DivWindow
4.97/5 (21投票s)
可调整大小、可拖动、最小化和最大化的浮动窗口,并具有布局持久性

目录
引言
我一直想要一个可调整大小、可最小化、可最大化的浮动窗口。像往常一样,我对在网上找到的东西不满意。以下
是三个最接近的例子,但它们要么缺乏我想要的所有行为,要么缺乏足够完整的 API,要么过于复杂,比如 jsFrame。然而,它们都为本次实现提供了很好的起点。我也不想仅仅为了这个功能而引入像 jqWidgets 或类似 Web UI 这样的大型包。所以,是时候重新发明轮子了,只不过这次要把它做得更像一个光滑的圆形轮子,而不是从岩石上粗糙凿出的东西。
主要特点
窗口可调整大小和拖动

窗口可最大化
这里的截图在右侧被裁剪

窗口可最小化到屏幕底部
![]()
容器内的窗口会最小化到容器底部
假设“原地最小化”标志为假。

窗口可原地最小化

完全控制关闭、最小化和最大化按钮

点击标题时自动置顶
与文章顶部的截图进行比较。

窗口包含在其包装 div 中
在这里,内部窗口被限制在外部 div 中

窗口嵌套

窗口状态可在会话之间持久化
您可以保存和重新加载整个文档或容器的 DivWindow 状态(位置、大小、状态)。
DivWindow 类 API
公共函数
public 方法为 DivWindow 提供了相当多的控制,这些方法是不言自明的。除了“get”函数,这些函数返回 DivWindow 实例,因此它们可以用于链式调用以实现流畅的语法风格。
constructor(id: string, options?: DivWindowOptions)
create(id: string, options?: DivWindowOptions)
setCaption(caption: string)
setColor(color: string)
setContent(html: string)
getPosition(): DivWindowPosition
getSize(): DivWindowSize
setPosition(x: string, y: string)
setSize(w: string, h: string)
setWidth(w: string)
setHeight(h: string)
close()
minimize(atPosition = false)
maximize()
restore()
静态函数
两个 static 函数处理布局的保存和加载
static saveLayout(id?: string)
static loadLayout(id?: string)
获取/设置属性
还定义了以下属性,主要用于 DivWindow 代码本身的便利。
get x()
set x(x: number)
get y()
set y(y:number)
get w()
set w(w: number)
get h()
set h(h: number)
用法
至少,需要创建一个包含某些内容的 div,例如
<div id="window1" caption="Another Window">
<p>All good men<br />Must come to an end.</p>
</div>
并使用以下代码初始化 DivWindow
new DivWindow("window1");
渲染

默认情况下,窗口将自动调整大小以适应内容的范围。
可以使用 divWindowOptions 属性以 JSON 值声明选项来声明性地定义选项
示例 1
<div id="outerwindow1" caption="Window 1" divWindowOptions='{"left":100, "top":50}'>
Window 1
</div>
示例 2
<div id="window3" caption=Example" divWindowOptions='{ "left":250, "top":50, "width":300,
"color": "darkred", "hasClose": false, "hasMaximize": false,
"moveMinimizedToBottom": false, "isMinimized": true }'>
Some Content
</div>
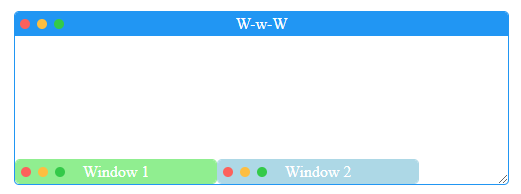
窗口中的窗口
声明外部窗口和内部窗口,例如
<div id="www" caption="W-w-W">
<div id="innerwindow1" caption="Window 1">
Inner Window 1
</div>
<div id="innerwindow2" caption="Window 2">
Inner Window 2
</div>
</div>
然后像这样初始化它们
new DivWindow("www")
.setPosition("50px", "300px")
.setSize("400px", "400px")
.create("innerwindow1").setPosition("10px", "50px").setColor("#90EE90")
.create("innerwindow2").setPosition("60px", "100px").setColor("#add8e6");
注意流畅的语法。这里的 create 没什么特别的,它就像调用 new DivWindow()。
这将呈现

