在 Python 中构建森林系列:红黑树
5.00/5 (3投票s)
使用 Python 构建红黑树。
本文继续《在 Python 中构建森林系列》。从《二叉搜索树:分析》中,我们知道树的高度是二叉搜索树性能的关键因素。本文和后续文章将实现一种二叉搜索树的变体,它将使树保持平衡:红黑树。
项目设置
遵循《在系列中构建森林》中其他文章的相同风格和假设,实现假定 Python 3.9 或更高版本。本文为我们的项目添加了两个模块:用于红黑树实现的 red_black_tree.py 和用于其单元测试的 test_red_black_tree.py。添加这两个文件后,我们的项目布局如下
forest-python
├── forest
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── binary_trees
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── binary_search_tree.py
│ │ ├── double_threaded_binary_tree.py
│ │ ├── red_black_tree.py
│ │ ├── single_threaded_binary_trees.py
│ │ └── traversal.py
│ └── tree_exceptions.py
└── tests
├── __init__.py
├── conftest.py
├── test_binary_search_tree.py
├── test_double_threaded_binary_tree.py
├── test_red_black_tree.py
├── test_single_threaded_binary_trees.py
└── test_traversal.py
(完整代码可在 forest-python 获取。)
什么是红黑树?
红黑树是具有自平衡能力的二叉搜索树的变体,其节点具有一个额外的属性:color,可以是红色或黑色。除了二叉搜索树属性外,红黑树还满足以下红黑树属性
- 每个节点都是红色或黑色。
- 根是黑色的。
- 每个叶子都是黑色的。
- 如果一个节点是红色的,那么它的两个子节点都是黑色的。
- 从每个节点到叶子的所有路径包含相同数量的黑色节点。
红黑树通过限制从节点到其后代叶子的任何简单路径上的节点颜色来确保没有一条路径比其他路径长两倍。换句话说,红黑树近似平衡。
典型的红黑树如下图所示

树数据结构的叶节点通常指没有任何子节点的节点。然而,我们使用 NIL 来表示红黑树的叶子,它们总是黑色的。此外,叶节点不包含任何数据,主要用于维护红黑树属性。
我们使用**黑高**来表示从节点到叶子的黑色节点数量(如果节点是黑色的则不包括节点)。下图显示了每个节点的黑高。

每个节点旁边是该节点的黑高,叶节点(NIL)的黑高为零。
构建红黑树
与我们之前实现的树一样,本节将详细介绍实现并讨论实现选择背后的一些想法。
由于所有叶子都是 NIL 并且根的父节点也可以指向 NIL,因此当我们实现红黑树时,我们可以定义一个 NIL 节点,并让根的父节点和所有支持指向 NIL 节点的节点指向该 NIL 节点。因此,上一节中所示的红黑树变为以下形式

这种方式简化了实现并节省了空间(即,实现中只需要一个 NIL 节点实例)。
为简单起见,本文其余部分将省略 NIL 节点,因此上面的红黑树将如下所示(但在实现中,NIL 节点必须存在;否则,它将违反红黑树属性)。

