DataGrid 中快速自定义公式、筛选和排序
通过使用编译后的 Linq 表达式,驯服 WinForms 和 WPF 内置 DataGrid 以处理 200,000+ 行数据
引言
以灵活的方式在 UI 控件中显示大量数据通常需要牺牲一些实现通用性,否则会发生性能下降。然而,这并不意味着精心设计的通用 DataGrid 不能专门用于处理相当大的数据量,同时仍能以用户可接受的方式运行。
本文使用一些高级技术来增强现有的内置 WinForms 和 WPF DataGrid,以处理 200,000+ 行和 100+ 列数据,实现以下功能:
- 提供用户定义的、经过解析和完全编译的涉及任何列的公式;
- 以类似方式进行实时筛选;
- 通过常见的列标题交互进行实时排序,并且完全编译;
- 无需重新绑定即可添加/删除列;
- 快速添加/更改行数据;
- 能够为每行分配唯一键和额外的元数据(如颜色);
- 基于已知的行/列更改集进行最佳重新计算策略。
请注意,相同的技术可以增强商业 WinForms DevExpress 网格,尽管它具有足够的筛选/排序/分组/刷新支持,但在处理其他方面非常糟糕。
动机
Excel 电子表格在金融行业(以及其他行业)中无处不在,主要原因是它们允许业务用户以直接的方式执行基本数据分析,而无需为每个任务聘请纯技术人员。
当这些项目在许多用户之间共享并对这些用户变得至关重要时,开发人员经常被召集来“产品化电子表格”。
结果是一个围绕 DataGrid 构建的 .NET 应用程序,其选择通常由公司策略和相关开发人员(通常很快过时)的经验驱动。
本文提出的解决方案最初是由需要使用此类商业网格(WinForms DevExpress)的需求驱动的,同时仍为自定义公式、大量列和按需数据更改提供可接受的性能。
这里的目的是表明,可以使用 .NET 附带的 DataGrid 来满足特定业务用户的定制和性能需求,而无需诉诸商业替代方案以及项目生命周期后期通常会带来的复杂性。
以下展示了 WPF 和 WinForms 示例程序,其中包含:
- 多列排序(`Price` + `Quantity`)
- `Custom2`,其表达式取决于 `Price`、`Quantity` 和 `Custom1`
- 根据 `Price` 和 `Custom1` 将 200,000 条记录筛选为 61,093 条


最终的屏幕截图显示了一个基本的表达式编辑器,在本例中,它正在编辑应用于每一行的复杂筛选器

性能
请注意,此示例(对于排序而言)是(故意地)病态糟糕的,因此形成了一个很好的最坏情况场景,在生产中不太可能经常发生,因为 a) 数据通常不是随机的,b) 筛选表达式不太可能涉及像 Sqrt 这样昂贵的计算。
上述屏幕截图中的时间显示,从文本中解析公式的时间通常比编译为 IL、跟踪依赖项和设置内部结构的时间更长。
例如,执行此解析(包括递归依赖树创建)大约需要 50 毫秒(ResetExpressions),而大约需要 30 毫秒(Recalculate)来
- 确定 200,000 个随机双精度浮点数,将其装箱并分配给 `Price` 列
- 类似地计算并存储 `Custom1` 为 `Quantity*Price`
- 类似地计算并存储 `Custom2` 为 `Price^2/Quantity` + `Custom1`
- 最后计算筛选器为 `Price>1 And Sqrt(Custom1)>3`
然而,以编程方式创建并编译多列比较器到 IL 只需大约 5 毫秒(SortingCreateComparer),而实际上对筛选后的 61,242 行执行排序需要大约 20 毫秒(SortingWithComparer),如果没有筛选器,这个数字会大大更高。
最后,“切换”按钮演示了如何快速添加/删除/重新排列列,而不会触发冗长的网格设置,这是此解决方案的目标之一。
表达式
所使用的表达式语法基于 SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) 表达式,如 报表定义语言 (RDL) 中所使用的。它实际上是 Visual Basic .NET 的一行版本,旨在供报表设计人员在创建报表时设置动态属性。
每个外部引用都必须使用“!”作为分隔符进行作用域限定。例如,当混合来自多个源的数据时,此作用域对于处理给定列在这些源之间重复的名称很有用。
在一般情况下,所有表达式都以“=”开头,以将其使用与原始文本值区分开来。
在随附的示例项目中,作用域已固定为单词“Field”。例如,这会按预期执行相关的算术运算
=Field!Price*2+Field!Quantity/3.14152
支持类似 Excel 的逻辑函数和内联运算符
=IIf(Field!Price>2, Field!Quantity Mod 12, Field!Price/2)
在语法之外实现了许多函数,以便于扩展
=Format(Today() + 5, "s")
目前,上述代码映射到 `DateTime.ToString("s")`,但是语法本身直接支持 `ToString()` 等“字段函数”,因此这很容易实现。
解析
解析的艺术已被广泛研究,是软件工程领域中拥有成熟良好算法的领域之一。以下是基本步骤和术语的提醒:
- 文法 - 传统上用 BNF 编写
- 词法分析 - 传统上使用 Flex 教授
- 句法分析 - 传统上使用 YACC 教授
- 抽象语法树 - 结果作为内存中的树结构(参见 AST)
- AST 的处理 - 例如转换为 IL
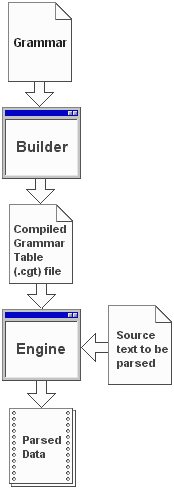
GOLD Parser 系统有详尽的文档,并且为过程的不同阶段提供了许多工具。下面是其中一个工具,显示了描述表达式语法的部分 BNF 语法文件

将语法文件加载到 Builder 中,然后可以输入测试表达式以显示解析器运行时可以公开的“事件”。下面显示了匹配语法行的部分展开

一旦编译后的语法表嵌入到程序集中,就需要一个适当的运行时来使用它。这取决于个人偏好,但我选择 Calitha 是因为它具有事件驱动的特性。
Linq 的 AST
谜题的最后一部分是重用现有的 Linq AST,它用于在运行时编译熟悉的 Linq-to-Object 表达式。Calitha 解析器的错误、匹配符号和匹配语法规则事件使用如下:
public Parser()
{
Errors = new List<string>();
FieldsNeeded = new SortedList<string,>(32);
ArrayParameter = Linq.Expression.Parameter(typeof(object[]), "Fields");
_Parser = _Reader.CreateNewParser();
_Parser.TrimReductions = true;
_Parser.StoreTokens = LALRParser.StoreTokensMode.NoUserObject;
_Parser.OnReduce += _Parser_OnReduce;
_Parser.OnTokenRead += _Parser_OnTokenRead;
_Parser.OnTokenError += _Parser_OnTokenError;
_Parser.OnParseError += _Parser_OnParseError;
}
`OnTokenRead` 用于处理语法中三个符号的匹配:字符串、数字和标识符。最简单的 Linq 表达式(常量)用于前两个,通过从处理程序返回它,它将在所有语法规则的 UserObject 属性中可用
static object RuleSymbolNumberHandler(Parser p, TerminalToken t)
{
//Known to be a valid number or integer already
//Culture has to be invariant because grammar has '.' hard-coded
if (t.Text.IndexOf('.') >= 0)
return Linq.Expression.Constant(double.Parse(t.Text, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
return Linq.Expression.Constant(int.Parse(t.Text, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
}
`OnReduce` 用于处理语法规则的匹配。下面的乘法规则有三部分:左表达式、乘法符号和右表达式。每个部分都将通过符号处理程序或另一个语法规则设置 UserObject。
static object RuleExpressionTimesHandler(Parser p, NonterminalToken t)
{
//<Mult Exp> ::= <Mult Exp> '*' <Negate Exp>
var r = Helpers.Promote(t.Tokens[0].UserObject, t.Tokens[2].UserObject);
return Linq.Expression.Multiply(r[0], r[1]);
}
然而,Linq 表达式的类型必须与正在应用的任何运算符或函数正确匹配;这不是自动完成的。在此类型提升过程中必须应用优先级,目前使用的是字符串、DateTime、双精度浮点数,然后是十进制数。
没有 Linq 强制转换表达式,只有 'As' 和 'Convert'。反向工程后者会发现它处理所有情况,如果可能则进行强制转换,如果必要则进行装箱/拆箱。以下是 `Helpers.Promote` 例程中的一个示例:
//1. If either is double, ensure both are double
if (res[0].Type == typeof(double))
{
if (res[1].Type != typeof(double))
res[1] = Linq.Expression.Convert(res[1], typeof(double));
}
else if (res[1].Type == typeof(double))
{
if (res[0].Type != typeof(double))
res[0] = Linq.Expression.Convert(res[0], typeof(double));
}
编译
对 Calitha 引擎的调用将返回根语法令牌,其 UserObject 将设置为相应的 Linq AST 根
var token = _Parser.Parse(input);
Debug.Assert(token != null || Errors.Count > 0);
//Failed
if (token == null) return null;
var expression = (Linq.Expression)token.UserObject;
ResultType = expression.Type;
Description = expression.ToString();
