Kaldoku 游戏
Kaldoku - 一个类似数独的益智游戏
引言
这是一款类似于数独的益智游戏。它也可以称为 Calcudoku、Mathdoku 或 Kenken。
目标
您选择的棋盘大小决定了您在谜题中使用的数字。
例如,4x4 的棋盘要求您使用数字 1-4,而 9x9 的棋盘则要求使用数字 1-9。
所有数字都必须填入单元格,并且同一行或同一列中不得有重复的数字。
目标数字必须与运算后单元格内数值的总和相匹配。
例如,如果区块大小是 4 AND 目标数字是 10 WITH 运算符是 + (10+)
这些是有效值的示例
1,2,3,4
4,3,2,1
只要区块中的数字不在同一行或同一列,就可以包含重复数字。例如,如果区块形状如下所示,目标数字是 14,它可以包含重复值,如下所示
它不能包含如下值
项目类图。
Board.cs
这是代表棋盘信息的类。它包含表示棋盘大小、每个单元格的目标数字以及棋盘上棋子的列表的属性。
棋盘用于存储值的有两个变量。
Cell[,] CellTable 和 public List lstPiece
我们只需要其中一个变量,但我使用了两个变量来更轻松地跟踪棋盘值。
CellTable 是一个 Cell 对象的二维数组。
lstPiece 是棋子对象的集合。
public class Board
{
Cell[,] CellTable = new Cell[6, 6];
int[,] TargetCellValue = new int[6, 6];
private const int BlankCellValue = -1;
public int BoardSize { get; private set; } = 6;
public Board() => this.ClearBoard();
public Board(int pBoardSize)
{
this.BoardSize = pBoardSize;
this.ClearBoard();
}
public static Board Create(int boardSize,String piecesString,
int[,] tarGetCellValue, Boolean IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber)
{
Board newBoard = new Board(boardSize);
/*
* Example of Parameter value
* boardSize:4
* pieceString:J3_Rotate270_0_0|J2_Rotate180_1_0|
I2_Rotate360_0_3|J3_Rotate90_2_0|L2_Rotate180_2_2|
* int[,] targetNumber = new int[,]
{
{ 1,2,3,4 },
{ 2,3,4,1},
{ 3,4,1,2},
{ 4,1,2,3}
};
*/
string[] arrPieces = piecesString.Split(new char[] { '|' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
int i;
/*loop though arrPieces to create Piece object to put into a newBoard
* Example J3_Rotate270_0_1 means
* J3 piece type
* Rotate at 270
* Row in a board 0
* Column in a board 1
*/
for (i = 0; i < arrPieces.Length; i++)
{
string[] arrPieceType = arrPieces[i].Split(new char[] { '_' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string pieceTypeString = arrPieceType[0] + "_" + arrPieceType[1];
int rowPut = int.Parse(arrPieceType[2]);
int colPut = int.Parse(arrPieceType[3]);
Piece piece = Piece.Create(pieceTypeString);
newBoard.Put(rowPut, colPut, piece);
}
newBoard.SetTargetNumber(tarGetCellValue);
newBoard.AssignOperationToPiece(IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber);
newBoard.CalTargetNumberForAllPieces();
return newBoard;
}
public List<Point> Dir = new List<Point>()
{
new Point(-1, 0) ,
new Point(0, 1) ,
new Point(1, 0) ,
new Point(0, -1) ,
};
public Boolean IsValidNumberInBoard()
{
int i;
int j;
int iMax = CellTable.GetLength(0);
for (i = 0; i < CellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if (CellTable[i, j].Value == BlankCellValue)
{
return false;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < CellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
if (!IsValidNumberInRow(i))
{
return false;
}
if (!IsValidNumberInCol(i))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean IsValidNumberInRow(int iRow)
{
HashSet<int> hshRow = new HashSet<int>();
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if (CellTable[iRow, j].Value == 0)
{
continue;
}
if (hshRow.Contains(CellTable[iRow, j].Value ))
{
return false;
}
else
{
hshRow.Add(CellTable[iRow, j].Value );
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean IsValidNumberInCol(int iCol)
{
