使用 Postbuild 实现 .NET COM 互操作
4.81/5 (20投票s)
使用一个小型后编译器实现 COM 互操作。因此,可以结合 COM 接口使用多线程。
目录
- 简介
- “后编译器”
- 使用代码
- 所有 COM 对象的基类
- “后编译器”的自定义属性
- 使用“后编译器”
- 示例 (CoreAudio-API 导入)
- 运行示例
- 调试
- 关注点
- 历史
- 许可证
引言
前段时间我为我的音频库 CSCore 编写了一个 DirectSound 包装器。为了访问 DirectSound COM 接口,我不得不导入它们。我使用了传统的方式导入 COM 接口,即结合 GuidAttribute、ComImportAttribute 和 InterfaceTypeAttribute 使用接口。当我完成接口导入后,我发现我无法在多线程环境下使用这些接口。我尝试了几乎所有方法,但它一直返回 E_NOINTERFACE 错误码。
我寻找了一种在 C# 中访问 COM 接口的替代方法。Alexandre Mutel 告诉我关于 Calli 指令。该指令使用方法入口点的指针,并通过指针直接调用方法。您可以在此处阅读更多信息。
由于 Calli 指令不是 C# 的一部分,我必须手动将其放置在程序集中。为此,我必须通过在后期构建中执行一个小型“后编译器”来扩展构建过程。
“后编译器”必须搜索标记有自定义属性的虚拟方法的调用。如果找到这样的方法调用,它将被替换为 calli 指令(包括方法调用的参数)。为了找到上述调用,后编译器必须处理每个类型、每个方法等。

编写“后编译器”以访问 Calli 指令
后编译器不过是一个简单的控制台应用程序。要编辑程序集,您可以使用许多不同的库。我正在使用 Mono.Cecil,它可以通过 nuget 获取。
AssemblyPatcher 类将使用此方法处理程序集中的每个方法(包括属性 getter 和 setter)
private void ProcessMethod(MethodDefinition method)
{
if (method.HasBody)
{
ILProcessor ilProcessor = method.Body.GetILProcessor();
//process every instruction of the methods body
for(int n = 0; n < ilProcessor.Body.Instructions.Count; n++)
//foreach won't work because iterator length is bigger than count??
{
var instruction = ilProcessor.Body.Instructions[n];
//check whether the instruction is a call to a method
if (instruction.OpCode.Code == Code.Call && instruction.Operand is MethodReference)
{
//get the called method
MethodReference methodDescription = (MethodReference)instruction.Operand;
//get the attributes of the called method
var attributes = GetAttributes(methodDescription.Resolve());
//check whether the called method is marked with the given calli attribute
if (attributes.Contains(_calliAttributeName))
{
//create a callsite for the calli instruction using stdcall calling convention
var callSite = new CallSite(methodDescription.ReturnType)
{
CallingConvention = MethodCallingConvention.StdCall
};
//iterate through every parameter of the original method-call
for (int j = 0; j < methodDescription.Parameters.Count; j++)
//foreach won't work because iterator length is bigger than count??
{
var p = methodDescription.Parameters[j];
if (p.ParameterType.FullName == "System.Boolean")
{
MessageIntegra-tion.WriteWarning("Native bool has a size of 4 bytes." +
" Use any type which as a size of 32bit instead of System.Boolean.",
methodDescription.FullName);
}
//append every parameter of the method-call
//to the callsite of the calli instruction
callSite.Parameters.Add(p);
}
//create a calli-instruction including the just built callSite
var calliInstruction = ilProcessor.Create(OpCodes.Calli, callSite);
//replace the method-call by the calli-instruction
ilProcessor.Replace(instruction, calliInstruction);
_replacedCallsCount++;
}
}
}
}
}
由于后编译器修改了程序集,因此 PDB 文件也必须重新写入。您可以将原始 pdb 文件作为参数传递,或者后编译器会自动搜索它,将已处理程序集的扩展名更改为 .pdb。
//check whether the pdbfile has been passed through application parameters
if (pdbfile == null)
{
//if not use the default pdbfilepath by changing the extension of the assembly to .pdb
pdbfile = Path.ChangeExtension(filename, "pdb");
}
//check whether the original pdb-file exists
bool generatePdb = File.Exists(pdbfile);
//if the original pdb-file exists -> prepare for rewriting the symbols file
wp.WriteSymbols = generatePdb;
rp.ReadSymbols = generatePdb;
if (rp.ReadSymbols)
{
rp.SymbolReaderProvider = new PdbReaderProvider();
}
如果发生任何错误,MessageIntegration 类将以与 Microsoft Build 过程兼容的格式打印错误。因此,错误将显示在 Visual Studio 错误窗口中
public static void WriteError(string message, string location)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("{0}:error:[CSCli]{1}", location, message);
}
public static void WriteWarning(string message, string location)
{
Console.Error.WriteLine("{0}:warning:[CSCli]{1}", location, message);
}
Using the Code
为所有 COM 对象创建基类
ComObject 基类存储本机 COM 指针并提供对 IUnknown 接口的访问。它还提供对 GetMethodPtr 方法的访问,该方法根据本机 COM 指针和方法索引计算方法指针。为了确定索引,我们需要头文件或 idl 文件。例如,我们可以查看 IMMDeviceCollection 接口。它是 mmdeviceapi.h 头文件的一部分
MIDL_INTERFACE("0BD7A1BE-7A1A-44DB-8397-CC5392387B5E")
IMMDeviceCollection : public IUnknown
{
public:
virtual /* [helpstring][id] */ HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE GetCount(
/* [annotation][out] */
_Out_ UINT *pcDevices) = 0;
virtual /* [helpstring][id] */ HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE Item(
/* [annotation][in] */
_In_ UINT nDevice,
/* [annotation][out] */
_Out_ IMMDevice **ppDevice) = 0;
};
您可以看到 IMMDeviceCollection 派生自 IUnknown。因此,如果我们想知道 GetCount 方法的索引,我们首先必须确定 IUnknown 接口有多少个方法。我们会发现 IUnknown 接口有三个方法。所以 GetCount 方法的索引是 3。总而言之,您必须计算每个基类/接口中的每个方法,并将其添加到您想要指针的方法的索引中。在上面的示例中,Item 方法的索引将是 4。GetMethodPtr 的实现如下所示
public unsafe void* GetMethodPtr(int methodIndex)
{
return GetMethodPtr(methodIndex, 3); //default start index of 3
}
public unsafe void* GetMethodPtr(int methodIndex, int startIndex)
{
return ((void**)(*(void**)_comPtr))[methodIndex + startIndex];
}
创建 Calli 和 RemoveTypeAttribute
“后编译器”使用了这些属性。CalliAttribute 用于标识必须由 calli 指令替换的虚拟方法。RemoveTypeAttribute 用于标识包含虚拟方法的虚拟类。所有标记有 RemoveTypeAttribute 的类在处理程序集后将自动删除(包括 Calli- 和 RemoveTypeAttribute)。
[RemoveType]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method)]
public class CalliAttribute : Attribute
{
}
[RemoveType]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)]
public class RemoveTypeAttribute : Attribute
{
}
将后编译器添加到后期构建
要自动运行后编译器,我们必须在后期构建事件命令行中创建一个条目。打开应用程序的属性。打开“构建事件”选项卡并将以下命令行添加到后期构建事件中
call "$(SolutionDir)CSCli\$(OutDir)CSCli.exe" -file:"$(TargetPath)"
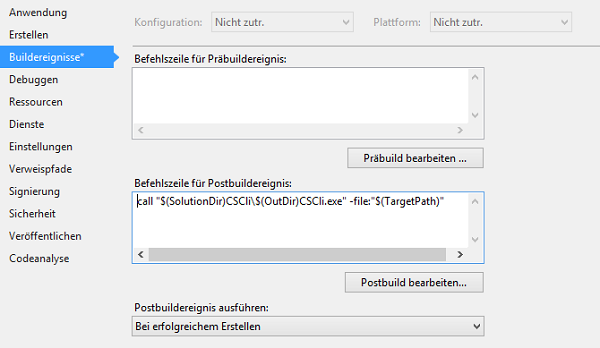
现在在解决方案资源管理器中选择一个项目。在项目菜单上,选择项目依赖项。选择“依赖项”选项卡,然后从下拉菜单中选择您的应用程序。现在勾选“依赖于”字段中的 CSCli 项目。