内部窗口被限制在外部窗口内。
容器元素中的窗口
这是一个简单的例子,窗口被包含并限制在一个容器元素中。
<div style="position:absolute; left:600px; top:100px; width:600px;
height:400px; border:1px solid black;">
<div id="window1" caption="A Window">
<p>All good men<br />Must come to an end.</p>
</div>
<div id="window2" caption="My Window">
Hello World!
</div>
<div id="window3" caption="Three by Three"
divWindowOptions='{ "left":250, "top":75, "width":300,
"color": "darkred", "hasClose": false, "hasMaximize": false,
"moveMinimizedToBottom": false, "isMinimized": true }'>
<p>Some content</p>
</div>
</div>
初始化示例
new DivWindow("window1").setPosition("0px", "0px");
new DivWindow("window2", { hasMaximize: false });
new DivWindow("window3");
其渲染效果为

实现
在这里,我将介绍实现的更有趣的方面,因为大部分代码都应该很明显。没有使用 jQuery!
关于 require.js 的注意事项
因为我打算将它用作我在其他项目中使用的组件,而我在这些项目中使用 require.js,所以有一些少量的样板代码来支持 export 关键字。
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>DivWin</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="divWindow.css" type="text/css" />
<script data-main="AppConfig" src="require.js"></script>
</head>
AppConfig.ts:
import { AppMain } from "./AppMain"
require(['AppMain'],
(main: any) => {
const appMain = new AppMain();
appMain.run();
}
);
AppMain.ts(用于初始化演示)
import { DivWindow } from "./divWindow"
export class AppMain {
public run() {
document.getElementById("saveLayout").onclick = () => DivWindow.saveLayout();
document.getElementById("loadLayout").onclick = () => DivWindow.loadLayout();
new DivWindow("outerwindow1");
new DivWindow("outerwindow2");
new DivWindow("window1").setPosition("0px", "0px");
new DivWindow("window2", { hasMaximize: false });
new DivWindow("window3");
new DivWindow("www")
.setPosition("50px", "300px")
.setSize("400px", "400px")
.create("innerwindow1").setPosition("10px", "50px").setColor("#90EE90")
.create("innerwindow2").setPosition("60px", "100px").setColor("#add8e6");
new DivWindow("exampleContent").setPosition("100px", "700px").w = 200;
}
}
我在没有 require.js 的情况下项目运行良好,但我真的很想让实现以其最终形式用于其他项目,但是很容易恢复——只需删除所有类上的 export 关键字,并将页面初始化方式更改为 window.onLoad = () => {...initializate stuff....};
事件
捕获每个窗口的以下事件
document.getElementById(this.idCaptionBar).onmousedown = () => this.updateZOrder();
document.getElementById(this.idWindowDraggableArea).onmousedown =
e => this.onDraggableAreaMouseDown(e);
document.getElementById(this.idClose).onclick = () => this.close();
document.getElementById(this.idMinimize).onclick = () => this.minimizeRestore();
document.getElementById(this.idMaximize).onclick = () => this.maximizeRestore();
窗口模板
讽刺的是,我最挣扎的是将自己添加到包含 DIV 元素的模板。这里的挣扎在于如何让元素处于正确的父子关系中,以便关闭/最小化/最大化点击事件能够触发!这在读者看来可能很傻,但我在一开始将子元素定义为包含“按钮”的 div 的兄弟元素时遇到了问题。这是最终形式
protected template = '\
<div id="{w}_windowTemplate" class="divWindowPanel" divWindow>\
<div id="{w}_captionBar" class="divWindowCaption" style="height: 18px">\
<div class="noselect"
style="position:absolute; top:3px; left:0px; text-align:center; width: 100%">\
<div id="{w}_windowCaption"
style="display:inline-block">\</div>\
<div style="position:absolute; left:5px; display:inline-block">\
<div id="{w}_close" class="dot"
style="background-color:#FC615C; margin-right: 3px"></div>\
<div id="{w}_minimize" class="dot"
style="background-color: #FDBE40; margin-right: 3px"></div>\
<div id="{w}_maximize" class="dot"
style="background-color: #34CA49"></div>\
</div>\
</div>\
<div id="{w}_windowDraggableArea" class="noselect"
style="position:absolute; top:0px; left:55px;
width: 100%; height:22px; cursor: move; display:inline-block"> </div>\
</div>\
<div id="{w}_windowContent" class="divWindowContent"></div>\
</div>\
';
请注意,所有 {w} 都将替换为容器的元素 ID。因此,在构造函数中,您会看到
const divwin = document.getElementById(id);
const content = divwin.innerHTML;
divwin.innerHTML = this.template.replace(/{w}/g, id);
document.getElementById(this.idWindowContent).innerHTML = content;
这段代码首先获取声明性定义的内容,然后用模板替换内容(已设置模板元素的 id),最后用原始 DIV 元素的内容替换模板的内容区域。因此,一个声明性描述为
<div id="exampleContent" caption="Enter Name">
<div>
<span style="min-width:100px; display:inline-block">First Name:</span> <input />
</div>
<div style="margin-top:3px">
<span style="min-width:100px; display:inline-block">Last Name:</span> <input />
</div>
</div>
并初始化为
new DivWindow("exampleContent").setPosition("100px", "700px").w = 300;
渲染为