//List<HashSet<int>> lstRow = new List<HashSet<int>>();
HashSet<int> hshCol = new HashSet<int>();
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(0); j++)
{
if (CellTable[j, iCol].Value == 0)
{
continue;
}
if (hshCol.Contains(CellTable[j, iCol].Value ))
{
return false;
}
else
{
hshCol.Add(CellTable[j, iCol].Value );
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean HasIsolateCell(Cell[,] cellTable)
{
int i;
int j;
int k;
StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
List<Cell> lstCell = new List<Cell>();
for (i = 0; i < cellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < cellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if(cellTable[i,j].Value != BlankCellValue)
{
continue;
}
Boolean hasBlankNeighbor = false;
for (k = 0; k < Dir.Count; k++)
{
int neighborCellRow = i + Dir[k].X;
int neighborCellCol = j + Dir[k].Y;
if (!IsPositionInRange(neighborCellRow, neighborCellCol))
{
continue;
}
if (cellTable[neighborCellRow,
neighborCellCol].Value == BlankCellValue)
{
hasBlankNeighbor = true;
continue;
}
}
if (!hasBlankNeighbor)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public List<Piece> lstPiece = new List<Piece>();
public void PutNumber(Piece pPiece, List<int> lst)
{
int k = 0;
int iRow = pPiece.RowPut;
int iCol = pPiece.ColPut;
for (k = 0; k < pPiece.lstCell.Count; k++)
{
int iPieceRow = pPiece.lstCell[k].Row;
int iPieceCol = pPiece.lstCell[k].Col;
CellTable[iRow + iPieceRow, iCol + iPieceCol].Value = lst[k];
}
pPiece.HasPutNumber = true;
}
}
Create()
Create 方法从棋盘布局和目标数字的字符串表示形式创建一个新的 Board 对象。
以下是其参数:
| 数据类型 | 参数名称 | 示例数据 | 描述 |
int | boardSize | 4 | 棋盘的大小,有效值为 4-9 之间的数字 |
字符串 | piecesString | J3_Rotate270_0_0|J2_Rotate180_1_0 | 表示棋子信息列表的字符串。它使用竖线字符分隔每个棋子,您需要查看函数注释了解更多详细信息 |
int[,] | tarGetCellValue | { 1,2,3,4 }, { 2,3,4,1}, { 3,4,1,2}, { 4,1,2,3} | 表格的正确答案。 |
布尔值 | IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber | True | 如果此值为 true,则目标数字可以是负数。 |
例如,如果这是棋盘。
(我高亮了棋盘上的三个区块来解释我的说明。)
这些将是参数
| 参数名称 | 值 |
boardSize | 4 |
piecesString | L3_Rotate90_0_0|L2_Rotate90_1_1|L2_Rotate180_2_2|I2_Rotate360_0_3|J3_Rotate90_2_0| |
tarGetCellValue | {1,2,4,3},{4,3,1,2},{2,1,3,4},{3,4,2,1} |
此棋盘大小为 4,有 5 个区块
| 区块编号 | 值 | 颜色高亮 | 描述 | 旋转角度 | 行 | Column |
| 1 | L3_Rotate90_0_0 | 橙色 | L形区块,高度为 3 个单元格 | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | L2_Rotate90_1_1 | 蓝色 | L形区块,高度为 2 个单元格 | 90 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | L2_Rotate180_2_2 | - | L形区块,高度为 2 个单元格 | 180 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | I2_Rotate360_0_3 | 紫色 | I形区块,高度为 2 个单元格 | 360 | 0 | 3 |
| 5 | J3_Rotate90_2_0 | - | J形区块,高度为 3 个单元格 | 90 | 2 | 0 |
关于目标数字和运算符
例如 11+,5+,11+,6x,12x
我们在调用 create() 函数时,不包含目标数字和运算符。
这些值将在 create() 方法内计算。
IsValidNumberInBoard()
检查棋盘是否包含所有必需的数字,并且每行和每列都没有重复。
HasIsolateCell()
如果没有相邻的空白单元格,此函数将返回 true。
Piece.cs
棋盘包含许多棋子,而棋子包含许多单元格。
棋子存储 Operation、PieceType、Rotation。
这展示了 Piece 类中的一些代码。
为减少重复代码,我省略了 create 方法中的部分代码。
这是棋子的一个例子。
图中的棋子是 J 形棋子,高 3 个单元格,旋转角度为 90 度。
它的操作是 Add,目标数字是 11。
如果此棋子未旋转,它将如下所示
public class Piece
{
public enum PieceOperation
{
Add,
Subtract,
Multiply,
Divide
}
public enum PieceType // Shape of piece
