无锁双向链表
5.00/5 (5投票s)
摘要
基于锁的同步会遇到优先级反转和死锁等问题。即便如此,无锁同步并未获得太多关注。这是因为编写正确且高效的无锁代码非常困难。我们提出了一种实用且易于理解的无锁双向链表实现。这是第二种仅需要单字比较交换(compare-and-swap)原子原语的无锁实现(第一种是 Håkan Sundell 的)。实验结果表明,我们提出的解决方案与 Håkan Sundell 的无锁双向链表相比具有优势。
引言
双向链表是项目的列表,项目可以位于内存中的任何位置。每个项目包含两个字段。Next 字段指向列表中的下一个项目。Prev 字段指向列表中的上一个项目。这两个字段允许双向遍历列表。双向链表支持插入和删除操作。这些操作的实现很简单。但在多线程环境中,最常用的方法是互斥,这会遇到死锁和优先级反转的情况。解决这些问题的答案是无锁。在无锁系统中,当一个线程执行几步操作后,整个系统就会取得进展。根据定义,无锁系统不会发生死锁。但是存在饥饿的风险。无等待系统是无锁的,而且它们还可以避免饥饿。
相关工作
[Greenwald99] 提出了一种基于不可用的 DCAS 原子原语的通用无锁双向链表实现。
[Valois 95] 勾勒出了一个使用比较交换 (CAS) 的无锁双向链表结构的实现,但不支持删除。
[Håkan Sundell 2008] 的解决方案是将双向链表视为带有 prev 指针辅助信息的单向链表,其中 next 指针先于 prev 指针更新。因此,next 指针始终构成一个一致的单向链表,但 prev 指针仅提供查找前一个节点的线索。这是可能的,因为“滞后”的未更新 prev 指针总是指向当前节点的前一个节点或几个节点之前,并且可以从该“线索”位置通过 next 指针遍历到达直接的前一个节点。
算法
本节将详细描述通用双向链表数据结构的所有基本操作。为了使双向链表无锁,我们使用比较交换 (CAS)。
无锁链表数据结构定义如下:
__declspec(align(InterLockedAlign)) struct Node
{
int data;
__declspec(align(InterLockedAlign)) Node *rlink;
__declspec(align(InterLockedAlign))Node *llink;
};
这个“Node”结构与双向链表的常见顺序实现中发现的结构相同。有一个区别是它进行 32 位对齐。
无锁链表数据结构与顺序链表在以下方面有所不同;
-顺序双向链表的每个操作(插入、删除)都有一个参数列表和局部变量。
在无锁双向链表中,操作的参数和局部变量的值会记录在相应操作的结构中。例如,以下是插入和删除操作的结构:
//Following is the structure for Insert operation
struct Insert
{
//Following is the structure for arguments passed to Insert
struct Arguments
{
Node *p;//node to be inserted
Node *x;//p is inserted next to x
}args;
struct LocalVariables
{
Node *x_rlink_llink;//This announces the value of x->rlink->llink which needs to be set to p.
Node **x_rlink_llink_address;//This announces the address of x->rlink->llink which is used as destination in InterlockedCompareExchange.
Node *x_rlink;//This announces the value of x->rlink which needs to be set to p.
Node **x_rlink_address;//This announces the address of x->rlink which is used as destination in InterlockedCompareExchange.
}lv;
};
//Following is the structure for Delete operation
struct Delete
{
//Following is the structure for arguments passed to Delete
struct Arguments
{
Node *x;//node to be deleted.
}args;
struct LocalVariables
{
//Following variables announce the values and addresses of pointers found in nodes around x (including x as well).
Node *x_llink;
Node **x_llink_address;
Node *x_rlink;
Node **x_rlink_address;
Node *x_llink_rlink;
Node **x_llink_rlink_address;
Node *x_rlink_llink;
Node **x_rlink_llink_address;
Node *x_llink_llink;
Node **x_llink_llink_address;
Node *x_rlink_rlink;
Node **x_rlink_rlink_address;
Node *x_llink_llink_rlink;
Node **x_llink_llink_rlink_address;
Node *x_rlink_rlink_llink;
Node **x_rlink_rlink_llink_address;
Node *replacement_x_llink;//This points to the replacement for the node left to x.
