ASP.NET MVC 5 Identity:扩展和修改角色
在最近的一篇文章中,我详细研究了扩展 ASP.NET 5 Identity 模型,向基本的 IdentityUser 类添加了一些自定义属性,以及一些基本的基于角色的身份管理。除了用一些非常基础的角色来管理应用程序访问权限来填充数据库之外,我们没有讨论修改、扩展或直接处理角色。
在最近的一篇文章中,我详细研究了 扩展 ASP.NET 5 Identity 模型,向基本的 IdentityUser 类添加了一些自定义属性,以及一些基本的基于角色的身份管理。除了用一些非常基础的角色来管理应用程序访问权限来填充数据库之外,我们没有讨论修改、扩展或直接处理角色。
从管理角度扩展基本的 ASP.NET IdentityRole 类并直接处理角色,需要仔细考虑,并且在代码方面需要不少的变通方法。
图片 作者:Hay Kranen | 某些权利保留
原因有二
- 正如我们在上一篇文章中看到的,ASP.NET 团队让扩展
IdentityUser变得相当容易,也让一些基本的用户角色管理变得可行。 - 当角色用于强制执行应用程序内的访问限制时,它们基本上是硬编码的,通常通过
[Authorize]属性。如果应用程序管理员能够添加、修改和删除角色,但又不能修改[Authorize]提供的访问权限,那么这些功能的作用就非常有限了。
尽管如此,有时我们可能希望为基本角色添加一些属性,例如简短的描述。
在这篇文章中,我们将看到如何通过添加一个额外的属性来扩展 IdentityRole 类。我们还将添加创建、编辑和删除角色的基本能力,以及其中涉及的所有内容,尽管向应用程序中添加或删除角色的任何优势都受到应用程序中硬编码的 [Authorize] 权限的限制。
在下一篇文章 ASP.NET MVC 5 Identity:实现基于组的权限管理 中,我们将探讨如何绕过 Role/[Authorize] 模型来创建更细粒度的基于角色的访问控制系统。
如果您正在使用 Identity 2.0 框架
本文重点介绍 ASP.NET Identity 框架 **1.0 版本**的自定义和修改。如果您使用的是最近发布的 2.0 版本,本文中的代码将无法正常工作。有关使用 Identity 2.0 的更多信息,请参阅:
- ASP.NET Identity 2.0:理解基础知识
- ASP.NET Identity 2.0:自定义用户和角色
- ASP.NET Identity 2.0:设置账户验证和双因素身份验证.
- ASP.NET Identity 2.0 扩展身份模型并使用整数键而不是字符串
本文实现的许多自定义功能在 Identity Samples 项目中都已包含。我在新的文章 ASP.NET Identity 2.0:自定义用户和角色 中讨论了 Identity 2.0 中扩展和自定义 IdentityUser 和 IdentityRole。
如果您正在使用 Identity 1.0 框架
更新:2014/2/24 - 感谢 Code Project 用户 Budoray 抓出了代码中的一些拼写错误。EditRoleViewModel 和 RoleViewModel 类在多个地方被错误引用,导致项目无法正常构建。已修复!
- 克隆源码
- 扩展 Identity Role 类
- 更新 Identity Manager 类
- 更新现有类和视图
- 我们真的要编辑角色吗?
- 在 Identity Manager 中添加删除角色方法
- 角色控制器使用的 ViewModel 和视图
- 运行迁移并构建数据库
- 在处理安全和认证时请多加注意!