{
I2,
I3,
I4,
L2,
L3,
J2,
J3,
S,
T,
Z,
O,
Dot,
}
public enum PieceRotation{
Rotate90,
Rotate180,
Rotate270,
Rotate360
}
private Board _Board;
public PieceOperation Operation { get; set; } = PieceOperation.Add;
private int _Number = -1;
public int TargetNumber { get; private set; } = -1;
public static Piece Create(String pieceTypeString)
{
string[] arrTemp= pieceTypeString.Split('_');
Piece.PieceType pieceType = dicPieceType[arrTemp[0]];
Piece.PieceRotation pieceRotation = dicRotation[arrTemp[1]];
return Create(pieceType, pieceRotation);
}
public static Piece Create(PieceType pType,PieceRotation pRotation){
Piece p=null;
List<Cell> lst = new List<Cell>();
Dictionary<PieceType, Dictionary<PieceRotation, List<System.Drawing.Point>>>
Dic = new Dictionary<PieceType,
Dictionary<PieceRotation, List<System.Drawing.Point>>>();
if(hshCannotRotate.Contains (pType ))
{
if(pRotation == PieceRotation.Rotate180 ||
pRotation== PieceRotation.Rotate270 )
{
pRotation = PieceRotation.Rotate360 ;
}
}
// Showing only 2 types of Piece to reduce the sample of the code
switch (pType)
{
case PieceType.Dot :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
break;
case PieceType.L2 :
switch (pRotation)
{
case PieceRotation.Rotate360:
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 1));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate90 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 1));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate180 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 1));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 1));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate270 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, -1));
break;
}
break;
}
//p=new Piece ();
p = new Piece(pType, pRotation, lst);
p.lstCell = lst;
return p;
}
Cell.cs
Cell 类定义了属性来表示单元格的行、列、值、目标值、棋盘上的行和棋盘上的列。它有一个属性 _Piece 来保存其所属的棋子对象的引用。
Cell 的目标值用于生成棋子的目标数字,用户不一定需要输入与单元格目标值匹配的值。
例如,如果棋子由 2 个单元格组成,棋子的目标数字是 5+,单元格的目标数字是 4 和 1。
这 4 种情况都是 Cell1 和 Cell2 的有效值,它们不一定是 4 和 1。
枚举 enCellStatus 用于指示单元格的状态。
Row 和 RowOnBoard、Column 和 ColOnBoard 之间的区别是
Row 和 Column 指的是在区块中的位置,而 RowOnBoard 和 ColOnBoard 指的是在棋盘上的位置。
例如
在上图中,高亮显示的区块由 4 个单元格组成。
| 单元格编号 | 目标 | 行 | Column | RowOnBoard | ColOnBoard |
1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
public class Cell
{
private Piece _Piece = null;
public enum enCellStatus
{
Blank,
Duplicate, //Duplicate with other cell in row/column
PieceIsNotComplete, //Contain blank cell
PieceIsNotCorrect, //No blank cell but contains duplicate
//or does not match with target value
PieceIsCorrect, // no match
PieceMatchbutContainDuplicate,
}
public enCellStatus CellStatus { get; set; } = enCellStatus.Blank;
public void SetPiece(Piece pPiece)
{
_Piece = pPiece;
_Piece.PieceBeingPutOnBoard += _Piece_PieceBeingPutOnBoard;
}
public void UnboundFromPiece()
{
_Piece = null;
}
private void _Piece_PieceBeingPutOnBoard(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.RowOnBoard = this.Row + _Piece.RowPut;
this.ColOnBoard = this.Col + _Piece.ColPut;
}
public int Row { get; private set; }
public int Col { get; private set; }