Node *replacement_x_rlink;//This points to the replacement for the node right to x.
}lv;
};enum OperationName
{
NONE,INSERT,DELET
};
//Following structure contains the operations defined earlier.
struct AnnounceOp
{
OperationName opName;
union
{
struct Insert insert;
struct Delete del;
};
};这里的想法是,当一个线程尝试开始一个操作时,它会在调用结构 (AnnounceOp) 中记录该调用,该结构的字段包括操作名称 (OperationName) 和每个操作结构的匿名联合。
__declspec(align(InterLockedAlign))struct LinkedList
{
volatile AnnounceOp *announce;//current announcement
Node *first;//first node
Node *end;//end node
};
LinkedList l;
最后,无锁双向链表是一个包含 Announce Op、首尾节点和尾节点的结构。“initialize”函数将双向链表初始化为包含四个虚拟节点。由于初始化始终在隔离环境中运行,因此“initialize”函数不需要任何无锁同步。
void initialize()
{
//current announcement is that no operation is in progress
l.announce=(AnnounceOp*)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct AnnounceOp),InterLockedAlign );//new AnnounceOp;
assert(l.announce);
l.announce->opName=NONE;
//create 4 node doubly linked list
l.first=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );//new Node;
assert(l.first);
l.end=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );
assert(l.end);
l.first->rlink=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );
assert(l.first->rlink);
l.first->rlink->rlink=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );
assert(l.first->rlink->rlink);
l.first->llink=0;
l.first->rlink->llink=l.first;
l.first->rlink->rlink->rlink=l.end;
l.first->rlink->rlink->llink=l.first->rlink;
l.end->rlink=0;
l.end->llink=l.first->rlink->rlink;
}
构建无锁双向链表的主要难点在于节点在遍历过程中可能被删除的情况。一种解决方案是在遇到已删除节点时重新开始遍历。插入操作很简单。声明插入开始。然后使用 CAS 将插入点节点的 rlink 字段指向新节点,并将插入点后一个节点的 llink 字段指向新节点。如果操作成功,新节点已链接到列表中,否则重试操作。
删除操作并不那么直接,因为当我们读取(待删除)节点的 rlink 字段并在前驱节点的 rlink 字段与该值之间进行插入时,可能会发生插入。这可能导致新插入的节点与我们实际要删除的节点一起被删除。同样,在并发删除相邻节点的情况下,即使成功执行了删除操作,一个(待删除)节点仍然存在。
给定的双向链表最初包含四个虚拟节点:开始、结束和两个中间节点。我们有虚拟开始节点,因为我们不希望在任何操作中更改开始和结束。我们有虚拟结束节点,因为我们需要 NULL 指针不具有列表末尾标记的特殊含义,因为 NULL 指针用于将内存单元从双向链表中解链,这要求 NULL 指针不具有列表末尾标记的特殊含义。我们有中间虚拟节点,因为我们不希望开始节点发生变化,但我们需要替换任何地方的节点以防止 ABA 问题。通过这种方式,我们可以避免替换开始节点,因为插入总是发生在中间虚拟节点之后。使用 CAS 的一个缺点是 ABA 问题。可以通过确保变量在其他线程读取该值并打算在 CAS 中使用该值时永远不会获得相同的值来避免 ABA 问题。这通常可以通过仅使用指针类型的变量,并确保通过替换新的内存单元来防止指针值再次出现来避免。我们有两个中间虚拟节点,因为我们不希望开始节点发生变化,而且我们还要求替换任何地方的节点以防止 ABA 问题。通过这种方式,我们可以避免替换开始节点,因为插入总是发生在两个中间虚拟节点之间。
插入操作的第一部分(参见列表 1)和删除操作(参见附录 B)执行参数验证。之后是变量声明,用于保存临时值(如果有)。之后是一个 while 循环,尝试执行操作。一开始,它尝试准备 AnnounceOp 当前状态的一致浅拷贝。
成功复制后,还有两种情况需要考虑:
- 情况 1:如果当前没有调用,则该线程尝试通过在调用结构中记录操作名称、参数和局部变量来启动操作。它尝试使用 CAS 原子地更新 announce 变量。然后,它调用操作的第二部分。
- 情况 2:如果当前有调用,则表示某个操作可能正在进行中,该线程尝试通过调用相应操作的第二部分来协助该操作。
//insert node p to the right of node x
int Insert(Node *p,Node *x)
{
if(p==0||x==0) return 0;
AnnounceOp *curAnnouncedOp;
AnnounceOp *nextAnnounceOp=(AnnounceOp*)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct AnnounceOp),InterLockedAlign );//To announce an insert operation.
