如何将 C# 源文件中的 XML 注释转换为 HTML 页面
5.00/5 (7投票s)
本文介绍了一个将 C# 源文件中的 XML 注释转换为 HTML 页面的工具。
目录
1. 背景 
最近在 CodeProject 上有许多关于将 C# 源文件中的 XML 注释转换为 HTML 页面的讨论。本文介绍了一个能够执行此类服务的工具。
2. 简介 
在我职业生涯中,我编写了无数的 API,它们要么支持我的工作,要么支持他人的工作。直到最近(大约 2010 年),我不得不编写注释来指导他人和我使用这些 API。这个过程很繁琐。更糟糕的是,有时注释不再反映 API 的内容。
我不知道的是,微软已经开发了所谓的“XML 注释”,并将其集成到 C# 编译器中。它们是 C# IntelliSense [^] 的一部分,在源代码中输入方法时提供自动完成列表。
3. XML 注释 
XML 注释是用于生成 API 文档的结构化注释。在微软的观点中,C# 编译器使用这些注释生成一个 XML 文件,其中包含表示注释和 API 签名的结构化数据。微软建议“其他工具可以处理该 XML 输出,以生成网页或 PDF 文件形式的可读文档。”
编译器生成的 XML 文件存在的问题是它不完整。它未能为没有 XML 注释的命名空间和类生成 XML 元素。此外,类别的 XML 元素与没有区分的接口、结构、枚举和委托的 XML 元素相同。最后,XML 注释的文档编写得很糟糕,有些部分完全不充分。正是由于这些原因,我决定开发一个工具,将嵌入 C# 源文件中的 XML 注释转换为 HTML 文档。
3.1. 识别和处理的 XML 注释标签 
以下显示了 XML2HTML 处理的 XML 注释标签(红色的项目未被处理)。
<summary>description</summary> <remarks>description</remarks> <returns>description</returns> <param name="name">description</param> <paramref name="name"/> <exception cref="member">description</exception> <value>property-description</value> <para>paragraph</para> <list type="bullet|number|table"> <listheader> <term>term</term> <description>description</description> </listheader> <item> <term>Assembly</term> <description>description</description> </item> </list> <c>text</c> <code> var index = 5; index++; </code> <example> This shows how to increment an integer. <code> var index = 5; index++; </code> </example> <inheritdoc [cref=""] [path=""]/> <include file='filename' path='tagpath[@name="id"]'/> <see cref="member"/> <see cref="member">Link text</see> <see href="link">Link Text</see> <see langword="keyword"/> <seealso cref="member"/> <seealso href="link">Link Text</seealso> <typeparam name="TResult">The type returned from this method</typeparam> <typeparamref name="TKey"/>
之所以删除这些标签,是因为这些标签要么引用了 C# 编译器才知道的值(XML2HTML 不知道),例如“cref”或“TResult”,要么描述这些标签的文档写得很糟糕,有些部分完全不充分(<list type="table">...)。<see href=... 被删除,因为与 <seealso href=... 可以获得相同效果。
3.2. HTML 文档的格式 
C# 源文件中的方法和构造函数的顺序没有限制。私有和公共方法可能会相互穿插。然而,在文档方面,顺序对于读者的理解非常重要。考虑到这一点,定义了一个 HTML 页面格式,并显示如下。
<class-name> CLASS
Definition
Assembly: <library-name>.dll
Namespace: <namespace>
<description>
Remarks
<remarks>
Example
<example>
See Also
<see-also>
<class-name> Constructors
<class-name> Constructor
<signature> <description>