使用后编译器导入 CoreAudio-API 的部分
要导入新的 COM 接口,请创建一个新的类,该类派生自之前创建的 ComObject 类和 GUID 属性。您可以通过查看接口定义(参见上一个示例)找到类的 GUID。
[Guid("0BD7A1BE-7A1A-44DB-8397-CC5392387B5E")]
public class MMDeviceCollection : ComObject
{
public MMDeviceCollection(IntPtr comPtr)
: base(comPtr)
{
}
}
现在我们必须添加接口的方法。第一个方法是 GetCount,索引为 3(因为 IUnknown)
public unsafe int GetCountNative(out int deviceCount)
{
fixed (void* pdeviceCount = &deviceCount)
{
deviceCount = 0; //to avoid compiler errors
return InteropCalls.CallI(ComPtr, pdeviceCount, GetMethodPtr(0));
}
}
现在让我们看一下实现:首先,我们需要查看头文件中的定义
virtual /* [helpstring][id] */ HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE GetCount(
/* [annotation][out] */
_Out_ UINT *pcDevices) = 0;
我们可以看到 GetCount 方法有一个类型为 UINT* 的参数。我们还可以看到它将在调用 GetCount 方法后接收其值(参见 [out] 或 _Out_)。因此,我们在 GetCountNative 方法中添加了一个类型为 int(或 uint)的新参数和 out 关键字。
由于我们需要一个指向 UINT 值的指针,我们可以使用 fixed 关键字将 deviceCount 参数固定在内存中并获取其内存位置的指针。之后,我们需要创建一个名为 InteropCalls 的虚拟类(您可以选择自己的名称)。该虚拟类将包含所有将由后编译器替换的虚拟调用。别担心。编译并运行后编译器后,该虚拟类将被删除。创建虚拟类 InteropCalls 后(您只需要执行一次),我们可以使用所需的参数调用我们的虚拟方法。首先,您始终必须将 Com 接口作为第一个参数,将方法指针作为最后一个参数。第一个参数您始终可以通过 ComObject 基类的 ComPtr 属性获取。最后一个参数您始终可以通过 GetMethodPtr 方法获取。请注意,您可以传递索引 0 而不是 3,因为 GetMethodPtr 的第一个重载会自动添加 startIndex 3。在第一个参数和最后一个参数之间,您必须放置所调用 com 方法的参数。将所有内容结合起来,代码应类似于上面的示例代码。
由于仍然存在编译器错误,告诉我们没有定义名为 CallI 的方法,我们可以选择生成,Visual Studio 将自动生成该方法。