这种表达式在编译之前有一个简洁的 Debug View 功能,可以显示详细信息,例如前面使用的复杂筛选器表达式

剩下就是编译调用,它接受参数占位符(`ArrayParameter`)并生成所需类型的 DynamicMethod。
//Box if necessary
if (expression.Type.IsValueType)
expression = Linq.Expression.Convert(expression, typeof(object));
CompiledDelegate = (Func<object[], object>)
Linq.Expression.Lambda(expression, ArrayParameter).Compile();
所需的信息,例如此表达式所需的任何字段(作为对象在 `ArrayParameter` 中传递)和结果类型,都可作为 Parser 类的字段获得。
行比较器
这些是通过程序化地创建 Linq AST 来实现的,实际上比刚才讨论的解析方法更为复杂。(可以说,这些应该使用低级 Reflection.Emit 来创建,以避免 Linq 的冗长,但这个话题留待未来文章。)
这是例程的一个示例
/// <summary>
/// Creates a row comparer for one or more columns
/// </summary>
/// <param name="columns" />One type for each column, with true for asc and false for desc sort order
/// <returns>
public Func<object[][], int, int, int> CreateComparer(params KeyValuePair<Type, bool>[] columns)
{
if (columns == null || columns.Length == 0) throw new ArgumentNullException("columns");
var arg0 = Linq.Expression.Parameter(typeof(object[][]), "columns");
var arg1 = Linq.Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "firstRowIdx");
var arg2 = Linq.Expression.Parameter(typeof(int), "secondRowIdx");
var nullConstant = Linq.Expression.Constant(null);
var equalConstant = Linq.Expression.Constant(0);
var returnLabel = Linq.Expression.Label(typeof(int), "Result");
var returnGreater = Linq.Expression.Return(returnLabel,
Linq.Expression.Constant(1), returnLabel.Type);
var returnLess = Linq.Expression.Return(returnLabel,
Linq.Expression.Constant(-1), returnLabel.Type);
设置参数和常量后,创建返回 1 表示大于和 -1 表示小于的返回标签。然后,输入中的每一列都会生成一个代码块,如下所示(完整详细信息请参阅源代码):
var block = Linq.Expression.Block(
Linq.Expression.Label(thisLabel),
//if both null or same string instance then are equal so try next column
//(or return equal)
Linq.Expression.IfThen(bothValuesAreSameInstance, valuesAreEqual),
//if first is null then less
Linq.Expression.IfThen(firstValueIsNull, returnFirstIsLess),
//if second is null then greater
Linq.Expression.IfThen(
secondValueIsNull, Linq.Expression.Return(returnLabel, returnFirstIsGreater)),
//if unboxed values are equal try next column (or return equal)
Linq.Expression.IfThen(
Linq.Expression.Equal(typedFirstValue, typedSecondValue), valuesAreEqual),
//final typed check
typedFinalCheck
);
最终表达式以通常的方式编译,引用前面定义的参数
var res = Linq.Expression.Lambda(Linq.Expression.Block(comparisons), arg0, arg1, arg2);
return (Func<object[][], int, int, int>)res.Compile();
数据源
表达式、它们所需的依赖关系和计算顺序之间的协调器是 DataSource。因此,它必须包含许多列,有些只包含数据,有些包含表达式。DataSource 提供的一些功能是使其可用于 UI 组件,包括:
- 维护一个 DataColumn 集合,可通过用户定义的名称、内部绑定名称或索引进行双向查找;
- 维护一个 DataRow 集合,以提供某些 DataGrid 所需的可绑定虚拟行;
- 每列可以有相关的用户定义的元数据;
- 每行可以有一个唯一的 Key 以及其他用户定义的元数据,并且可以通过其 Key 查找行;
- 列包含一个用于数据对象的数组,具有保守的重新大小调整和最优的交换删除;
- 行只包含索引和用户定义的元数据:它们具有某些 DataGrid 所需的直通式可绑定属性;
- 提供筛选枚举器,以确定某行是否通过任何已分配的筛选器;
- 维护计算顺序并协调任何已分配表达式(包括筛选器)的状态;
- 允许对特定更改的列或更改的行键进行优化重新计算。
这本质上是内置 `DataTable` 的轻量级版本,但数据按列而非行排列。重点在于频繁更改列和行时的内存效率,而不是添加新行。
基本用法
这是一个模板类,设计用于直接使用,而不是隐藏在绑定之后
//Example metadata to associate with a given row
public struct RowMetaData
{
public bool IsSpecial;
}
//Example column metadata to associate with a given column
public class ColMetaData
{
public DataGridColumn Column;
}
//Datasource
readonly DataSource<RowMetaData, ColMetaData> _source
= new DataSource<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>();
//Expression Parser (shared: only one needed per concurrent thread)
readonly Parser _parser = new Parser();
DataSource 期望每列有一种类型(但仅在调试版本中检查,以避免显著的速度问题)。定义放入其中的第一列:
//Number of rows to use
const int Rows = 10 * 1000;
//Note that the names must look like: Category.Name
//This is the initial set of columns
static readonly KeyValuePair<string, Type>[] _InitialColumns = new[]
{
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Description", typeof(string)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Quantity", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Price", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Custom1", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Custom2", typeof(double)),
};
//Add a few sample columns to the source
//Note that the names must look like: Category.Name
_source.AppendColumns(_InitialColumns);
填充数据只需一次性为行创建所有空间(避免逐个创建,因为重新调整大小算法只针对小增量进行调整),然后进行设置。
//Fill in the string column for a sample set of rows
_source.AddNewRows(Rows);
var col0 = _source.Columns[0];
var col1 = _source.Columns[1];
for (int i = 0; i < Rows; i++)
{
//Description
col0[i] = string.Format("Row {0:N0}", i);
//Quantity
col1[i] = 1.3m;
}
对于实际情况,通常会添加特定的行元数据,例如格式化,以及当然是键的分配。键重要性的一个例子是当用户在 DataGrid 中选择一系列行时,您需要将这些行映射到与 DataSource 中 DataRows 关联的实际业务对象,以运行某些业务流程。另一个可能只是为了访问底层原始类型数据。这里我只是将第八行设置为“特殊”——在示例中,它用于更改背景颜色。
//Set custom metadata on row #7
var custom = new RowMetaData { IsSpecial = true };
_source.SetMetaDataContainer(7, custom, key: null);
现在可以分配表达式了,请仔细注意 '.' 和 '!' 的用法。
var exps = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>>();