Parameters
<parameters>
Remarks
<remarks>
Example
<example>
See Also
<see-also>
<class-name> Methods
<class-name> Method
<signature> <description>
Parameters
<parameters>
Returns
<returns>
Remarks
<remarks>
Example
<example>
See Also
<see-also>
这种顺序是数据驱动的(通过 Object_Type,在 Object_Type.cs 中,用于主要项目(CLASS, CONSTRUCTOR, METHOD 等)的排序;通过 Symbol,在 Symbols.cs 中,用于 XML 标签的排序)。
4. 关于解析的说明 
解析是 XML2HTML 的内在部分。然而,有两种方式
- 解析 C# 源文件。
- 解析 XML 注释。
4.1. 解析 C# 源文件 
C# 源文件解析相对直接。在 C# 源文件中需要识别的只有包含 XML 注释和相关公共签名的行。
set in_XML_comment to false
repeat
read a c# source line
if ( not c# source file eof )
trim line of leading spaces
if ( the first three characters are "///" )
if ( not in_XML_comment )
set in_XML_comment to true
create XML_comment object
endif
append line to text of XML_comment
else if ( in_XML_comment )
set in_XML_comment to false
collect signature
if ( signature contains "public" )
add XML_comment to XML_comments_list
else
discard XML_comment object
endif
else
ignore c# source line
endif
endif
until c# source file eof
必须识别的唯一符号是
| syassignment | '=' |
| syclass | "class" |
| syclosebracket | ']' |
| sycolon | ':' |
| sycomment | "//" |
| sydelegate | "delegate" |
| syenum | "enum" |
| syeof | 文件结束 ("‡") |
| syeoln | 行结束 ('†') |
| syinterface | "interface" |
| synamespace | "namespace" |
| syopenbrace | '{' |
| syopenbracket | '[' |
| syopenparen | '(' |
| sypublic | "public" |
| sysemicolon | ';' |
| syslash | '/' |
| syspace | ' ' |
| systruct | "struct" |
| syXMLcomment | "///" |
4.2. 解析 XML 注释 
当 C# 源文件解析完成后,所有生成 C# 文件 HTML 页面所需的数据都已收集完毕。XML 注释已按其出现的顺序收集到 XML_comment_list 中。每个 XML_comment 块还包含前面带有 XML 注释的公共签名。
XML2HTML 现在必须处理 XML_comment_list 的 XML_comment 节点中的数据。对于 XML2HTML 的这个工作部分,解析采用了完整的词法分析器功能。语法分析在某种程度上是简化的,因为 XML2HTML 不是为了正确性而解析输入。
出于这些原因,强烈建议提交给 XML2HTML 工具的 C# 项目文件能够成功编译。为确保 XML 注释有效,项目应指定编译器生成项目的 XML 文档文件。应检查此编译器生成的 XML 文档文件是否存在编译器报告的任何问题,并在将项目提交给 XML2HTML 之前修复任何问题。
5. XML2HTML 工具 
该工具经历了三个版本。
- 用户指定一个 C# 文件名,工具根据嵌入的 XML 注释生成一个 HTML 页面。
- 用户指定 C# 编译器生成的 XML 文件名,工具根据其中包含的 XML 树生成 HTML 页面。
- 用户指定一个 C# 项目文件名,工具根据构成该项目的 C# 文件中嵌入的 XML 注释生成 HTML 页面。
由于第三个版本最终成为了 XML2HTML 工具,因此本次讨论将仅限于该版本。
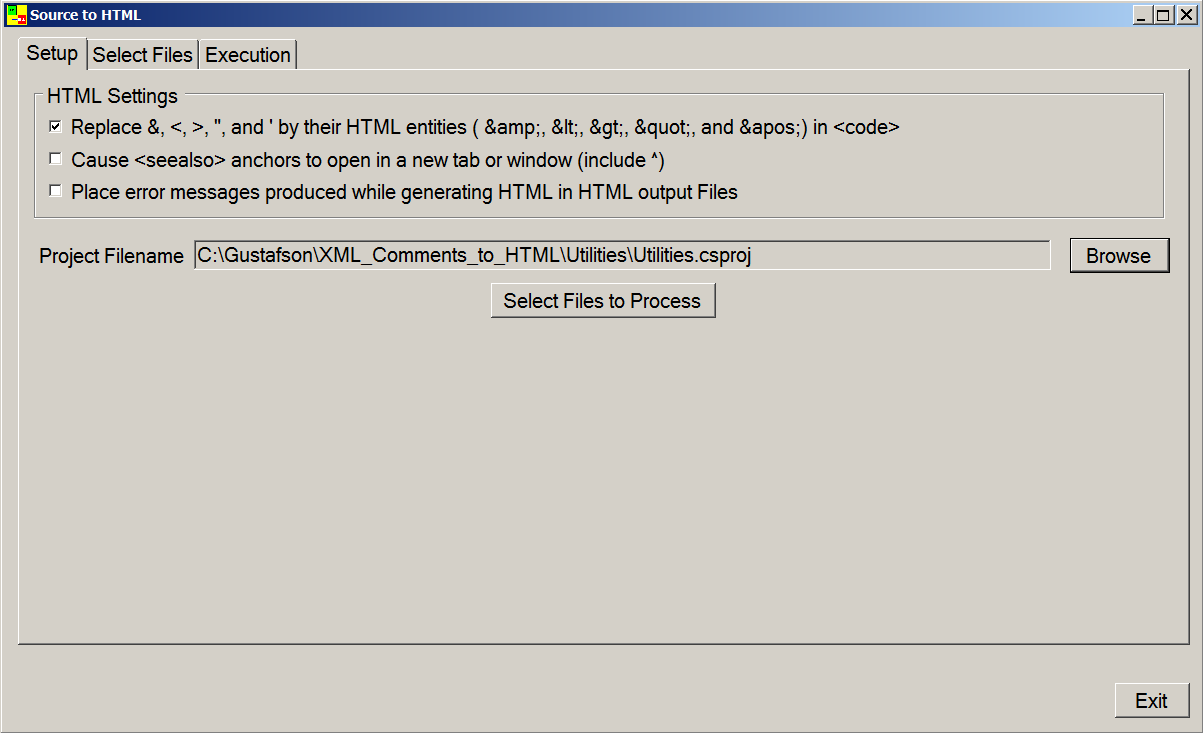
5.1. 设置阶段 
用户必须指定要使用的 C# 项目文件。这在工具的“设置”页面上完成。
(本文中的所有图像都是缩略图,点击后会放大到完整尺寸。)