- 其他资源和感兴趣的项目
入门 - 借鉴之前的工作
我们在上一篇关于 扩展 Identity 账户 的文章中已经为我们要做的打下了基础,所以我们将克隆该项目并在已完成的工作基础上进行构建。在该项目中,我们
- 创建了一个受限的内部访问 MVC 站点。
- 删除了与社交媒体账户登录和其他我们不需要的功能相关的多余代码。
- 扩展了 IdentityUser 类以包含一些附加属性,例如名字/姓氏和电子邮件地址。
- 添加了将用户分配给预定义角色的能力,这些角色控制着对我们应用程序各种功能的访问。
克隆源码
您可以克隆 原始项目 并跟随学习,也可以从我的 Github 仓库获取已完成的项目。要获取原始项目并跟随本文进行学习,请从以下位置克隆源代码:
如果您想查看 完成的项目,请从以下位置克隆源代码:
首先,进行一点重构
在原始项目中,我将所有与 Identity 相关的模型保留在默认项目模板创建的单个文件中。在开始之前,我将每个类提取到自己的代码文件中。此外,我们将重建数据库和迁移。
克隆源码后,我删除了现有的迁移(不是 Migrations 文件夹,只是其中的名为 *201311110510410_Init.cs* 的迁移文件。我们将保留 *Migrations/Configuration.cs* 文件,因为我们将在此基础上继续发展。
如果您正在跟随学习,请注意,我还 重命名了项目和解决方案、命名空间等,因为我将把此项目单独推送到 Github,而不是与原始项目放在一起。
这个项目还有很多改进空间,但目前为止就可以了。让我们开始吧。
入门
之前,我们能够定义模型类 ApplicationUser,该类扩展了 Identity 类 IdentityUser,运行 EF Migrations,并相对容易地在应用程序中所有以前使用 IdentityUser 的地方将其替换为 IdentityUser。然而,在扩展 IdentityRole 方面,事情并非如此简单。
IdentityRole 是 ASP.NET 应用程序授权机制的核心组成部分。因此,我们可能期望 Identity 系统能够抵制对 IdentityRole 类本身进行的随意修改,并且可能同样重要的是,抵制其余身份系统接受其派生类的方式。因此,我们需要找到一种方法来实现我们的目标,而不损害 Identity 机制的完整性,或者损害那些依赖 IdentityRole 实例来完成工作的下游组件。
首先,让我们看看我们现有的 ApplicationDbContext 类
ApplicationDbContext 类
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser>
{
public ApplicationDbContext()
: base("DefaultConnection")
{
}
}
在上面,我们可以看到我们继承自 IdentityDbContext<TUser> 类,这允许我们指定一个自定义类型,只要该类型是从 IdentityUser 派生的。因此,Identity 系统似乎通常提供了扩展 IdentityUser 的内置机制。是否存在扩展 IdentityRole 的类似途径?事实证明是存在的。某种程度上。
扩展 Identity Role 类
首先,我们当然需要创建派生类 ApplicationRole。将以下类添加到 *Models* 文件夹:
Application Role 类
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models
{
public class ApplicationRole : IdentityRole
{
public ApplicationRole() : base() { }
public ApplicationRole(string name, string description) : base(name)
{
this.Description = description;
}
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
}
}
正如我们所见,我们创建了一个派生类,并实现了一个简单的新的 Description 属性,以及一个新的重写构造函数。接下来,我们需要修改我们的 ApplicationDbContext,以便在运行 EF Migrations 时,我们的数据库能够反映正确的模型。打开 ApplicationDbContext 类,并为 OnModelCreating 方法添加以下重写:
在代码文件顶部添加这些命名空间
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System;
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure;
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.Configuration;
using System.Data.Entity.Validation;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
然后将以下代码添加到 ApplicationDbContext 类中:
注意:这段代码很密集,有点杂乱。不必担心理解其中的细节——只需从高层次的角度来看,并尝试掌握这段代码如何将我们的代码对象映射到数据库表。特别是,它如何建模表之间的外键关系。
重写 OnModelCreating 方法
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
if (modelBuilder == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("modelBuilder");
}
// Keep this:
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUser>().ToTable("AspNetUsers");
// Change TUser to ApplicationUser everywhere else -
// IdentityUser and ApplicationUser essentially 'share' the AspNetUsers Table in the database:
EntityTypeConfiguration<ApplicationUser> table =
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().ToTable("AspNetUsers");
table.Property((ApplicationUser u) => u.UserName).IsRequired();
// EF won't let us swap out IdentityUserRole for ApplicationUserRole here:
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().HasMany<IdentityUserRole>((ApplicationUser u) => u.Roles);
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserRole>().HasKey((IdentityUserRole r) =>
new { UserId = r.UserId, RoleId = r.RoleId }).ToTable("AspNetUserRoles");
// Leave this alone:
EntityTypeConfiguration<IdentityUserLogin> entityTypeConfiguration =
