLeft = 1,
eSiblingRight = 2,
eFirstSibling = 3,
eLastSibling = 4,
eNextSibling = 5,
ePreviousSibling = 6,
eAncestre = 7,
eParent = 8,
eTopParent = 9,
eChild = 10,
eFirstChild = 11,
eLastChild = 12,
eDescendant = 13,
ePreviousWord = 14,
eNextWord = 15,
eFirstWord = 16,
eLastWord = 17
};
static shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> Construct(string dNodeDesc,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *allPOSNodes = NULL,
unsigned int dStartPosition = 0, unsigned int dEndPosition = 0,
unsigned int dBridgePosition = 0, string data = "");
static void ConstructSequence(string dSequence,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> *allPOSNodes);
POSNode();
POSNode(POSEntry dPOS,
string dSpelling = "",
unsigned int dStartPosition = 0,
unsigned int dEndPosition = 0,
unsigned int dBridgePosition = 0,
string data = "");
virtual ~POSNode();
string GetNodeDesc();
void SetParent(shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dParent);
unsigned int GetStartPosition();
unsigned int GetEndPosition();
unsigned int GetBridgePosition();
virtual void ClearAnalyzed(bool includingSelf);
void SetBridgePosition(unsigned int dPosition);
POSEntry GetPOSEntry() { return m_POS; }
virtual int CompareSpellings(POSNode &dNode);
virtual int Compare(POSNode &dNode);
virtual string GetSpelling(int debugLevel = 0);
virtual string GetID();
virtual string GetData();
virtual void SetData(string data);
virtual shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> Navigate(
EDirection direction, POSNode *constraint = NULL);
virtual void ManageTransientParents(
Persistent<Context> context, bool recursive = false);
virtual void UpdateFromChildValues();
static bool CompareNodes(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> elem1,
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> elem2);
virtual void SetSortRequirement(ESortType dRequirement);
virtual void SetConstructionLine(string dLine);
virtual string GetConstructionLine();
virtual vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>>
BuildPredicates(string wpstr = "");
virtual void AddInitializer(string dPredicateString) throw();
virtual void SetWordIndex(unsigned int dIndex) throw();
virtual unsigned int GetWordIndex() const throw();
virtual void UpdateNodesCount() throw();
virtual string Inspect(int indentCount) throw();
int ChildNodeCount();
virtual shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> GetChild(int index);
virtual shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> GetParent();
virtual void SetSpelling(string dSpelling);
virtual void SetStartPosition(unsigned int dPosition);
virtual void SetEndPosition(unsigned int dPosition);
virtual void UpdateDebugStrings();
virtual void SetTransientParent(
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> dTransientParent);
virtual bool HasConceptualDefinition();
virtual void OutputTransformLineInfo();
protected:
virtual bool ValidatePredicates();
virtual void AddPredicate(
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> dPredicate,
bool bringUp);
virtual bool IsLeaf();
virtual void FlagPacketAnalyzed();
virtual bool Analyzed();
static int m_maxSpellingLength;
Persistent<Context> m_context;
POSEntry m_POS;
string m_spelling;
string m_constructionLine;
string m_data;
POSNode* m_transientParent;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> m_children;
unsigned int m_startPosition;
unsigned int m_endPosition;
unsigned int m_bridgePosition;
unsigned int m_wordIndex;
unsigned int m_totalNodesUnder;
ESortType m_sortRequirement;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> m_initializers;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> m_predicates;
int m_inCurInitializer;
bool m_analyzed;