节点
红黑树节点与二叉搜索树节点类似,但多了一个属性——color。

由于 color 必须是红色或黑色,我们可以将其定义为一个 枚举 类。
import enum
class Color(enum.Enum):
RED = enum.auto()
BLACK = enum.auto()
为什么要使用枚举?
根据 PEP-435,“枚举是一组绑定到唯一、常量值的符号名称。在枚举中,值可以通过身份进行比较,并且枚举本身可以进行迭代。” 将颜色属性定义为 enum 类是合理的,因为其值(红色或黑色)是常量,我们可以识别颜色属性并进行比较。此外,enum 类提供了更强大的类型安全性。如果我们不使用 enum,我们可以将颜色属性定义为常量字符串。但是,类型检查工具(例如 mypy)将无法检查某个值是 color 属性还是普通字符串。另一种替代方案是将 color 属性定义为普通类或数据类,如下所示
@dataclass
class Color:
RED: str = "red"
BLACK: str = "black"
这种方法仍然存在一些缺点。例如,底层类型仍然是 string。我们可以将其与任何 strings 进行比较。此外,类是可变的。换句话说,我们可以在运行时修改 Color 类,这与颜色的定义相矛盾。因此,使用 enum 定义 color 属性最有意义。它增加了类型安全性并简化了实现。
红黑树节点
像其他二叉树节点一样,我们利用 dataclass 来定义红黑树节点。
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Node:
"""Red-Black Tree non-leaf node definition."""
key: Any
data: Any
left: Union["Node", Leaf] = Leaf()
right: Union["Node", Leaf] = Leaf()
parent: Union["Node", Leaf] = Leaf()
color: Color = Color.RED
叶节点
如红黑树定义中所述,我们使用 NIL 来表示叶节点,它可以通过以下方式简单定义
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Leaf:
color = Color.BLACK
类概述
与“构建森林”项目中的其他类型的二叉树一样,红黑树类具有类似的功能。
class RBTree:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self._NIL: Leaf = Leaf()
self.root: Union[Node, Leaf] = self._NIL
def __repr__(self) -> str:
"""Provie the tree representation to visualize its layout."""
if (self.root is None) or (self.root == self._NIL):
return "empty tree"
return (
f"{type(self)}, root={self.root}, "
f"tree_height={str(self.get_height(self.root))}"
)
def search(self, key: Any) -> Optional[Node]:
…
def insert(self, key: Any, data: Any) -> None:
…
def delete(self, key: Any) -> None:
…
@staticmethod
def get_leftmost(node: Node) -> Node:
…
@staticmethod
def get_rightmost(node: Node) -> Node:
…
@staticmethod
def get_successor(node: Node) -> Union[Node, Leaf]:
…
@staticmethod
def get_predecessor(node: Node) -> Union[Node, Leaf]:
…
@staticmethod
def get_height(node: Union[Leaf, Node]) -> int:
…
def inorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
…
def preorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
…
def postorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
…
def _transplant(
self, deleting_node: Node, replacing_node: Union[Node, Leaf]
) -> None:
…
def _left_rotate(self, node_x: Node) -> None:
…
def _right_rotate(self, node_x: Node) -> None:
…
def _insert_fixup(self, fixing_node: Node) -> None:
…
def _delete_fixup(self, fixing_node: Union[Leaf, Node]) -> None:
…
请注意,除了所有二叉树的常用方法外,RBTree 类还具有一些额外的方法。_left_rotate()、_right_rotate()、_insert_fixup() 和 _delete_fixup() 是在插入和删除后维护红黑树属性的辅助函数。insert 和 delete 操作都会修改树;因此,这些操作可能会违反红黑树属性。这就是我们需要这些函数的原因。
叶节点是 NIL,因此来自《二叉树遍历》的遍历例程(使用 None 判断是否到达叶节点)不适用于 RBTree 类(需要使用 Leaf 判断是否到达叶节点)。因此,RBTree 类需要提供其遍历例程。
Insert
因为 insert 操作会修改红黑树,所以结果可能会违反红黑树属性(删除操作也是如此)。为了恢复红黑树属性,我们需要改变一些节点的颜色并更新红黑树的结构。更新二叉树结构的方法称为旋转。修复被违反的红黑树属性的技术来自《算法导论》,红黑树插入的思想可以概括为以下几点
- 以与二叉搜索树插入相同的方式插入颜色为红色的新节点:通过从根遍历树并比较新节点的键与沿途每个节点的键来找到插入新节点的正确位置(即新节点的父节点)。
- 通过旋转和着色修复被破坏的红黑树属性。
由于新节点是红色的,我们可能会违反红黑树属性——如果一个节点是红色的,那么它的两个子节点都是黑色的,我们可以在插入后修复这种违反。
我们可以用类似于普通二叉搜索树插入的方式来实现红黑树的插入。
def insert(self, key: Any, data: Any) -> None:
# Color the new node as red.
new_node = Node(key=key, data=data, color=Color.RED)
parent: Union[Node, Leaf] = self._NIL
current: Union[Node, Leaf] = self.root
while isinstance(current, Node): # Look for the insert location
parent = current
if new_node.key < current.key:
current = current.left
elif new_node.key > current.key:
current = current.right
else:
raise tree_exceptions.DuplicateKeyError(key=new_node.key)
new_node.parent = parent
# If the parent is a Leaf, set the new node to be the root.
if isinstance(parent, Leaf):
new_node.color = Color.BLACK
self.root = new_node
else:
if new_node.key < parent.key:
parent.left = new_node
else:
parent.right = new_node
# After the insertion, fix the broken red-black-tree-property.
self._insert_fixup(new_node)
与二叉搜索树的一个不同之处在于,我们使用 isinstance 来检查节点是普通 Node 还是 Leaf,而不是检查它是否为 None。这是因为我们有用于叶节点的 Leaf 类型和用于普通节点的 Node 类型。
一旦新节点插入到红黑树中,我们需要修复被破坏的红黑树属性。以下小节将讨论如何使用旋转和着色来修复被破坏的红黑树。
旋转
旋转操作旨在改变红黑树的结构,同时保持其二叉搜索属性。旋转有两种类型:左旋和右旋。
左旋