assert(nextAnnounceOp);
while(1)
{
curAnnouncedOp=(AnnounceOp *)l.announce;
AnnounceOp *hp0=curAnnouncedOp;
if(curAnnouncedOp!=l.announce) continue;
if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==NONE)
{
try
{
if(l.first==x||l.end==x||l.end->llink==x)//insertion should not be after first or after end or after one node before end
{
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
return 0;
}
p->llink=x;//set p's left as x
p->rlink=x->rlink;//set p's right as x's right
if(p->rlink==0||p->llink==0) goto label;
nextAnnounceOp->opName=INSERT;//set INSERT as the next operation
nextAnnounceOp->insert.args.p=p;
nextAnnounceOp->insert.args.x=x;
//announce the value of x->rlink which needs to be set to p
nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink=x->rlink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink==0) goto label;//node x is no more in the linked list
Node *hp2=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink;//set hazard pointer
if(x->rlink!=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink) goto label;//check that hazard pointer has been set accurately
nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_address=&x->rlink;//announce the address of x->rlink to be used as destination in InterlockedCompareExchange
//announce the value of x->rlink->llink which needs to be set to p
nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink->llink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink==0) goto label;//node next to node x is unlinked
Node *hp1=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink;//set hazard pointer
if(nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink->llink!=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink) goto label;//check hazard pointer is set correctly
nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink->llink;//announce the address of x->rlink->llink to be used as destination in InterlockedCompareExchange.
//Check that announced addresses has not changed
/*if(&x->rlink->llink!=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink_address) goto label;
if(&x->rlink!=nextAnnounceOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_address) goto label;*/
//To announce the start of insert operation.
void *v1=reinterpret_cast<void>(nextAnnounceOp);
void *v2=reinterpret_cast<void>(curAnnouncedOp);
void *res=(void *)InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(&l.announce),(LONG)v1,(LONG)v2);
if(res==v2)
{
//RetireNode(curAnnouncedOp);
InsertHelper(nextAnnounceOp);
return 1;
}
}
catch(...)
{
printf("Exception in Insert\n");
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
return 0;
}
}
else if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==INSERT)
{
InsertHelper(curAnnouncedOp);
}
else if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==DELET)
{
DeleteHelper(curAnnouncedOp);
}
}
label:
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
return 0;
}
列表 1
插入操作的第二部分(参见列表 2)尝试通过对 x->rlink 执行 CAS 来链接新节点,然后是另一个 CAS,它尝试通过对 x->rlink->llink 执行 CAS 来链接新节点。最后,通过 CAS 宣布操作完成。
//Second part of insert
void InsertHelper(AnnounceOp *curAnnouncedOp)
{
//set x's right link to node p (newly created node)
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_address),(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->insert.args.p,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->insert.lv.x_rlink);
//set the left pointer of node next to x to point to p
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink_address),(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->insert.args.p,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->insert.lv.x_rlink_llink);
//To announce that insert operation is complete.