bool m_hasConceptualDefinition;
EPredicateCalculusCycle m_curCycle;
string m_debugString;
};
#endif
因此,每个单词都是一个 POSNode 对象;然而,一些单词序列由其他 POSNode 对象组成。POSNode::BuildPredicates 方法为给定的 POSNode 对象计算所有有效的 CPredicate 对象。仔细研究一下这个方法是值得的。

如流程图中的黄色步骤所示,POSNode::BuildPredicates 有三个不同的阶段
m_curCycle为eCalculatingPOSScript:如果在 POS 脚本目录中存在该词性名称的 JavaScript 文件,则执行它,并将结果返回。
eNotCalculating是POSNode对象中m_curCycle的默认值,该对象从未通过POSNode::BuildPredicates访问过,并且在进入时设置为eCalculatingPOSScript。- 在此计算阶段,可以通过引用
curPredicate的属性desc从 JavaScript 中重新实例化POSNode::BuildPredicates。这将导致重新实例化POSNode::BuildPredicates,并将m_curCycle设置为eCalculatingConstructionLineScript。 - 如果 POS 脚本目录中不存在该词性名称的 JavaScript 文件,则将
m_curCycle设置为eCalculatingConstructionLineScript,算法继续。
m_curCycle为eCalculatingConstructionLineScript:如果在排列脚本目录中存在构造行名称的 JavaScript 文件,则执行它,并将结果返回。
- 使用的构造行是创建
POSNode的语法转换行的名称。 - 在此计算阶段,可以通过引用
curPredicate的属性desc从 JavaScript 中重新实例化POSNode::BuildPredicates。这将导致重新实例化POSNode::BuildPredicates,并将m_curCycle设置为eCalculatingWordScript。 - 如果排列脚本目录中不存在构造行名称的 JavaScript 文件,则将
m_curCycle设置为eCalculatingWordScript,算法继续。
- 使用的构造行是创建
m_curCycle为eCalculatingWordScript:概念分析目录中与POSNode拼写对应的 JavaScript 文件分两个阶段执行
- 在第一阶段,
curPredicate.initialized()为false,算法通过调用curNode.addInitializer来累积初始化程序。这对应于扫描知识对象。这是关于什么的?此时,感兴趣的不是动作,而是确定动作是关于哪个概念实体。虽然在“The car is red”这样的句子中识别知识对象可能看起来很容易,但当想到“The fact that I am happy is not a surprise to anyone”这样的句子时,它就变得不那么容易了。在第二个句子中,这是一个完整的句子;从概念上讲,这就是知识对象:“我很高兴的事实”。知识对象是谓词的骨架。它首先被识别,然后被概念化。然后才将动作原语和其他角色-填充对聚合到该骨架上。 - 在第二阶段,通过在第一阶段调用
curNode.addInitializer添加的每个谓词被设置为curPredicate,并且每个POSNode都被重新调用。此时,知识对象已被识别并放置在curPredicate中;每个谓词生成器脚本协同工作以构建一个有效的谓词是其责任。
不允许通过引用
curPredicate的属性desc从 JavaScript 中重新调用POSNode::BuildPredicates。- 在第一阶段,
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> POSNode::BuildPredicates(string wpstr)
{
if (m_inCurInitializer != -1)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> dReturn;
dReturn.push_back(m_initializers[m_inCurInitializer]);
return dReturn;
}
if (wpstr != "")
{
m_predicates.clear();
}
if ((m_predicates.size() > 0) && (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating))
{
return m_predicates;
}
EPredicateCalculusCycle keepCycle = m_curCycle;
if (m_curCycle == eCalculatingWordScript)
{
throw new exception("Infinite loop detected!");
}
else
{
m_curCycle = EPredicateCalculusCycle((int)m_curCycle + 1);
}
g_nodeContext.push(this);
try
{
bool executed = false;
if (m_curCycle == eCalculatingPOSScript)
{
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> wp1(new CPredicate());
wp1->Abort();
wp1 = CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(
m_context, m_POS.GetDescriptor(),
wp1, this, executed, m_curCycle);
if ((wp1.get() != NULL) && (!wp1->HasAbort()))
{
AddPredicate(wp1, (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating));
}
if (executed)
{
m_curCycle = eNotCalculating;
}
else
{
m_curCycle = eCalculatingConstructionLineScript;
}
}
executed = false;
if (m_curCycle == eCalculatingConstructionLineScript)
{
if (m_constructionLine != "")
{
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> wp1(new CPredicate());
wp1->Abort();
wp1 = CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(m_context,
m_constructionLine, wp1, this, executed, m_curCycle);
if ((wp1.get() != NULL) && (!wp1->HasAbort()))
{
AddPredicate(wp1, (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating));
}
if (executed)
{
m_curCycle = eNotCalculating;
}
else
{
m_curCycle = eCalculatingWordScript;
}
}
else
{
m_curCycle = eCalculatingWordScript;
}
}
if (m_curCycle == eCalculatingWordScript)
{
if (m_children.size() > 0)
{
int initializersCount = 0;
// We do 2 passes... The first one to find the primitive
// for working predicates, the second to parse...