左旋将两个节点(图中 x 和 y)从上方的树转移到下方的树中,并保留其二叉搜索树属性。
def _left_rotate(self, node_x: Node) -> None:
node_y = node_x.right # Set node y
if isinstance(node_y, Leaf): # Node y cannot be a Leaf
raise RuntimeError("Invalid left rotate")
# Turn node y's subtree into node x's subtree
node_x.right = node_y.left
if isinstance(node_y.left, Node):
node_y.left.parent = node_x
node_y.parent = node_x.parent
# If node's parent is a Leaf, node y becomes the new root.
if isinstance(node_x.parent, Leaf):
self.root = node_y
# Otherwise, update node x's parent.
elif node_x == node_x.parent.left:
node_x.parent.left = node_y
else:
node_x.parent.right = node_y
node_y.left = node_x
node_x.parent = node_y
注意,节点 x 的右子节点不能是 Leaf(即 NIL);旋转 Leaf 没有意义。
右旋

右旋与左旋对称,可以按以下方式实现
def _right_rotate(self, node_x: Node) -> None:
node_y = node_x.left # Set node y
if isinstance(node_y, Leaf): # Node y cannot be a Leaf
raise RuntimeError("Invalid right rotate")
# Turn node y's subtree into node x's subtree
node_x.left = node_y.right
if isinstance(node_y.right, Node):
node_y.right.parent = node_x
node_y.parent = node_x.parent
# If node's parent is a Leaf, node y becomes the new root.
if isinstance(node_x.parent, Leaf):
self.root = node_y
# Otherwise, update node x's parent.
elif node_x == node_x.parent.right:
node_x.parent.right = node_y
else:
node_x.parent.left = node_y
node_y.right = node_x
node_x.parent = node_y
修复
为了恢复红黑树属性,我们需要知道在插入后哪些红黑树属性可能会被破坏。
红黑树属性
- 每个节点都是红色或黑色(**不能被破坏**)。
- 根是黑色的。
- 每个叶子都是黑色的(**不能被破坏,因为每个新节点的子节点都指向
Leaf**)。 - 如果一个节点是红色的,那么它的两个子节点都是黑色的。
- 从每个节点到叶子的所有路径包含相同数量的黑色节点(又称黑高)。
对于第 5 个属性,黑高仍然相同。新节点(红色)替换了一个 Leaf(NIL),但它的子节点也是 Leaf(NIL)。因此,插入后黑高属性仍然成立。
因此,由于新节点的颜色是红色,只有属性 2 和属性 4 可能被违反。如果新节点的父节点也是红色,则属性 4 被破坏。关于属性 2,如果新节点是根节点或者根节点在修复属性 4 时变为红色,则可能被违反。我们可以在修复例程结束时将根节点着色为黑色来修复属性 2。
关于修复属性 4,我们可以将其分解为六种情况(两种三种情况对称)。这六种情况由新节点的父节点及其兄弟节点的位置和颜色决定。
| 新节点的父节点位置 | 新节点父节点的兄弟节点的颜色 | 新节点位置 | |
| 案例 1 | 左子节点 | 红色 | 无关紧要 |
| 案例 2 | 左子节点 | 黑色 | 右子节点 |
| 案例 3 | 左子节点 | 黑色 | 左子节点 |
| 案例 4 | 右子节点 | 红色 | 无关紧要 |
| 案例 5 | 右子节点 | 黑色 | 左子节点 |
| 案例 6 | 右子节点 | 黑色 | 右子节点 |
从新节点(fixing_node)开始。
案例 1
- 将
fixing_node的父节点和父节点的兄弟节点的颜色更改为**黑色**。 - 将
fixing_node的祖父节点的颜色更改为**红色**。 - 将当前位置移动到
fixing_node的祖父节点。
注意,新节点的位置无关紧要。下图展示了情况 1:新节点 (7) 是左子节点,以及情况 2:新节点 (18) 是右子节点。

案例 2
- 对
fixing_node的父节点执行**左旋**操作(此操作将**情况 2 转换为情况 3**)。

案例 3
- 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色改为**黑色** - 将
fixing_node的祖父节点颜色改为**红色** - 对
fixing_node的祖父节点执行**右旋**操作

案例 4(与案例 1 相同)
- 将
fixing_node的父节点和父节点的兄弟节点的颜色更改为**黑色** - 将
fixing_node的祖父节点颜色改为**红色** - 将当前位置移动到
fixing_node的祖父节点

案例 5
- 对
fixing_node的父节点执行**右旋**操作(此操作将**情况 5 转换为情况 6**)。

案例 6
- 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色改为**黑色**。 - 将
fixing_node的祖父节点的颜色更改为**红色**。

在修复 fixing_node 的红黑树属性时,修复过程可能会导致 fixing_node 的父节点或祖父节点(取决于情况)违反红黑树属性。当这种情况发生时,fixing_node 的父节点(或祖父节点)成为新的 fixing_node。然后我们可以根据这六种情况来解决它。重复此步骤,直到我们到达根节点。如果在修复操作后根节点变为红色(属性 2 被违反),我们可以通过将根节点着色为黑色来修复它。
下图展示了构建红黑树的完整插入操作。