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserLogin>().HasKey((IdentityUserLogin l) =>
new { UserId = l.UserId, LoginProvider = l.LoginProvider, ProviderKey
= l.ProviderKey }).ToTable("AspNetUserLogins");
entityTypeConfiguration.HasRequired<IdentityUser>((IdentityUserLogin u) => u.User);
EntityTypeConfiguration<IdentityUserClaim> table1 =
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityUserClaim>().ToTable("AspNetUserClaims");
table1.HasRequired<IdentityUser>((IdentityUserClaim u) => u.User);
// Add this, so that IdentityRole can share a table with ApplicationRole:
modelBuilder.Entity<IdentityRole>().ToTable("AspNetRoles");
// Change these from IdentityRole to ApplicationRole:
EntityTypeConfiguration<ApplicationRole> entityTypeConfiguration1 =
modelBuilder.Entity<ApplicationRole>().ToTable("AspNetRoles");
entityTypeConfiguration1.Property((ApplicationRole r) => r.Name).IsRequired();
}
在上面,我们基本上是在告诉 Entity Framework 如何将我们的继承结构映射到数据库。但是,我们可以告诉 EF 以一种方式建模我们的数据库,使得我们的两个派生类都可以使用相同的表,并且实际上可以扩展它们以包含我们的自定义字段。请注意,在上面的代码中,我们首先告诉 modelBuilder 将 IdentityUser 类指向 "AspNetUsers" 表,然后也告诉它将 ApplicationUser 指向同一个表?之后,我们对 ApplicationRole 做了同样的事情。
可以看出,实际上无法摆脱 IdentityUser 或 IdentityRole 类——两者都在 Identity 系统内部被使用。我们只是利用了多态性,使得在我们的应用程序层面,我们可以使用派生类,而在底层,Identity 将它们识别为其基类实现。稍后我们将看到这对我们的应用程序有何影响。
更新 Identity Manager 类
现在,我们可以将应用程序中其余大部分部分的 IdentityRole 替换为 ApplicationRole,并开始使用我们新的 Description 属性。我们将从 IdentityManager 类开始。我顺便做了一些重构,所以如果您正在跟随学习,这段代码看起来会与原始项目中的代码略有不同。只需粘贴这段代码(但请确保您的命名空间匹配!)。我还添加了一些新的 using 语句到代码文件顶部。
修改后的 Identity Manager 类
public class IdentityManager
{
// Swap ApplicationRole for IdentityRole:
RoleManager<ApplicationRole> _roleManager = new RoleManager<ApplicationRole>(
new RoleStore<ApplicationRole>(new ApplicationDbContext()));
UserManager<ApplicationUser> _userManager = new UserManager<ApplicationUser>(
new UserStore<ApplicationUser>(new ApplicationDbContext()));
ApplicationDbContext _db = new ApplicationDbContext();
public bool RoleExists(string name)
{
return _roleManager.RoleExists(name);
}
public bool CreateRole(string name, string description = "")
{
// Swap ApplicationRole for IdentityRole:
var idResult = _roleManager.Create(new ApplicationRole(name, description));
return idResult.Succeeded;
}
public bool CreateUser(ApplicationUser user, string password)
{
var idResult = _userManager.Create(user, password);
return idResult.Succeeded;
}
public bool AddUserToRole(string userId, string roleName)
{
var idResult = _userManager.AddToRole(userId, roleName);
return idResult.Succeeded;
}
public void ClearUserRoles(string userId)
{
var user = _userManager.FindById(userId);
var currentRoles = new List<IdentityUserRole>();
currentRoles.AddRange(user.Roles);
foreach (var role in currentRoles)
{
_userManager.RemoveFromRole(userId, role.Role.Name);
}
}
}
更新迁移配置中的 Add Users and Roles 方法
我们还想更新 AddUsersAndRoles() 方法,该方法由 EF 迁移的 Configuration 文件中的 Seed() 方法调用。我们希望用使用我们新的扩展属性的角色来填充数据库。
更新后的 Add Users and Roles 方法
bool AddUserAndRoles()
{
bool success = false;
var idManager = new IdentityManager();
// Add the Description as an argument:
success = idManager.CreateRole("Admin", "Global Access");
if (!success == true) return success;
// Add the Description as an argument:
success = idManager.CreateRole("CanEdit", "Edit existing records");
if (!success == true) return success;
// Add the Description as an argument:
success = idManager.CreateRole("User", "Restricted to business domain activity");
if (!success) return success;