for (unsigned int pass = 1; pass <= 2; pass++)
{
if (wpstr != "")
{
pass = 2;
initializersCount = 1;
}
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < m_children.size(); i++)
{
if ((pass == 2) && (initializersCount == 0))
{
if ((DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->FailureReason()) ||
(DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetJavascriptTrace()))
{
printf("FAILURE REASON (potential): No initializer was " +
"found while calculating the node %s.\n",
m_spelling.c_str());
}
}
switch (pass)
{
case 1:
{
// On the first pass, we accumulate initializers...
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>
dNewPredicate(new CPredicate());
bool executed = false;
CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(
m_context, m_children[i]->GetSpelling(),
dNewPredicate, m_children[i],
executed, m_curCycle);
if (!m_children[i]->IsLeaf())
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>>
newInitializers =
m_children[i]->BuildPredicates();
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <
newInitializers.size(); j++)
{
if (newInitializers[j]->GetPrimitive() !=
CPredicate::UNSET)
{
m_children[i]->
m_initializers.push_back(
newInitializers[j]);
}
}
}
if ((m_children.size() == 1) &&
(m_children[0]->m_initializers.size() > 0))
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <
m_children[0]->m_initializers.size(); j++)
{
AddPredicate(m_children[0]->m_initializers[j],
(m_curCycle == eNotCalculating));
}
}
initializersCount +=
m_children[i]->m_initializers.size();
}
break;
case 2:
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>>
initializers = m_children[i]->m_initializers;
if (wpstr != "")
{
if (i > 0)
{
break;
}
initializers.clear();
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> wp(new CPredicate());
wp->SetPredicateString(wpstr);
initializers.push_back(wp);
}
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> wp(new CPredicate());
wp->ClearAbort();
for (unsigned int k = 0; ((k < initializers.size()) &&
(wp.get() != NULL) && (!wp->HasAbort())); k++)
{
string wpOnEntrance;
if (wp->GetPrimitive() != CPredicate::UNSET)
{
wpOnEntrance = wp->ToString(false);
}
wp->SetPredicateString(
m_children[i]->m_initializers[k]->ToString(false));
if (wpstr != "")
{
m_children[i]->m_inCurInitializer = -1;
}
else
{
m_children[i]->m_inCurInitializer = k;
}
wp->ClearAbort();
for (unsigned int j = 0; ((j < m_children.size()) &&
(wp.get() != NULL) && (!wp->HasAbort())); j++)
{
if ((i != j) || (wpstr != ""))
{
if ((!m_children[j]->Analyzed()) ||
(wpstr != ""))
{
string keepDesc = wp->ToString(false);
wp->Abort();
bool executed = false;
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> res =
CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(
m_context, m_children[j]->GetSpelling(),
wp, m_children[j], executed, m_curCycle);
if ((res.get() == NULL) || (res->HasAbort()))
{
if ((DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->
FailureReason())
|| (DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->
GetJavascriptTrace()))
{
printf("FAILURE REASON (potential): " +
"The node '%s' aborted (or did not " +
"populate curPredicate) when called " +
"with predicate %s.\n",
m_children[j]->GetSpelling().c_str(),
keepDesc.c_str());
}
break;
}
wp = res;
}
}
}
m_children[i]->m_inCurInitializer = -1;
if ((wp.get() != NULL) &&
(!wp->HasAbort()) && (wpOnEntrance != ""))
{
try
{
string dSource =
CPredicate::LoadFunctions("Hooks");
if (dSource != "")
{
dSource += "\r\n\r\n";
dSource += "entityJunction(\"" +
wp->ToString(false) + "\",\"" +
wpOnEntrance + "\")";
HandleScope handle_scope;
StackBasedContext localcontext;
Context::Scope context_scope(
*localcontext.getV8Object());
Handle<Value> dReturnVal =
ExecuteJavascriptString(
*localcontext.getV8Object(),
dSource, "POSNode::Hooks");
String::AsciiValue
dReturnStr(dReturnVal);
wp->SetPredicateString(*dReturnStr);
}
else
{
throw(exception("No hooks found"));
}
}
catch (exception e)
{
wp->SetPredicateString("AND[VALUE1:" +
wp->ToString(false) + "/VALUE2:" +
wpOnEntrance + "]");
}
}
}
if ((wp.get() != NULL) && (!wp->HasAbort()) &&
(wp->GetPrimitive() != CPredicate::UNSET))
{
AddPredicate(wp, (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating));