在此表单的顶部,用户可以指定一些 HTML 选项。当点击“浏览”按钮时,将弹出一个模态对话框,允许用户选择一个 C# 项目文件。
XML2HTML 工具会跟踪最后选择的目录。首次运行时,last_directory 初始化为“C:\”。一旦指定了 C# 项目文件,last_directory 将被赋值为项目文件目录,并保存在注册表中以供以后检索。
对所选目录有一个要求:它必须是用户可写目录。如果不是,则会显示一条消息。测试是通过以下代码执行的。
try
{
File.Open ( project_filename,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.ReadWrite ).
Dispose ( );
set_last_directory ( project_filename );
output_directory = last_directory;
project_directory =
Path.GetDirectoryName ( project_filename );
success = true;
}
catch (IOException)
{
MessageBox.Show (
String.Format (
"Cannot write to directory {0}",
last_directory ),
"Write Permission Required",
MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Exclamation );
get_project_filename ( );
}
此要求的原因是:XML2HTML 将选定文件的 HTML 输出写入项目文件目录下的 HTML 目录,并将 HTML 文件 index.html 写入项目文件目录。
选择项目文件后,“选择要处理的文件”按钮就会出现。
5.2. 提取阶段 
当用户指定感兴趣的 C# 项目文件时,XML2HTML 会从该文件中提取数据。
5.2.1. C# 项目文件数据 
C# 项目文件是一个 XML 文档。该文件需要的是
- OutputType - 必须是“Library”
- AssemblyName - 用作 dll 名称
- RootNamespace - 用作命名空间
- 在 Compile 标签下的文件名
提取项目文件名的示例是
XmlDocument document = new XmlDocument();
XmlNodeList nodes;
.
.
.
document.Load ( project_filename );
.
.
.
nodes = document.GetElementsByTagName ( "Compile" );
foreach ( XmlNode node in nodes )
{
if ( node.Attributes [ "Include" ] != null )
{
string filename = node.Attributes [
"Include" ].Value;
available.Add ( filename,
colorize ( filename ) );
}
}
其中
using SLsc = System.Collections.Generic.SortedList<
string,
System.Drawing.Color>;
.
.
.
SLsc available = new SLsc ( );
而 colorize 是
// ************************************************** colorize
Color colorize ( string filename )
{
Color color = Color.Black;
string html_directory = String.Empty;
// last_directory ends with \
html_directory = String.Format ( @"{0}HTML",
last_directory );
if ( Directory.Exists ( html_directory ) )
{
string cs_filename = String.Empty;
string html_filename = String.Empty;
cs_filename = String.Format ( @"{0}{1}",
last_directory,
filename );
html_filename = String.Format (
@"{0}\{1}.html",
html_directory,
filename.Replace ( ".cs",
String.Empty ) );
if ( File.Exists ( html_filename ) )
{
color =
( File.GetLastWriteTime ( cs_filename ) >
File.GetLastWriteTime ( html_filename ) ) ?