// While you're at it, change this to your own log-in:
var newUser = new ApplicationUser()
{
UserName = "jatten",
FirstName = "John",
LastName = "Atten",
Email = "jatten@typecastexception.com"
};
// Be careful here - you will need to use a password which will
// be valid under the password rules for the application,
// or the process will abort:
success = idManager.CreateUser(newUser, "Password1");
if (!success) return success;
success = idManager.AddUserToRole(newUser.Id, "Admin");
if (!success) return success;
success = idManager.AddUserToRole(newUser.Id, "CanEdit");
if (!success) return success;
success = idManager.AddUserToRole(newUser.Id, "User");
if (!success) return success;
return success;
}
我们在这里所做的只是向 CreateRole() 方法传递了一个额外的参数,以便种子角色能够显示我们的新属性。现在,我们需要对 AccountController、视图模型和视图进行一些调整。
更新 Select Role Editor 视图模型
在上一篇文章中,我们创建了一个 SelectRoleEditorViewModel,它接受一个 IdentityRole 实例作为构造函数参数。我们需要修改这里的代码,以便能够处理我们在扩展 IdentityRole 时添加的任何新属性。对于我们的示例,我们只添加了一个新属性,所以这相当容易。
修改后的 SelectRoleEditorViewModel
public class SelectRoleEditorViewModel
{
public SelectRoleEditorViewModel() { }
// Update this to accept an argument of type ApplicationRole:
public SelectRoleEditorViewModel(ApplicationRole role)
{
this.RoleName = role.Name;
// Assign the new Descrption property:
this.Description = role.Description;
}
public bool Selected { get; set; }
[Required]
public string RoleName { get; set; }
// Add the new Description property:
public string Description { get; set; }
}
更新相应的编辑器视图模型
回想一下,为了 以 HTML 表单的形式显示带有复选框的角色列表,我们可以从用户那里返回所做的选择,我们需要定义一个与我们的 EditorViewModel 类对应的 EditorViewModel.cshtml 文件。在 *Views/Shared/EditorViewModels* 中打开 SelectRoleEditorViewModel.cshtml 并进行以下更改:
修改后的 SelectRoleEditorViewModel
@model AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.SelectRoleEditorViewModel
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.RoleName)
<tr>
<td style="text-align:center">
@Html.CheckBoxFor(model => model.Selected)
</td>
<td style="padding-right:20px">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.RoleName)
</td>
<td style="padding-right:20px">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Description)
</td>
</tr>
同样,我们在上面需要做的只是为新属性添加一个表数据元素。
更新用户角色视图
到目前为止,我们实际上只有一个显示我们角色的视图——UserRoles 视图,我们在其中将用户分配给应用程序中的一个或多个角色。再说一次,我们只需要添加一个表头元素来表示我们的新 Description 属性:更新后的 UserRoles 视图。
@model AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.SelectUserRolesViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "User Roles";
}
<h2>Roles for user @Html.DisplayFor(model => model.UserName)</h2>
<hr />
@using (Html.BeginForm("UserRoles", "Account", FormMethod.Post, new { encType = "multipart/form-data", name = "myform" }))
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.UserName)
</div>
</div>
<h4>Select Role Assignments</h4>
<br />
<hr />
<table>
<tr>
<th>
Select
</th>
<th>
Role
</th>
<th>
Description
</th>
</tr>
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Roles)
</table>
<br />
<hr />
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
我们真的要编辑角色吗?
在这里,您可能需要仔细考虑一下。请考虑——在 ASP.NET 应用程序中使用角色的主要原因是为了管理授权。我们通过 [Authorize] 属性将访问权限硬编码到控制器和/或特定方法中。如果我们使角色可创建/可编辑/可删除,可能会出现什么问题?嗯,很多。首先,如果我们部署应用程序,然后添加一个角色,我们实际上无法就上述安全问题利用新角色,除非在添加新角色到我们希望用它来保护的任何方法后,重新编译并重新部署我们的应用程序。
更改角色名称,或者更糟的是,删除角色,情况也是如此。事实上,一个野心勃勃的管理员用户可能会完全锁定自己离开应用程序!然而,在某些情况下,我们可能仍希望拥有此功能。例如,如果您是开发人员,并且通过 [Authorize] 向现有应用程序添加了一些新的角色权限,那么通过前端添加新角色比手动添加到数据库或使用 Migrations 重新填充应用程序更方便。此外,如果您的应用程序已上线,那么重新运行迁移实际上是不可行的。无论如何,在我之前的帖子中,许多评论者都表达了修改或删除角色的愿望,所以让我们继续前进!