}
}
break;
}
}
}
}
else
{
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> dNewPredicate(new CPredicate());
bool executed = false;
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> res =
CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(m_context,
GetSpelling(), dNewPredicate, this, executed, m_curCycle);
if (!((res.get() == NULL) || (res->HasAbort())))
{
AddPredicate(res, (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating));
}
}
m_curCycle = eNotCalculating;
}
}
catch (exception e)
{
m_predicates.clear();
if ((DigitalConceptBuilder::GetCurCalculationContext()->FailureReason()) ||
(DigitalConceptBuilder::GetCurCalculationContext()->GetJavascriptTrace()))
{
printf("FAILURE REASON: Exception: %s.\n", e.what());
}
}
g_nodeContext.pop();
m_curCycle = keepCycle;
if ((m_predicates.size() > 0) && (m_curCycle == eNotCalculating))
{
m_analyzed = true;
}
if ((m_predicates.size() > 0) && (m_curCycle != eNotCalculating))
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> dReturn = m_predicates;
m_predicates.clear();
return dReturn;
}
return m_predicates;
}
C++ 和 JavaScript 之间
虽然本文的目的不是详细介绍 Google V8,并且关于该主题有其他文档来源,但这里简要概述了该项目中的 JavaScript 集成。
上面流程图中以绿色显示的步骤是能够桥接到 JavaScript 的步骤。为了使算法在谓词构建方面尽可能可扩展,并避免需要 C++ 知识来填充概念词典,JavaScript 是选定的语言。Google V8 是用于公开两个类:POSNode 和 CPredicate 的 JavaScript 引擎。
需要桥接到 JavaScript 的每个类都继承自 JSObjectSupport 模板。这种方法以独立于类本身的方式实现了通用的 JavaScript 服务。
template <class T> class JSObjectSupport
{
public:
JSObjectSupport();
Handle<Object> CreateJavascriptInstance();
void SetToJavascriptVariable(Handle<Context> context,
string variableName);
static T* GetJavascriptVariable(
Persistent<Context> context,
string variableName);
static void JavascriptSetup();
protected:
static bool m_setUpDone;
static Handle<FunctionTemplate> m_node_templ;
static Handle<ObjectTemplate> m_node_proto;
static Handle<ObjectTemplate> m_node_inst;
};
使用 JavascriptSetup() 的模板特化来设置所需的 JavaScript 服务。以下是 POSNode 和 CPredicate 的实现:
template <> void JSObjectSupport<POSNode>::JavascriptSetup()
{
m_setUpDone = true;
m_node_templ = FunctionTemplate::New();
m_node_templ->SetClassName(String::New("POSNode"));
m_node_proto = m_node_templ->PrototypeTemplate();
m_node_proto->Set("navigate", FunctionTemplate::New(JSNavigate));
m_node_proto->Set("debug", FunctionTemplate::New(JSBreak));
m_node_proto->Set("addInitializer",
FunctionTemplate::New(JSAddInitializer));
m_node_proto->Set("toPredicate",
FunctionTemplate::New(JSToPredicate));
m_node_proto->Set("trace", FunctionTemplate::New(JSNodeTracing));
m_node_inst = m_node_templ->InstanceTemplate();
m_node_inst->SetInternalFieldCount(1);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("constructionLine"),
JSGetConstructionLine, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("spelling"), JSGetSpelling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("data"), JSGetData, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("posType"), JSGetPOSType, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("wordIndex"), JSGetWordIndex, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("parent"), JSGetParent, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eSibling"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eSibling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eSiblingLeft"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eSiblingLeft, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eSiblingRight"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eSiblingRight, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eFirstSibling"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eFirstSibling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eLastSibling"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eLastSibling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eNextSibling"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eNextSibling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("ePreviousSibling"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_ePreviousSibling, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eAncestre"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eAncestre, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eParent"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eParent, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eTopParent"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eTopParent, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eChild"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eChild, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eFirstChild"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eFirstChild, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eLastChild"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eLastChild, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eDescendant"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eDescendant, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("ePreviousWord"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_ePreviousWord, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eNextWord"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eNextWord, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eFirstWord"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eFirstWord, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("eLastWord"),
JSPOSNodeEnum_eLastWord, NULL);
}
template <> void JSObjectSupport<CPredicate>::JavascriptSetup()
{
m_setUpDone = true;
m_node_templ = FunctionTemplate::New();
m_node_templ->SetClassName(String::New("Predicate"));
m_node_proto = m_node_templ->PrototypeTemplate();
m_node_proto->Set("setRoleFillerPair",
FunctionTemplate::New(JSSetRoleFillerPair));
m_node_proto->Set("replaceAll", FunctionTemplate::New(JSReplaceAll));
m_node_proto->Set("initialized", FunctionTemplate::New(JSIsInitialized));
m_node_proto->Set("setPredicate", FunctionTemplate::New(JSSetPredicate));
m_node_proto->Set("is", FunctionTemplate::New(JSIsA));
m_node_proto->Set("has", FunctionTemplate::New(JSHas));
m_node_proto->Set("search", FunctionTemplate::New(JSSearch));
m_node_proto->Set("abort", FunctionTemplate::New(JSAbort));
m_node_proto->Set("trace", FunctionTemplate::New(JSPredicateTracing));
m_node_proto->Set("getRole", FunctionTemplate::New(JSGetRole));
m_node_proto->Set("getFiller", FunctionTemplate::New(JSGetFiller));
m_node_proto->Set("getVariable", FunctionTemplate::New(JSGetVariable));
m_node_proto->Set("setVariable", FunctionTemplate::New(JSSetVariable));
m_node_proto->Set("setRoleOperation",
FunctionTemplate::New(JSSetRoleOperation));
m_node_inst = m_node_templ->InstanceTemplate();
m_node_inst->SetInternalFieldCount(1);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("desc"), JSGetDesc, NULL);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("primitive"),
JSGetPrimitive, JSSetPrimitive);
m_node_inst->SetAccessor(String::New("output"), JSGetOutput, NULL);
}
一些不与任何对象关联的通用 C++ 入口点也在 JSObjectSupport::InitJavascriptGlobal 中实现。
void InitJavascriptGlobal()
{
if (global.IsEmpty())
{
global = v8::ObjectTemplate::New();
global->Set(String::New("alert"), FunctionTemplate::New(JSAlert));
global->Set(String::New("print"), FunctionTemplate::New(JSPrint));
global->Set(String::New("new_predicate"),
FunctionTemplate::New(JSNewPredicate));
global->Set(String::New("setResultPredicate"),
FunctionTemplate::New(JSSetResultPredicate));
global->Set(String::New("getResultPredicate"),
FunctionTemplate::New(JSGetResultPredicate));
}
}
概念词典
语法到概念的转换是如何完成的?这是概念词典的责任,它保存所有三个可以调用的脚本级别,并且它们协同工作以构建有效的谓词。让我们先看一些谓词生成器脚本的例子。
switch (curNode.posType)
{
case "VERB":
case "AUX":
{
if (curPredicate.initialized())
{
// "Is X Y" is comparing 2 objects of knowledge
// if both X and Y are the same part-of-speech.
// For example, "Is a turtle an animal?", both are NOUN-PHRASE.
// Or, "Is eating chewing?", both are VERB-PHRASE.
dNextNode = curNode.navigate(curNode.eNextSibling);
if (dNextNode != 0)
{
dOtherNode = dNextNode.navigate(curNode.eNextSibling);
if (dOtherNode != 0)
{
if ((dNextNode.toPredicate() != 0) &&
(dOtherNode.toPredicate() != 0))
{
curPredicate.setPredicate("DO[OPERATION:IS/VALUE1:" +
dNextNode.toPredicate().desc + "/VALUE2:" +
dOtherNode.toPredicate().desc+"]");
break;
}
}
}
if (curNode.posType == "VERB")
{
// "X is Y" is a unifier in this case if both X and Y are the
// same part-of speech.
