实现数组 Tries 的 C# 库
4.91/5 (6投票s)
实现、测试和实际使用一个实现数组 Trie 的 C# 库
引言
Trie(发音为“try”)是一种用于从给定数据集中访问键(字符串)的数据结构。大多数时候,Trie 是由字符字符串构建的,并表示为树,其中一个节点到其每个子节点的链接都用一个唯一的字符标记。根据维基百科上题为“Trie”的页面,Trie 的概念最早由 Axel Thue 在 1912 年抽象地描述,Rene de la Briandais 在 1959 年以计算的术语描述了 Trie。1960 年,Edward Fredkin 创造了 trie 这个术语。
以下两图说明了 Trie 的树形表示。第一幅图是从网上 Trie 的示例图片获得的。树的每个分支都以一个标记为“EOW”(表示“end-of-word”)的节点结束。正如在库的实现中所见,此类节点并非必需。

第二幅图来自维基百科上题为“Trie”的页面。在原图中,树缺少两个链接:一个从节点“te”到节点“ten”,一个从节点“in”到节点“inn”。这两个链接已用红色添加。

从示例图中可以看出,Trie 是多叉树,这意味着 Trie 中的一个节点可以有任意数量的子节点。
在他 1960 年发表的有影响力的论文《Trie Memory》(Communications of the ACM, Vol. 3, No. 9, pp. 490-499)中,Edward Fredkin 描述了使用内存寄存器来存储 Trie。(顺便说一句,作者仅通过 ResearchGate 网站免费访问了 Fredkin 论文的第一页。要获取完整论文,用户不仅要支付“加入”费,还要支付论文的费用,对于这样一篇旧论文来说,这些费用加起来是一笔不小的数目。)
Fredkin 论文中的图 1 显示了 Trie 内存中单词存储的示意图,如下图所示

为简单起见,Fredkin 将字符集限制为字母表的前五个字母加上一个符号(在此复制中为 Ω),以表示“空格”或单词结尾。行代表寄存器,列标有字符集。表中每个非空条目包含要检查的下一个寄存器的编号。检索单词的过程始终从寄存器 1(底部行)开始。
由于无法访问 Fredkin 论文的其余部分,必须以某种方式弄清楚示意图的工作原理。例如,条目 (1,D) 包含数字 2;条目 (2,A) 包含数字 3;条目 (3,B) 包含数字 4;最后,条目 (4,Ω) 包含特殊字符“|”,从而指示单词“DAB”的结束。使用寄存器(行)1 中的其余一些非空条目执行此过程,可以获得对该示意图的部分解释如下。