public int Value { get; set; }
public int TargetValue { get; set; }
public int RowOnBoard { get; private set; }
public int ColOnBoard { get; private set; }
public Cell(int pRow, int pCol)
{
this.InitializeProperty(pRow, pCol, 0);
}
private void InitializeProperty(int pRow, int pCol, int pValue)
{
Row = pRow;
Col = pCol;
Value = pValue;
}
public Cell(int pRow, int pCol, int pValue)
{
this.InitializeProperty(pRow, pCol, pValue );
}
}
此时,您已经了解了棋盘的构建方式,下一步是准备棋盘的值。
如何生成棋盘
- 首先,生成一个包含空白单元格的区块列表。
我们不需要知道目标数字是什么,只需要一个有效的区块列表,如下所示 - 生成数字
1243431221343421 -
为每个单元格分配数字。
-
随机为每个区块分配运算符。
-
计算区块目标数字。
生成包含空白单元格的区块列表
最初,当我创建程序时,程序只需要动态生成一个包含空白单元格的区块列表。
程序在 4x4 到 7x7 的棋盘大小下运行正常,但在 8x8 或 9x9 的棋盘大小下,有时会卡死,因为它无法生成有效的区块。
所以我决定提前生成一个区块列表,然后先将它们存储在文本文件中,当程序需要使用时。
只需从文本文件中读取值。
您可以查看 PregeneratedBlankBlock 文件夹。您会看到一个文本文件列表,例如 4x4.txt 和 5x5.txt。
这些文件包含此类值。
Z_Rotate360_0_0|L3_Rotate90_2_1|J2_Rotate180_0_2|I3_Rotate360_1_0|I2_Rotate90_3_2|
J2_Rotate270_0_0|I3_Rotate90_2_1|I3_Rotate360_1_0|I2_Rotate90_0_2|I2_Rotate90_1_2|
I3_Rotate90_3_1|
每一行都是棋盘的有效值。
如果您想自己生成,可以查看 GenerateBlankBlocks() 在 FormGenerateBlankBlock.cs 中
- 生成随机棋子。
- 尝试将生成的棋子放到棋盘上,
如果程序可以放置,则重复 #1。 - 如果程序无法放置棋子,
增加程序无法放置的次数,
然后我们继续执行 #1。
如果程序无法放置的次数 >numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece,则移除最后一个棋子 - 如果 #3 仍然不够好,我们调用
UnputLastNPiece来移除多个棋子。
private void GenerateBlankBlocks(Board board)
{
GeneratePiece generatePiece = new GeneratePiece(new BasicPieceGenerator());
int maximumAttemptLoopAllow = 50000000;
int numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece = 40;
int numberofTimesUnputLastPiece = 0;
int numberofTimeBeforeUnputLastNPiece = 30;
int countLoop = 0;
int countCannotPut = 0;
int numberofUnputLastNPiece = 3;
Boolean isSuccess = true;
while (!board.IsFullWithBlock() && countLoop < maximumAttemptLoopAllow)
{
Piece generatedPiece = generatePiece.GenPiece();
Boolean canPut = board.TryToPut(generatedPiece);
countLoop++;
if (canPut)
{
countCannotPut = 0;
continue;
}
countCannotPut++;
if (countCannotPut >= numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece)
{
countCannotPut = 0;
board.UnputLastPiece();
numberofTimesUnputLastPiece++;
if (numberofTimesUnputLastPiece >= numberofTimeBeforeUnputLastNPiece)
{
board.UnputLastNPiece(numberofUnputLastNPiece);
numberofTimesUnputLastPiece = 0;
}
}
if (countLoop >= maximumAttemptLoopAllow)
{
isSuccess = false;
}
}
if (!isSuccess)
{
throw new Exception("Sorry I failed to generate blank blocks,
you can try again");
}
}
private void btnGenereateBlankBlock_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int i;
try
{
/* Keep the existing generate block to make sure that the
* output will not duplicate
*/
HashSet<String> hshGenBlock = new HashSet<string>();
int boardSize = int.Parse(this.txtBoardSize.Text);
int numberOfBoardNeedToGenerate = int.Parse(this.txtNumberofBoard.Text);
StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
for (i = 0; i < numberOfBoardNeedToGenerate; i++)
{
bool hasGenerate = false;
while (!hasGenerate)
{
var Board = new Board(boardSize);
GenerateBlankBlocks(Board);
string ListPiece = Board.GetListPieceString();
if (hshGenBlock.Contains(ListPiece))
{