为什么不行?添加 Roles Controller
当我构建完所有内容并尝试使用 Visual Studio 的内置脚手架添加新的 Roles Controller 时,我遇到了一些问题。显然,通过我们扩展 IdentityRole 的方式,Entity Framework 在基于 ApplicationRole 模型脚手架一个新的控制器时遇到了一些麻烦(EF 检测到 IdentityRole 和 ApplicationRole 之间存在一些歧义)。我没有花太多时间纠缠这个问题——用老式的方法编写一个简单的 CRUD 控制器很容易,所以我就是这样做的。这是我手工编写的 RolesController,已准备就绪:
Roles Controller
using AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Controllers
{
public class RolesController : Controller
{
private ApplicationDbContext _db = new ApplicationDbContext();
public ActionResult Index()
{
var rolesList = new List<RoleViewModel>();
foreach(var role in _db.Roles)
{
var roleModel = new RoleViewModel(role);
rolesList.Add(roleModel);
}
return View(rolesList);
}
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult Create(string message = "")
{
ViewBag.Message = message;
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include =
"RoleName,Description")]RoleViewModel model)
{
string message = "That role name has already been used";
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var role = new ApplicationRole(model.RoleName, model.Description);
var idManager = new IdentityManager();
if(idManager.RoleExists(model.RoleName))
{
return View(message);
}
else
{
idManager.CreateRole(model.RoleName, model.Description);
return RedirectToAction("Index", "Account");
}
}
return View();
}
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult Edit(string id)
{
// It's actually the Role.Name tucked into the id param:
var role = _db.Roles.First(r => r.Name == id);
var roleModel = new EditRoleViewModel(role);
return View(roleModel);
}
[HttpPost]
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult Edit([Bind(Include =
"RoleName,OriginalRoleName,Description")] EditRoleViewModel model)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var role = _db.Roles.First(r => r.Name == model.OriginalRoleName);
role.Name = model.RoleName;
role.Description = model.Description;
_db.Entry(role).State = EntityState.Modified;
_db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(model);
}
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public ActionResult Delete(string id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
var role = _db.Roles.First(r => r.Name == id);
var model = new RoleViewModel(role);
if (role == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(model);
}
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(string id)
{
var role = _db.Roles.First(r => r.Name == id);
var idManager = new IdentityManager();
idManager.DeleteRole(role.Id);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
}
在上面,请注意,当我们删除角色时,我们会调用 IdentityManager 类中的一个名为 DeleteRole() 的方法。为什么这么复杂,John?为什么不直接从数据存储中删除角色?这有一个原因……
关于删除角色
想想看。如果您有一个或多个用户分配给一个角色,当您删除该角色时,您需要先将其用户从中删除。否则,您将遇到数据库中的外键问题,这些问题将不允许您删除该角色。因此,我们需要向 IdentityManager 添加一些重要的方法。
在 Identity Manager 中添加删除角色方法
显然,为了删除角色,我们首先需要先从中删除所有用户。然后我们才能删除角色。但是,我们必须采用一种小技巧来实现这一点,因为 Identity 框架本身并没有实现 RemoveRole() 方法。哦,它就在那里——如果你仔细找,就能找到。RoleStore<IRole> 类实际上定义了一个 DeleteAsync 方法。但是,它会抛出 "Not Implemented" 异常。以下是我如何解决这个问题。将以下两个方法添加到 IdentityManager 类:
在 Identity Manager 类中添加 DeleteRole 和 RemoveFromRole 方法
public void RemoveFromRole(string userId, string roleName)
{
_userManager.RemoveFromRole(userId, roleName);
}
public void DeleteRole(string roleId)
{
var roleUsers = _db.Users.Where(u => u.Roles.Any(r => r.RoleId == roleId));
var role = _db.Roles.Find(roleId);
foreach (var user in roleUsers)