鼓励读者添加单词“BE”、“BED”和“A”的链接。
Trie 库的实现
在本节中,将从底层到顶层描述 Trie 库的 C# 实现,即从基本数据结构和函数到更抽象的函数。完整代码在本文附带的 ZIP 文件中。假定本节中的所有代码都位于 TriesLib 命名空间中。
Trie 节点
Trie 中的节点包含编码 string 中字符所需的信息。
public class TrieNode
{
private char ch; // Character at some position in a string.
private int limit, index; // Number of subtrie nodes and index of the trie node.
private TrieNode[] subtrie; // Array of all possible trie nodes that can follow 'ch'.
/// <summary>Create an instance of a TrieNode with the given parameters.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="_ch">Character in the trie node.</param>
/// <param name="_limit">Number of subtrie nodes.</param>
/// <param name="_index">Index of the trie node.</param>
/// <param name="endOfString">Whether or not the end of a string has been reached.
/// </param>
public TrieNode( char _ch, int _limit, int _index, bool endOfString )
{
ch = _ch;
limit = _limit;
subtrie = new TrieNode[ limit ];
for ( int i = 0; i < limit; ++i )
{
subtrie[ i ] = null;
}
index = endOfString ? _index : -1;
}// TrieNode (constructor)
构造函数接收以下参数:要存储在节点中的字符、节点将拥有的子 Trie 节点的数量、节点的索引以及指示字符是否为正在处理的字符串结尾的标志。
要访问节点的私有数据成员的值,有三个只读(get)属性:Ch、Limit 和 Index。以下访问器函数用于获取或设置节点的子 Trie 元素。
/// <summary>Get or Set the i-th subtrie of a trie node.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="i">Index of the subtrie.</param>
/// <returns>If the index {i} is valid, the i-th subtrie of a trie node.
/// </returns>
public TrieNode this[ int i ]
{
get
{
if ( 0 <= i && i < limit )
{
return subtrie[ i ];
}
else
{
InvalidIndex( i );
return null;
}
}
set
{
if ( 0 <= i && i < limit )
{
subtrie[ i ] = value;
}
else
{
InvalidIndex( i );
}
}
}// this
函数 InvalidIndex 仅显示一个 MessageBox,说明传递给它的索引无效。
Tries
Trie 是通过创建 Trie 节点来构建的。在上一节的示例中,Trie 被表示为树。在正在描述的 Trie 库中,Trie 的实现是基于数组的。
public class Trie
{
private TrieNode root; // Root node of the trie.
private int limit; // Limit on the possible subtries of a trie node.
public Trie()
{
limit = TLconst.asciiTrieLimit;
root = new TrieNode( '@', limit, -1, false ); // Root node.
}// Trie (constructor)
每次调用前面的构造函数时,都会创建一个根 TrieNode,其可能的子 Trie 数量由以下类设置
public static class TLconst
{
public static readonly
int
asciiTrieLimit = 256; // A Trie contains characters from the standard ASCII code.
}// TLconst (static class)
这意味着每个 Trie 节点最多可以有 256 个可能的子 Trie。这允许处理包含标准 ASCII 字符集中任何可能字符组合的字符串。
将单词插入 Trie
假设一个示例应用程序有一个 static 类 ATconst,其中包含一个要插入的单词数组,将创建一个 Trie 并按如下方式插入单词
Trie trie = new Trie();
for ( int j = 0; j < ATconst.words.Length; ++j )
{
trie.Insert( ATconst.words[ j ], j );
}
以下两个函数处理将 string 的字符插入 Trie。
/// <summary>Insert the characters of a string into the trie.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str">String containing the characters to be inserted.</param>
/// <param name="_index">Index of {str} in a data set.
/// </param>
public void Insert( string str, int _index )
{
if ( !string.IsNullOrEmpty( str ) )
{
TraverseToInsert( str, _index, root );
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show( "Trie class error: null or empty strings cannot be inserted" );
}
}// Insert
/// <summary>Traverse the trie to insert the characters of a non-null, non-empty string.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str">String containing the characters to be inserted.</param>
/// <param name="_index">Index of {str} in a data set.</param>
/// <param name="node">Current trie node.
/// </param>
private void TraverseToInsert( string str, int _index, TrieNode node )
{
int n = str.Length, m = n - 1;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i )
{
char _ch = str[ i ];
int j = (int)_ch; // ASCII code of {_ch}.
// {node[ j ] is {node.subtrie[ j ]} accessed through {node.this[ j ]}
if ( node[ j ] == null )
{
node[ j ] = new TrieNode( _ch, limit, _index, i == m );
}
node = node[ j ];
}
}// TraverseToInsert
例如,从一个空的 Trie 开始,插入字符串“CAB”的字符后,Trie 的状态将如下图所示