color = Color.Red :
color = Color.Green;
}
}
return ( color );
} // colorize
在处理的此时,一个着色的 C# 文件列表已收集到 available 列表中。
如果没有选择要处理的文件,“创建 HTML 索引文件”按钮是唯一的选项。如果选择了一个或多个文件进行处理,“执行”按钮会出现。
无论点击哪个按钮,XML2HTML 都会作为一个单独的线程执行。这个 worker 线程执行两个单独的函数:
- 处理所有选定的文件。
- 创建 index.html 文件。
5.3. 处理选定的文件 
XML2HTML 逐个处理选定的文件。有两个独立的操作:
- 提取 XML 注释和签名
- 处理 XML 注释并生成 HTML 文档
如前所述,XML2HTML 工具严格来说并不是一个 C# 编译器:它执行词法分析,但其语法分析非常有限。它不识别 C# 错误,也不报告有缺陷的 XML 注释。
5.3.1. XML 注释/签名提取 
XML2HTML 识别的 XML 注释形式是单行 XML 注释分隔符,即三个斜杠 (///)。根据微软文档:
您可以通过编写由三个斜杠指示的特殊注释字段来为代码创建文档。注释字段包括描述注释后面代码块的 XML 元素。 ... 您可以设置 GenerateDocumentationFile 或 DocumentationFile 选项,编译器会查找源代码中所有带有 XML 标签的注释字段,并从此类注释中创建一个 XML 文档文件。启用此选项后,编译器将为项目中声明的任何未包含 XML 文档注释的公共可见成员生成 CS1591 警告。
文件中的每一行都会被读取和处理。一行被定义为后跟换行符 ('\n')、回车符 ('\r') 或紧跟换行符的回车符 ("\r\n") 的字符序列。System.IO.StreamReader.ReadLine 返回的字符串不包含终止的回车符或换行符。如果到达输入流的末尾,则返回值为 null。XML2HTML 的 read_next_line 方法会在文件末尾附加一个双匕首 (‡);XML2HTML 附加一个匕首 (†) 来表示行结束。
// ******************************************** read_next_line
public static bool read_next_line ( ref string message )
{
bool success = false;
Global.first_in_line = 0;
Global.last_in_line = 0;
message = String.Empty;
if ( Global.sr == null )
{
message = String.Format ( "{0} is not open",
Global.filename );
}
else if ( Global.sr.EndOfStream )
{
Global.line = "‡"; // syeof
Global.first_in_line = 0;
Global.last_in_line = 0;
}
else if ( ( ( Global.line =
Global.sr.ReadLine ( ).
TrimEnd ( ) ) == null ) ||
( Global.line.Length == 0 ) )
{
Global.line = "†"; // syeoln
Global.line_number++;
Global.first_in_line = 0;
Global.last_in_line = 0;
}
else
{
success = true;
Global.line += "†";
Global.line_number++;
Global.first_in_line = 0;
Global.last_in_line = Global.line.Length - 1;
}
return ( success );
} // read_next_line
Global 类保存跨 XML2HTML 方法使用的变量的持久副本。
当 XML2HTML 扫描文件内容时,每个 XML 注释块及其关联的签名会被收集到一个 XML_Comments 对象中。
// ******************************************** class XML_Comments
// XML_Comments are generated for each XML comments/signature pair
// found in the source file.
public class XML_Comments
{
public string name = String.Empty;
public Type object_type =
Object_Type.Type.UNKNOWN;
public int parameter_count = 0;
public bool parameter_heading_emitted = false;
public Dictionary <
string,
Parameter > parameter_dictionary = new
Dictionary < string,
Parameter > ( );
public StringBuilder signature = new StringBuilder ( );
public StringBuilder text = new StringBuilder ( );
} // class XML_Comments
例如,在收集完 set_placeholder 方法的 XML 注释块和关联的公共签名后,将记录以下数据:
name = "set_placeholder"
object_type = METHOD
parameter_count = 2
parameter_dictionary = Count = 2
[0] = {[control, XML2HTML.Parameter]}
Key = "control"
Value = {XML2HTML.Parameter}
description = ""
name = "control"
referenced = false
type = "Control"
[1] = {[text, XML2HTML.Parameter]}
Key = "text"
Value = {XML2HTML.Parameter}
description = ""
name = "text"
referenced = false
type = "string"
parameter_heading_emitted = false
signature = {Label set_placeholder ( Control control,
string text )}
text =
<summary>
Sets placeholder text on a control (may not work for some
controls).
</summary>
<param name="control">
The control on which to set the placeholder.
</param>
<param name="text">
The text to display as the placeholder.
</param>
<returns>
The newly-created placeholder Label.
</returns>
当 C# 文件被扫描时,每个 XML_comment 都被添加到 XML_comments_list 中。
public static LinkedList <
XML_Comments > XML_comments_list;
当 C# 文件关闭时,唯一剩下的构件是 XML_comments_list。HTML 生成和分析将在此列表上执行。
5.3.2. 处理 XML 注释并生成 HTML 文档 
首先需要按 XML_comment 的 object_type(CLASS, INTERFACE, STRUCT, ENUM, DELEGATE, CONSTRUCTOR, METHOD, FIELD, PROPERTY)然后按 name,最后按 parameter_count(降序)对 XML_comments_list 进行排序。使用的 System.Linq 排序语句是:
var ordered =
Global.XML_comments_list.