curPredicate.setPredicate(
"DO[OPERATION:UNION/VALUE:" + curPredicate.desc+"]");
}
}
}
break;
}
对于单词“is”的概念定义,我们观察到,除非 curPredicate.initialized() 返回 true,否则不会执行任何操作。这意味着“is”不能产生知识对象。对于计算本文提供的测试用例,定义了两种语法变体:“X is Y”和“Is Y X”。显然,英语语言中“is”这个词的多样性比脚本中的要多,而当前的概念定义在其能实现的功能上是有限的,但可以通过此介质观察可用的可扩展性。
switch (curNode.posType)
{
case "NOUN":
if (!curPredicate.initialized())
{
curNode.addInitializer(
"PP[TYPE:VEHICLE/CLASS:CAR/WHEELCOUNT:4/QUANTITY:1]");
}
else if (curPredicate.primitive == "PP")
{
curPredicate.setPredicate("DO[OPERATION:UNION/OBJECT:" +
curPredicate.desc +
"/VALUE:PP[TYPE:VEHICLE/CLASS:CAR/WHEELCOUNT:4/QUANTITY:1]]");
}
else
{
curPredicate.abort();
}
break;
}
在“car”的概念定义中,我们可以看到“car”可以作为知识对象出现。但是,“car”这个词也可以完成一个已存在的知识对象,如果它具有相同的原语(PP),在这种情况下,它会将两个谓词统一到一个相同的谓词下(例如,“a red car”——一个 PP 是红色的,也是一辆车)。
通过这些简单的概念定义,可以将简单的语法结构转换为概念。例如,位于单词“is”的谓词生成器脚本中的 navigate 方法对于成功的实现至关重要。它允许在所有方向(兄弟、子节点、父节点)上导航 POSNode。概念性地定义一个单词有很多与导航节点和从不同来源捕获表示一部分有关。这与用于从语法重构概念的认知过程兼容。也就是说,单词本身不是概念,但它们是构建概念的关键元素,只有当它们与其他单词建立关系时,概念才会产生。
如 CPredicate::PerformConceptualAnalysis 中所示,对于从语法分析生成的有针对性词性的所有语法排列,或者直到计算出的谓词不再模糊,都会重复相同的过程。下一节将进一步介绍...
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> CPredicate::PerformConceptualAnalysis(
Persistent<Context> context, shared_auto_ptr<POSList> dList)
{
bool continueProcessing = true;
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> dEmpty;
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->SetResultPredicate(dEmpty);
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> dReturn;
vector<shared_auto_ptr<POSNode>> dSentences =
dList->AccumulateAll(POSNode::Construct(FormattedString("[%s]",
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetTargetPOS().GetDescriptor().c_str())),
POSNode::eSortLargestToSmallestNode);
for (unsigned int i = 0; ((i < dSentences.size()) &&
((int)i < DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetMaxConceptualAnalysis())); i++)
{
CPredicate::m_permutationCount = (i + 1);
ExecuteJavascriptString(context,
FormattedString("curSequence = '%s:%d';",
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetId().c_str(), (i+1)),
"DigitalConceptBuilder::PerformConceptualAnalysis");
JSTrace::globTrace.SetSyntacticContext(
dSentences[i]->GetSpelling(2));
if ((DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->OutputSyntaxPermutations()) ||
(DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetTransformLine()))
{
if (i == 0)
{
printf("\n");
}
printf("%s:%d. %s\n",
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetId().c_str(),
i+1, dSentences[i]->GetSpelling(2).c_str());
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetTransformLine())
{
printf("\n");
dSentences[i]->OutputTransformLineInfo();
printf("\n");
}
}
string dId = FormattedString("%s:%d",
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetId().c_str(), i+1);
// Set-up so that parents are linked
// by children (this is transient)...
dSentences[i]->UpdateNodesCount();
dSentences[i]->ManageTransientParents(context);
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> result =
dSentences[i]->BuildPredicates();
bool hadPredicates = (result.size() > 0);
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->OutputPredicates())
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < result.size(); j++)
{
printf("\n");
printf(result[j]->ToString(true).c_str());
printf("\n");
if (j == (result.size() - 1))
{
printf("\n");
}
}
}
for (unsigned int k = 0;
k < DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetPostProcessing().size(); k++)
{
vector<shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate>> postResult;
// Perform post-processing here...
