客户端 Web 应用程序报告错误时的安全顾虑
5.00/5 (3投票s)
Web 从服务器端页面转向客户端页面可能会带来安全问题,如果我们不修改传统的错误报告方式。
引言
报告错误似乎是一项微不足道的工作,但如果您不仔细分析您的系统,您可能会遇到安全问题,或者无法向用户和技术支持提供正确的信息来报告和解决问题。在本文中,我们将介绍实际问题,如何在开发和生产的不同阶段进行管理,以及一个用于管理的示例代码。
背景
在早期基于服务器代码的 Web API 中,将错误发送到 Web 的问题并不复杂。服务器处理到 API 的请求,当发生错误时,您可以将技术错误信息连同所有解决 bug 的信息一起发送到 Web 服务器,而 Web 服务器只向浏览器中的用户发送友好的错误信息。在这种环境中,您无需限制您的 API 发送给 Web 服务器的信息量,因为通信仅在服务器之间进行。假设您的服务在内网或您使用的是加密协议。

随着 Angular 等框架的客户端 Web 的普及,对 API 服务的调用直接来自浏览器。这意味着,如果您继续以 ASP.NET 或 NET MVC 等服务器端 Web 类型中使用的相同方式发送错误信息,那么该错误的详细技术信息将以明文形式暴露在浏览器中,任何潜在的黑客都可以发现,无论您使用何种协议来保护信息。这种情况是我们系统中的一个重要的安全漏洞。

提出的解决方案:将 Logger 中的错误日志与发送到应用程序的消息关联起来
一个可能的解决方案是创建一个字段,该字段与发送到浏览器的友好消息一起发送,并将相同的值存储在 logger 系统中作为已记录信息的一部分。这样,您就可以在 logger 中找到有关错误的详细技术信息。将错误与 logger 中的记录关联起来,可以在不冒安全风险的情况下,解决向技术支持提供必要信息以纠正生产环境中 bug 的问题。

您可以使用时间戳作为字段来关联错误和 logger 系统中的日志。我们来看一个示例(见下图)。
假设微服务“Users”抛出了一个异常,系统会创建一个时间戳,并将技术信息发送到 logger 系统,同时也将相同的时间戳和有关错误的友好信息消息发送到客户端浏览器,该消息还包括失败的服务名称。用户致电支持中心,并提供标识该错误的时间戳,支持中心会将电子邮件发送给负责生产错误的开发人员。开发人员会转到“user”微服务 logger,并在给定的日期时间查找该条目,其中包含识别问题所需的所有信息。

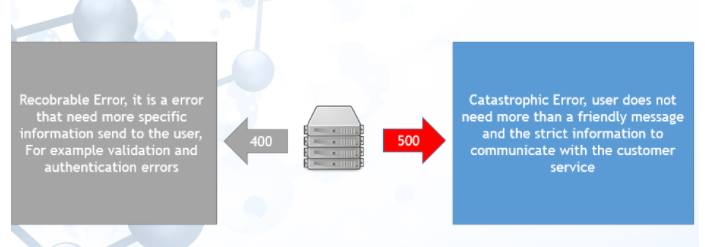
可恢复错误和灾难性错误
另一个需要解决的问题是我们应将哪种 HTTP 错误代码发送给 API 客户端。当错误是灾难性的时候,逻辑选择是 500 错误代码,表示在调用 API 时发生了无法恢复的情况。在这种情况下,很容易选择将与技术错误日志关联的友好错误发送到浏览器。
如果错误是用户通过某种操作可以恢复的,那么可以使用 400 错误类型,它可以涵盖数据验证、数据缺失或其他类似错误。通常,400 错误不应阻止用户继续操作或更正服务的响应。在这种情况下发送给用户的错误消息应能够向最终用户解释发生了什么以及可以采取哪些措施来避免它。让我们在生产和开发条件下看看这两种错误。
管理生产环境中的灾难性错误
生产环境中未恢复的错误仅应报告发生了灾难性错误,原因有两个:一是安全顾虑,二是用户无法采取任何措施来解决错误。我们可以做的是向用户发送一个带有时间戳的友好错误,并将技术问题连同相同的时间戳发送到 logger 系统。发送给用户的友好错误应通过时间戳与 logger 条目相关联,从而可以轻松地在 logger 中找到相关错误的技术条目。

管理开发环境中的灾难性错误
在开发环境中,我们可以直接将技术错误发送到浏览器,因为只有开发人员和可能的 QA 团队能够看到这些信息。此外,我们还需要将错误发送到 logger 系统,并保持发送到浏览器与日志条目之间的关联。

管理生产环境中的可恢复错误
对于可恢复的错误,我们可以向用户发送允许他们从错误中恢复的信息。例如,对于验证错误:更改不正确的名称或填写缺失的字段。
在生产环境中记录此类错误的选择是可选的,您可以选择记录此类错误,在这种情况下,建议将此类错误的级别提高到 WARN 或 INFO,以便仅通过 ERROR 过滤掉灾难性信息错误。

管理开发环境中的可恢复错误
在开发环境和验证错误的场景下,我们与生产环境类似,将所有可能的信息发送给客户端。但我们建议将此信息记录在 logger 系统中。这对于解决问题很有重要,因为不良的 API 请求。