AnnounceOp *nextAnnounceOp=(AnnounceOp*)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct AnnounceOp),InterLockedAlign );
assert(nextAnnounceOp);
nextAnnounceOp->opName=NONE;
void *v1=reinterpret_cast<void>(nextAnnounceOp);
void *v2=reinterpret_cast<void>(curAnnouncedOp);
if(InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(&l.announce),(LONG)v1,(LONG)v2)==(LONG)v2)
{
//RetireNode(v2);
}
else
{
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
}
}
列表 2
在删除的情况下,我们不能简单地将节点的序的 rlink 指针设置为其后继节点,因为这会导致 ABA 问题。假设线程 T1 在 A 和 C 之间插入节点 B。其他线程 T2 正在协助此插入,但在链接 B 之前被抢占。现在,另一个线程 T3 出现并删除了 B。最后,线程 T2 恢复协助并重新链接已删除的节点(参见图 1)。
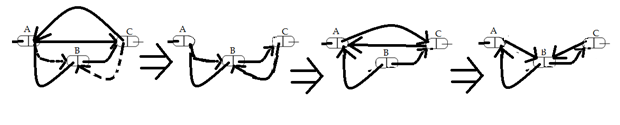
图 1
这个问题的一个解决方案是,在执行删除时,替换节点的序和后继节点,因此在给定的场景中,A 将被 A1 替换,已删除的节点将不会被 A1 链接。
现在我们来看删除操作的第二部分(参见列表 3)。删除操作的第二部分用第一部分创建的副本替换节点的序和后继,并尝试通过将已删除节点、其序和后继的 rlink 和 llink 指针设置为 0 来将其标记为确实已从链表中删除。最后,这后面是另一个 CAS 来宣布操作完成。
//Second part of delete
void DeleteHelper(AnnounceOp *curAnnouncedOp)
{
//replace 2 nodes around x including x with two new nodes
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink_address),(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.replacement_x_llink,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink);
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink_address),(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.replacement_x_rlink,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink);
//Set 3 retired nodes pointer fields to 0
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink);
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink);
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink);
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink);
InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink);
if(InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile>(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink_address),(LONG)0,(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink)==(LONG)curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink)
{
//RetireNode(x);
//RetireNode(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_llink);
//RetireNode(curAnnouncedOp->del.lv.x_rlink);
}
//To announce that delete operation is complete.
AnnounceOp *nextAnnounceOp=(AnnounceOp*)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct AnnounceOp),InterLockedAlign );
assert(nextAnnounceOp);
nextAnnounceOp->opName=NONE;
void *v1=reinterpret_cast<void *>(nextAnnounceOp);
void *v2=reinterpret_cast<void *>(curAnnouncedOp);
if(InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile LONG *>(&l.announce),(LONG)v1,(LONG)v2)==(LONG)v2)
{
//RetireNode(curAnnouncedOp);
}
else
{
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
}
}列表 3
正确性