{
this.RemoveFromRole(user.Id, role.Name);
}
_db.Roles.Remove(role);
_db.SaveChanges();
}
首先,请注意我们传递的是一个简单的 RoleId 而不是一个实例或 ApplicationRole?这是因为,为了让 Remove(role) 方法正常工作,作为参数传递的角色必须来自同一个 ApplicationDbContext 实例,如果我们从控制器传递一个,则不会如此。还请注意,在调用 _db.Roles.Remove(role) 之前,我们检索了属于该角色的用户集合,并将它们删除。这解决了外键关系问题,并防止了数据库中 AspNetUserRoles 表出现孤立记录。
角色控制器使用的 ViewModel 和视图
请注意,在我们的控制器中,我们使用了两个新的视图模型,RoleViewModel 和 EditRoleViewModel。我已将它们添加到 *AccountViewModels.cs* 文件中。代码如下:
RoleViewModel 和 EditRoleViewModel 类
public class RoleViewModel
{
public string RoleName { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public RoleViewModel() { }
public RoleViewModel(ApplicationRole role)
{
this.RoleName = role.Name;
this.Description = role.Description;
}
}
public class EditRoleViewModel
{
public string OriginalRoleName { get; set; }
public string RoleName { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public EditRoleViewModel() { }
public EditRoleViewModel(ApplicationRole role)
{
this.OriginalRoleName = role.Name;
this.RoleName = role.Name;
this.Description = role.Description;
}
}
角色控制器使用的视图
RolesController 使用的视图是通过右键单击关联的 Controller 方法并选择“添加视图”来创建的。我在此包含它是为了完整性,但这里没有什么革命性的东西。每个代码如下。
Index Role 视图
显示角色列表,以及指向 Edit 或 Delete 的操作链接。
Create Role 视图的代码
@model IEnumerable<AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.RoleViewModel>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Application Roles";
}
<h2>Application Roles</h2>
<p>
@Html.ActionLink("Create New", "Create")
</p>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.RoleName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Description)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.RoleName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Description)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "Edit", new { id = item.RoleName }) |
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "Delete", new { id = item.RoleName })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
Create Role 视图
显然,它允许创建新角色。
Create Role 视图的代码
@model AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.RoleViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
}
<h2>Create Role</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<h4>RoleViewModel</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
@if(ViewBag.Message != "")
{
<p style="color: red">ViewBag.Message</p>
}
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.RoleName,
new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.RoleName)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.RoleName)
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Description,
new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Description)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Description)
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}
Edit Roles 视图
用于,嗯,编辑角色……
Edit Roles 视图的代码
@model AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.EditRoleViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Edit";
}
<h2>Edit</h2>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-horizontal">
<h4>EditRoleViewModel</h4>
<hr />
@Html.ValidationSummary(true)
@*Hide the original name away for later:*@
@Html.HiddenFor(model => model.OriginalRoleName)
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.RoleName,
new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.RoleName)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.RoleName)