插入修复的实现如下所示
def _insert_fixup(self, fixing_node: Node) -> None:
while fixing_node.parent.color == Color.RED:
if fixing_node.parent == fixing_node.parent.parent.left:
parent_sibling = fixing_node.parent.parent.right
if parent_sibling.color == Color.RED: # Case 1
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
parent_sibling.color = Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.parent.color = Color.RED
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent.parent
else:
# Case 2
if fixing_node == fixing_node.parent.right:
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent
self._left_rotate(fixing_node)
# Case 3
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.parent.color = Color.RED
self._right_rotate(fixing_node.parent.parent)
else:
parent_sibling = fixing_node.parent.parent.left
if parent_sibling.color == Color.RED: # Case 4
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
parent_sibling.color = Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.parent.color = Color.RED
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent.parent
else:
# Case 5
if fixing_node == fixing_node.parent.left:
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent
self._right_rotate(fixing_node)
# Case 6
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.parent.color = Color.RED
self._left_rotate(fixing_node.parent.parent)
self.root.color = Color.BLACK
搜索
搜索操作类似于二叉搜索树,但我们使用 Leaf(NIL)来判断是否到达叶子。
- 从根节点开始遍历树,并比较键与沿树遍历的每个节点的键。
- 如果键匹配,则找到了该节点。
- 如果到达
Leaf,则树中不存在该节点。
搜索的实现类似于二叉搜索树的 search 函数。
def search(self, key: Any) -> Optional[Node]:
current = self.root
while isinstance(current, Node):
if key < current.key:
current = current.left
elif key > current.key:
current = current.right
else: # Key found
return current
# If the tree is empty (i.e., self.root == Leaf()), still return None.
return None
删除
与红黑树插入类似,删除操作会修改红黑树,结果可能会违反红黑树属性。因此,在删除节点后,我们需要恢复红黑树属性。
红黑树删除的基本思想与普通二叉搜索树类似。我们有一个 transplant 方法来用以 replacing_node 为根的子树替换以 deleting_node 为根的子树。我们还有三种基本的删除情况:没有子节点、只有一个子节点和有两个子节点。最后,我们需要修复被破坏的红黑树属性。
移植
transplant 方法是在 二叉搜索树 的基础上修改的,因此它适用于红黑树。修改之处在于我们使用 isinstance 来检查节点是普通 Node 还是 Leaf,而不是检查它是否为 None。
def _transplant(
self, deleting_node: Node, replacing_node: Union[Node, Leaf]
) -> None:
if isinstance(deleting_node.parent, Leaf):
self.root = replacing_node
elif deleting_node == deleting_node.parent.left:
deleting_node.parent.left = replacing_node
else:
deleting_node.parent.right = replacing_node
if isinstance(replacing_node, Node):
replacing_node.parent = deleting_node.parent
整个 delete 过程类似于普通二叉搜索树,但有一些修改。
- 找到要删除的
node(deleting_node)。 - 保留
deleting_node的color。 - 如果
deleting_node没有或只有一个子节点,则使用transplant方法将deleting_node替换为NIL或唯一的子节点。 - 如果
deleting_node有两个子节点,则找到deleting_node的后继作为replacing_node。保留replacing_node的颜色。使用transplant方法取出replacing_node,并继续跟踪要替换replacing_node的节点,可以是NIL或replacing_node的原始右子节点。使用transplant方法用replacing_node替换deleting_node。将replacing_node的color设为deleting_node的color。 - 通过改变颜色和执行旋转来修复被破坏的红黑树属性。
基于上面的 delete 过程,我们可以按以下方式实现 delete 方法
def delete(self, key: Any) -> None:
if (deleting_node := self.search(key=key)) and (
not isinstance(deleting_node, Leaf)
):
original_color = deleting_node.color
# Case 1: no children or Case 2a: only one right child
if isinstance(deleting_node.left, Leaf):
replacing_node = deleting_node.right
self._transplant(
deleting_node=deleting_node, replacing_node=replacing_node
)
# Fixup
if original_color == Color.BLACK:
if isinstance(replacing_node, Node):
self._delete_fixup(fixing_node=replacing_node)
# Case 2b: only one left child
elif isinstance(deleting_node.right, Leaf):
replacing_node = deleting_node.left
self._transplant(
deleting_node=deleting_node, replacing_node=replacing_node
)
# Fixup
if original_color == Color.BLACK:
self._delete_fixup(fixing_node=replacing_node)
# Case 3: two children
else:
replacing_node = self.get_leftmost(deleting_node.right)
original_color = replacing_node.color
replacing_replacement = replacing_node.right
# The replacing node is not the direct child of the deleting node
if replacing_node.parent != deleting_node:
self._transplant(replacing_node, replacing_node.right)
replacing_node.right = deleting_node.right
replacing_node.right.parent = replacing_node
self._transplant(deleting_node, replacing_node)
replacing_node.left = deleting_node.left
replacing_node.left.parent = replacing_node
replacing_node.color = deleting_node.color
# Fixup
if original_color == Color.BLACK:
if isinstance(replacing_replacement, Node):
self._delete_fixup(fixing_node=replacing_replacement)
需要提及的是
- 我们保留
deleting_node的原始color(original_color)。 - 如果被删除的节点有两个子节点,我们将
original_color更新为该节点的color(replacing_node)。 - 在每种情况的末尾,如果
original_color是black,则意味着一些红黑树属性被破坏,我们需要修复它们。
在恢复被违反的红黑树属性之前,我们需要知道在删除例程中哪些红黑属性可能会被破坏。
红黑树属性
- 每个节点都是
red或black。 - 根是
black。 - 每个叶子都是
black(不能被破坏,因为每个新节点的子节点都指向Leaf)。 - 如果一个节点是
red,那么它的两个子节点都是black。 - 从每个节点到叶子的所有路径包含相同数量的
black节点(又称black高度)。
情况 1:要删除的节点没有子节点