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < result.size(); j++)
{
bool executed = false;
result[j]->ClearAbort();
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> dNewPredicate =
result[j]->ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(context,
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetPostProcessing()[k],
result[j],
dSentences[i],
executed,
eCalculatingPostProcessing);
if ((executed) && (dNewPredicate.get() != NULL) &&
(!dNewPredicate->HasAbort()))
{
result[j] = dNewPredicate;
postResult.push_back(dNewPredicate);
}
}
result = postResult;
}
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->OutputPredicates())
{
if (result.size() > 0)
{
printf("%d valid predicate%s following post-processing:\n",
result.size(), (result.size() > 1)?"s":"");
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < result.size(); j++)
{
printf("\n");
printf(result[j]->ToString(true).c_str());
printf("\n");
if (j == (result.size() - 1))
{
printf("\n");
}
}
}
else if (hadPredicates)
{
printf("Post-processing rejected all predicates.\n\n");
}
}
for (unsigned int j = 0; ((j < result.size()) &&
(continueProcessing)); j++)
{
CPredicate::Disambiguate(context, dReturn,
result[j], continueProcessing);
}
if ((!continueProcessing) ||
((DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetMaxSyntaxPermutations() != -1) &&
(CPredicate::m_permutationCount >=
DigitalConceptBuilder::
GetCurCalculationContext()->GetMaxSyntaxPermutations())))
{
break;
}
}
if (DigitalConceptBuilder::GetCurCalculationContext()->GetFeedback() != "")
{
shared_auto_ptr<CPredicate> workingPredicate;
shared_auto_ptr<POSNode> curNode;
bool executed = false;
CPredicate::ExecutePredicateBuilderScript(context,
DigitalConceptBuilder::GetCurCalculationContext()->GetFeedback(),
workingPredicate, curNode, executed, eFeedback);
}
m_fileCache.Clear();
return dReturn;
}
消歧
CLUE 具有迭代性的主要原因是语言固有的模糊性。从概念上讲,一串单词可以代表不同的概念。大多数语言处理都与消歧有关;处理过程的哪个部分执行消歧决定了该处理的准确性。在 CLUE 中,假设这种消歧最终必须在概念级别上针对已确定有效且相互竞争的概念执行。
以我们拥有的简单测试用例为例。其中大部分是问题。当提出一个可以导致“是”、“否”或“也许”的答案的问题时,人通常会以最高可能的值(是 > 也许 > 否)来回应。这就是为什么在回答审问时自然会倾向于说“是的,但只有在满足该条件的情况下”。答案是最高可能的结果,然后是满足该结果的条件。消歧过程评估响应,一旦遇到最高可能响应——“是”——它就会停止评估并产生反馈。如果消歧过程无法产生“是”的概念,它会选择在处理过程中遇到的最高概念。
这种逻辑在 Conceptual Analysis/Disambiguation/Interrogation.js 文件中的 JavaScript 中执行。没有什么能阻止该过程具有多样化的消歧,而不仅仅限于审问。例如,概念的纯粹性也是一个重要因素。也就是说,为了接受新概念,需要对其他已获得的概念进行多少适应?如果有人说:“我真的是一个来自水下的外星人”,最初的反应可能是这个人疯了,想到了小绿人以及水下亚特兰蒂斯。这需要对已有的概念网络进行太多适应才能同化这个新概念,因此同化“这个人疯了”的概念最终会成为互动的良好折衷。但是,如果同一个人继续说:“我的意思是,我真的是一个非法外来者,已经通过水路越境”,那就没问题了。接受这个新概念不需要进一步适应现有概念。第二个概念比第一个更纯粹。对航空公司响应系统的问题也是如此,例如:“634 次航班的状态是什么?”如果不存在 634 次航班,但有 600 次和 34 次航班,则问题很可能与这两个航班有关。查询的接收者(无论是自动的还是非自动的)都假定查询是关于有意义的事物,这也是消歧过程的一部分。