//Create one expression
//Note that the expressions refer to names like: Category!Name
exps.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Field.Custom1", "=Field!Quantity*Field!Price"));
//Assign expression columns (does not recalculate)
_source.ResetExpressions(_parser, exps);
最后一步必须是重新计算。在这里,所有行和列都将被处理,并且在计算停止之前,每列只允许出现十个表达式运行时异常。
//Evaluation stops after 10 errors on a single expression - this is a tough call because it could be the case that the errors are okay
//so ideally prompt the user and let them recalc with no threshold (-1).
var errorThreshold = 10;
_source.Recalculate(null /*changed columns*/, null /*changed row keys*/, ref errorThreshold);
if (errorThreshold > 0)
{
MessageBox.Show(this,
string.Format("Over 10 errors occurred in {0:N0} expression(s)", errorThreshold),
"Possible error in expression(s)", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Stop);
}
如果用户触发了某些 UI,意味着需要不同的字段集,那么最佳方法如下。请注意,这将重用任何已删除的列,因此顺序可能不符合规范。所有表达式都将被删除,因此您需要像首次设置 DataSource 时一样调用 `ResetExpressions()` 和 `Recalculate()`。
//This is an alternative set of columns to switch to
static readonly KeyValuePair<string, Type>[] _AlternateColumns = new[]
{
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Custom2", typeof(double)), //Moved to first
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Quantity", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Price", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Custom1", typeof(decimal)),
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Text", typeof(string)), //New one
new KeyValuePair<string, Type>("Field.Extra", typeof(string)), //New one
};
_source.AdjustColumns(_AlternateColumns);
//Same ResetExpressions() and Recalculate() as before
如果发生某些外部事件,并且某些列中的某些行有新数据可用,则可以使用最优的刷新路径。请仔细注意,只有 Price 列被标记为重新计算,但所有行仍将被处理。如果实际上只更新了行的子集,则可以提供 Key 以进一步缩短重新计算时间。
//1. Change the data in the source
var price = _source.GetColumn("Field.Price");
var random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < Rows; i++)
{
//Demo: leave 8th row's price null
if (i != 7) price[i] = (decimal)Math.Round(random.NextDouble() * 10, 2);
}
//2. Recalculate any custom columns that depend upon this change
_source.Recalculate(new [] { price.Index }, null /*changed row keys*/, ref errorThreshold);
//Same errorThreshold logic as before
过滤器。
可以分配可选的筛选器 - 可以使用任何生成布尔值的表达式。最佳解决方案是使用 `ResetExpressions()`,使用特殊名称 `_source.ExpressionFilterName` 传入筛选器以及任何其他表达式。
string FilterExpression = "=Field!Price>1";
var exps = new List<KeyValuePair<string, string>>();
//Create one expression
//Note that the expressions refer to names like: Category!Name
exps.Add(new KeyValuePair<string, string>("Field.Custom1", "=Field!Quantity*Field!Price"));
//Add filter as well using well known name
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(FilterExpression))
exps.Add(
new KeyValuePair<string, string>(_source.ExpressionFilterName, FilterExpression));
//And reset as usual
_source.ResetExpressions(_parser, exps);
//Usual Recalculate() etc
然而,筛选器是唯一可以直接添加、修改或删除的表达式,并且它有自己的重新计算方法。
//Alternatively, add/modify/delete the filter separately
_source.EditFilterExpression(_parser, FilterExpression);
_source.RecalculateFilter(null /*changed row keys*/, ref errorThreshold);
//Same errorThreshold logic as before
一旦分配了有效的筛选器并进行了重新计算,结果可以如下读取。目前没有索引访问可用,但使用常规的位掩码索引用于优化存储布尔值的 ulong 数组可以轻松实现。
if (_source.HasValidFilter)
{
foreach (var include in _source.FilterEnumerator())
{
if (include)
{
//DataRow 'i' passes the filter
}
i++;
}
}
装箱与绑定
对内置 WPF DataGrid 和 Winforms DevExpress DataGrid 进行逆向工程表明,绑定不仅是确保所有功能可用的唯一方式,而且它们都依赖于基本的 .NET 反射技术——即所有值类型都被装箱。对于这些网格以及内置的 Winforms DataGrid(在虚拟模式下),每当新行滚动到视图中时,就会发生这种通过反射的装箱。
这是 DataSource 将数据存储在对象数组中(每个 DataColumn 一个)而不采用更高级的类型化方法的一个关键原因(另一个原因是当列更改时能够重用昂贵的对象数组)。
上述两个 DataGrid 都最优地绑定到 `IBindingList` 和 `ITypedList` 实现,其中期望的是具有固定公共属性集的行集合。重新绑定是一项非常昂贵的任务,因为它被实现为即使只更改了一列,也像正在创建全新的列架构一样。
在实现这些接口时,必须像一个完全固定大小的静态列表一样工作,不支持通知。这样,就可以以最佳方式支持批量更新、表达式、过滤和排序。
- `IBindingList` 方法和属性要么返回 `false`,要么抛出 `NotImplementedException`。
- 如果使用默认的 `ListCollectionView`(不推荐),WPF 要求实现相当多的 `IList` 和 `ICollection` 成员,包括 `IndexOf` 和 `CopyTo`。
- 内置的 WinForms DataGrid 和 WinForms DevExpress DataGrid 需要最少的实现。
绑定时,DataSource 显示为 DataRows 列表,而 `ITypedList` 提供的所有属性都映射到列查找。这里的关键点是所有属性都在编译时定义;这主要是为了确保平滑的开发体验(当调试类型检查不可避免地失败时),并使代码更易于维护。
/// <summary>
/// Represents a virtual row within the datasource (which is represented as columns)
/// NOTE: DO NOT USE THIS CLASS - it is for binding purposes only
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="R">Match that used on the DataSource</typeparam>
/// <typeparam name="C">Match that used on the DataSource</typeparam>
public class DataRow<R, C>
where R : struct
where C : new()
{
/// <summary>
/// Class for meta data stored per row
/// </summary>
public struct MetaDataContainer<S> where S : struct
{
public Key Key;