证明的直观思想是,一旦线程 T1 成功宣布了一个操作,就可以保证它的操作将在系统采取的下一个有界数量的步骤内完成。每次在插入和删除操作的 while 1 循环中进行迭代,某个线程就会成功地向完成操作迈出一步。链表上的插入和删除操作通过其各自第一部分中的成功 CAS 来线性化。最后要展示的是,数据结构中对共享位置的写入的执行顺序与相应顺序实现中的顺序相同。这是因为链表实例上的插入或删除操作成功的 InterlockedCompareExchange.AnnounceOp 保证了 AnnounceOp 结构中变量的写入是有效的,但由于 ABA 问题,对其他共享变量的写入需要更多关注。在无锁双向链表的情况下,我们通过替换待删除节点的序和后继来解决此问题。这确保了节点 a rlink 和 llink 字段永远不会再次相同,除非没有线程对其拥有危险的 [Michael 2004] 引用。在垃圾回收环境中,内存回收是自动的。但是,在没有垃圾回收的情况下,我们需要小心回收内存,因为它可能导致悬空引用(对已回收内存单元的引用)。我们假设将使用 Hazard Pointers [Michael 2004] 进行安全的内存回收。危险指针方法在抽象层面是,线程在使用共享指针值进行容易发生 ABA 的比较之前,将其设置为全局(危险)指针等于该共享指针的值,并确保当共享指针的值使用 CAS 设置为新值时,该值不在共享指针先前达到的值中,并且危险指针具有该值。这确保了如果一个线程已将危险指针设置为共享指针的值,则该值不会被用于容易发生 ABA 的比较,因为计算共享指针新值的函数不会返回该值。我们将危险指针方法应用于无锁双向链表。您可以在注释中看到危险指针和 RetireNode 函数。有关更多详细信息,请阅读 [Michael 2004]。
非正式地说,无锁双向链表中的每个操作在最终 CAS 宣布操作完成时生效。这意味着无锁双向链表中的每个操作都在调用和响应之间瞬时生效,因此线性化因此而得名。双向链表是无锁的,因为已宣布的操作通过尝试 CAS 操作来取得进展。成功的 CAS 使操作更接近完成一步。而不成功的 CAS 意味着操作已经取得了进展。这样,已宣布的操作将在有限数量的 CAS 中完成。
实验评估
性能测试在 Intel(R) Core(TM) i3-2310M CPU @ 2.10GHz 2.10 GHz 处理器、3 GB RAM 上进行。使用的操作系统是 Windows 7 Professional。我们在没有其他用户使用系统的情况下运行了性能测试。
本节将介绍 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 和我们提出的双向链表的性能结果。实验通过改变以下参数进行:
- 线程数从 1 到 16(绘制在 x 轴上)
- 每个线程执行 15000 或 30000 次插入,称为 O,其中 O 等于 15000 或 30000
- 每个线程执行 15000 或 30000 次删除
- 每 10 次、50 次或 90 次,我们选择中断遍历并执行插入或删除。称为 T,其中 T 等于 10、50 或 90
当每十次中有一次选择中断遍历时,这意味着大部分时间都在插入或删除节点。在这种情况下,[Håkan Sundell 2008] 的表现更好。(参见附录 A)另一方面,当每五十次中有一次选择中断遍历时,这意味着大部分时间都在遍历节点。在这种情况下,我们提出的双向链表比 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 的表现更好。(参见附录 A)。图表显示,我们提出的双向链表的性能是 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 的两倍。原因是 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 提供的遍历函数性能较差。当 T=90 时,遍历花费的时间更多,因此 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 的性能下降。
摘要
本文介绍了第二种无锁双向链表(第一种是 [Håkan Sundell 2008]),它使用了可用的原子原语(CAS)。
我们进行了实验,将我们的双向链表与 [Håkan Sundell 2008] 进行了比较。实验表明,在大多数时间都在遍历双向链表的情况下,我们的实现性能明显更好。
参考文献
- [Michael 2004] Michael, M.M. “Hazard pointers: Safe memory reclamation for lock-free objects,” IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. 15, no. 8, Aug. 2004.
- [Valois 95] J. D. Valois, “Lock-free data structures,” Ph.D. dissertation, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York, 1995.
- [Greenwald99] M. Greenwald, “Non-blocking synchronization and system design,” Ph.D. dissertation, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 1999.
- [Håkan Sundell 2008]Håkan Sundell, Philippas TsigasLock-free deques and doubly linked lists, PDC 2008
附录 A
X轴:线程数
Y轴:时间(秒)
图 2 T=10 O= 150000

图 3 T=10 O=30000

图 4 T=50 O=15000

图 5 T=50 O=30000

图 6 T=90 O=15000

附录B
int Delete(Node *x)
{
if(x==0) return 0;
AnnounceOp *curAnnouncedOp;
AnnounceOp *nextAnnounceOp=(AnnounceOp*)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct AnnounceOp),InterLockedAlign );//new AnnounceOp;//To announce a delete operation.