if (curPredicate.is("DO[ACTION:RECEIVEINPUT/MOOD:INTEROGATIVE/" +
"OBJECT:DO[OPERATION:IS/VALUE1:{VALUE1}/VALUE2:{VALUE2}]]") == "YES")
{
var dNewPredicate = new_predicate();
dNewPredicate.setPredicate(curPredicate.getVariable("VALUE1"));
if (dNewPredicate.initialized())
{
var thisResult = dNewPredicate.is(curPredicate.getVariable("VALUE2"));
curPredicate.setVariable("ISTESTRESULT", thisResult);
if (thisResult == "YES")
{
curPredicate.abort();
setResultPredicate(curPredicate);
}
else if (getResultPredicate() != 0)
{
if ((getResultPredicate().getVariable("ISTESTRESULT") == "NO")
&& (thisResult == "MAYBE"))
{
setResultPredicate(curPredicate);
}
}
else
{
setResultPredicate(curPredicate);
}
}
else
{
curPredicate.abort();
}
}
else if (getResultPredicate() == 0)
{
setResultPredicate(curPredicate);
}
反馈
最后,承认了一个查询并不意味着可以为该查询制定响应。例如,查询:“生命的意义是什么?”可以轻松识别,但这并不意味着我们可以制定一个可接受的响应。响应生成是反馈 JavaScript 的责任,用于将明确识别的概念转换为响应。响应不一定是我们现在看到的 DOS 输出,它也可以是数据库插入、文本转语音声音的播放,或者其他什么。或者,它甚至可以是所有这些的组合。因为我们处理的是概念,所以我们不必将自己限制在一种响应类型上。诸如“在航班 634 到达前 30 分钟给我打电话,电话号码是 555-1212”之类的陈述,可以生成一个表示在给定相对时间进行的呼叫的数据库插入。
var reproduced = false;
var dPredicate = getResultPredicate();
if (dPredicate != 0)
{
if (dPredicate.getVariable("ISTESTRESULT") != 0)
{
print("\n" + dPredicate.getVariable("ISTESTRESULT") + ":\n\n");
print(dPredicate.output);
print("\n");
reproduced = true;
}
}
if (!reproduced)
{
print("\nNo inquiry to analyze here:\n\n");
print(dPredicate.output);
print("\n");
}
关注点
这种方法将自然语言理解提升到了一个新的水平。它允许自然语言理解以一种根据原始输入重构概念的方式发生。此外,它允许在灵活的自然语言输入的结果下进行概念操作。
如果我们这一代人有足够的远见将技术革命再提升一个台阶,我们可以构建一个真正模拟我们思维的计算机系统。我坚信,在我们获得技术革命的第二阶段之前,我们需要让我们的计算机去上语法和哲学课。
目前,限制这种方法的主要困难是需要生产一个足够完整的概念词典。考虑到制作传统词典所需的人年,这是可以预期的。然而,即使是像飞行响应系统这样的小型领域特定词典(例如,1000 个单词)也需要很少的努力来生产。
但是,让我们想象一下。要相对流利地掌握英语,需要一个合理的子集,大约是 50,000 个单词。如果 10 位语言学家每天创作 10 个单词,每年 200 天,那么他们需要两年半的时间才能对 50,000 个单词进行概念定义。
在我的下一篇文章中,我打算构建一个有限领域的词汇来展示 CLUE 的实际实现。该词汇应概念性地定义多达 1000 个单词,并提供交互示例,用于从电子邮件中提取会议相关信息。之后的下一篇文章将呈现类似的内容,但这次使用语音(音频)作为输入。为了实现这一点,我打算使用 SPHINX 或 ISIP 作为语音引擎,然后将 N-Best HMM 算法生成的点阵连接到概念语音识别处理器,以产生我们在本文中看到的类型结果。这以前已经完成过,但为了提供与本文相当的独立文章,需要进行一些返工。为此,使用语音作为输入的文章将需要大量的精力来制作,因为它涉及到连接到语音识别引擎。因此,如果社区中有人对 Sphinx 或 ISIP 的语音引擎有经验,并愿意与我合著这篇文章,请发送消息供审议。
其他许可说明
请随意在您的工作中引用此技术和代码;但是,请注意,存在有限的许可;该许可排除了未经作者事先授权的商业和商业非营利性部署。有关完整的许可协议,请参阅附件中的 license.txt 或 license.pdf。
历史
- 2010 年 1 月 7 日:本文初稿撰写完成。