如果 deleting_node 的颜色是红色,则没有红黑树属性被破坏。如果 deleting_node 的颜色是黑色,则属性 5 被违反。
情况 2:要删除的节点只有一个子节点
由于红黑树属性,红节点不可能只有一个黑子节点。黑节点也不可能只有一个黑子节点。因此,如果 deleting_node 只有一个子节点,则其 color 必须为 black,且 replacing_node 的 color 必须为 red。

根据上图,如果 deleting_node 是 black,则属性 4 和属性 5 可能会被破坏,如果 deleting_node 是根节点,则属性 2 也会被破坏。
情况 3:要删除的节点有两个子节点
在这种情况下,我们执行以下步骤
- 找到最左侧的节点(
replacing_node),作为从deleting_node的右子树中替换deleting_node的节点。 - 通过执行
transplant操作取出replacing_node。 - 将
replacing_node设置为deleting_node的右子树的新根。 - 执行
transplant操作,用以replacing_node为根的子树替换deleting_node。 - 将
replacing_node的颜色着色为deleting_node的颜色
在步骤 5 之后,replacing_node 的颜色与 deleting_node 相同,因此没有红黑树属性被破坏。唯一可能破坏红黑树属性的步骤是步骤 2。当我们对 replacing_node 执行 transplant 操作时,它最终会是情况 1 或情况 2。
以下图片展示了删除一个有两个子节点的节点可能或不可能违反红黑树属性的情况。
replacing_node 是 deleting_node 的直接子节点的情况。
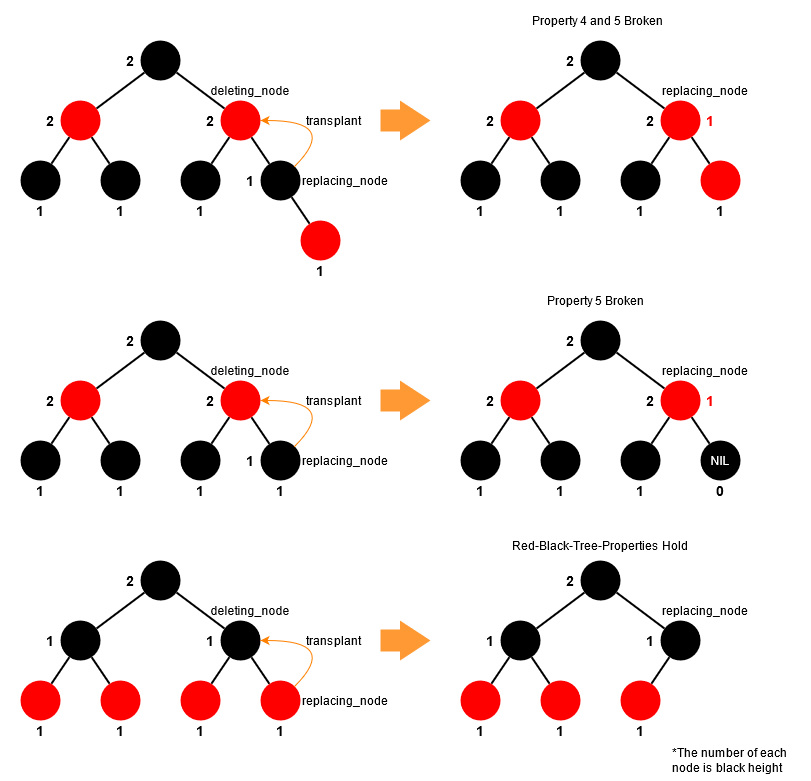
replacing_node 是 black 且不是 deleting_node 的直接子节点的情况。