continue;
}
hshGenBlock.Add(ListPiece);
hasGenerate = true;
strB.Append(ListPiece).Append(Environment.NewLine);
}
}
this.txtOutput.Text = strB.ToString();
} catch (Exception ex)
{
this.txtOutput.Text = ex.ToString();
}
}
生成数字
-
如果您查看 PrepareGenerateDigits 文件夹,您会看到类似 4_1.txt 到 4_4.txt 直到 9_1.txt 到 9_9.txt 这样的文件名。
-
这些文件表示
boardsize_thefirstdig,如果文件名是 4_1.txt,则表示该文件包含棋盘大小为 4 的数据,第一个数字是 1。
这是棋盘大小为 4 的数据。
| 行号 | 4_1.txt | 4_2.txt | 4_3.txt | 4_4.txt |
| 1 | 1234 | 2134 | 3124 | 4123 |
| 2 | 1243 | 2143 | 3142 | 4132 |
| 3 | 1324 | 2314 | 3214 | 4213 |
| 4 | 1342 | 2341 | 3241 | 4231 |
| 5 | 1423 | 2413 | 3412 | 4312 |
| 6 | 1432 | 2431 | 3421 | 4321 |
- 要生成数字,我们需要做的是从每个文件中随机选择值。
例如,我们选择
| 行号 | 从文件 | 我们得到值 |
| 2 | 4_1.txt | 1 2 4 3 |
| 1 | 4_2.txt | 2 1 3 4 |
| 6 | 4_3.txt | 3 4 2 1 |
| 5 | 4_4.txt | 4 3 1 2 |
此时,我们得到这样的值
1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
如果值无效,例如,这不是一个有效值。
在这种情况下,第 2 行第 2 和第 3 列的重复值为 4,程序将继续从文件中获取新值,直到棋盘值有效。
1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
现在我们已经获得了有效值。我们几乎完成了,只是行中的第一个值是有序的,所以我们只需要随机交换行,这样我们就能得到这个。
3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
我们在 PregenratedNumber.cs 中调用 getTargetCellNumber()。
public static int[,] getTargetCellNumber(int boardSize)
{
int i;
int j;
var TargetCellValue = new int[boardSize, boardSize];
int[] arrRowTemp = new int[boardSize];
Dictionary<int, List<List<int>>> DicList = GetDicList(boardSize, FileUtil.PregeneratedDigitsPath);
for (i = 1; i <= boardSize; i++)
{
Boolean IsValid = false;
while (!IsValid)
{
int indexRandommed = 0;
indexRandommed = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, DicList[i].Count);
List<int> lst = DicList[i][indexRandommed];
IsValid = true;
for (j = 0; j < lst.Count && IsValid; j++)
{
int k;
for (k = 0; k <= boardSize - 1; k++)
{
if (TargetCellValue[k, j] == lst[j])
{
IsValid = false;
}
}
}
if (IsValid)
{
for (j = 0; j < lst.Count; j++)
{
TargetCellValue[i - 1, j] = lst[j];
}
}
}
}
//Swap Row;
for (i = 0; i <= 30; i++)
{
int iFirstRow = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, boardSize);
int iSecondRow = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, boardSize);
if (iFirstRow == iSecondRow)
{
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j <= boardSize - 1; j++)
{
arrRowTemp[j] = TargetCellValue[iSecondRow, j];
TargetCellValue[iSecondRow, j] = TargetCellValue[iFirstRow, j];
TargetCellValue[iFirstRow, j] = arrRowTemp[j];
}
}
return TargetCellValue;
}
接下来,我们将进行其余的处理。
计算区块目标数字
在此步骤中,我们将
- 为每个单元格分配数字,程序仅调用
Board.SetTargetNumber() - 随机为每个区块分配运算符,通过调用
Board.AssignOperationToPiece() - 计算区块目标数字并调用
Board.CalTargetNumberForAllPieces()
private void AssignOperationToPiece(Boolean IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber, Dictionary<Piece.PieceOperation, int> dicOpertorChance)
{
int i;
// Set some of them to use divided
for (i = 0; i < this.lstPiece.Count; i++)
{
var piece = lstPiece[i];
// Set default Operation to be Add for all of the pieces
Piece.PieceOperation DefaultOperator = Piece.PieceOperation.Add;
piece.Operation = DefaultOperator;
// Calculate the chance that it will be other value more than add