最终的 HTML 结构是(右侧被剪裁)

需要注意的一些事项
有一个 DIV 专门用于指示可拖动区域,带有一个“移动”光标,它与标题中的按钮偏移,因此如果鼠标悬停在按钮上,光标会显示为指针
![]()
当您将光标向右移动时,它会变为“移动”光标
![]()
此外,请注意外部模板 DIV 中的属性 divWindow
<div id="{w}_windowTemplate" class="divWindowPanel" divWindow>\
这在几个地方用于获取特定于容器或文档的元素
protected getDivWindows(useDocument = false): NodeListOf<Element> {
const el = this.dw.parentElement.parentElement;
const els = ((el.localName === "body" || useDocument) ?
document : el).querySelectorAll("[divWindow]");
return els;
}
所有这些 ID
是的,模板有 8 个具有动态 ID 的元素,所以我发现这使得其余代码更具可读性
protected setupIDs(id: string): void {
this.idWindowTemplate = `${id}_windowTemplate`;
this.idCaptionBar = `${id}_captionBar`;
this.idWindowCaption = `${id}_windowCaption`;
this.idWindowDraggableArea = `${id}_windowDraggableArea`;
this.idWindowContent = `${id}_windowContent`;
this.idClose = `${id}_close`;
this.idMinimize = `${id}_minimize`;
this.idMaximize = `${id}_maximize`;
}
Z 轴顺序
protected updateZOrder(): void {
// Get all divWindow instances in the document
// so the current divWindow becomes topmost of all.
const nodes = this.getDivWindows(true);
const maxz = Math.max(
...Array.from(nodes)
.map(n =>
parseInt(window.document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(n).getPropertyValue("z-index"))
));
this.dw.style.setProperty("z-index", (maxz + 1).toString());
}
正如代码注释所指出的,每当点击一个窗口时,它就会被放置在任何其他窗口之上,包括其容器之外的任何窗口。这样做是为了在此和类似场景中

点击包含在 DIV 中的 A Window,它始终出现在其他窗口(例如 Window 1)前面
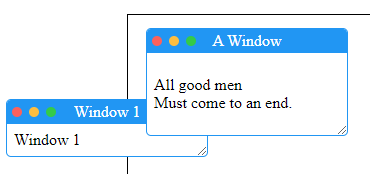
如果我们不这样做,用户最终不得不点击多次才能使窗口置顶,具体取决于容器内外选择的其他窗口。
是的,代码很糟糕,只是简单地在当前最大 z 轴顺序上加 1,但考虑到 JavaScript 的数字最大值为 1.7976931348623157e+308,我真的不认为我需要担心用户将窗口点击到前景并超出计数。
包含窗口
protected contain(dwx: number, dwy: number): DivWindowPosition {
let el = this.dw.parentElement.parentElement;
let offsety = 0;
// DivWindow within DivWindow?
if (el.id.includes("_windowContent")) {
// If so, get the parent container, not the content area.
el = el.parentElement;
// Account for the caption:
offsety = this.CAPTION_HEIGHT;
}
dwx = dwx < 0 ? 0 : dwx;
dwy = dwy < offsety ? offsety : dwy;
// Constrained within a parent?
if (el.localName !== "body") {
if (dwx + this.dw.offsetWidth >= el.offsetWidth) {
dwx = el.offsetWidth - this.dw.offsetWidth - 1;
}
if (dwy + this.dw.offsetHeight >= el.offsetHeight) {
dwy = el.offsetHeight - this.dw.offsetHeight - 1;
}
}
return { x: dwx, y: dwy };
}
这段代码以及代码中的其他一些地方都有一些魔法数字,例如 CAPTION_HEIGHT。我想我本可以查询标题元素的高度。关键是,包含的窗口不能超出其容器的边界移动。这包括在 body 元素中定义的窗口——窗口不能移出屏幕边界。
最小化窗口
public minimize(atPosition = false): DivWindow {
this.saveState();
this.dw.style.height = this.MINIMIZED_HEIGHT;
this.minimizedState = true;
this.maximizedState = false;
if (this.options.moveMinimizedToBottom && !atPosition) {
let minTop;
if (this.isContained()) {
let el = this.dw.parentElement.parentElement;
if (el.id.includes("_windowContent")) {
el = el.parentElement;
}
minTop = el.offsetHeight - (this.CAPTION_HEIGHT + 3);
} else {
minTop = (window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight ||
document.body.clientHeight) - (this.CAPTION_HEIGHT + 1);
}
const left = this.findAvailableMinimizedSlot(minTop);
// Force minimized window when moving to bottom to have a fixed width.
this.dw.style.width = this.MINIMIZED_WIDTH;
this.dw.style.top = minTop + "px";
this.dw.style.left = left + "px";
}
this.dw.style.setProperty("resize", "none");
if (this.options.moveMinimizedToBottom) {
document.getElementById
(this.idWindowDraggableArea).style.setProperty("cursor", "default");
}
return this;
}
如果窗口的 moveMinimizedToBottom === false,则它将原地最小化。否则,它将最小化到容器元素的底部,这可能是屏幕底部。上述代码处理以下场景
父元素为 body 的窗口最小化到屏幕底部

