使用渐进搜索生成阿拉伯语/英语填字游戏
4.68/5 (7投票s)
本文介绍了一个 ASP.NET 网页应用程序,该应用程序使用渐进搜索算法来生成填字游戏(阿拉伯语和英语)谜题。

引言
本帖的目的是描述一个填字游戏生成的网页应用程序及其相关的渐进搜索算法。
读者可以浏览英文版或阿拉伯语版。
渐进搜索是作者开发的一种随机迭代搜索算法,已被证明对各种优化问题有效;有关更多信息,请访问我的活动页面以及我关于算法的书籍《算法:开发与编程》。
填字游戏是流行的文字游戏,具有挑战性、娱乐性和教育性。填字游戏之所以受欢迎,是因为它们几乎是世界各地每份报纸上的固定栏目。教育工作者也发现填字游戏是衡量一个人对特定主题知识的有效手段。
在其基本形式中,填字游戏生成问题陈述如下:
给定一个具有特定尺寸的矩形(或方形)网格和一个单词列表(词汇表),生成一组水平单词和一组垂直单词,以及它们在网格中的行和列位置(单元格),用于填充空白单元格。对于无约束填字游戏,算法是确定黑色单元格的位置——其中一些需要用于分隔相邻单词。对于有约束填字游戏,黑色单元格的位置在开始时是固定的。
此处提出的算法适用于无约束填字游戏(也就是说,它包括用于确定黑色单元格的子算法,如下所述)。填字游戏生成问题不同于(且似乎比)填字游戏求解问题。后者要求根据给定的线索找到单词答案。
填字游戏也可以与数字相关。使用程序生成的词汇表(即,对于数字 z=x*y,z 是一个单词,x*y 是一个单词定义),可以生成一个网格尺寸为 10 的填字游戏,其中包含约 40 个相互关联的乘法问题,可用作三年级学生的练习。我们的填字游戏应用程序使用数字选项(参见上图)生成此类填字游戏。
在本文中,我们将解释用于生成填字游戏的渐进搜索算法,以及将其封装到程序组件(可编译为 DLL 的类库)以及基于 Web 的应用程序中。上图显示了界面的基本结构以及由该组件生成的填字游戏示例。
如何使用填字游戏组件
要创建填字游戏,如以下 ASPX 脚本所示,请创建 Crossword 类的实例,设置其属性(DBPath、GridSize 等),然后调用 CreateCrossword()。
<%@ Language="C#" debug="true" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Test Component</title>
<style type="text/css" >
td.cwcell { width:16px; text-align:center; background-color:white; }
td.cwstar { width:16px; text-align:center; background-color:gray; color:white; }
td { font-family:Tahoma; font-size: 10pt; }
</style>
</head>
<%
Crossword cw = new Crossword();
cw.DBPath=Server.MapPath("") + @"\crossword_dbs\crossword.mdb";
cw.TimeToStop = 2; // run for at most 2 seconds
cw.GridSize = 12;
cw.VPlacement = true; // use Fill2 to determine black cells
cw.MaxVWordLength = 4; // set the maximum length of a vertical word
// Progressive Search parameters
cw.QMAXSIZE = 40;
cw.NBSIZE = 50;
string msg = cw.CreateCrossWord(null); // returns crossword grid as body of an html table
msg = "<table border='0' cellspacing='1' bgcolor='gray'>" + cw.BestSolution.PrintGrid() + "</table>";
//string msg2 = cw.BestSolution.GetHWordList(); //get horizontal words as body of an html table
string msg3 =cw.BestSolution.GetVWordList(); //get vertical words as body of an html table
msg3 ="<table border='0' cellspacing='1' cellpadding='0' >" + msg3 + "</table>";
int invalidcount = cw.BestSolution.InvalidWordCount;
int scrambledcount = cw.BestSolution.ScrambledWordCount;
%>
<body>
<p><b> Unknown Words= <% =invalidcount %> Scrambled Words = <% =scrambledcount %></b>
</p>
<hr/>
