背包问题的遗传算法
4.98/5 (22投票s)
使用遗传算法解决背包问题
引言
本示例演示了一个遗传算法,该算法旨在解决 此 xkcd 漫画所提出的问题。遗传算法将使用 GALex 库实现。
关于问题
一群人走进一家餐厅,想正好花费 15.05 美元购买开胃菜。他们还希望尽快准备好。这给服务员留下了一个 NP 难题需要解决,这是 背包问题 的一个变种。
服务员需要解决的问题是从菜单中选择物品,使其价格正好等于顾客指定的金额。这个问题本身就是 NP 难题,但这还不够。顾客希望尽快准备好。因此,服务员不能选择任何满足价格要求的组合。他必须找到所有组合,以便他可以选择制作时间最少的那一个。
染色体
定义遗传算法要使用的染色体表示法以及设计良好的交叉和变异操作是关键步骤,它们通常特定于要解决的问题。
表示
设计遗传算法时应做的第一件事之一是选择合适的解决方案表示法。有几种编码解决方案的方法。一些可能的表示法是
- 无序链表,其中列表节点包含要提供的物品
- 存储要提供的物品数量的数组
![]()
链表表示法

数组表示法
选择的表示法将极大地影响其他遗传操作(如交叉或变异操作)的设计。在本例中,选择了链表表示法。
该表示法的一个优点是它允许遗传算法优化表示法本身。交叉可以随意排列染色体周围的物品块,而不会影响其适应度值。通过这种方式,遗传算法可以将好的物品组合聚集在一起。这些组合被称为“构建块”。这种分组减少了构建块被破坏的可能性,这是一个好现象,因为这种破坏通常会降低解决方案的质量及其适应度值。
列表中的每个节点将存储菜单上物品的索引。由于每个节点都可以有固定的一组值,因此将使用 GaAlleleGene 来表示基因。此基因除了基因值外,还存储等位基因集。等位基因集是允许基因具有的值的集合。 GaAlleleGene 是一种复杂的基因类型,因此必须使用 GaAdvanceListChromosome 类作为染色体类型。因此,通过几个 typedef,染色体表示法几乎准备就绪。
typedef Chromosome::Representation::GaAlleleGene<int> XkcdGene;
typedef Common::Data::GaList<XkcdGene> XkcdGeneList;
typedef Chromosome::Representation::GaAdvanceListChromosome<
int, Chromosome::Representation::GaAlleleGene>::GaType XkcdChromosome;
接下来需要定义的是染色体配置块 (CCB)。CCB 将包含开胃菜列表,包括它们的价格和制作所需的时间,以及染色体基因的等位基因集。
开胃菜的定义
struct Appetizer
{
std::string _name;
float _price;
float _time;
Appetizer();
Appetizer(const std::string& name,
float price,
float time);
};
CCB 的定义
class XkcdConfigBlock : public Chromosome::GaChromosomeConfigBlock
{
private:
Common::Data::GaSingleDimensionArray<Appetizer> _appetizers;
Chromosome::Representation::GaIntervalAlleleSet<int> _interval;
public:
XkcdConfigBlock(
const Common::Data::GaSingleDimensionArray<Appetizer>& appetizers) :
_appetizers( appetizers ),
_interval (
Chromosome::Representation::GaValueIntervalBounds<int>(
0, appetizers.GetSize() - 1 ),
Chromosome::Representation::GaValueIntervalBounds<int>(
0, appetizers.GetSize() - 1 ),
GaGlobalRandomIntegerGenerator ) { }
XkcdConfigBlock(const XkcdConfigBlock& rhs) :
GaChromosomeConfigBlock(rhs),
_appetizers(rhs._appetizers),
_interval(rhs._interval) { }
virtual GaChromosomeConfigBlock* GACALL Clone() const
{ return new XkcdConfigBlock( *this ); }
};
继承 GaChromosomeConfigBlock 的 XkcdConfigBlock 类代表此问题特定的 CCB。请注意,用户定义的 CCB 必须实现 Clone 方法,并且必须具有拷贝构造函数。
使用的等位基因集是 GaIntervalAlleleSet。此集包含定义范围内的所有值。这已经足够了,因为值应该是开胃菜列表中物品的索引。每个等位基因集还包含一组反向值,这对于某些遗传操作是必需的。在这种情况下,它集是相同的。
现在染色体类型已准备就绪,必须定义以下遗传操作
- 染色体初始化
- 染色体比较器
- 适应度操作
- 交叉操作
- 变异操作
染色体初始化
染色体初始化的方法很简单:确定随机数量的物品,然后随机选择物品直到达到所需的数量。如果需要用于交叉操作的新染色体,则返回一个空染色体。该操作还会为染色体设置 CCB。