OrderBy ( x => x.object_type ).
ThenBy ( x => x.name ).
ThenByDescending ( x => x.parameter_count ).
AsEnumerable ( );
请注意,object_type 声明中使用的顺序定义了生成 HTML 页面部分的顺序。
namespace XML2HTML
{
// ********************************************* class Object_Type
public class Object_Type
{
public enum Type
{
CLASS,
INTERFACE,
STRUCT,
ENUM,
DELEGATE,
CONSTRUCTOR, // order CONSTRUCTOR before
METHOD, // METHOD
FIELD,
PROPERTY,
EVENT,
NAMESPACE,
UNKNOWN,
NUMBER_TYPES // 12
}
} // class Object_Type
} // namespace XML2HTML
对 XML_comments_list 的节点排序后,将处理 XML_comment 节点中每个 XML_comment 的 text 对象。这是一个多步过程。
- XML_comment 中的 text 必须被解析,将每个 XML 标签的内容与其他内容分开。这将生成一个文本节点列表,其中每个节点包含一个被接受的 XML 标签(<summary>, <param>, <returns>, <remarks>, <exception>, <value>, <example>, 和 <seealso>)。
- 文本节点列表必须按文本节点中出现的符号进行排序。
- 对排序后的文本节点列表中的每个文本节点进行解析。
5.3.2.1. 解析 XML 注释文本 
parse_XML_comment_text 函数在不加注释的情况下显示。
// ************************************ parse_XML_comment_text
void parse_XML_comment_text ( XML_Comments XML_comment )
{
Symbol end_symbol = Symbol.systart;
Symbol next_symbol = Symbol.systart;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ( );
Symbol symbol = Symbol.systart;
Text_Node text_node;
Global.text_list = new LinkedList < Text_Node > ( );
while ( ( symbol = Global.scanner.next_symbol ( false ) ) !=
Symbol.syeof )
{
if ( Symbols.XML_start_symbols.Contains ( symbol ) )
{
end_symbol = Global.scanner.get_XML_end_symbol (
symbol );
text_node = new Text_Node ( );
text_node.symbol = symbol;
sb.Length = 0;
while ( ( ( next_symbol =
Global.scanner.next_symbol ( false ) ) !=
Symbol.syeof ) &&
( next_symbol != end_symbol ) )
{
sb.Append ( Global.spelling );
}
StringManipulation.trim_ends ( ref sb );
sb.Append ( "‡" );
text_node.text = sb.ToString ( );
Global.text_list.AddLast ( text_node );
}
else
{
sb.Append ( Global.spelling );
}
}
} // parse_XML_comment_text
Text_Node 声明如下:
// *********************************************** class Text_Node
public class Text_Node
{
public Symbol symbol = Symbol.syunknown;
public string text = String.Empty;
} // Text_Node
解析 XML 注释文本的结果是 text_list 中的一个文本节点列表。
5.3.2.2. 对文本节点列表中的文本节点进行排序 
再次调用 System.Linq 排序来对 text_list 的节点按 symbol 进行排序。
var ordered = Global.text_list.
OrderBy ( x => x.symbol ).
AsEnumerable ( );
5.3.2.3. 解析文本节点 
每个文本节点的形式为:
// *********************************************** class Text_Node
public class Text_Node
{
public Symbol symbol = Symbol.syunknown;
public string text = String.Empty;
} // Text_Node
符号是 syXMLsummary, syXMLparam, syXMLparamref, syXMLreturns, syXMLremarks, syXMLexception, syXMLvalue, syXMLexample, 或 syXMLseealso 之一。符号为 syXMLexception 或 syXMLvalue 的节点被忽略。
文本包含 XML 注释标签的内容,去除了 XML 注释标签(该标签现在出现在 Text_Node 符号中)。例如,一个 syXMLparam 节点可能包含:
name="pattern">
The pattern for which to search‡
字符 '‡' 由 XML2HTML 插入以表示行结束(实际是文件结束)。XML 注释 text 的解析由 process_text 执行。
// ********************************************** process_text
string process_text ( )
{
Symbol symbol = Symbol.systart;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ( );
string text = String.Empty;
while ( ( symbol = Global.scanner.next_symbol (
false ) ) != Symbol.syeof )
{
if ( Symbols.XML_internal_symbols.Contains (
symbol ) )
{
sb.Append ( process_internal_XML_symbol (
symbol ) );
}
else
{
sb.Append ( Global.spelling );
}
}
text = StringManipulation.trim_newlines (
sb.ToString ( ) );
return ( text );
} // process_text
如果 XML 注释 text 包含纯文本,则 process_text 只返回其内容。但是,如果遇到内部 XML 注释标签(例如 <c>, <code>, <list>, <para>, 或 <paramref>),则会调用 process_internal_XML_symbol。
// ******************************* process_internal_XML_symbol
string process_internal_XML_symbol ( Symbol internal_symbol )
{
string prefix = String.Empty;
string suffix = String.Empty;
