基于 DefaultValue 属性的属性初始化方法
4.82/5 (33投票s)
基于 DefaultValue 属性实现属性初始化的各种方法
引言
Microsoft Corporation 在 .NET 1.1 版本中引入了 DefaultValueAttribute 类。其文档中的歧义导致了一些关于该类如何使用和如何工作的混淆。为了消除混淆,Microsoft 发布了知识库文章 311339,其中指出:“DefaultValue 属性不会导致初始值使用该属性的值进行初始化。”因此,这种行为的实现留给了我们开发者。
本文介绍如何创建轻量级且高效的算法,以从 DefaultValue 属性初始化类属性。文章实现了、测试并分析了不同的方法。它还演示了如何将其实现为 AOP(面向切面编程)扩展,可以直接用于任何 C# 类。
背景
DefaultValueAttribute 用默认值注解属性。此信息随类型的元数据一起保存,可用于向运行时或设计时工具和环境进行描述。有关 DefaultValueAttribute 类的详细信息可在 MSDN 库中找到。该属性的典型用法示例如下:
public class TestClass
{
[DefaultValue(1)]
public int IntProperty { get; set; }
[DefaultValue(1)]
public long LongProperty { get; set; }
[DefaultValue(true)]
public bool BoolProptrty { get; set; }
}
*本文中的示例代码为简化起见,仅作演示。完整的实现请下载源代码。
各种方法和实现
原生初始化
最简单、最直接的方法是在构造函数中手动初始化所需的属性,如下所示:
public Constructor()
{
IntProperty = 1;
LongProperty = 1;
BoolProptrty = true;
}
public Constructor(int i)
{
IntProperty = 1;
LongProperty = 1;
BoolProptrty = true;
}
此解决方案的主要优点是简单,代码紧凑且速度快。此方法的缺点在于它是“手动”的。它需要手动同步 DefaultValueAttribute 中设置的值与此类型的所有构造函数,并且容易出现所有可能的人为错误。
使用 ComponentModel 服务进行初始化
在寻找此问题的解决方案时,我偶然发现了 Daniel Stutzbach 撰写的一篇文章,他在文章中提出了一种简单而有效的算法,该算法会遍历类的属性列表,并根据与其成员关联的 DefaultValue 属性设置默认值。
public Constructor()
{
// Iterate through each property
foreach (PropertyDescriptor prop in TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(this))
{
// Set default value if DefaultValueAttribute is present
DefaultValueAttribute attr = prop.Attributes[typeof(DefaultValueAttribute)]
as DefaultValueAttribute;
if (attr != null)
prop.SetValue(this, attr.Value);
}
...
}
在类的构造过程中,此算法会遍历每个属性,并检查该属性是否具有关联的 DefaultValueAttribute。如果存在这样的属性,则使用该属性中的值初始化该属性。
此算法的好处在于它消除了容易出错的手动同步,并允许值初始化与各种设计工具更加一致。
坏处是效率不高。该算法使用反射服务,并且在每次创建新对象时都会遍历所有属性。
使用 PropertyDescriptor.ResetValue(...) 进行初始化
下一个方法与 ComponentModel 初始化方法非常相似,只是它使用了 PropertyDescriptor 类的 ResetValue(…) 方法。根据 MSDN 文档,此方法按以下优先顺序重置属性到确定的值:
- 该属性有一个被覆盖的属性。
- 该属性有一个
DefaultValueAttribute。 - 已实现一个“
ResetMyProperty”方法,其中“MyProperty”是被重置的属性的名称。
因此,此实现的用法如下:
public Constructor()
{
// Iterate through each property and call ResetValue()
foreach (PropertyDescriptor property in TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(this))
property.ResetValue(this);
...
}
此方法比直接查询 DefaultValue 属性创建了更灵活的解决方案。它提供了重置属性值的替代方法,但并未提高其性能。
使用委托进行初始化
前两个算法相对较慢。很多 CPU 周期都花在了遍历集合和搜索要调用的正确方法上。如果所有 ResetValue 方法只解析一次,并且它们的引用存储在缓存中供以后使用,那么它们的性能可以得到提高。
private static Action<object><this> setter; // Reset multicast delegate
public Constructor()
{
// Attempt to get it from cache
if (null == setter)
{
// If no initializers are added do nothing
setter = (o) => { };
// Go through each property and add method calls to multicast delegate
foreach (PropertyDescriptor prop in TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(this))
{
// Add only these which values can be reset
if (prop.CanResetValue(this))
setter += prop.ResetValue;
}
}
// Initialize member properties
setter(this);
}
此算法与前两个类似,但它不是在每个属性上调用 ResetValue 方法,而是将该方法的引用添加到多播委托中。一旦所有属性都被迭代,调用此委托就会将它们重置为适当的值。每次连续实例化该类时,只需调用此多播委托,而无需再次重新构建它。
此方法创建了最灵活、最完整的重置属性为其默认值的机制。与其他方法相比,它通过收集属性描述符和属性的迭代来消除不必要的迭代,从而提高了它们的性能。不幸的是,在性能方面,它仍然无法与直接初始化方法相比。
使用预编译的 Setter 进行初始化
带有委托缓存的解决方案消除了对 ResetValue 方法的重复查询。不幸的是,它仍然在每次调用时搜索每个属性的默认值。如果既没有使用覆盖属性,也没有使用“ResetMyProperty”方法来初始化默认值,那么就可以消除这些搜索。每个属性的初始常量值只能从 DefaultValue 属性中检索一次,并与适当的 SetValue 委托一起存储在缓存中以备将来使用。
通过使用 lambda 表达式,我们可以在运行时生成自定义代码,并创建以下方法:
(object o){ o.PropertySetter(constant); }
其中 o 是对象的实例,PropertySetter 是指向适当的 set 方法的委托,而 constant 是从 DefaultValue 属性检索到的值。
这些表达式的列表可以被编译并添加到多播委托中以供将来使用。
// Default Value multicast delegate