replacing_node 是红色且不是 deleting_node 的直接子节点的情况。

因此,我们可以总结需要修复被破坏红黑树属性的情况
| 无子节点 | 如果要删除的节点是 |
| 只有一个子节点 | 如果要删除的节点是 |
| 两个子节点 | 如果要替换删除节点的节点(从要删除节点的右子树中最左侧的节点)是 |
该摘要还意味着在以下情况下,红黑树属性仍然成立
- 要删除的节点是
red,并且它少于两个子节点。 - 要删除的节点有两个子节点,并且替换节点是
red。
原因如下
- 黑高不变。属性 5 成立。
- 对于第一种情况,如果要移除的节点是根节点,则它不能是
red;对于第二种情况,最左侧的节点不能是根节点。属性 2 成立。 - 如果节点(第一种或第二种情况)是
red,则它的父节点和子节点(或子节点们)不能是red。因此,移除它或移动它之后,不会出现连续的red节点。属性 4 成立。
修复
为了修复被破坏的红黑树属性,我们借鉴了《算法导论》中的思想,修复过程首先通过引入双黑和红黑的概念来修复属性 5(从节点到叶子的每个节点的黑高都相同)。对于黑高,双黑和红黑分别贡献 2 或 1。我们使用以下图标来表示双黑和红黑节点。

当我们使用 transplant 函数将一个节点替换为另一个节点时,我们不替换节点,而是保留两个节点的颜色,并使用双黑和红黑来表示其颜色。因此,如果待删除的节点少于两个子节点,在 transplant 函数之后,替换节点的 color 变为双黑或红黑。如果待删除的节点有两个子节点,当我们将 transplant 函数用于取出以待删除节点为根的子树的最左侧节点时,最左侧节点的替换节点的颜色变为双黑或红黑。为简单起见,我们使用 fixing_node 来表示其 color 为双黑或红黑的节点。请注意,我们并没有在代码实现中真正将 fixing_node 着色为双黑或红黑。我们只是假装 fixing_node 多了一个黑色或红色。
通过这样做,无效的黑高问题得到解决,潜在的破坏情况变为以下几点
要删除的节点没有子节点。

要删除的节点只有一个子节点。

要删除的节点有两个子节点。
如果要删除的节点有两个子节点,则取代最左侧节点位置的节点会破坏红黑树属性。
replacing_node 是 deleting_node 的直接子节点。

replacing_node 不是 deleting_node 的直接子节点。

因为 fixing_node 的颜色既不是红色也不是黑色,所以属性 1 也被破坏。现在,我们需要恢复红黑树属性 1、2 和 4。
如果 fixing_node 的颜色是红黑,我们可以通过将其着色为 black 来修复它。所有被破坏的红黑树属性都将恢复。


剩下的被破坏情况是双 black。其修复过程可以分解为四个对称情况。

这些情况由 fixing_node 的位置、fixing_node 的兄弟节点的颜色以及兄弟节点的子节点的颜色来识别。
| 修复节点 | 兄弟节点的颜色 | 兄弟左子节点的颜色 | 兄弟右子节点的颜色 | |
| 案例 1 | 左子节点 | 红色 | 无关紧要 | 无关紧要 |
| 案例 2 | 左子节点 | 黑色 | 黑色 | 黑色 |
| 案例 3 | 左子节点 | 黑色 | 红色 | 黑色 |
| 案例 4 | 左子节点 | 黑色 | 黑色 | 红色 |
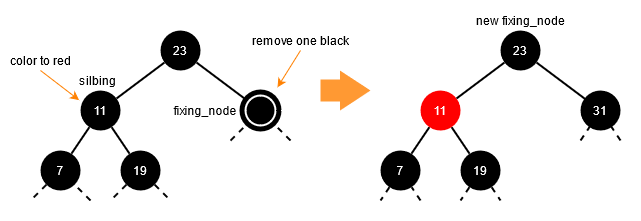
| 案例 5 | 右子节点 | 红色 | 无关紧要 | 无关紧要 |
| 案例 6 | 右子节点 | 黑色 | 黑色 | 黑色 |
| 情况 7 | 右子节点 | 黑色 | 黑色 | 红色 |
| 情况 8 | 右子节点 | 黑色 | 红色 | 黑色 |
从 fixing_node 开始。
案例 1
- 将兄弟节点的颜色更改为
black。 - 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色更改为red。 - 对
fixing_node的父节点执行左旋操作。 - 更新兄弟节点(兄弟节点因左旋而改变)。
- 经过上述操作后,情况 1 转换为**情况 2、情况 3 或情况 4**。

案例 2
- 将兄弟节点的颜色改为**红色**
- 将
fixing_node向上移动,即新的fixing_node成为原来的fixing_node的父节点

案例 3
- 将兄弟节点的左子节点的颜色更改为**黑色**。
- 将兄弟节点的颜色更改为**红色**。
- 对兄弟节点执行右旋操作。
- 经过上述操作后,情况 3 转换为**情况 4**。