Using the Code
在本文中,我们提出一个对象,该对象允许我们管理此处讨论的所有不同类型的错误。为此,我们使用以下类
/// <summary>
/// Error Message
/// </summary>
public class ErrorManager : IErrorManager
{
/// <summary>
/// This link the log record with the error
/// message
/// </summary>
public DateTime DateCreated { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// List of Validations or internal Errors
/// Used to reported error conditions that does
/// not raise exceptions. Normally Error 400 Type
/// </summary>
public List<ErrorResponse> Errors { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Friendly description, Reserved for
/// Exceptions raised Errors type 500
/// </summary>
public string Description { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// This is the technological Error, should only be
/// used in non production environment.
/// Must be empty in production
/// </summary>
public Exception DebugException { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Return a initializated error Manager
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public static IErrorManager Factory()
{
IErrorManager manager = new ErrorManager();
manager.Errors = new List<ErrorResponse>();
return manager;
}
}
以及存储错误响应列表的类
/// <summary>
/// Hold error information only for the developer
/// or technical service
/// </summary>
public class ErrorResponse
{
/// <summary>
/// Can be a numeric code
/// </summary>
public string Code { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Description of the error, can be a
/// portion of the stack trace.
/// </summary>
public string Description { get; set; }
}
正如您在每个属性的注释中所看到的,您可以在 Web 应用程序中使用这些属性来存储 400 或 500 错误类型的所有信息,无论是在生产环境还是开发阶段。您需要注意的只是根据所遇到的错误使用这些属性。
此类应与 logger 系统配合使用,以允许将已记录的错误与发送给用户的信息进行关联。
现在让我们看看如何在 .NET Core 3.1 应用程序中管理通用错误。以下代码片段解释了如何在 `startup.cs` 文件中配置此类以用于应用程序的通用错误处理。
/// <summary>
/// This method gets called by the runtime.
/// Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app"></param>
/// <param name="env"></param>
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
// General Manager for Exceptions
app.UseExceptionHandler(errorApp =>
{
errorApp.Run(async context =>
{
var errorFeature = context.Features.Get<IExceptionHandlerFeature>();
DateTime errorReportedtime = DateTime.UtcNow;
ErrorManager errorManager = new ErrorManager()
{
DateCreated = errorReportedtime,
};
if (!env.IsProduction())
{
errorManager.DebugException = errorFeature.Error;
errorManager.Description = errorFeature.Error.Message;
}
else
{
// Production
errorManager.Description = $" {errorManager.DateCreated}:
Please call our service that a error happen in NetCoreDemo";
}
// Call the Logger to enter the information
// TODO: Process the information to the logger using the errorManager
// TODO: Enter the information in the Logger included in the errorReportedTime
// Send the response back
var content = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(errorManager);
context.Response.StatusCode = 500; // 500 reserved for exceptions in app.
await context.Response.WriteAsync(content);
});
});
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRouting();
// continue the code for other configurations....
}
请注意,代码区分了生产环境和其他环境。在生产环境中,只向浏览器发送一个带有 TimeStamp 的通用错误。在其他环境中,则向用户发送详细的错误报告。
在这两种情况下,详细的技术信息都应存储在 Logger 中,并且 logger 应通过时间戳与发送到浏览器客户端的消息相关联。
其余代码用于获取该对象并使用上下文响应对象将其返回。
对于 400 错误,您可以在请求管道中使用验证,并将相同配置的对象发送到客户端浏览器。执行此操作的代码如下
/// <summary>
/// This method gets called by the runtime.
/// Use this method to add services to the container.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="services"></param>
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllers()
// Resolving the 400 Validation Error Type
.ConfigureApiBehaviorOptions(options =>
{
options.InvalidModelStateResponseFactory = context =>
{
IErrorManager errorManager = ErrorManager.Factory();
StringBuilder messageb = new StringBuilder();
foreach (var item in context.ModelState)
{
messageb.Append($"Validation Failure in
{context.ActionDescriptor.DisplayName}
Parameter: {item.Key} Error: ");
foreach (var i in item.Value.Errors)
{
messageb.Append($" {i.ErrorMessage} - ");
}
errorManager.Errors.Add(new ErrorResponse()
{
Code = "400",
Description = messageb.ToString()
});
}
// Enter the data time
DateTime errorTime = DateTime.UtcNow;
errorManager.DateCreated = errorTime;
errorManager.Description =
$"{errorTime}: Validation Error in NetCoreDemo";
// Call the Logger to enter the information
// TODO: Process the information to the logger using the errorManager
// TODO: Enter the information in the Logger
// included in the errorReportedTime
var error = new BadRequestObjectResult(errorManager);
return error;
};
});
// Code continue ....
}
在此代码中,我们使用 Errors 属性的 Errors 数组来列出模型状态验证中存在的验证错误。此外,我们在此处提供错误的描述以及指向发送到 Logger 系统的相同错误的链接。请注意,我们在此处为生产和开发环境发送相同的信息。
此示例的完整代码可从 此处 下载。
关注点
- 在生产环境中,您不应向基于 Web 的 Angular 等客户端发送技术错误,而应将错误的技术数据存储在 logger 系统中,并仅向用户发送友好错误。
- 您应随友好消息发送关联友好消息与 logger 系统中存储的信息的可能性。
- 应尽可能始终使用同一对象来报告所有类型的错误。您应该为生产和开发环境定制该对象。
- 您也可以在视频格式中观看此信息: https://youtu.be/Sq39bscnNtU
历史
- 2021年6月13日:初版
- 添加视频伴侣