private static Action<object><this> setter;
public CompiledComponentModelInitialization()
{
// Attempt to get it from cache
if (null == setter)
{
ParameterExpression objectTypeParam = Expression.Parameter(typeof(object),
"this");
// If no initializers are added do nothing
setter = (o) => { };
// Iterate through each property
foreach (PropertyInfo prop in this.GetType().GetProperties(
BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance))
{
// Skip read only properties
if (!prop.CanWrite)
continue;
// There are no more then one attribute of this type
DefaultValueAttribute[] attr = prop.GetCustomAttributes(
typeof(DefaultValueAttribute), false) as DefaultValueAttribute[];
// Skip properties with no DefaultValueAttribute
if ((null == attr) || (null == attr[0]))
continue;
// Build the Lambda expression
// Create constant expression with value from DefaultValue attribute
// and convert it into appropriate type
Expression dva = Expression.Convert(Expression.Constant(attr[0].Value),
prop.PropertyType);
// Create expression describing call to appropriate setter and
// passing it instance and value parameters
Expression setExpression = Expression.Call(Expression.TypeAs(
objectTypeParam, this.GetType()),
prop.GetSetMethod(), dva);
// Create lambda expression describing proxy method which receives
// instance parameter and calls instance.setter( constant )
Expression<Action<object><action><this>> setLambda =
Expression.Lambda<action><this><Action<object><action><this>>(
setExpression, objectTypeParam);
// Compile and add this action to multicast delegate
setter += setLambda.Compile();
}
}
// Initialize member properties
setter(this);
}
首次创建该类的实例时,将遍历所有 public 可写属性,生成 Lambda 表达式,编译并添加到多播委托。下次实例化该类型的对象时,只需通过该委托调用这些预编译的方法。
此方法在首次实例初始化时需要大量资源和时间,但在所有其他实例初始化过程中,几乎消除了与使用 DefaultValue 属性相关的所有开销。在性能方面,一旦代理方法被构建和编译,这是唯一能够与直接初始化方法媲美的算法。
测试结果
在多次执行此测试应用程序以消除随机结果后,可以得出以下平均值:
| 执行周期数 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 | 100000 | 1000000 |
| 直接初始化 | 973 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 使用 ComponentModel | 11211 | 88 | 40 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 38 | 37 | 30 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 26 |
| 使用 Reset Property | 4423 | 57 | 35 | 34 | 34 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 34 | 33 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 | 26 |
| 使用多播委托进行初始化 | 8194 | 44 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 17 | 16 |
| 使用预编译的 Setter 进行初始化 | 18999 | 14 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
从这些数字可以看出,第一次实例化类需要很长时间,即使初始化时没有任何特殊操作。在类至少实例化一次之后,性能会提高。
以下图表展示了本文所述所有方法的相对性能图。
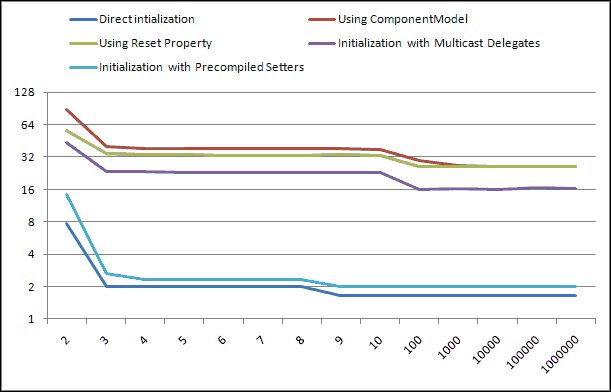
*此图未包含第一个周期,以提高缩放比例。
AOP 实现
面向切面编程 (AOP) 是一种编程范式,其中将次要或支持性函数与主程序业务逻辑隔离。这些初始化方法提供的功能非常适合此类。
C# 提供了一种特殊的机制,允许为任何类类型扩展自定义行为。这种机制称为扩展方法。有关此技术的详细信息,请访问MSDN。
此实现提供了两种算法:“委托缓存的 PropertyDescriptor.ReserValue() 调用”和“预编译的 setter”。这些方法分别称为 ResetDefaultValues() 和 ApplyDefaultValues()。为了使用这些方法,请执行以下步骤:
- 下载 AOP.zip,解压缩并将其文件 AOP.cs 添加到您的项目中。
- 通过在类源文件中添加行:
using AOP;将 AOP 命名空间引入作用域。 - 在需要使用默认值初始化参数时,在代码中添加语句
this.ResetDefaultValues();或this.ApplyDefaultValues();
using System;
using System.Linq;
using AOP;
namespace YourNamespace
{
public class YourClass
{
public Constructor()
{
this.ApplyDefaultValues();
}
...
}
}
历史
- 2010 年 3 月 16 日 - 文章首次发布
- 2010 年 3 月 18 日 - 在 Steve Hansen 的精彩建议下,缓存查找中的
try…catch…finally序列已被Dictionary.TryGetValue替换。 - 2010 年 3 月 19 日 - 在 Miss Julia Lutchenko 的帮助下,修复了一些语法和风格问题。
- 2010 年 3 月 25 日 - 修复了一个小 bug 并添加了多线程支持。
欢迎任何批评、评论、 bug 修复或改进。