int iOperationChance = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, 100);
foreach (Piece.PieceOperation Oper in dicOpertorChance.Keys)
{
int iSum = 0;
if(iOperationChance > dicOpertorChance[Oper])
{
continue;
}
var AssignOperator = Oper;
if (AssignOperator == Piece.PieceOperation.Subtract)
{
if (!IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber)
{
/*Set AssignOperator to be Add if the result is a Negative
This is a process to prevent the result from being a negative number.
Supposing this is the value of the cell in piece
cell1:5
cell2:3
cell3:4
1. set iSum to be 5
2. iSum - 3 - 4;
3. if iSum < 0 we will not use Substract as Operator
we will ust use Add instead.
*/
//1. Assign iSum to be the first cell value
iSum = piece.lstCell[0].TargetValue;
int j;
//2. Subtract iSum value from the rest of the cell in piece
for (j = 1; j < piece.lstCell.Count; j++)
{
iSum -= piece.lstCell[j].TargetValue;
}
//3. If iSum is less than 0 we will force the operation to be Add instead.
if (iSum < 0)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
}
}
else if (AssignOperator == Piece.PieceOperation.Divide)
{
/*The condition that we will use Divide.
1. The number of cell must be 2
2. The result after from the division must be integer
For example
case 1
cell1:6
cell2:3
This case is valid because 2=6/3
case 2
cell1:5
cell2:2
This case is invalid because 2.5=5/2
*/
if (piece.lstCell.Count != 2)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
else
{
double doubleResult = (double)(piece.lstCell[0].TargetValue) /
(double)(piece.lstCell[1].TargetValue);
Boolean IsResultAfterDiviedInteger = (doubleResult % 1 == 0);
if (!IsResultAfterDiviedInteger)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
}
}
if (piece.PType == Piece.PieceType.Dot)
{
//For Dot piece type, we don't allow other operators besides Add
piece.Operation = Piece.PieceOperation.Add;
}
else
{
piece.Operation = AssignOperator;
}
break;
}
}
}
Piece.cs 的 CalculateTargetNumber 不同于 CalculateNumber ,在 CalculateNumber 中,您需要计算减法和除法的两种情况。
例如
该棋子有 2 个单元格,棋子目标值为 =1。
如果用户输入 3,1 或用户输入 1,3,这两种情况都将被视为正确。
该棋子有 2 个单元格,棋子目标值为 /2,
如果用户输入 4,2 或用户输入 2,4,这两种情况都将被视为正确。
public int CalculateTargetNumber()
{
int i;
int iSum = 0;
for(i=0;i<this.lstCell.Count;i++)
{
switch (this.Operation) {
case PieceOperation.Add:
iSum += lstCell[i].TargetValue ;
break;
case PieceOperation.Subtract:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum -= lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Multiply:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum *= lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Divide:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum = iSum / lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
}
}
return iSum;
}
private const int InvalidValue = int.MinValue;
public void CalculateNumber(ref int Number1, ref int Number2)
{
int i;
Number1 = InvalidValue;
Number2 = InvalidValue;
int numberTemp = 0;
for (i = 0; i < this.lstCell.Count; i++)
{
switch (this.Operation)
{
case PieceOperation.Add:
if (i == 0)
{
Number1 = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 += lstCell[i].Value;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Subtract:
if (i == 0)
{
numberTemp = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 = numberTemp - lstCell[i].Value;
Number2 = lstCell[i].Value - numberTemp;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Multiply:
if (i == 0)
{
Number1 = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 *= lstCell[i].Value;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Divide:
if (i == 0)
{
numberTemp = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
int tempNumber1 = CalculateDivide(numberTemp, lstCell[i].Value);
int tempNumber2 = CalculateDivide(lstCell[i].Value, numberTemp);
if(tempNumber1 != InvalidValue)
{
Number1 = tempNumber1;
}
if(tempNumber2 != InvalidValue)
{
Number2 = tempNumber2;
}
}
break;
}
}
}
绘制棋盘
UI/pictureBoxTable 负责绘制棋盘。
我想专注于绘制边框,因为其他内容只是简单地绘制背景色。
绘制边框的算法是
-
每个单元格有 4 个边框,
North、West、South、East -
我们绘制所有边框,如果边框旁边没有其他单元格,就绘制边框。如果有,我们就绘制单元格之间的线。
在上图中,该单元格没有属于同一区块的其他单元格,因此绘制了所有 4 个边框。
在上图中,单元格 1 不需要绘制南边框,单元格 2 不需要绘制北边框。
-
我们可以通过使用此算法来确定边框旁边是否有同一区块中的其他单元格。
循环遍历其他单元格-
3.1 如果其他单元格与检查单元格具有相同的行,如果其他单元格的列小于检查单元格,则无需绘制西边框。
-
3.2 与 #3.2 相同,但如果其他单元格的列大于检查单元格,则无需绘制东边框。
-
3.3 如果其他单元格与检查单元格具有相同的列,如果其他单元格的行小于检查单元格,则无需绘制上边框。
-
3.4 与 #3.3 相同,但如果其他单元格的行大于检查单元格,则无需绘制南边框。
-
- 例如,在下图所示的单元格 1 中,不需要绘制东边框,因为它有其他单元格(2,3)与它处于同一行,但列大于单元格 1。
-
单元格 1 不需要绘制南边框,因为它有其他单元格(4)与它处于同一列,但行大于单元格 1。
private void RenderBorder(Graphics g,Board pBoard)
{
int indexPiece = 0;
// loop for the list of pieces.
for (indexPiece = 0; indexPiece < pBoard.lstPiece.Count; indexPiece++)
{
Kaldoku.Piece Piece = pBoard.lstPiece[indexPiece];
int indexCell;
//loop all cell in piece.
for (indexCell = 0; indexCell < Piece.lstCell.Count; indexCell++)
{
Kaldoku.Cell Cell = Piece.lstCell[indexCell];
int indexOtherCell = 0;
Point p1 = new Point(0, 0);
Point p2 = new Point(0, 0);
int col = Piece.ColPut + Cell.Col;
int row = Piece.RowPut + Cell.Row;
int extrapixel = 2;
Point northBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset - extrapixel,
row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point northEnd = new Point(northBegin.X + CellWidth +
extrapixel, northBegin.Y);
Point westBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset,
row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point westEnd = new Point(westBegin.X, westBegin.Y + CellWidth + 1);
Point eastBegin = new Point((col + 1) * CellWidth + xOffset,
row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point eastEnd = new Point(eastBegin.X, eastBegin.Y + CellWidth + 1);
Point southBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset - extrapixel,
(row + 1) * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point southEnd = new Point(southBegin.X + CellWidth +
extrapixel, southBegin.Y);
Boolean isNeedToDrawNorthBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawWestBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawSouthBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawEastBorder = true;
PointF pointF = new PointF(col * CellWidth, row * CellWidth);
pointF = new PointF(col * CellWidth + (CellWidth / 4) + 3,
row * CellWidth + (CellWidth / 4));
// Check other cell part.