StringBuilder text = new StringBuilder ( );
switch ( internal_symbol )
{
// <c>...</c>
case Symbol.syXMLc:
prefix_suffix ( internal_symbol,
ref prefix,
ref suffix ) ;
text.Append ( extract_to_end_symbol (
internal_symbol ) );
break;
// <code>...</code>
case Symbol.syXMLcode:
prefix_suffix ( internal_symbol,
ref prefix,
ref suffix ) ;
text.Append ( process_XML_code ( ) );
break;
// <para>...</para>
case Symbol.syXMLpara:
prefix_suffix ( internal_symbol,
ref prefix,
ref suffix ) ;
text.Append ( extract_to_end_symbol (
internal_symbol ) );
break;
// <paramref name="name"/>
case Symbol.syXMLparamref:
prefix_suffix ( internal_symbol,
ref prefix,
ref suffix ) ;
text.Append ( extract_to_end_symbol (
internal_symbol ) );
break;
// <list type="bullet|number|table">
case Symbol.syXMLlist:
text.Append ( process_XML_list ( ) );
break;
// following are internal
// components of <list>
case Symbol.syXMLdescription:
case Symbol.syXMLitem:
case Symbol.syXMLlistheader:
case Symbol.syXMLterm:
// processed in process_XML_list
break;
default:
// ERROR
break;
}
text.Insert ( 0, prefix + Environment.NewLine );
text.Append ( Environment.NewLine +
suffix +
Environment.NewLine );
return ( text.ToString ( ) );
} // process_internal_XML_symbol
给定一个符号,prefix_suffix 返回将包围文本的 HTML 标签。
更有趣的解析在 process_XML_code 中执行。
// ****************************************** process_XML_code
/*
From MSDN documentation:
The <code> tag is used to indicate multiple lines of code.
The tag is replaced by <pre>. This means that the author must insure
that the characters &, <, >, ", and ' are replaced by their respective
HTML entities ( &, <, >, ", and '). Alternatively
the user may select, during setup, to replace these HTML characters
with their HTML entities automatically.
The processing of the <code>...</code> pair differs from that of other
tag pairs. Effectively whatever is contained with the pair of tags is
copied verbatim into the <pre>...</pre> pair. This requires that no
processing of contained contents is performed. To accomplish this end,
the following algorithm is employed:
1. The variable text is assigned the current Lexical_Scanner buffer.
2. The position, within text, of the first </code> tag is found. This
recognizes that there may be more than one <code>...</code> pair in
the text.
3. The Lexical_Scanner position is revised to point to the text
position immediately following the </code> tag. This allows
scanning to resume using the Lexical_Scanner.
4. The text is assigned the substring from the current start (0) to
the position of the first </code> tag.
5. The position of the first <code> tag is found.
6. Text is extracted from this position to the end of the text string.
7. If the user required that characters be replaced by their HTML
entities, the text will be modified accordingly.
8. The contents of the Lexical_Scanner buffer upto the </code> is
removed (allowing multiple <code>...</code> tags).
9. The text is returned.
*/
string process_XML_code ( )
{
int at = 0;
string text = String.Empty;
text = Lexical_Scanner.contents;
at = text.IndexOf ( "</code>" );
if ( at < 0 )
{
// error
return ( String.Empty );
}
Lexical_Scanner.position = ( at + "</code>".Length );
text = text.Substring ( 0, at );
at = text.IndexOf ( "<code>" );
if ( at < 0 )
{
// error
return ( String.Empty );
}
text = text.Substring ( at + "<code>".Length );
text = StringManipulation.trim_newlines ( text );
if ( replace_HTML_entities )
{
text.Replace ( "&", "&" ); // must come first
text.Replace ( "<", "<" ).
Replace ( ">", ">" ).
Replace ( "\"", """ ).
Replace ( "'", "'" );
}
// revise
// Lexical_Scanner.contents
// and
// Lexical_Scanner.position
Lexical_Scanner.contents = Lexical_Scanner.contents.