最小化到另一个窗口的底部
最小化非窗口容器的底部

此外,最小化器以一种笨拙的方式试图变得智能。它将最小化窗口的宽度设置为 200 像素,并将其按顺序水平放置在底部。如果一个窗口被恢复,其他最小化的窗口不会移动位置

但是当一个窗口再次最小化时,空槽会再次被填满(参见上一个截图)。
这种行为完全是我的选择,显然如果你不喜欢这种行为,你可以很容易地根据自己的喜好进行更改,我想象起来相当容易。
保存布局
public static saveLayout(id?: string): void {
const els = (id ? document.getElementById(id) : document).querySelectorAll("[divWindow]");
const key = `divWindowState${id ?? "document"}`;
const states: DivWindowState[] = Array
.from(els)
.map(el => DivWindow.divWindows.filter(dw => dw.idWindowTemplate === el.id)[0])
.filter(dw => dw) // ignore windows we can't find, though this should not happen.
.map(dw => ({
id: dw.idWindowTemplate,
minimizedState: dw.minimizedState,
maximizedState: dw.maximizedState,
left: dw.x,
top: dw.y,
width: dw.w,
height: dw.h,
restoreLeft: dw.left,
restoreTop: dw.top,
restoreWidth: dw.width,
restoreHeight: dw.height
}) as DivWindowState);
window.localStorage.setItem(key, JSON.stringify(states));
}
这段代码应该是不言自明的,其思想是使用 DivWindow 的应用程序可以确定是保存整个文档的布局还是仅保存容器内的窗口。
通常,人们可能会有一个包装类来管理所有 DivWindow 实例,但这似乎有点杀鸡用牛刀,所以您会注意到这是一个 static 函数(以及 loadLayout),并且 DivWindow 类实现了
export class DivWindow {
protected static divWindows: DivWindow[] = [];
我没有理由仅仅为了管理 DivWindow 实例的集合而实现一个单独的类。但是,如果您正在实现一个像单页应用程序 (SPA) 那样具有多个不同窗口布局的页面,那么我建议修改代码,以便每个“页面”都维护自己的集合。
另请注意,使用了本地存储,以便布局在会话之间持久化。
加载布局
public static loadLayout(id?: string): void {
const key = `divWindowState${id ?? "document"}`;
const jsonStates = window.localStorage.getItem(key);
if (jsonStates) {
const states = JSON.parse(jsonStates) as DivWindowState[];
states.forEach(state => {
const dw = DivWindow.divWindows.filter(dw => dw.idWindowTemplate === state.id)[0];
// Is it in our list, and does it exist (maybe the user closed it?)
if (dw && document.getElementById(dw.idWindowTemplate)) {
dw.minimizedState = state.minimizedState;
dw.maximizedState = state.maximizedState;
dw.left = state.restoreLeft;
dw.top = state.restoreTop;
dw.width = state.restoreWidth;
dw.height = state.restoreHeight;
dw.setPosition(state.left + "px", state.top + "px");
dw.setSize(state.width + "px", state.height + "px");
if (dw.maximizedState) {
document.getElementById(dw.idWindowTemplate).style.setProperty("resize", "none");
document.getElementById
(dw.idWindowDraggableArea).style.setProperty("cursor", "default");
} else if (dw.minimizedState) {
document.getElementById(dw.idWindowTemplate).style.setProperty("resize", "none");
if (dw.options.moveMinimizedToBottom) {
document.getElementById
(dw.idWindowDraggableArea).style.setProperty("cursor", "default");
}
} else {
document.getElementById(dw.idWindowTemplate).style.setProperty("resize", "both");
document.getElementById
(dw.idWindowDraggableArea).style.setProperty("cursor", "move");
}
}
});
}
}
这里唯一需要注意的是,根据恢复窗口的最小化/最大化状态以及“原地”最小化选项,对调整大小和光标状态的管理。
全套初始化选项
这些是创建窗口时可以指定的所有选项
export class DivWindowOptions {
public left?: number;