public S Data;
}
private readonly DataSource<R, C> _source;
/// <summary>
/// The index of the row in the data source
/// </summary>
public readonly int RowIndex;
//This must be in ASCII sortable order
public object c00 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 0]; } }
public object c01 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 1]; } }
public object c02 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 2]; } }
public object c03 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 3]; } }
public object c04 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 4]; } }
public object c05 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 5]; } }
public object c06 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 6]; } }
public object c07 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 7]; } }
public object c08 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 8]; } }
public object c09 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 9]; } }
public object c10 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 10]; } }
public object c11 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 11]; } }
public object c12 { get { return _source[RowIndex, 12]; } }
//ETC
实践中的表达式
单独来看,DataSource 和表达式解析都相当简单;当它们结合在一起时,事情就变得棘手了。
- 如果 DataSource 元数据正在保存和重新加载,那么表达式所使用的列的可用性和类型可能已更改;
- 如果一个表达式编译正常,但在运行时抛出异常(例如类型不匹配),这可能导致 UI 长时间无响应;
- 单个表达式可能依赖于其他表达式,依此类推,导致循环依赖,从而使应用程序挂起;
- 任何表达式实际上都可能是一个运行时常量,因此只应计算一次。
状态
DataSource 中的每列通过 `DataColumnExpression` 类跟踪已分配表达式的状态,该类具有以下属性:
/// <summary>
/// The user-entered formula, starting with '='
/// </summary>
public readonly string Expression;
/// <summary>
/// The fixed Error that occurred during Parsing or Compilation
/// (Check this first)
/// </summary>
public string Error { get; internal set; }
/// <summary>
/// The friendly version of the parsed Expression
/// </summary>
public string Description { get; internal set; }
/// <summary>
/// Non-null only if formula needs other columns
/// </summary>
public readonly ISet<int> ColumnsNeeded;
/// <summary>
/// The order of the columns needed or null
/// </summary>
public readonly int[] DelegateArguments;
/// <summary>
/// The compiled delegate - may be null if in error or derived class doesn't use it
/// </summary>
public Func<object[], object> CompiledDelegate { get; protected set; }
/// <summary>
/// How many row(s) were in error during last recalculation
/// </summary>
public int LastErrorCount { get; internal set; }
在当前设计中,由于上述 `ColumnsNeeded` 缓存,任何列的重新排序都会立即使表达式失效。此类的创建展示了 `Parser`、其他可用字段以及字段名称到列索引的映射如何结合在一起以初始化表达式状态,值得仔细研究。
internal DataColumnExpression(Parser parser, string expression,
IDictionary<string, Type> fields, Func<string, int> nameToIndexMapper)
{
Expression = expression;
//Requires subsequent recalculation
HasNeverBeenCalculated = true;
if (Parse(parser, expression, fields))
{
Description = parser.Description;
if (parser.FieldsNeeded.Count > 0)
{
//Cache columns and arguments using the immutable column indicies
ColumnsNeeded = new HashSet<int>();
foreach (var pair in parser.FieldsNeeded)
{
ColumnsNeeded.Add(nameToIndexMapper(pair.Key));
}
DelegateArguments = new int[parser.FieldsNeeded.Count];
foreach (var pair in parser.FieldsNeeded)
DelegateArguments[pair.Value] = nameToIndexMapper(pair.Key);
}
}
else
{
Error = string.Join("\n", parser.Errors);
}
}
创建
`ResetExpressions()` 函数构成了表达式在 DataSource 中集成的核心。表达式的解析、编译和赋值大致如下所示(完整详细信息请参阅源代码):
foreach (var pair in expressions)
{
var idx = _LookupColumnByName[pair.Key];
_ColumnsWithExpressions.Add(idx);
var col = _Columns[idx];
//Marks column as !HasNeverBeenCalculated
var exp = new DataColumnExpression(parser, pair.Value, dict,
name => _LookupColumnByName[name]);
if (exp.Error == null)
{
col.ResetTypeOnly(parser.ResultType);
dict[pair.Key] = parser.ResultType;
}
col.Expression = exp;
//Handle constant columns (parse errors are handled later)
if (exp.Error == null && exp.ColumnsNeeded == null)
{
processed.Add(idx);
object constant = null;
try
{
constant = exp.CompiledDelegate(null);
exp.HasNeverBeenCalculated = false;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
exp.Error = ex.Message;
//Errors handled later
continue;
}
col.SetConstantValue(constant);
}
}
确定顺序
一旦所有表达式都被解析,它们的依赖关系被记录,并且所有常量表达式都被处理,剩下的表达式将决定计算顺序。强制执行 `StackLimit` 以防止可能的长循环依赖,任何错误都将导致所有相应的列数据被清除。
//Recursively determine calculation order, watching out for loops
foreach (var idx in _ColumnsWithExpressions)
{
var col = _Columns[idx];
var expression = col.Expression;
if (!processed.Contains(idx))
{
if (expression.Error == null)
{
var stackDepth = StackLimit;
order.Clear();
_RecurseExpressionDependencies(expression, processed, order,
ref stackDepth);
//If no error occurred, watch out for stack overflow
if (expression.Error == null)
{
if (stackDepth >= 0)
{
_CalculationOrder.AddRange(order);
_CalculationOrder.Add(idx);
}