案例 4
- 将兄弟节点的颜色更改为与
fixing_node的父节点相同 - 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色更改为black - 将兄弟节点右子节点的颜色更改为
black - 对
fixing_nopde的父节点执行左旋操作 - 经过上述操作后,所有被违反的红黑树属性都已恢复。

案例 5
- 将兄弟节点的颜色更改为
black - 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色更改为red - 对
fixing_node的父节点执行右旋操作 - 更新兄弟节点(兄弟节点因右旋而改变)
- 经过上述操作后,情况 1 转换为**情况 6、情况 7 或情况 8**

案例 6
- 将兄弟节点的颜色改为**红色**
- 将
fixing_node向上移动,即新的fixing_node成为原来的fixing_node的父节点
情况 7
- 将兄弟节点的右子节点颜色改为**黑色**
- 将兄弟节点的颜色改为**红色**
- 对兄弟节点执行左旋操作
- 经过上述操作后,情况 7 转换为**情况 8**

情况 8
- 将兄弟节点的颜色更改为与
fixing_node的父节点相同 - 将
fixing_node的父节点颜色改为**黑色** - 将兄弟节点左子节点的颜色改为**黑色**
- 对
fixing_nopde的父节点执行右旋操作 - 经过上述操作后,所有被违反的红黑树属性都已恢复。

以下实现总结了上面讨论的修复过程。
def _delete_fixup(self, fixing_node: Union[Leaf, Node]) -> None:
while (fixing_node is not self.root) and (fixing_node.color == Color.BLACK):
if fixing_node == fixing_node.parent.left:
sibling = fixing_node.parent.right
# Case 1: the sibling is red.
if sibling.color == Color.RED:
sibling.color == Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.RED
self._left_rotate(fixing_node.parent)
sibling = fixing_node.parent.right
# Case 2: the sibling is black and its children are black.
if (sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK) and (
sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK
):
sibling.color = Color.RED
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent # new fixing node
# Cases 3 and 4: the sibling is black and one of
# its child is red and the other is black.
else:
# Case 3: the sibling is black and its left child is red.
if sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK:
sibling.left.color = Color.BLACK
sibling.color = Color.RED
self._right_rotate(node_x=sibling)
# Case 4: the sibling is black and its right child is red.
sibling.color = fixing_node.parent.color
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
sibling.right.color = Color.BLACK
self._left_rotate(node_x=fixing_node.parent)
# Once we are here, all the violation has been fixed, so
# move to the root to terminate the loop.
fixing_node = self.root
else:
sibling = fixing_node.parent.left
# Case 5: the sibling is red.
if sibling.color == Color.RED:
sibling.color == Color.BLACK
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.RED
self._right_rotate(node_x=fixing_node.parent)
sibling = fixing_node.parent.left
# Case 6: the sibling is black and its children are black.
if (sibling.right.color == Color.BLACK) and (
sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK
):
sibling.color = Color.RED
fixing_node = fixing_node.parent
else:
# Case 7: the sibling is black and its right child is red.
if sibling.left.color == Color.BLACK:
sibling.right.color = Color.BLACK
sibling.color = Color.RED
self._left_rotate(node_x=sibling)
# Case 8: the sibling is black and its left child is red.
sibling.color = fixing_node.parent.color
fixing_node.parent.color = Color.BLACK
sibling.left.color = Color.BLACK
self._right_rotate(node_x=fixing_node.parent)
# Once we are here, all the violation has been fixed, so
# move to the root to terminate the loop.
fixing_node = self.root
fixing_node.color = Color.BLACK
辅助函数
除了核心函数(即 insert、search 和 delete),红黑树还可以有其他有用的函数,例如获取最左侧节点、获取节点的后继节点和获取树的高度,它们的实现类似于二叉搜索树的辅助函数,但有一些修改。
获取高度
要计算红黑树的树高,我们可以像二叉搜索树那样,递归地将每个子节点的高度加一。如果一个节点有两个子节点,我们使用 max 函数获取子节点中较高的那个高度,然后将最高高度加一。主要区别在于我们使用 isinstance 来检查节点是否为叶节点。
@staticmethod
def get_height(node: Union[Leaf, Node]) -> int:
if isinstance(node, Node):
if isinstance(node.left, Node) and isinstance(node.right, Node):
return (
max(RBTree.get_height(node.left), RBTree.get_height(node.right)) + 1
)
if isinstance(node.left, Node):
return RBTree.get_height(node=node.left) + 1
if isinstance(node.right, Node):
return RBTree.get_height(node=node.right) + 1
return 0
获取最左侧和最右侧节点
红黑树获取给定(子)树的最右侧节点和最左侧节点的方式与二叉搜索树相同。我们再次使用 isinstance 来检查节点是常规红黑树节点还是叶节点。
最左侧
@staticmethod
def get_leftmost(node: Node) -> Node:
current_node = node
while isinstance(current_node.left, Node):
current_node = current_node.left
return current_node
最右侧
@staticmethod
def get_rightmost(node: Node) -> Node:
current_node = node
while isinstance(current_node.right, Node):
current_node = current_node.right
return current_node
前驱和后继
红黑树获取节点的前驱和后继的方式与二叉搜索树相同。
前驱
@staticmethod
def get_predecessor(node: Node) -> Union[Node, Leaf]:
if isinstance(node.left, Node):
return RBTree.get_rightmost(node=node.left)
parent = node.parent
while isinstance(parent, Node) and node == parent.left:
node = parent
parent = parent.parent
return node.parent
后继
@staticmethod
def get_successor(node: Node) -> Union[Node, Leaf]:
if isinstance(node.right, Node):
return RBTree.get_leftmost(node=node.right)
parent = node.parent
while isinstance(parent, Node) and node == parent.right:
node = parent
parent = parent.parent
return parent
遍历
由于叶节点的存在,我们无法使用我们在《二叉树遍历》中实现的遍历函数。但是,遍历的概念是相同的。我们只需要一个简单的修改:使用 isinstance 来检查节点是常规红黑树节点还是叶节点。
中序遍历
def inorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
return self._inorder_traverse(node=self.root)
def _inorder_traverse(self, node: Union[Node, Leaf]) -> traversal.Pairs:
if isinstance(node, Node):
yield from self._inorder_traverse(node.left)
yield (node.key, node.data)
yield from self._inorder_traverse(node.right)
前序遍历
def preorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
return self._preorder_traverse(node=self.root)
def _preorder_traverse(self, node: Union[Node, Leaf]) -> traversal.Pairs:
if isinstance(node, Node):
yield (node.key, node.data)
yield from self._preorder_traverse(node.left)
yield from self._preorder_traverse(node.right)
后序遍历
def postorder_traverse(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
return self._postorder_traverse(node=self.root)
def _postorder_traverse(self, node: Union[Node, Leaf]) -> traversal.Pairs:
if isinstance(node, Node):
yield from self._postorder_traverse(node.left)
yield from self._postorder_traverse(node.right)
yield (node.key, node.data)
请注意,返回类型 (traversal.Pairs) 在《二叉树遍历》中的 traversal.py 中定义。
测试
一如既往,我们应该尽可能为我们的代码编写单元测试。在这里,我们使用在《构建二叉搜索树》中创建的 conftest.py 中的 basic_tree 函数来测试我们的红黑树。查看 test_red_black_tree.py 获取完整的单元测试。
分析
正如我们在《二叉搜索树:分析》中讨论的,我们知道二叉搜索树的操作运行时基于树的高度。红黑树是一种自平衡二叉搜索树,其高度最多为 2 * lg (n+1) = O(lg n),其中 n 是节点数。(证明可参考《算法导论》引理 13.1)。因此,红黑树的时间复杂度可总结如下表