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Description,
new { @class = "control-label col-md-2" })
<div class="col-md-10">
@Html.EditorFor(model => model.Description)
@Html.ValidationMessageFor(model => model.Description)
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
<div>
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
@section Scripts {
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jqueryval")
}
Delete Roles 视图
Delete Roles 视图的代码
@model AspNetExtendingIdentityRoles.Models.RoleViewModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Delete";
}
<h2>Delete</h2>
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<div>
<h4>RoleViewModel</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="dl-horizontal">
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.RoleName)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.RoleName)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Description)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Description)
</dd>
</dl>
@using (Html.BeginForm()) {
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
<div class="form-actions no-color">
<input type="submit" value="Delete" class="btn btn-default" /> |
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
</div>
}
</div>
修改 _Layout.cshtml 以添加 Users 和 Roles 链接
我修改了 *\_Layout.cshtml* 文件,将原来的“Admin”链接更改为“Users”,并添加了一个新的“Roles”链接,如下所示:
修改 _Layout.cshtml
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Home", "Index", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("About", "About", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Contact", "Contact", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Users", "Index", "Account")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Roles", "Index", "Roles")</li>
</ul>
@Html.Partial("_LoginPartial")
</div>
运行迁移并构建数据库
好的,您现在应该能够添加一个新的迁移,运行它,并构建出数据库。如果您是 EF Migrations 的新手,您可能需要回顾一下配置 Entity Framework 迁移。 在本例中,克隆的项目已经启用了迁移,所以我们只需要构建,然后在程序包管理器控制台中输入:
添加新迁移(删除之前的迁移文件,或选择一个新名称)
Add-Migration init
然后,如果一切顺利,
更新数据库
Update-Database
运行应用程序
如果一切顺利(并且我在本文中没有遗漏任何内容!),我们应该能够运行我们的应用程序,登录,然后导航到“Users”选项卡。然后,选择列出的单个用户的“Roles”链接。您应该看到类似以下的内容:
User Roles 视图: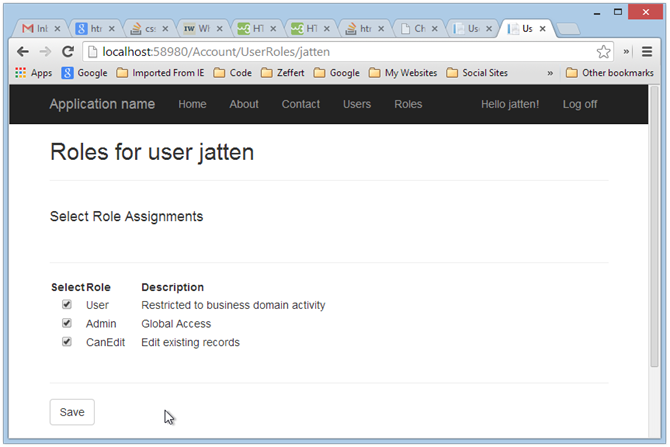
我们可以看到,我们的新属性显现出来了。
一些结语
这篇文章为了实现相对较小的功能而写得相当长。然而,我们触及了一些概念,如果您需要从新的 Identity 系统获得比开箱即用更多的功能,这些概念可能会有所帮助。此外,我正在为下一篇文章做准备,届时我将研究设置用户可以分配到的“角色组”。在这种场景下,我们可以使用内置的角色在代码中设置相当精细化的访问权限,然后将用户分配到预定义的“角色权限组”,这在某种程度上模仿了熟悉的域权限。
在处理认证和安全时请多加注意!
我在处理 membership 或 Identity 时,会尽力遵守 ASP.NET 团队设定的界限和机制。我离安全专家还差得很远(尽管我最近确实买了一本关于它的书!),那些人对创建安全的授权系统比我所希望的了解得多。在前一篇关于扩展 IdentityUser 和向我们的应用程序添加角色的文章中,我们一直严格遵守 Identity 的预期用途。
在本文中,我稍微偏离了一些,扩展了一个似乎 ASP.NET 团队并未打算轻易扩展的类。此外,我还实现了一种在应用程序用户级别创建、编辑和删除角色的方法。我假设这些功能之所以没有内置,是有原因的。最有可能的原因是我之前讨论过的。
当您的安全和授权需求变得足够复杂时,可能需要考虑 Identity 系统之外的更强大的替代方案。毕竟,Identity 系统最初的设计目标是保护面向公众的 Web 应用程序,具有有限数量的用户角色和管理要求。此外,NET 团队最近发布了 ASP.NET Identity 2 预览版,其中包含更多令人感兴趣的发展。
话虽如此,据我所知,我们在这里所做的并没有明确损害我们应用程序的安全性或 Identity 系统的完整性。我们的 ApplicationRole 类通过继承和多态性,被 ASP.NET Identity 系统的内部机制正确使用,同时提供了我们所需的任何附加属性。
您有什么想法?看到了什么改进之处?
如果您看到我有什么错误,或者在将代码移入本文时遗漏了什么,请在评论中告知我,或将邮件发送到“关于作者”侧边栏中的地址。如果您对如何改进本文中的内容有任何建议,请告知我,或在 Github 上提交一个 Pull Request。我很乐意整合任何好的想法。敬请关注下一篇关于实现组和权限的文章!
其他资源和感兴趣的项目
Identity v2.0
Identity 1.0 及其他项目
- 本文的 Github 源代码
- 扩展 ASP.NET MVC 5 中的身份账户并实现基于角色的认证
- 配置 ASP.NET MVC 5 和 Visual Studio 2013 中 Identity 账户的数据库连接和 Code-First 迁移
- ASP.NET MVC 显示带有复选框的 HTML 表格以选择行项目
- ASP.NET MVC 中的自定义路由
- ASP.NET MVC 中的路由基础