<table>
<tr><td><% =msg %></td><td><b>Vertical Words</b><br/><% =msg3 %></td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
前面的脚本(当通过浏览器访问时)将产生与以下屏幕截图类似的输出。
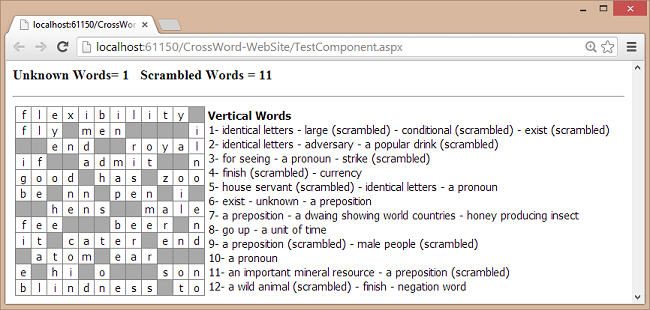
使用渐进搜索生成填字游戏
提出的填字游戏生成算法首先用水平单词填充网格,然后计算该解决方案的成本度量——例如,未知(不在词汇表中的)垂直单词的数量——这代表了要最小化的目标函数。然后,作为当前解决方案的变异,算法选择一个水平单词,并用相同长度的随机选择的词汇表单词替换它。使用这种变异可以保证在向最终解决方案进展过程中生成的所有解决方案都具有有效的水平单词;因此,可以通过扫描网格列并计算未知或乱码单词来计算解决方案的成本。这种想法与渐进搜索的结合可以概述如下。
- 通过水平填充生成初始解决方案X,并计算其优度量f(X),这是一些与未知或乱码垂直单词数量相关的表达式。将X保存为当前最佳解决方案,并将X入队。
- 渐进搜索:重复地从队列中取出(或随机选择)一个解决方案S,通过变异从S生成解决方案的邻域,并将成本在预设阈值内的解决方案入队。如果找到了最优解决方案(即成本=0)或已用时间超过了预设时间段,则终止。
如作者的数独文章所述,我们将使用渐进搜索的一种实现方式,其中项目通过成本的负值入队,以避免阈值计算。
填字游戏组件包含两个类:Crossword 类负责处理输入和输出(包括从指定数据库加载词汇表),以及 Solution 类,该类编码在搜索空间探索过程中生成的任何解决方案。Solution 类从属于 Crossword 类。为了方便访问 Crossword 类中定义的成员,Solution 类包含一个指向 Crossword 类实例的成员 cw。
以下列表显示了 Crossword 类的部分程序代码。
public string CreateCrossWord(Solution s1)
{
if (Numeric)
{ MaxWordLength = GenWords(ref WordList, ref WordDescList);
FreqChar = new char[] { '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9' };
MinWordLength = 2;
goto cont;
}
if (Arabic)
FreqChar = new char[] { 'ع', 'ب', 'ت', 'ي', 'ن', 'م', 'ل', 'و' };
else FreqChar = new char[] { 'e', 'r', 'a', 'i', 'n', 't', 'o', 's' };
if (s1 != null)
{ this.WordList = s1.cw.WordList;
this.WordDescList = s1.cw.WordDescList;
this.WordSigList = s1.cw.WordSigList;
this.MaxWordLength = s1.cw.MaxWordLength;
goto cont;
}
MaxWordLength = GetLexicon(DBPath, ref WordList, ref WordDescList, ref WordSigList);
// check for gaps in Wordlength
int max = MaxWordLength;
if (GridSize < MaxWordLength) max = GridSize;
for (int i = MinWordLength; i <= max; i++)
if (WordList[i].Count == 0)
return "Maximum Word Length:" + MaxWordLength + " Supply Words of Length:" + i;
cont:
if (s1 == null) s1 = new Solution(this, false);
if (TimeToStop == -1) return ComputeFillMeasure();
if (TimeToStop == 0) // used to report starting solution
{ BestSolution = s1;
StatusInfo = "";
}
else BestSolution = ProgressiveSearch(s1);
return ""; // indicate success
}
以下列表显示了 Solution 类的部分程序代码。这里基本信息是,填满填字游戏网格的任何内容都代表我们搜索空间中的一个解决方案(节点)。因此,一个解决方案完全由其填充的网格或其 ItemList(水平单词及其相应位置的列表)来表征。然而,为了清晰起见和加快变异过程,我们选择了同时保留这两种结构,这在以下 Solution 类部分列表的初始行中显而易见。
struct SolutionItem
{ internal int row, col;
internal string word;