XkcdInitializator 类负责创建新染色体。它继承自 GaInitializator,后者代表用户定义初始化器的基类。库调用 operator () 来创建和初始化新染色体。
class XkcdInitializator : public Chromosome::GaInitializator
{
public:
virtual Chromosome::GaChromosomePtr GACALL operator ()(
bool empty,
const Chromosome::GaInitializatorParams& parameters,
Common::Memory::GaSmartPtr<
Chromosome::GaChromosomeConfigBlock> configBlock) const;
virtual Common::GaParameters* GACALL CreateParameters() const
{ return NULL; }
};
由于此初始化器实现不使用操作参数,因此 CreateParameters 返回 NULL。
染色体比较器
染色体比较器由 XkcdChromosomeComparator 类实现,它继承自 XkcdChromosomeComparator,后者是用户定义比较器的基类。
class XkcdChromosomeComparator :
public Chromosome::GaChromosomeComparator
{
public:
virtual float GACALL operator ()(
const Chromosome::GaChromosome& chromosome1,
const Chromosome::GaChromosome& chromosome2,
const Chromosome::GaChromosomeComparatorParams& parameters) const
{ return Equal( chromosome1, chromosome2, parameters ) ? 0.0f : 1.0f; }
virtual bool GACALL Equal(
const Chromosome::GaChromosome& chromosome1,
const Chromosome::GaChromosome& chromosome2,
const Chromosome::GaChromosomeComparatorParams& parameters) const
{ return ( (const XkcdChromosome&)chromosome1 ).GetGenes() ==
( (const XkcdChromosome&)chromosome2 ).GetGenes(); }
virtual Common::GaParameters* GACALL CreateParameters() const
{ return NULL; }
};
此实现使用列表容器定义的简单比较方法,并返回 true/false(或 1/0)。如果算法应使用适应度共享缩放 (GaShareFitnessScaling),则需要不同的实现,并且比较必须返回染色体之间的相似度比率。
适应度操作
适应度操作负责计算染色体的适应度值。所述问题有两个标准:开胃菜的成本和制作它们所需的时间,因此遗传算法在计算染色体的适应度时应同时考虑这两者。由于价格在此情况下比时间更重要,因此可以相应地为这些值分配权重,而无需进行实际的多目标优化和 Pareto 集。考虑到所有值及其权重,适应度函数应如下所示:

适应度函数: f - 适应度值,wp - 价格标准的权重,wt - 时间标准的权重,tp - 目标价格,n - 开胃菜数量,api - 第 i 个开胃菜的价格,ati - 制作第 i 个开胃菜所需的时间
由于价格更重要,因此应为 wp 分配比 wt 更高的权重。在本例中,wp 设置为 2.0,wt 设置为 1.0。
库中提供的基于权重的适应度值表示法,由 GaWeightedFitness 类实现,非常适合此示例。它可以保留两个标准(价格和时间)的值,以便显示它们,可以通过适应度参数为这些值分配权重,并且实现会自动计算加权值的总和来计算总适应度。
typedef Fitness::Representation::GaWeightedFitness<float, float> XkcdFitness;
这样就有了适应度值表示法,可以由适应度操作和库的其他部分使用。
GALex 有两种不同的方法来评估染色体的适应度值
- 基于种群 - 同时评估种群中所有染色体的适应度。当染色体的适应度函数与其他种群染色体不独立时,必须使用此方法。
- 基于个体 - 染色体的适应度独立于其他染色体进行评估。首选此方法,因为它允许库优化其他遗传操作,如选择和耦合……
此问题的适应度函数定义方式使其可以使用基于个体的方法。
操作由 XkcdFitnessOperation 类实现,它继承自 GaChromosomeFitnessOperation,后者是基于个体适应度操作的基类。由于存在目标价格,因此必须通过操作参数指定,这些参数由使用 GaFitnessOperationParams 作为基类的 XkcdFitnessOperationParams 类实现。
class XkcdFitnessOperationParams :
public Fitness::GaFitnessOperationParams
{
private:
float _targetPrice;
public:
XkcdFitnessOperationParams(float targetPrice) :
_targetPrice( targetPrice ) { }
XkcdFitnessOperationParams(const XkcdFitnessOperationParams& params) :
_targetPrice( params._targetPrice ) { }
virtual GaParameters* GACALL Clone() const
{ return new XkcdFitnessOperationParams( *this ); }
inline float GACALL GetTargetPrice() const { return _targetPrice; }
inline void GACALL SetTargetPrice(float price)
{ _targetPrice = price; }
};
class XkcdFitnessOperation :
public Chromosome::GaChromosomeFitnessOperation
{
public:
virtual Fitness::GaFitness* GACALL
CreateFitnessObject(
Common::Memory::GaSmartPtr<
const Fitness::GaFitnessParams> params) const
{ return new XkcdFitness( params ); }
virtual void GACALL operator ()(const GaObjectType& object,
Fitness::GaFitness& fitness,
const Fitness::GaFitnessOperationParams& operationParams) const;
virtual Common::GaParameters* GACALL CreateParameters() const
{ return new XkcdFitnessOperationParams(); }
};
当库需要创建适应度值对象时,会调用 CreateFitnessObject,而 operator () 代码负责评估染色体的适应度值。
交叉操作
交叉操作的目的是通过组合现有解决方案来生成新解决方案。交叉操作的实现取决于表示法。如前所述,该算法使用链表表示法,因此可以使用简单的单点交叉操作。

交叉操作
该库已提供此类交叉操作的实现。它由 GaListMultipointCrossover 类表示。
变异操作
变异操作负责保留种群中染色体的遗传多样性。这是通过随机更改新产生的染色体中的基因来完成的。
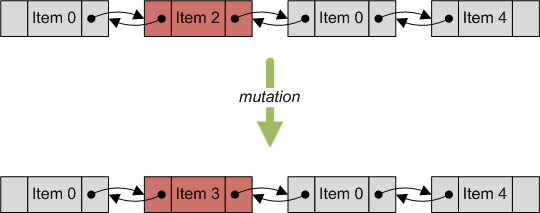
变异操作
该操作由 XkcdMutationOperation 类实现。它继承自 GaMutationOperation,后者是所有用户定义变异操作的基础。 operator () 负责对染色体执行变异。此操作需要参数来告诉它应该为哪个 GaMutationSizeParams 类更改多少基因。
class XkcdMutationOperation : public Chromosome::GaMutationOperation
{
public:
virtual void GACALL operator ()(Chromosome::GaChromosome& chromosome,
const Chromosome::GaMutationParams& parameters) const;
virtual Common::GaParameters* GACALL CreateParameters() const
{ return new Chromosome::GaMutationSizeParams(); }
};
交配操作
交配操作控制新染色体的生产周期。周期包括生成新染色体所需执行的所有遗传操作及其参数。基本周期包括调用交叉操作生成新染色体,并在这些染色体上调用变异操作。此周期在库中由 GaBasicMatingOperation 类实现。用户可以通过实现自定义交配操作来定制生产周期。 GaMatingOperation 是所有交配操作的基类。
整合各部分
最后一步是定义种群,选择合适的算法,并选择选择和替换操作。算法配置和参数
| 变异概率 | 30% |
| 变异大小 | 1 个基因 |
| 仅接受改进适应度的变异 | 是 |
| 交叉概率 | 80% |
| 交叉点 | 1 |
| 算法类型 | 增量式(重叠种群) |
| 种群大小 | 32 条染色体 |
| 排序种群 | 是 |
| 适应度排序 | 最大化 |
| 适应度权重 | 2.0, 1.0 |
| 选择类型 | 轮盘赌 |
| 选择大小 | 8 |
| 耦合类型 | 无(选择执行交配) |
| 要产生的后代数量 | 8 |
| 缩放类型 | 无缩放 |
| 替换类型 | 替换最差的 |
| 要替换的染色体 | 8 |
| 停止标准类型 | 适应度变化 |
| 停止标准深度 | 1000 代 |
将所有部分组合起来创建遗传算法的代码如下所示:
// create mating operation with:
// crossover - 80% probability, 2 offspring, 1 crossover point
// mutation - 30% probability, accept only improving mutations, 1 gene