else expression.Error = "Circular references detected";
}
}
processed.Add(idx);
}
//Clear error columns (propagation handled by recursion)
if (expression.Error != null && col != null) col.SetConstantValue(null);
}
每个表达式的 `ColumnsNeeded` 属性都会针对表达式进行处理,依此类推,直至递归限制。请注意,所使用的集合类型很重要,因为必须严格维护顺序。
void _RecurseExpressionDependencies(DataColumnExpression expression, ISet<int> processed,
List<int> order, ref int stackDepth)
{
stackDepth--;
if (stackDepth < 0) return;
if (expression.ColumnsNeeded != null)
{
string errors = null;
foreach (var idx in expression.ColumnsNeeded)
{
if (processed.Contains(idx)) continue;
var col = _Columns[idx];
if (col.Expression != null)
{
if (col.Expression.Error == null)
{
_RecurseExpressionDependencies(col.Expression, processed, order,
ref stackDepth);
//Expression dependencies have been calculated
order.Add(col.Index);
}
//Stop on first error
if (col.Expression.Error != null)
{
processed.Add(idx);
errors = col.Expression.Error;
break;
}
}
processed.Add(idx);
}
expression.Error = errors;
}
}
计算
所有表达式的重新计算都在 `Recalculate()` 中进行,即使没有表达式,它也会用于向任何侦听器发送更改通知——例如,本文后面描述的 `DataSourceView` 使用此更改集通知来确定何时重新应用任何排序和筛选到其视图。
简化版本的例程具有启发性——有关完整详细信息,请参阅源代码。
首先,任何调用者提供的更改列列表都将导致主重新计算的一个子集。这对于重新计算时间有很大影响,特别是对于像只更改筛选器表达式这样的事情。
public ICollection<int> Recalculate(ICollection<int> changedColumns,
ICollection<Key> rows, ref int errorThreshold)
{
var order = _CalculationOrder;
//Calculate reduced list based on changed columns
if (changedColumns != null && changedColumns.Count > 0)
{
order = new List<int>(_CalculationOrder.Count);
var columnsToCalculate = new SortedSet<int>(changedColumns);
foreach (var idx in _CalculationOrder)
{
var exp = _Columns[idx].Expression;
if (!exp.HasNeverBeenCalculated && !changedColumns.Contains(idx))
{
//Has been calculated at least once and user is not forcing a
//recalculation then only recalculate if any of its
//dependencies are being recalculated.
var neededFields = exp.ColumnsNeeded;
//Constant and error expressions have already been set
if (neededFields == null) continue;
if (!columnsToCalculate.Overlaps(neededFields)) continue;
}
columnsToCalculate.Add(idx);
order.Add(idx);
}
}
然后,按照(可能缩减的)计算顺序处理包含表达式的列,使用 `ColumnsNeeded` 的缓存列表来形成所需的输入列数组。
foreach (var idx in order)
{
var col = _Columns[idx];
var expression = col.Expression;
var error = expression.Error;
//Valid and non-constant column
if (error == null && expression.ColumnsNeeded != null)
{
var args = new object[expression.DelegateArguments.Length];
var cols = new DataColumn<C>[args.Length];
for (int a = 0; a < args.Length; a++)
{
cols[a] = _Columns[expression.DelegateArguments[a]];
}
expression.LastErrorCount = 0;
expression.HasNeverBeenCalculated = false;
//Finally loop over all rows in target column
for (int i = 0; i < RowCount; i++)
{
object value;
if (_DoOneRow(i, expression, cols, args, out value, errorThreshold))
{
col[i] = value;
continue;
}
//And clear rest of column
col.SetConstantValue(null, i);
res++;
break;
}
}
}
最后,仅当该行上的所有输入列数据都不为空时,才为每行计算表达式(目前不支持可为空的值类型)。
static bool _DoOneRow(int i, DataColumnExpression expression, DataColumn<C>[] cols,
object[] args, out object res, int errorThreshold)
{
int nullColumns = 0;
for (int a = 0; a < cols.Length; a++)
{
var arg = cols[a][i];
args[a] = arg;
if (arg == null) nullColumns++;
}
//Force to null if all inputs are null
if (nullColumns > 0)
{
res = null;
return true;
}
//And call
try
{
res = expression.CompiledDelegate(args);
return true;
}
catch (Exception)
{
//TODO: show error somewhere but not in column due to type
res = null;
expression.LastErrorCount++;
if ((errorThreshold >= 0) && (expression.LastErrorCount > errorThreshold))
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
WPF 实现
WPF 绑定方法的问题在于它过于努力地试图始终有效,即使结果永远无法扩展。一个很好的例子是,它有时非常乐意使用 `IEnumerable`,从而需要多次枚举才能确定数据项的索引。
此外,即使提供了用于批量集合更改的新 `INotifyCollectionChanged` 接口,也不意味着像内置 WPF DataGrid 或其关联的 `ICollectionView` 这样的控件可以一次处理多个通知。内置的排序和筛选速度 notoriously 缓慢,主要是因为试图过于泛化,并将 DataGrid 和 ICollectionView 与数据解耦。
DataSourceView
经过大量的逆向工程,克服这些(以及其他)缺陷的最佳方法是继承 `CollectionView` 类并实现所需的 `IItemProperties` 和 `IEnumerator` 接口。
internal class DataSourceView<R, C> : CollectionView, IItemProperties, IEnumerator, IComparer<int>
where R : struct
where C : new()
{
/// <summary>
/// The underlying source
/// </summary>
public readonly DataSource<R, C> Source;
构造包括连接到 DataSource 和排序集合,以跟踪任何筛选或排序何时发生变化。
//Track filter changes
Source.OnFilterChanged = (exp, isValid) => _filterChanged = true;
//Track sort changes
_sortDescriptions = new SortDescriptionCollection();
((INotifyCollectionChanged)_sortDescriptions).CollectionChanged
+= (s, e) => { _sortChanged = true; _sort = null; };
//Track data changes
Source.OnCalculation = OnSourceCalculation;
刷新通过在所有更改完成后仅触发一次集合重置事件来手动处理。
readonly NotifyCollectionChangedEventArgs _CollectionResetArgs =
new NotifyCollectionChangedEventArgs(NotifyCollectionChangedAction.Reset);