for (indexOtherCell = 0; indexOtherCell < Piece.lstCell.Count;
indexOtherCell++)
{
if (indexOtherCell == indexCell)
{
continue;
}
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Row ==
Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Row)
{
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Col >
Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Col)
{
isNeedToDrawEastBorder = false;
}
else
{
isNeedToDrawWestBorder = false;
}
}
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Col ==
Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Col)
{
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Row >
Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Row)
{
isNeedToDrawSouthBorder = false;
}
else
{
isNeedToDrawNorthBorder = false;
}
}
}
Pen pen = isNeedToDrawNorthBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, northBegin, northEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawWestBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, westBegin, westEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawSouthBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, southBegin, southEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawEastBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, eastBegin, eastEnd);
}
}
}
其他游戏
我还有另外两款与 Kaldoku 类似的游戏,当您下载源代码/EXE 时,您会看到它们。
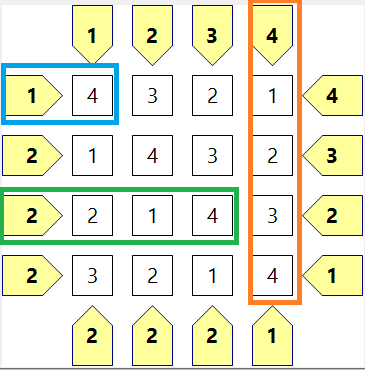
Tower (塔)
这款游戏也称为 Skyscraper (摩天大楼),是一款类似数独的益智游戏。
如何玩 Tower
-
每个单元格都必须填入一个数字。数字代表塔的高度。如果棋盘大小为 4x4,则有效数字为 1,2,3,4 (数字从 1 到棋盘大小)。
-
每个行和每个列中的数字不能重复。
-
如果您看向箭头的方向,棋盘侧面的箭头数字表示您从箭头位置可以看到多少座塔。
-
为了使您可以看到的塔的数字与箭头处的数值匹配,您必须在列中输入适当的数字。
示例
此图显示了棋盘上所有单元格的正确值。蓝色矩形表示箭头处的数值为 1,因为当您从箭头位置看时,您只能看到 4 层高的塔。
绿色和橙色也一样。对于绿色,您可以看到 2 和 4,所以总共可以看到 2 座塔。
对于红色,您可以看到 1, 2, 3, 4,这就是为什么箭头处的数值为 4。
Kakurasu (格列)
这是一款类似数独的益智游戏,但更简单。
如何玩
-
您选择想要设为黑格的单元格。
-
目标是使黑格的权重总和等于行/列的总和值。
-
棋盘顶部和左侧有一些数字,代表单元格的权重(蓝色)。
图中是 1, 2, 3, 4, 5。
棋盘右侧和底部有一些数字,代表单元格权重的正确总和(橙色)。
图中,行 9 的总和为 10, 6, 10, 10, 11;列的总和为 9, 13, 8, 12, 8。 -
图中,第一行是正确的,因为第一行有 3 个黑格,并且第一行 3 个黑格的总和是 10 (2 + 3 + 5)。
-
图中,第一列是正确的,因为第一列有 3 个黑格,并且第一列 3 个黑格的总和是 9 (2 + 3 + 4)。
-
您继续选择值,直到所有行/列的总和都正确。
这 3 款游戏有什么用
除了玩它们之外,如果您想出版一本关于益智游戏的书,请随时使用这些程序。
参考
历史
- 2024 年 2 月 4 日:初始版本