Chromosome::CrossoverOperations::GaListMultipointCrossover crossover;
Problems::XKCD::XkcdMutationOperation mutation;
Chromosome::MatingOperations::GaBasicMatingOperation mating;
Chromosome::GaMatingConfig matingConfiguration(
Chromosome::GaCrossoverSetup( &crossover,
&Chromosome::GaCrossoverPointParams( 0.8f, 2, 1 ), NULL ),
Chromosome::GaMutationSetup( &mutation,
&Chromosome::GaMutationSizeParams( 0.3f, true, 1L ), NULL ) );
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer appetizers[] =
{
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("mixed fruit", 2.15f, 3),
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("french fries", 2.75f, 2),
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("side salad", 3.35f, 5),
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("hot wings", 3.55f, 3),
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("mozzarella sticks", 4.20f, 4),
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer("sampler plate", 5.80f, 7),
};
// create chromosome initializator
Problems::XKCD::XkcdInitializator initializator;
Chromosome::GaInitializatorSetup initializatorSetup( &initializator,
NULL, &Chromosome::GaInitializatorConfig(
&Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock(
Common::Data::GaSingleDimensionArray<
Problems::XKCD::XkcdConfigBlock::Appetizer>( appetizers, 6 ) ) ) );
// create fitness comparator for maximizing fitness value
Fitness::Comparators::GaSimpleComparator fitnessComparator;
Fitness::GaFitnessComparatorSetup fitnessComparatorSetup(
&fitnessComparator,
&Fitness::Comparators::GaSimpleComparatorParams(
Fitness::Comparators::GACT_MAXIMIZE_ALL ), NULL );
// fitness operation
Problems::XKCD::XkcdFitnessOperation fitnessOperation;
Population::GaCombinedFitnessOperation populationFitnessOperation(
&fitnessOperation );
// create population statistics trackers
// for fitness values and population size
Population::GaPopulationSizeTracker sizeTracker;
Population::GaRawFitnessTracker rawTracker;
Algorithm::Stubs::GaSimpleGAStub::GaStatTrackersCollection trackers;
trackers[ Population::GaPopulationSizeTracker::TRACKER_ID ] = &sizeTracker;
trackers[ Population::GaRawFitnessTracker::TRACKER_ID ] = &rawTracker;
trackers[ Population::GaScaledFitnessTracker::TRACKER_ID ] = &scaledTracker;
// create selection operation that:
// uses roulette wheel method and
// selects 8 parents and produces 8 offspring chromosomes
// using defined mating