Remove ( 0,
Lexical_Scanner.position );
Lexical_Scanner.position = 0;
return ( text );
} // process_XML_code
process_XML_list 使用 XML 注释 text 的 XML 树来执行其解析。
// ****************************************** process_XML_list
/*
From MSDN documentation:
The <listheader> block is used to define the heading row of either a
table or definition list. When defining a table, you only need to
supply an entry for term in the heading. Each item in the list is
specified with an <item> block. When creating a definition list,
you'll need to specify both term and description. However, for a
table, bulleted list, or numbered list, you only need to supply an
entry for description. A list or table can have as many <item> blocks
as needed.
This implies:
General form:
<list type="bullet|number|table">
<listheader>
<term>term</term>
<description>description</description>
</listheader>
<item>
<term>term</term>
<description>description</description>
</item>
</list>
Bulleted List form:
<list type="bullet"> <ul>
<listheader> <li>
<description>desc</description> desc
</listheader> </li>
<item> <li>
<description>desc</description> desc
</item> </li>
</list> </ul>
The <listheader> in type="bullet" will be ignored since it
does not make sense in the <ul> tag
Numbered List form:
<list type="number"> <ol>
<listheader> <li>
<description>desc</description> desc
</listheader> </li>
<item> <li>
<description>desc</description> desc
</item> </li>
</list> </ol>
The <listheader> in type="number" will be ignored since it
does not make sense in the <ol> tag
Table form:
<list type="table"> <table>
<listheader> <thead>
<tr>
<th>
<term>term</term> term
</th>
<tr>
</listheader> </thead>
<tbody>
<item> <tr>
<td>
<description>desc</description> desc
</td>
</item> </tr>
</tbody>
</list> </table>
The type="table" is poorly conceived. It will not be implemented.
*/
string process_XML_list ( )
{
XmlNodeList descriptions = null;
Symbol end_symbol = Symbol.syXMLendlist;
XmlElement root = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder ( );
Symbol symbol = Symbol.systart;
string type = String.Empty;
XmlDocument XML_document = new XmlDocument ( );
sb.Append ( Global.spelling ); // "<list "
while ( ( ( symbol = Global.scanner.next_symbol (
false ) ) != Symbol.syeof ) &&
( symbol != end_symbol ) )
{
sb.Append ( Global.spelling );
}
sb.Append ( Global.spelling ); // "</list>"
XML_document.LoadXml ( sb.ToString ( ) );
// extract type
root = XML_document.DocumentElement;
type = root.Attributes [ "type" ].Value;
if ( !set_prefix_suffix ( type ) )
{
html.AppendFormat (
" <h3><span class='RedBold'>" +
"{1} is either not supported or unrecognized</span></h3>{0}",
Environment.NewLine,
type );
return ( String.Empty );
}
sb.Length = 0; // clear StringBuilder
descriptions = XML_document.GetElementsByTagName (
"description" );
if ( descriptions.Count == 0 )
{
html.AppendFormat (
" <h3><span class='RedBold'>" +
"There is no description for {1} list</span></h3>{0}",
Environment.NewLine,
type );
return ( String.Empty );
}
sb.AppendFormat (
String.Format (
"{1}{0}",
Environment.NewLine,
prefix ) ); // <ul> or <ol>
foreach ( XmlNode description in descriptions )
{
sb.AppendFormat (
String.Format (
" {1}{0} {2}{0} {3}{0}",
Environment.NewLine,
item_prefix, // <li>
StringManipulation.trim_newlines (
description.InnerText ).Trim ( ),
item_suffix ) ); // </li>
}
sb.AppendFormat (
String.Format (
"{1}{0}",
Environment.NewLine,
suffix ) ); // </ul> or </ol>
return ( sb.ToString ( ) );
} // process_XML_list
在解析完每个输入文件后,worker 线程会关闭 HTML 文件并报告其状态。当所有输入文件都处理完毕后,worker 线程会创建 index.html(如果用户选择的话)。
5.4. 创建 index.html 文件 
index.html 文件在项目文件目录中创建。它提供了一种方便的方式来浏览项目库集合的内容。index.html 文件的创建由 build_html_index_file 执行。
// ************************************* build_html_index_file
bool build_html_index_file ( ref string message )
{
string [ ] html_files;
bool success = true;
message = String.Empty;
try
{
html_directory = project_directory + @"\HTML";
html_files = Directory.GetFiles ( html_directory );
members_present = new List < string > ( html_files );
if ( members_present.Count > 0 )
{