Trie 中有四个节点。最顶端的节点对应于 Trie 的根。在根节点的子 Trie 数组的索引 67(字符‘C’的 ASCII 码)处创建了一个新的 TrieNode。在第二个节点的子 Trie 数组的索引 65(字符‘A’的 ASCII 码)处创建了一个新的 TrieNode。最后,在第三个节点的子 Trie 数组的索引 66(字符‘B’的 ASCII 码)处创建了一个新的 TrieNode。第四个节点的子 Trie 数组的所有元素都为 null,并准备好在必要时插入更多字符。
Trie 中条目的反向列表
为了验证数据集中所有字符串都已插入 Trie,使用该库的应用程序可以调用以下函数,该函数将 Trie 中节点的索引收集到一个列表中。该函数依赖于一个执行实际收集的辅助函数。索引以相反的顺序收集,没有特定原因。
/// <summary>Generate a backward listing of the trie indices.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>List of the indices.
/// </returns>
public List<int> BackwardListingOfEntries()
{
List<int> indices = new List<int>();
DescListNode( root, indices );
return indices;
}// BackwardListingOfEntries
/// <summary>Descending listing of the indices in a trie.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node">Current node in the trie.</param>
/// <param name="indices">List containing the indices of entries in the trie.
/// </param>
private void DescListNode( TrieNode node, List<int> indices )
{
if ( node != null )
{
if ( node.Index != -1 )
{
indices.Add( node.Index );
}
for ( int i = limit - 1; i >= 0; --i )
{
DescListNode( node[ i ], indices );
}
}
}// DescListNode
检索以给定前缀开头的单词
Trie 的一个重要应用是查找数据集中所有以给定前缀开头的字符串。假设字符串未排序,对于小数据集,可以容忍穷举搜索。但是,对于大数据集,这种方法是不可接受的。如果字符串存储在 Trie 中,则根本不需要搜索,检索目标字符串的索引所需的时间与字符串的数量成正比。
检索以给定前缀开头的单词如下。从 Trie 的根开始,遍历前缀直到到达对应于前缀最后一个字符的节点。然后收集该节点下所有节点的索引。此算法由以下三个函数实现
/// <summary>Collect the indices in the trie of all the strings that
/// have the same prefix.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="prefix">Prefix for which the indices must be collected.</param>
/// <returns>List of indices from the trie.
/// </returns>
public List<int> Collect( string prefix )
{
List<int> indices = new List<int>();
if ( !string.IsNullOrEmpty( prefix ) )
{
int n = prefix.Length;
TrieNode startNode;
startNode = TraverseStr( prefix, root );
if ( startNode != null )
{
CollectAll( startNode, indices );
}
}
return indices;
}// Collect
/// <summary>Get to the node corresponding
/// to the last character of the prefix of a string.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="prefix">String to traverse in the trie.</param>
/// <param name="startNode">Start node for the traversal of {prefix}.</param>
/// <returns>Node in the trie corresponding to the last character of {prefix}.
/// </returns>
private TrieNode TraverseStr( string prefix, TrieNode startNode )
{
TrieNode node = startNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < prefix.Length; ++i )
{
char _ch = prefix[ i ];
int j = (int)_ch; // ASCII code of {_ch}
if ( node[ j ] != null )
{
node = node[ j ];
}
else
{
node = null;
break;
}
}
return node;
}// TraverseStr
/// <summary>Collect the indices of all the nodes under
/// a given node in a trie.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node">Current node in the trie.</param>
/// <param name="indices">List of all indices to collect.
/// </param>
private void CollectAll( TrieNode node, List<int> indices )
{
if ( node != null )
{
if ( node.Index != -1 )
{
indices.Add( node.Index );
}
for ( int i = 0; i < limit; ++i )
{
CollectAll( node[ i ], indices );
}
}
}// CollectAll
前面的函数中未说明的假设是数据集驻留在内存中,并且通过从 Trie 检索的索引列表来访问目标字符串。
测试库
可以通过一个简单的控制台应用程序来测试实现数组 Trie 的库,如下所示。ZIP 文件中的代码包含更多产生预期结果的测试用例。
using TriesLib;
namespace ArrayTries
{
class Program
{
static void Main( string[] args )
{
Trie trie = new Trie();
for ( int j = 0; j < Constants.words.Length; ++j )
{
trie.Insert( Constants.words[ j ], j );
}
ShowBackwardListing( trie.BackwardListingOfEntries() );
ShowCollection( "a", trie );
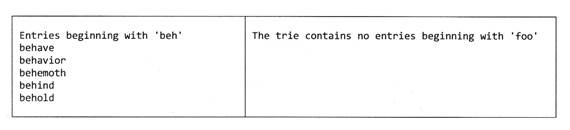
ShowCollection( "beh", trie );
ShowCollection( "foo", trie );
Console.WriteLine();
}// Main
public static void ShowBackwardListing( List<int> indices )
{
if ( indices.Count == 0 )
{
Console.WriteLine( "\nThe trie contains no entries\n" );
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine( "\nBackward listing of trie entries\n" );
foreach ( int i in indices )
{
Console.WriteLine( Constants.words[ i ] );
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}// ShowBackwardListing
public static void ShowCollection( string prefix, Trie trie )
{
List<int> indices = trie.Collect( prefix );
if ( indices.Count == 0 )
{
Console.WriteLine(
string.Format( "\nThe trie contains no entries beginning with '{0}'", prefix ) );
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine( string.Format( "\nEntries beginning with '{0}'", prefix ) );
foreach ( int i in indices )
{
Console.WriteLine( Constants.words[ i ] );
}
}
}// ShowCollection
}// Program (class)
}// ArrayTries (namespace)
为节省空间,程序输出组织成表格形式,并在以下两图中展示