Population::SelectionOperations::GaRouletteWheelSelection selection;
Population::GaSelectionSetup selectionSetup( &selection,
&Population::SelectionOperations::GaDuplicatesSelectionParams( 8, 1, 2 ),
&Population::GaCouplingConfig(
Chromosome::GaMatingSetup( &mating, NULL, &matingConfiguration ) ) );
// create replacement operation that:
// replaces 8 worst chromosomes in the population
Population::ReplacementOperations::GaWorstReplacement replacement;
Population::GaReplacementSetup replacementSetup( &replacement,
&Population::GaReplacementParams( 8 ),
&Population::GaReplacementConfig(
Chromosome::GaChromosomeComparatorSetup(
&chromosomeComparator, NULL, NULL ) ));
// creates scaling operation that just copies raw fitness value
Population::ScalingOperations::GaNoScaling scaling;
Population::GaScalingSetup scalingSetup( &scaling, NULL,
&Population::GaScalingConfig() );
// weights used to calculate fitness value
float fitnessWights[] = { 2.0f, 1.0f };
// create simple algorithm stub:
// population - 32 chromosomes, 0 crowding size, sort by raw fitness
Algorithm::Stubs::GaSimpleGAStub simpleGA(
WDID_POPULATION,
WDID_POPULATION_STATS,
initializatorSetup,
Population::GaPopulationFitnessOperationSetup(
&populationFitnessOperation,
&Problems::XKCD::XkcdFitnessOperationParams( targetPrice ),
&Fitness::GaFitnessOperationConfig(
&Fitness::Representation::GaWeightedFitnessParams<float>(
fitnessWights, 2 ) ) ),
fitnessComparatorSetup,
Population::GaPopulationParams( 32, 0,
Population::GaPopulationParams::GAPFO_FILL_ON_INIT ),
trackers,
Chromosome::GaMatingSetup(),
selectionSetup,
Population::GaCouplingSetup(),
replacementSetup,
Population::GaScalingSetup(),
Population::GaFitnessComparatorSortingCriteria( fitnessComparatorSetup,
Population::GaChromosomeStorage::GAFT_RAW ) );
// create workflow
Common::Workflows::GaWorkflow workflow( NULL );
workflow.RemoveConnection(
*workflow.GetFirstStep()->GetOutboundConnections().begin(), true );
// connect algorithm stub to workflow
Common::Workflows::GaWorkflowBarrier* br1 =
new Common::Workflows::GaWorkflowBarrier();
simpleGA.Connect( workflow.GetFirstStep(), br1 );
Common::Workflows::GaBranchGroup* bg1 =
(Common::Workflows::GaBranchGroup*)workflow.ConnectSteps(
br1, workflow.GetLastStep(), 0 );
// create stop criteria that will stop the algorithm if:
// raw fitness of the best chromosome in the population
// has not been changed for the last 1000 generations.