string index_page_filename = project_directory +
@"\index.html";
if ( build_index_page ( ref index_page_filename,
ref message ) )
{
File.WriteAllText ( index_page_filename,
index_page_html.ToString ( ) );
message =
String.Format (
"HTML index page written to {0}",
index_page_filename );
success = true;
}
else
{
message =
String.Format (
"Failed to write HTML index file{0}{1}",
Environment.NewLine,
index_page_filename );
success = false;
}
}
else
{
members_present.Clear ( );
success = false;
message = String.Format (
"No HTML files in (0}",
html_directory );
}
}
catch ( Exception ex )
{
members_present.Clear ( );
success = false;
message = String.Format (
"Failed to build_html_index_file{0}{1}",
Environment.NewLine,
ex.Message );
}
return ( success );
} // build_html_index_file
index.html 页面相对简单。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang='en'>
<head>
<title>Utilities Library</title>
<meta http-equiv='Content-type'
content='text/html;charset=UTF-8' >
<meta name='viewport'
content='width=device-width, initial-scale=1' >
<style>
body
{
margin-left:10px;
width:850px;
}
.container
{
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 150px 700px;
}
ul
{
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
li
{
padding: 2% 4%;
}
button
{
text-decoration: underline;
color: Blue;
}
.members_description
{
font-size: large;
font-weight: bold;
color: #000000;
}
.title
{
font-size: xx-large;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 0px;
color: #0000FF;
padding-left: 150px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p class='title'>Utilities Library</p>
</div>
<div class='container'>
<div id='sidebar'>
<p class='members_description'>Members</p>
<ul>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'ASCIICodes' )">ASCIICodes</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'BoyerMoore' )">BoyerMoore</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'FileIO' )">FileIO</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'Placeholder' )">Placeholder</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'RegistryUtilities' )">RegistryUtilities</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'TabControls' )">TabControls</button>
</li>
<li>
<button onclick="switch_page ( 'TextFileIO' )">TextFileIO</button>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<p class='members_description'>Description</p>
<iframe
id='webpage'
src='about:blank'
width='800'
height='500'>
</iframe>
</div>
</div>
<div style='width:850px;'>
<p style='font-size: small; text-align: right; font-weight: bold;'>
XML2HTML 1.1.8978 07/31/2024-10:11
</p>
</div>
<script>
var webpage_id = document.getElementById ( 'webpage' );
window.addEventListener ( 'beforeunload', page_refresh, false );
window.onload =
function ( )
{
webpage_id.src = 'about:blank';
};
function switch_page ( new_page )
{
var reference = './HTML/' +
new_page +
'.html';
webpage_id.src = reference;
};
function page_refresh ( )
{
webpage_id.src = 'about:blank';
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
初次显示时,HTML 页面会显示一个空的 iframe,其中 HTML 文件列表显示为按钮,每个 HTML 文件对应一个按钮。(本例显示了从 XML2HTML 项目的源文件中创建的文件。)
当选择一个成员时(通过单击带有成员名称的按钮),将显示该成员的 HTML 页面。
6. 结论 
本文介绍了一个名为 XML2HTML 的工具,该工具可将项目中的 C# 源文件中的 XML 注释转换为 HTML 页面。
7. 参考文献 
- C# IntelliSense [^]
- 文档注释 [^]
- 示例 XML 文档注释 [^]
- C# 文档注释推荐标签 [^]
8. 开发环境 
XML2HTML 工具在以下环境中开发:
| Microsoft Windows 7 专业版 SP 1 |
| Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 专业版 SP1 |
| Firefox Developer Browser 115.0b9 |
| Nu HTML 校验器 [^] |
| JSHint [^] |
| FileZilla 3.67.1 [^] |
9. 目录结构 
执行时,XML2HTML 会为包含至少一个 XML 注释块并紧跟公共签名的每个 C# 源文件创建 HTML 页面。如果用户愿意,XML2HTML 还会创建一个 index.html 文件,该文件可以访问生成的 HTML 文件。
HTML 页面放置在项目文件目录下的新创建的 HTML 目录中。index.html 文件放置在项目文件目录中。对于本项目,Utilities 目录结构变为:
蓝色项目由 XML2HTML 工具创建。
为了使 index.html 文件按预期工作,必须将 HTML 目录和 index.html 文件复制到 Web 服务器。例如,该目录和文件被复制到了 gggustafson.com [^]。
10. 下载 
下载内容是 ZIP 文件中的 XML2HTML 项目源文件,不包括 bin 和 obj 目录。我建议将 ZIP 文件下载到 C:\ 目录并解压缩到一个 XML2HTML 目录。由于该项目是使用 Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 开发的,因此当您在您的 Visual Studio 版本中运行 XML_Comments_to_HTML.sln 时,您可能需要执行转换。
11. 历史记录 
| 8/4/2024 | 原文 |