internal SolutionItem(int r, int c, string w)
{ row = r; col = c; word = w; }
}
public class Solution
{ internal Crossword cw; // a reference to Crossword instance
Random rand;
// A solution is a grid and an ItemList (a list of horizontal words)
internal char[,] grid; // The crossword grid
internal int GridSize;
ArrayList ItemList = new ArrayList(); // a list of "SoultionItem" objects
public float Cost; // Cost measure
public int InvalidWordCount, ScrambledWordCount;
public Solution(Crossword cw, bool empty)
{ // empty is passed as true to generate a solution object with undefined grid or ItemList
this.cw = cw;
GridSize = cw.GridSize;
this.rand = cw.rand;
if (empty) return;
grid = new char[GridSize, GridSize];
if (cw.VPlacement || (cw.MaxVWordLength == -1))
Fill_2();
else Fill_1();
Cost = ComputeMeasure(); // compute and set Solution's cost
}
// ... some other methods omitted
void PlaceWord(string wrd, int row, int col)
{ if (wrd.Length == 1)
{ grid[row, col] = wrd[0]; return; }
SolutionItem it = new SolutionItem(row, col, wrd);
ItemList.Add(it);
if (cw.Arabic)
for (int i = col; i < wrd.Length; i++)
{ grid[row, col+i] = wrd[wrd.Length - 1 - i]; }
else
for (int i = col; i < wrd.Length; i++)
{ grid[row, col+i] = wrd[i]; }
}
}
Solution 类中的大多数方法都是与语言无关的。PlaceWord() 方法(如上所示)是依赖于语言的。该函数通过在 row 和 col 参数指定的位置水平放置一个单词(由 wrd 参数指定)来修改解决方案。
Solution 类中的一个关键方法是 NewSolution(),定义如下:
internal Solution NewSolution()
{ Solution s1 = this.CopySolution(); // copy grid only to s1; s1 will have empty ItemList
// Select a horizontal word
int r = rand.Next(ItemList.Count);
SolutionItem it = (SolutionItem) ItemList[r];
// Get a random lexicon word of a specified length
string wrd = cw.GetWord(it.word.Length);
s1.PlaceWord(wrd, it.row, it.col);// Place word in grid and add it to ItemList
// Build the list of horizontal words for s1
foreach (SolutionItem itx in ItemList)
if ( (itx.row!=it.row) || (itx.col!=it.col))
s1.ItemList.Add(new SolutionItem(itx.row,itx.col,itx.word));
s1.ComputeMeasure(); // Compute and set Solution’s cost
return s1;
}
其工作原理如下。我们必须将解决方案 S 变异为新解决方案 S1。我们首先将 S1 设为 S 的副本。然后,我们随机选择网格中的一个水平单词w(相当于从 ItemList 中选择一个项目)。然后,我们选择一个随机的词汇表单词wrd,并用它替换单词w。最后这个操作通过调用 PlaceWord() 体现在 S1 的网格中。然后,我们使用 foreach 循环构建 S1 的 ItemList。最后,我们调用 ComputeMeasure() 来计算并设置 S1 的成本。
使用什么目标函数?