Algorithm::StopCriteria::GaStatsChangesCriterion stopCriterion;
Algorithm::StopCriteria::GaStopCriterionStep* stopStep =
new Algorithm::StopCriteria::GaStopCriterionStep(
Algorithm::StopCriteria::GaStopCriterionSetup(
&stopCriterion,
&Algorithm::StopCriteria::GaStatsChangesCriterionParams(
Population::GADV_BEST_FITNESS, 1000), NULL ),
workflow.GetWorkflowData(), WDID_POPULATION_STATS );
// connect stop criterion to workflow and algorithm stub
Common::Workflows::GaBranchGroupTransition* bt1 =
new Common::Workflows::GaBranchGroupTransition();
bg1->GetBranchGroupFlow()->SetFirstStep( stopStep );
bg1->GetBranchGroupFlow()->ConnectSteps( stopStep, bt1, 0 );
workflow.ConnectSteps( bt1, simpleGA.GetStubFlow().GetFirstStep(), 1 );
// subscribe handler to event raised before new generation cycle begins
Common::Workflows::GaDataCache<Population::GaPopulation> population(
workflow.GetWorkflowData(), WDID_POPULATION );
population.GetData().GetEventManager().AddEventHandler(
Population::GaPopulation::GAPE_NEW_GENERATION, &newGenHandler );
// start algorithm and wait for it to finish
workflow.Start();
workflow.Wait();
结果
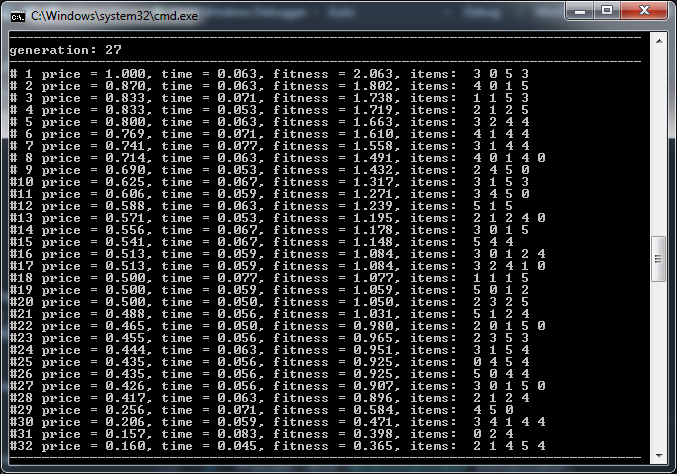
以下部分展示了目标价格为 15.05 美元的一次运行结果。它显示了染色体适应度值及其组件在运行过程中的进展。X 轴表示种群代数,Y 轴表示适应度值或其某个组件。
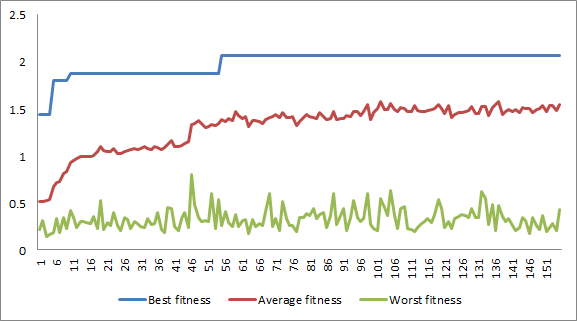
种群中最佳染色体和最差染色体的加权适应度值和平均值
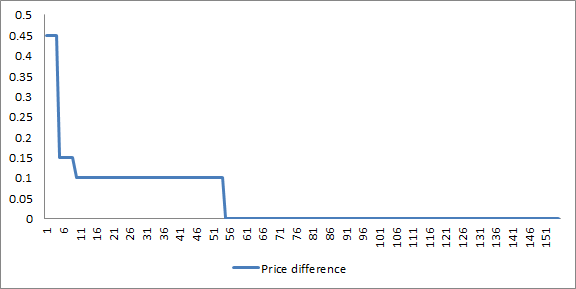
种群中最佳染色体的价格组成部分 - 它与目标价格的偏差程度
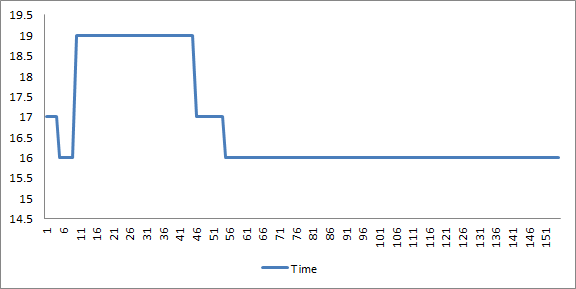
种群中最佳染色体的时间组成部分 - 制作开胃菜所需的时间
历史
- 2013 年 6 月 18 日 - 添加了结果和统计信息
- 2013 年 6 月 17 日 - 发布了原始文章