protected override void RefreshOverride()
{
//Change detection, filtering and sorting occurs here
//- see DataSourceView.cs for more detail
base.OnCollectionChanged(_CollectionResetArgs);
}
一般视图设计是在筛选或排序生效时,仅维护视图与行之间以及反向的基于一的映射。因此,筛选例程的关键部分如下所示:
//Source -> View mapping must be done post any sorting
if (!bIsSorting) Array.Clear(_mapToView, 0, _mapToView.Length);
if (Source.HasValidFilter)
{
foreach (var include in Source.FilterEnumerator())
{
if (include)
{
//Use one-based
_mapToSource[_viewCount] = i + 1;
_viewCount++;
//Source -> View mapping must be done post any sorting
if (!bIsSorting) _mapToView[i] = _viewCount;
}
i++;
}
}
else
{
//Transitioned from having a filter to none while sorting
while (i < _sourceCount)
{
//Use one-based
_mapToSource[i] = i + 1;
//Source -> View mapping must be done post any sorting
if (!bIsSorting) _mapToView[i] = i + 1;
i++;
}
_viewCount = _sourceCount;
}
//Clear any remainder
Array.Clear(_mapToSource, _viewCount, _mapToSource.Length - _viewCount);
//Cannot update view map without re-applying sorting
if (bIsSorting) _sortChanged = true;
相应的排序例程首先必须(重新)创建已编译的比较器
if (_sort == null)
{
//Create comparer
var input = new KeyValuePair<Type, bool>[sdCount];
for (int i = 0; i < input.Length; i++)
{
var sd = _sortDescriptions[i];
var col = Source.Columns[Source.TryGetColumnIndexByBindingName(sd.PropertyName)];
_sortArgs[i] = (object[])col;
input[i] = new KeyValuePair<Type, bool>
(col.Type, sd.Direction == ListSortDirection.Ascending);
}
_sort = _parser.CreateComparer(input);
}
然后对整数数组应用排序算法,例如 `Array.Sort(_mapToSource, 0, _viewCount, /*comparer*/)`
//Sort the view -> source map by the source itself
//In v4.0, this is pure QuickSort; in v4.5, it is mixed with HeapSort etc
//Array.Sort(_mapToSource, 0, _viewCount, this);
//TimSort - this is stable so better for sorting a grid data from a user perspective
TimSort.ArrayTimSort<int>.Sort(_mapToSource, 0, _viewCount, _Comparer);
//And recreate the source -> view map to match
Array.Clear(_mapToView, 0, _mapToView.Length);
for (int i = 0; i < _viewCount; i++)
{
//One based
var src = _mapToSource[i] - 1;
_mapToView[src] = i + 1;
}
这些映射然后用于视图中的两个关键功能。请注意,映射数组是基于一的,以避免在筛选器导致行数大幅波动时需要重新分配它们。
public override object GetItemAt(int viewIndex)
{
if (_usingMapping)
{
viewIndex = _mapToSource[viewIndex] - 1;
Debug.Assert(viewIndex >= 0,
"DataSourceView.GetItemAt: an invalid ViewIndex was requested");
}
return _sourceAsList[viewIndex];
}
public override int IndexOf(object item)
{
var row = item as DataRow<R, C>
if (row != null)
{
var res = row.RowIndex;
if (_usingMapping)
{
//Will be -1 if item is in the datasource but not in the view
res = _mapToView[res] - 1;
}
return res;
}
return -1;
}
基本用法
最优化方法是在 `Window` 的构造函数中手动绑定,并启用 `AutoGenerateColumns`
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
DataContext = this;
var cvs = new DataSourceView<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>(_source, _parser);
uiGrid.ItemsSource = cvs;
}
在网格可见之前,隐藏列并启用排序
void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Hide all columns and set sort path
for (int i = 0; i < uiGrid.Columns.Count; i++)
{
var ui = (DataGridTextColumn)uiGrid.Columns[i];
ui.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Collapsed;
var binding = (Binding)ui.Binding;
ui.SortMemberPath = binding.Path.Path;
ui.CanUserSort = true;
}
}
要使用行元数据来更改颜色,如 DataSource 部分所述,请使用行事件
Brush _brushSaved;
void uiGrid_LoadingRow(object sender, DataGridRowEventArgs e)
{
var row = (DataRow<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>)e.Row.Item;
//Format the row
var md = _source.GetMetaData(row.RowIndex);
if (md.IsSpecial)
{
_brushSaved = e.Row.Background;
e.Row.Background = Brushes.Plum;
}
}
void uiGrid_UnloadingRow(object sender, DataGridRowEventArgs e)
{
var row = (DataRow<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>)e.Row.Item;
//Clear formatting
var md = _source.GetMetaData(row.RowIndex);
if (md.IsSpecial)
{
e.Row.Background = _brushSaved;
}
}
首次使用时重置 DataGrid 涉及使用前面描述的 DataSource 例程并根据需要控制 UI 列的可见性。
void ResetButton_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
//Hide all columns, resetting display order
for (int i = 0; i < _source.ColumnCount; i++)
{
var col = uiGrid.Columns[i];
col.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Collapsed;
col.SortDirection = null;
//Doing this cannot be deferred at the view level
col.DisplayIndex = i;
}
这里的关键点是,由于所有 UI 列实际上都是预绑定的(即使它们并非都作为真实列存在于 DataSource 中),因此每个 UI 列都必须仔细回收。
//Recycle columns from the grid
for (int i = 0; i < _InitialColumns.Length; i++)
{
var name = _InitialColumns[i].Key;
var header = name.Split('.')[1];
var ui = uiGrid.Columns[i];
ui.Header = header;
ui.Visibility = System.Windows.Visibility.Visible;
//And store in the meta data for easier searching later
_source.Columns[i].MetaData = new ColMetaData { Column = ui };
}
由于列的动态性质,需要以编程方式分配样式,字符串格式化也是如此。分配给 Binding 的自定义转换器提供了最灵活的方法,因为格式化字符串可以存储在列元数据中。