现在导航到生成的 CallI 方法并向其添加 CSCalli 属性
[CSCalli]
internal static unsafe int CallI(void* ComPtr, void* ppc, void* p)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
就这样。现在您可以编译您的项目,我们可以看看结果
.method public hidebysig instance int32
GetCountNative([out] int32& deviceCount) cil managed
{
// Code size 33 (0x21)
.maxstack 4
.locals init ([0] native int& pinned pdeviceCount,
[1] int32 CS$1$0000)
.line 32,32 : 9,10 ''
//000030:
//000031: public unsafe int GetCountNative(out int deviceCount)
//000032: {
IL_0000: nop
.line 33,33 : 20,53 ''
//000033: fixed (void* pdeviceCount = &deviceCount)
IL_0001: ldarg.1
IL_0002: stloc.0
.line 34,34 : 13,14 ''
//000034: {
IL_0003: nop
.line 35,35 : 17,33 ''
//000035: deviceCount = 0; //to avoid compiler errors
IL_0004: ldarg.1
IL_0005: ldc.i4.0
IL_0006: stind.i4
.line 36,36 : 17,82 ''
//000036: return InteropCalls.CallI(ComPtr, pdeviceCount, GetMethodPtr(0));
IL_0007: ldarg.0
IL_0008: call instance void* System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComObject::get_ComPtr()
IL_000d: ldloc.0
IL_000e: conv.i
IL_000f: ldarg.0
IL_0010: ldc.i4.0
IL_0011: call instance void* System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComObject::GetMethodPtr(int32)
IL_0016: calli unmanaged stdcall int32(void*,void*)
IL_001b: stloc.1
IL_001c: leave.s IL_001e
IL_001e: nop
.line 38,38 : 9,10 ''
//000037: }
//000038: }
IL_001f: ldloc.1
IL_0020: ret
} // end of method MMDeviceCollection::GetCountNative
正如您所看到的,“后编译器”用 calli 指令替换了对 InteropCalls.CallI 方法的调用(参见 IL_0016)。现在让我们尝试运行示例应用程序。
ComInteropTest 示例
对于示例项目,您可以查看 ComInteropTest 项目。它提供了对 CoreAudio API 的一些接口的访问。运行示例,您将看到所有可用的音频设备

调试
由于后编译器重写了符号文件,您仍然可以调试整个应用程序。

由于虚拟调用在构建过程中被移除,您无法单步执行它们。它们被 calli 指令替换,这意味着您现在调用的是 COM 方法而不是虚拟方法。
关注点
如果您导入任何 com 接口,请始终提醒自己,您必须自己进行所有封送处理。这意味着您必须传递与 C 函数期望的值完全相同的值。例如,您不能用托管类型 System.Boolean 替换非托管类型 BOOL。BOOL = 1 字节,System.Boolean = 4 字节。
一个 com 兼容 bool 类型的示例实现将是这样的
[Serializable]
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Size = 4)]
public struct NativeBool : IEquatable<nativebool>
{
public static readonly NativeBool True = new NativeBool(true);
public static readonly NativeBool False = new NativeBool(false);
private int _value;
public NativeBool(bool value)
{
_value = value ? 1 : 0;
}
public bool Equals(NativeBool other)
{
return this._value == other._value;
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (obj is NativeBool || obj is Boolean)
return Equals((NativeBool)obj);
return false;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return _value.GetHashCode();
}
public static bool operator ==(NativeBool left, NativeBool right)
{
return left.Equals(right);
}
public static bool operator !=(NativeBool left, NativeBool right)
{
return !(left == right);
}
public static implicit operator bool(NativeBool value)
{
return value._value != 0;
}
public static implicit operator NativeBool(bool value)
{
return new NativeBool(value);
}
public override string ToString()
{
return this ? "True" : "False";
}
}
历史
- 07.09.2013 - 添加
NativeBool代码 - 06.09.2013 - 修正拼写错误
- 05.09.2013 - 添加历史记录
- 02.09.2013 - 添加兴趣点
- 27.08.2013 - 添加标签
- 27.08.2013 - 初始版本