assert(nextAnnounceOp);
Node *replacement_x_llink=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );//new Node;
assert(replacement_x_llink);
Node *replacement_x_rlink=(Node *)_aligned_malloc(sizeof(struct Node),InterLockedAlign );//new Node;
assert(replacement_x_rlink);
while(1)
{
curAnnouncedOp=(AnnounceOp *)l.announce;
AnnounceOp *hp0=curAnnouncedOp;
if(curAnnouncedOp!=l.announce) continue;
if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==NONE)
{
try
{
if(l.first==x||l.end==x||l.first->rlink==x||l.end->llink==x) //check x is not one of the four dummy nodes
{
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_llink);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_rlink);
return 0;
}
//set Delete as the next operation
nextAnnounceOp->opName=DELET;
nextAnnounceOp->del.args.x=x;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink=x->llink;//announce the value of x->llink to be used in CAS
Node *hp1=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink;//set hazard pointer
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink!=x->llink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink==0) goto label1;//check hazard pointer is set accurately and x->llink is not zero
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_address=&x->llink;//announce the address of x->llink to be used in CAS
//Following statements are on the same pattern as above i.e. announce the value of variable
//set hazard pointer. check hazard pointer is set accurately. Announce the address of that variable
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink=x->rlink;
Node *hp2=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink!=x->rlink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_address=&x->rlink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->rlink;
Node *hp3=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->rlink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->rlink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->llink;
Node *hp4=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->llink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->llink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->rlink;
Node *hp5=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->rlink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->rlink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->llink;
Node *hp6=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->llink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->llink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink->rlink;
Node *hp7=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink->rlink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink->rlink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink->llink;
Node *hp8=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink!=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink->llink||nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink==0) goto label1;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink_address=&nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink->llink;
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.replacement_x_llink=replacement_x_llink;//announce the replacement for the node left to x
nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.replacement_x_rlink=replacement_x_rlink;//announce the replacement for the node right to x
replacement_x_llink->data=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink->data;//copy data
replacement_x_rlink->data=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink->data;//copy data
//build the chain
//x_llink_llink//replacement_x_llink//replacement_x_rlink//x_rlink_rlink
// --------- ------- -------- -------
// | | | |-----------| | | |
// | |===| |===========| |==============| |
// ------- ------- -------- -------
replacement_x_llink->rlink=replacement_x_rlink;
replacement_x_llink->llink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink;
replacement_x_rlink->llink=replacement_x_llink;
replacement_x_rlink->rlink=nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink;//x->rlink->rlink;
//check addresses has not changed
/*if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_address!=&x->llink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_address!=&x->rlink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_rlink_address!=&x->llink->rlink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_llink_address!=&x->rlink->llink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_address!=&x->rlink->rlink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_address!=&x->llink->llink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_llink_llink_rlink_address!=&x->llink->llink->rlink) goto label1;
if(nextAnnounceOp->del.lv.x_rlink_rlink_llink_address!=&x->rlink->rlink->llink) goto label1;*/
//To announce the start of delete operation.
void *v1=reinterpret_cast<void *>(nextAnnounceOp);
void *v2=reinterpret_cast<void *>(curAnnouncedOp);
void *res=(void *)InterlockedCompareExchange(reinterpret_cast<volatile LONG *>(&l.announce),(LONG)v1,(LONG)v2);
if(res==v2)
{
//RetireNode(curAnnouncedOp);
DeleteHelper(nextAnnounceOp);
return 1;
}
}
catch(...)
{
printf("Exception in Delete\n");
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_llink);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_rlink);
return 0;
}
}
else if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==INSERT)
{
InsertHelper(curAnnouncedOp);
}
else if(curAnnouncedOp->opName==DELET)
{
DeleteHelper(curAnnouncedOp);
}
}
label1:
_aligned_free(nextAnnounceOp);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_llink);
_aligned_free(replacement_x_rlink);
return 0;
}