示例
由于其自平衡能力,红黑树在软件程序中被广泛使用,包括实现其他数据结构。例如,C++ STL map 就是以红黑树实现的。本节将使用我们在这里实现的红黑树来实现一个键值 Map。
from typing import Any, Optional
from forest.binary_trees import red_black_tree
from forest.binary_trees import traversal
class Map:
"""Key-value Map implemented using Red-Black Tree."""
def __init__(self) -> None:
self._rbt = red_black_tree.RBTree()
def __setitem__(self, key: Any, value: Any) -> None:
"""Insert (key, value) item into the map."""
self._rbt.insert(key=key, data=value)
def __getitem__(self, key: Any) -> Optional[Any]:
"""Get the data by the given key."""
node = self._rbt.search(key=key)
if node:
return node.data
return None
def __delitem__(self, key: Any) -> None:
"""Remove a (key, value) pair from the map."""
self._rbt.delete(key=key)
def __iter__(self) -> traversal.Pairs:
"""Iterate the data in the map."""
return self._rbt.inorder_traverse()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize the Map instance.
contacts = Map()
# Add some items.
contacts["Mark"] = "mark@email.com"
contacts["John"] = "john@email.com"
contacts["Luke"] = "luke@email.com"
# Retrieve an email
print(contacts["Mark"])
# Delete one item.
del contacts["John"]
# Check the deleted item.
print(contacts["John"]) # This will print None
# Iterate the items.
for contact in contacts:
print(contact)
(完整示例可在 rbt_map.py 中获取。)
摘要
尽管维护红黑树属性很复杂,但其自平衡能力使得红黑树比二叉搜索树具有更好的性能。在许多情况下,保持树的平衡至关重要,因此红黑树的复杂性是值得的。在接下来的文章中,我们将实现另一种著名的自平衡树,AVL 树。
历史
- 2021 年 5 月 1 日:初始版本