这涉及到 ComputeMeasure() 用于解决方案成本的表达式(即,它离最优(成本=0)解决方案有多远)。
给定填字游戏的一个解决方案S,令u表示未知垂直单词的数量,w表示乱码垂直单词的数量。作为解决方案S的简单成本函数,我们定义f(S) = u。然而,这种函数会在未知垂直单词数量达到零时终止,而可能仍有大量乱码垂直单词,这通常是不希望的。为了考虑乱码单词,表达式f(S) = u+0.5*w 是一个更好的选择(未知单词的权重是乱码单词的两倍)。进一步思考表明,这种函数无法区分具有相同数量的未知和乱码单词但这些单词的长度在不同解决方案之间变化很大的解决方案。直觉表明,沿着减少未知单词 [乱码单词] 长度的方向移动,最终会减少未知单词 [乱码单词] 的数量。因此,一个更好的表达式是f(S) = len(u) + 0.2*len(w),其中len(u)是未知垂直单词的总长度,len(w)是乱码垂直单词的总长度(注意:我们发现系数 0.2 比 0.5 效果更好)。
填充策略
网格填充(确定黑色单元格的位置)的基本策略如下:
按行处理网格,并为每一行放置随机选择的单词。
但是,有几个问题需要解决。首先,我们希望能够有长度为一的单词槽,并且希望任何行的最左边(或最右边)单元格可以是黑色的。这表明,单词槽(等同于单词长度)的确定应基于生成零和最大单词长度 MaxWordLength(从输入词汇表中确定)之间的随机数,其中单词长度为零表示当前单元格(通常是单词的开头)将被加黑。长度为一的单词是从八个最常用的英文字母集中随机选择的。这种策略仍然有一个小问题与垂直视图有关;一列可能最终有许多相邻的白色单元格,例如,以后难以匹配一个 9 个字母的单词。为了解决这个问题,并改变黑色单元格的密度,填充策略会增加一个参数 MaximumVWordLength(任何垂直单词的最大长度)。
此策略的实现如以下列表中的 Fill_1() 方法所示。
void Fill_1()
{ int k, wlen, remlen; int[] cc = new int[GridSize];
for (int i = 0; i < GridSize; i++)
{ cc[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < GridSize; j++)
{ grid[i, j] = '*'; }
}
for (int i = 0; i < GridSize; i++)
{ int j = 0;
while (j < GridSize)
{ remlen = GridSize - j;
if (remlen > cw.MaxWordLength) remlen = cw.MaxWordLength;
if (remlen > 3)
wlen = rand.Next(remlen + 1); // allow a word-length of 0 to allow * to appear in column 0
else wlen = remlen;
for (k = j; k < j + wlen; k++)
{ if (cc[k] >= cw.MaxVWordLength) break;
cc[k]++;
}
wlen = k - j; // shorten word length in order not to exceed MaxVWordLength
if (k < GridSize) cc[k] = 0;
if (wlen > 0) PlaceWord(cw.GetWord(wlen), i, j);
j = j + wlen + 1;
}
}
}
我们使用一个向量 cc[0..GridSize-1],其中 cc[k] 是第 k 列的白色单元格计数。另外,请注意,首先,单词长度 wlen 被选择为零和(MaxWordLength、remlen)之间的最小值,其中 remlen 是当前行中剩余未填充的单元格数。如果 remlen ≤ 3,则 wlen 被重置为 remlen。然后,wlen 进一步减小,以确保跨越当前单词的列满足 cc[k] ≤ MaxVWordLength。
另一种填充策略在以下列表的 Fill_2() 方法中给出。
void Fill_2()
{
for (int i = 0; i < GridSize; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < GridSize; j++)
{ grid[i, j] = 'X'; }
for (int col = 0; col < GridSize; col++)
{ int row = 0;
while (row < GridSize)
{ // allow a wordlength of 0 to allow * to appear in column 0
int wlen = rand.Next(cw.MaxVWordLength + 1);
row = row + wlen;
if (row >= GridSize) break;
if ((row > 0) && (grid[row - 1, col] == '*')) continue;
grid[row, col] = '*';
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < GridSize; i++)
{ int wlen = 0; int startpos = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= GridSize; j++)
{ if (j == GridSize)
{ if (wlen > 0) PlaceWord(cw.GetWord(wlen), i, startpos);
break;
}
if ((grid[i, j] == 'X') && (wlen < cw.MaxWordLength)) wlen++;
else //found * or wlen= MaxWordLen
{ if (wlen > 0) PlaceWord(cw.GetWord(wlen), i, startpos);
grid[i, j] = '*'; //needed if wlen= MaxWordLength
wlen = 0;
startpos = j + 1;
}
}
}
}
在此策略中,黑色单元格是基于垂直视图选择的,通过按列处理网格并生成随机单词长度(最多 MaximumVWordLength)。然后按行处理网格以填充水平单词。
结论
填字游戏生成是展示渐进搜索有效性的一个很好的例子。该应用程序已在流行的浏览器上进行了测试,并被发现可以正常工作。
历史
- 2013 年 12 月 4 日:版本 1.0。