var cellStyle = new Style(typeof(TextBlock));
cellStyle.Setters.Add(new Setter
(TextBlock.HorizontalAlignmentProperty, HorizontalAlignment.Right));
//Format the columns
for (int i = 1; i < _InitialColumns.Length; i++)
{
var ui = (DataGridTextColumn)uiGrid.Columns[i];
ui.ElementStyle = cellStyle;
//Bindings are immutable once used so recreate every time
var binding = (Binding)ui.Binding;
binding = new Binding(binding.Path.Path);
binding.Converter = _N2Converter;
ui.Binding = binding;
}
最后,视图被要求执行刷新,这最终会进入重写的 `RefreshOverride()` 例程。
void RefreshVewOnly()
{
//This will in practise schedule a dispatcher rebind of only the visible rows
var view = (DataSourceView<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>)uiGrid.ItemsSource;
view.Refresh();
}
三态排序
按住 Shift 键并对多列进行排序以及再次关闭排序是标准功能,令人恼火的是内置 WPF DataGrid 还没有这些功能。以下代码独立于自定义视图和自定义 DataSource,除了刷新功能可能不适用于所有视图。
void uiGrid_Sorting(object sender, DataGridSortingEventArgs e)
{
//Cancel default sorting
e.Handled = true;
var view = (ICollectionView)uiGrid.ItemsSource;
var ui = (DataGridTextColumn)e.Column;
var toMatch = ui.SortMemberPath;
var sorts = view.SortDescriptions;
//Cycle: ascending, descending, off
if (ui.SortDirection == ListSortDirection.Descending)
{
if ((Keyboard.Modifiers & ModifierKeys.Shift) == ModifierKeys.Shift)
{
//Still holding shift so only remove this sort
for (var i = 0; i < sorts.Count; i++)
{
if (sorts[i].PropertyName == toMatch)
{
sorts.RemoveAt(i);
ui.SortDirection = null;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
_ClearSorting(sorts);
}
}
else if (ui.SortDirection == ListSortDirection.Ascending)
//etc
else
//etc
}
//Refresh view
view.Refresh();
}
有关添加/更改排序的其他两种情况如何处理的更多详细信息,请参阅 WPF 示例应用程序。
WinForms 实现
内置 WinForms DataGrid 的问题在于它通过事件将抽象带到了新的愚蠢高度,如此多的解耦使其几乎无法用于实际世界的数据大小。
幸运的是,DataGrid 具有完全虚拟化的数据模式,可以避免使用绑定,并且有足够的扩展点可以在事件冒泡过远之前抑制它们。
DataSourceView
简单地修改 WPF DataSourceView 以尽可能与 WPF 方法相似地支持筛选和排序似乎是明智的。
internal class DataSourceView<R, C> : IComparer<int>
where R : struct
where C : new()
{
/// <summary>
/// The underlying source
/// </summary>
public readonly DataSource<R, C> Source;
/// <summary>
/// Set collection to change it; can be same instance
/// </summary>
public ListSortDescriptionCollection SortDescriptions {
get { return _ListSortDescriptions; }
set
{
//Track sort changes
_ListSortDescriptions = value;
_sortChanged = true; _sort = null;
}
}
构造包括连接到 DataSource 和排序集合(上文),以跟踪任何筛选或排序何时发生变化。
//Track filter changes
Source.OnFilterChanged = (exp, isValid) => _filterChanged = true;
//Track data changes
Source.OnCalculation = OnSourceCalculation;
刷新必须由开发人员在 WinForms 级别手动处理;此 DataSourceView 所做的只是指示是否有整行因筛选或排序而发生更改。
/// <summary>
/// Call to refresh the view before refreshing the grid itself
/// </summary>
/// <returns>
/// True if all rows may have changed
/// - i.e. due to sorting, filtering or transitioning away from them.
/// </returns>
public bool Refresh()
{
//Usual logic but also tracking 'possibleRowChanges' - see source for more details
return possibleRowChanges || _usingMapping;
}
不幸的是,删除行的实现非常糟糕,我还没有找到任何方法可以覆盖它。到目前为止最好的解决方法是,一旦行数变得“太多”,就立即切换到完全重置,这只能凭经验确定。(尝试使用行可见性反而引发了内部 UI 行类不再在所有行之间共享以及其他问题的整个问题。)
另一个问题是,调用原始的 `Refresh()`(导致集合重置)比仅使列失效慢得多。以下两种解决方法都已实现,以获得良好的速度效果。
void RefreshVewOnly(ICollection<int> changes = null)
{
var possibleRowChanges = _view.Refresh();
//Estimate at which point removal becomes slower than clearing and re-adding
const int Tolerance = 200;
var diff = uiGrid.RowCount - _view.Count;
if (diff > Tolerance)
{
//Workaround: Adding is a cheap operation but removing is terribly slow
//Cannot use Visibility of rows because then DataGridViewRows will no longer
//be shared so rely on a (suppressed) collection reset
uiGrid.Rows.Clear();
}
uiGrid.RowCount = _view.Count;
//And tell the grid to pull in the data
if (!uiGrid.Refresh())
{
//Now must ask grid to redraw
if (possibleRowChanges || changes == null || changes.Count == 0)
{
//Invalidate everything - this approach is much faster than the
//original DataGridView.Refresh()
foreach (DataGridViewColumn col in uiGrid.Columns)
{
if (col.Visible)
{
uiGrid.InvalidateColumn(col.Index);
continue;
}
//Assume only invisible due to re-use so there won't be any holes
break;
}
}
else
{
foreach (var change in changes)
{
var col = _source.Columns[change].MetaData.Column;
uiGrid.InvalidateColumn(change);
}
}
}
}
不幸的是,为了抑制集合更改事件,必须创建一个自定义 DataGridView,它本身将创建一个自定义 DataGridViewRowCollection。
public class CustomDataGridViewRowCollection : DataGridViewRowCollection, ICollection
{
readonly static CollectionChangeEventArgs _RefreshCollectionArgs =
new CollectionChangeEventArgs(CollectionChangeAction.Refresh, null);
protected override void OnCollectionChanged(CollectionChangeEventArgs e)
{
//Suppress
((CustomDataGridView)base.DataGridView).OnRowCollectionDirty();
}
internal void Refresh()
{