一个简单的应用:自动完成模拟
大多数(如果不是全部)提供搜索功能的图形用户界面 (GUI) 程序都具有自动完成功能。当用户在搜索框中键入字符时,搜索“引擎”会显示建议以自动完成搜索文本。很可能此类“引擎”使用存储在 Trie 中的数据来呈现这些建议。
上一节控制台应用程序中的主程序可以扩展为调用以下函数,以模拟用户在搜索框中键入字符以及搜索引擎在每一步的自动完成字符串列表。
public static void SimulateAutoComplete( string target, Trie trie )
{
int n = target.Length;
if ( n > 4 )
{
Console.WriteLine( "\nSimulating auto-complete with string '{0}'\n", target );
for ( int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i )
{
string prefix = target.Substring( 0, i + 1 );
Console.WriteLine( "prefix: '{0}'", prefix );
ShowCollection( prefix, trie );
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}// SimulateAutoComplete
例如,函数调用...
SimulateAutoComplete( "behemoth", trie );
...将生成下图所示的输出。同样,输出也被组织成表格形式。

实现库
本文附带的 ZIP 文件包含三个实现库的文件:TrieNode.cs、Trie.cs 和 TLconst.cs。在 Visual Studio 中,创建一个名为 TriesLib 的新 Visual C# 类库。在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击 Visual Studio 选择的默认类名(通常是 Class1.cs),将其重命名为 TrieNode.cs,然后复制 TrieNode.cs 文件中的代码。右键单击解决方案名称,选择添加->新项。在出现的菜单中,选择类,将其命名为 Trie.cs,然后复制 Trie.cs 文件中的代码。在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击引用,然后选择添加引用。在出现的窗口中,选择.NET选项卡,并添加对 System.Windows.Forms 库的引用。右键单击解决方案名称,选择添加->新项。在出现的菜单中,选择类,将其命名为 TLconst.cs,然后复制 TLconst.cs 文件中的代码。生成解决方案,bin\Debug 目录将包含库文件 TriesLib.dll。
使用库
ZIP 文件还包含一个名为 Program.cs 的文件,它实现了一个使用该库的简单控制台应用程序,以及一个名为 ATconst.cs 的文件,其中包含要插入 Trie 的示例字符串。在 Visual Studio 中,创建一个名为 ArrayTries 的新控制台应用程序。在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击引用,然后选择添加引用。在出现的窗口中,选择浏览选项卡,然后导航到包含库文件 TriesLib.dll 的 bin\Debug 目录。选择库文件,然后单击确定。用 Program.cs 文件中的文本替换空的 Program.cs 文件。右键单击解决方案名称,选择添加->新项。在出现的菜单中,选择类,将其命名为 ATconst.cs,然后复制 ATconst.cs 文件中的代码。生成解决方案并运行它。
结论
本文介绍了实现数组 Trie 的 C# 库的实现、测试和实际使用。该库可以被任何需要高效访问内存中存储的数据的托管代码 Visual Studio 应用程序使用。如果主键是 strings,则可以将代码改编为访问数据库中的数据。本文描述的所有代码均使用 Visual Studio 2010 开发。然后将代码移植到 Visual Studio 2019,并且在无需任何修改的情况下运行。
历史
- 2021年6月11日:初始版本