public top?: number;
public width?: number;
public height?: number;
public hasClose? = true;
public hasMinimize?= true;
public hasMaximize?= true;
public moveMinimizedToBottom?= true;
public color?: string;
public isMinimized?: boolean;
public isMaximized?: boolean;
}
未定义的任何选项(无双关语)都将恢复为默认行为。
CSS
出于某种原因,人们喜欢看 CSS,所以这里是
.divWindowPanel {
left: 300px;
width: 200px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 100;
overflow: hidden;
resize: both;
border: 1px solid #2196f3;
border-top-left-radius: 5px;
border-top-right-radius: 5px;
border-bottom-left-radius: 5px;
border-bottom-right-radius: 5px;
background-color: white;
}
.divWindowCaption {
padding: 3px;
z-index: 10;
background-color: #2196f3;
color: #fff;
}
.divWindowContent {
text-align: left;
padding: 7px;
}
/* https://stackoverflow.com/a/4407335 */
/* We have this attribute in the caption because dragging the panel
with selected text causes problems. */
.noselect {
-webkit-touch-callout: none; /* iOS Safari */
-webkit-user-select: none; /* Safari */
-moz-user-select: none; /* Old versions of Firefox */
-ms-user-select: none; /* Internet Explorer/Edge */
user-select: none; /* Non-prefixed version, currently supported by
Chrome, Edge, Opera and Firefox */
}
.dot {
height: 10px;
width: 10px;
border-radius: 50%;
display: inline-block;
}
注意 noselect CSS。我曾遇到一个有趣的问题,当我点击标题时,它会突出显示文本,并在随后拖动窗口时导致奇怪的行为。通过使标题不可选择,这个问题得到了解决。
结论
实现这个功能很有趣,我终于有了一个简单但全面的窗口组件,现在可以将其用于其他应用程序,例如我的 自适应分层知识管理 系列,我并没有忘记它,但我确实需要一个不错的窗口管理模块来完成第三部分!
一些遗留问题
- 对于受限窗口,当拖动它超出父容器的范围时,鼠标会继续移动并失去“移动”光标及其相对于窗口标题的位置。
- 如果缩小一个本身包含
DivWindows的DivWindow,内部的DivWindows将不会调整以保持受限,这包括容器内最小化的窗口。 - 过长的窗口标题会与关闭/最小化/最大化按钮冲突。
- 我有一个临时方案,当最大化窗口时,避免滚动条。
DivWindows嵌套DivWindows嵌套DivWindows等可能有效,但我尚未测试此场景。- 我没有处理 resize 事件,因为这无法连接到元素,而且我不想深入研究这个问题,因此可以将包含的窗口调整到超出容器大小的范围。
- 如果您调整一个包含最小化子
DivWindows的DivWindow的大小,子DivWindows不会自动移动到父DivWindow的底部。 - 代码会阻止拖动最小化或最大化的窗口,但您可以更改它。
- 我决定不实现任何应用程序可以挂钩的事件触发器,但如果您需要应用程序根据窗口状态变化执行某些操作,或者您想覆盖默认行为,则可以轻松添加。
- 样式选项(您希望最小化、最大化和关闭按钮采用 Windows 样式 _、box 和 X 吗?)未实现,我真的不想深入研究样式选项。
修订日期:2021-06-12
我添加了以下事件
public onMinimize?: (dw: DivWindow) => void;
public onMaximize?: (dw: DivWindow) => void;
public onRestore?: (dw: DivWindow) => void;
public onSelect?: (dw: DivWindow) => void;
public onClose?: (dw: DivWindow) => void;
这些事件何时触发应该很明显。
对于原地最小化的窗口,如果它们被拖动到另一个位置然后恢复,它们现在会在原地恢复
protected restoreState(): void {
if (this.minimizedState || this.maximizedState) {
// restore in place?
if ((this.options.moveMinimizedToBottom && this.minimizedState) ||
this.maximizedState) {
this.dw.style.left = this.left;
this.dw.style.top = this.top;
}
this.dw.style.width = this.width + "px";
this.dw.style.height = this.height + "px";
this.dw.style.setProperty("resize", "both");
document.getElementById
(this.idWindowDraggableArea).style.setProperty("cursor", "move");
}
}
历史
- 2021年7月6日:初始版本
- 2021年7月12日:添加事件和原地恢复功能