base.OnCollectionChanged(_RefreshCollectionArgs);
}
}
这个自定义 DataGridViewCollection 在自定义 DataGridView 中将自身标记为脏。
public class CustomDataGridView : DataGridView
{
protected override DataGridViewRowCollection CreateRowsInstance()
{
return new CustomDataGridViewRowCollection(this);
}
internal void OnRowCollectionDirty()
{
//Called by row collection when it is suppressing its collection reset event
_state |= States.RowCollectionDirty;
}
/// <summary>
/// Perform any pending actions, returning false if invalidation is still needed
/// </summary>
public new bool Refresh()
{
if (_state.HasFlag(States.RowCollectionDirty))
{
((CustomDataGridViewRowCollection)Rows).Refresh();
_state &= ~States.RowCollectionDirty;
return true;
}
//Still need redraw
return false;
}
通用视图设计是在筛选或排序生效时,在视图与行之间以及反向保持基于一的映射。它与 WPF 版本具有相同的实现,因此在此不再赘述。
基本用法
必须手动创建网格,并启用 `VirtualMode`。
public Form1()
{
//Avoid the inevitable rippling effect when painting each cell one by one
this.DoubleBuffered = true;
SuspendLayout();
InitializeComponent();
#region Create subclassed GridView
uiGrid = new CustomDataGridView();
uiGrid.AllowUserToAddRows = false;
uiGrid.AllowUserToDeleteRows = false;
uiGrid.AllowUserToOrderColumns = true;
uiGrid.AllowUserToResizeRows = false;
uiGrid.MultiSelect = true;
uiGrid.Name = "uiGrid";
uiGrid.ReadOnly = true;
uiGrid.SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect;
uiGrid.CellFormatting += uiGrid_CellFormatting;
uiGrid.CellValueNeeded += uiGrid_CellValueNeeded;
uiGrid.ColumnHeaderMouseClick += uiGrid_ColumnHeaderMouseClick;
#endregion
//The normal DataGridView is best used in virtual mode instead
uiGrid.VirtualMode = true;
ResumeLayout(true);
//And use a simplified version of the WPF CollectionView
_view = new DataSourceView<RowMetaData, ColMetaData>(_source, _parser);
//Metrics
_view.OnMetric = OnMetric;
}
重写所需的事件以提供 VirtualMode 的数据
void uiGrid_CellValueNeeded(object sender, DataGridViewCellValueEventArgs e)
{
//Bug: this can be called asking for cell (0,0) when transitioning to empty view
if (!_view.IsEmpty) e.Value = _view.GetItemAt(e.RowIndex, e.ColumnIndex);
}
要使用行元数据来更改颜色,如 DataSource 部分所述,请使用事件。
void uiGrid_CellFormatting(object sender, DataGridViewCellFormattingEventArgs e)
{
//E.g. formatting switch determined by the source
//NOTE: Ideally the cell style should be shared
if (e.ColumnIndex == 0)
{
var md = _source.GetMetaData(e.RowIndex);
if (md.IsSpecial) e.CellStyle.BackColor = Color.Plum;
}
}
首次使用时重置 DataGrid 涉及使用前面描述的 DataSource 例程并仅删除所有 UI 列。
void uiReset_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Remove columns and clear the datasource
uiGrid.SuspendLayout();
uiGrid.Columns.Clear();
然后像往常一样创建列
//Create the columns in the grid
for (int i = 0; i < _InitialColumns.Length; i++)
{
var name = _InitialColumns[i].Key;
var header = name.Split('.')[1];
uiGrid.Columns.Add(name, header);
}
现在设置格式和排序模式。格式信息可以存储在列元数据中,而不是硬编码。
//Format the columns
for (int i = 0; i < _InitialColumns.Length; i++)
{
var ui = uiGrid.Columns[i];
ui.SortMode = DataGridViewColumnSortMode.Programmatic;
if (i == 0)
{
ui.DefaultCellStyle.Alignment = DataGridViewContentAlignment.TopLeft;
ui.DefaultCellStyle.Format = null;
}
else
{
//e.g. could be in source meta data
ui.DefaultCellStyle.Alignment = DataGridViewContentAlignment.TopRight;
ui.DefaultCellStyle.Format = "N2";
}
//And store in the meta data for easier searching later
_source.Columns[i].MetaData = new ColMetaData { Column = ui };
}
//Usual layout
uiGrid.ResumeLayout();
最后,视图被要求执行刷新:详细信息请参阅前面讨论的 `RefreshVewOnly()`。
三态排序
按住 Shift 键并对多列进行排序以及再次关闭排序是标准功能,令人恼火的是内置 WinForms DataGrid 还没有这些功能。
void uiGrid_ColumnHeaderMouseClick(object sender, DataGridViewCellMouseEventArgs e)
{
var ui = uiGrid.Columns[e.ColumnIndex];
var toMatch = _view.Properties[e.ColumnIndex];
var sorts = _view.SortDescriptions;
var newSorts = new List<ListSortDescription>(sorts.Count + 1);
//Cycle: ascending, descending, off
if (ui.HeaderCell.SortGlyphDirection == SortOrder.Descending)
{
if ((ModifierKeys & Keys.Shift) == Keys.Shift)
{
//Still holding shift so only remove this sort
for (var i = 0; i < sorts.Count; i++)
{
if (sorts[i].PropertyDescriptor == toMatch)
{
ui.HeaderCell.SortGlyphDirection = SortOrder.None;
continue;
}
newSorts.Add(sorts[i]);
}
}
else
{
_ClearSorting(sorts);
}
}
else if (ui.HeaderCell.SortGlyphDirection == SortOrder.Ascending)
//etc
else
//etc
}
_view.SortDescriptions = new ListSortDescriptionCollection(newSorts.ToArray());
//Refresh view
RefreshVewOnly(changes: null);
}
有关添加/更改排序的其他两种情况如何处理的更多详细信息,请参阅 WinForms 示例应用程序。
参考文献
问题
- WPF 网格仅在 .NET v4.5 上成功绑定
增强功能
- 引入对可空(值)类型的支持;
- 显示每个表达式的第一个运行时错误;
- 将 DataRow 和 Metadata 列表合并为单个集合并替换为数组(带增量分配);
- 实现 Field 表达式(如 `Expression.ToString()`)的处理程序;
- 扩展 DataColumn 以支持一次性表达式筛选,其中结果作为单独的数据集提供,以实现类似 Excel 的下拉筛选列表;
- 研究分组如何在 WPF 网格中通过使用排序和行元数据或 DataRow 来工作;
- 考虑一个所有表达式的 MRU 缓存,以避免不必要的解析。
历史
- 1.0 - 初次撰写
- 1.1 - 添加“实践中的表达式”
- 1.2 - 添加“问题”部分
