ApiFrame:一个用于 Web API 安全、异常和版本控制的简单库
一个简单的 C#.NET 库,实现了 HMAC 身份验证、全局异常处理和 API 版本控制

相关文章
如何在 ASP.NET Web API 应用程序中集成 ApiFrame[^]
目录
引言
ApiFrame 是一个简单的 .NET 库,实现了 ASP.NET WEB API 开发所需的核心组件。它是一个 C# 类库,具有逻辑分离的服务器(提供者)、客户端(使用者)和支持框架(基础设施)。服务器组件提供了一个接口来实现 Web API 方法的安全(身份验证和授权)、异常处理和版本控制。此库中实现的机制是 HMAC(哈希消息身份验证码)身份验证。HMAC 使用的一个例子是 Amazon Web Service (AWS),并且此库中的身份验证过程使用了 HMAC-SHA 签名,这与 AWS 的方法相同。客户端部分提供了一个网关组件,.NET 客户端可以通过引用该组件来调用 WEB API。
本文档将作为 ApiFrame 的简单文档,重点介绍库中类组件的基本描述。下图显示了组件架构的轮廓。
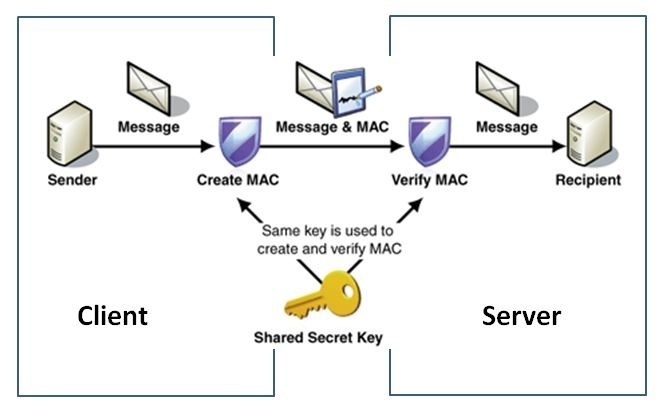
HMAC 身份验证 – 概述
HMAC 身份验证提供了一种简单的方法,通过客户端和服务器都知道的密钥来验证 HTTP 请求。客户端和服务器都可以访问该密钥。通常,这个密钥是一个在注册时创建并存储在数据库中的唯一 ID。客户端使用密钥和基于请求内容的的消息,通过 HMAC 算法生成签名(MAC),并将此签名附加到 HTTP 请求的授权头中。当服务器收到请求时,它会从请求头中提取哈希签名(MAC),并计算自己的签名版本,以验证收到的签名是否与计算出的签名匹配。如果两个签名匹配,系统就认为请求有效并应予以处理。如果两个签名不匹配,请求将被丢弃,系统将以错误消息响应。
框架
框架提供了令牌模型、配置类、常量值、辅助函数和扩展来支持服务器和客户端组件的实现。此外,它还提供了一个接口,可以通过依赖注入与其他应用程序集成。
令牌
HMAC 身份验证依赖于基于令牌的通信。令牌是一小块数据,附加到每个 API 请求的授权头中。通常,令牌是用于 HTTP 请求的身份验证和授权的密钥。在下面的类图中,您会注意到基类“ApiBaseToken”具有以下属性:
- AccessToken: 访问令牌是公钥
- SecretToken: 密钥令牌是用于使用哈希算法生成签名的私钥
- AuthScheme: AuthScheme 是一个简单的缩写文本,表示使用者(应用程序/客户)的名称
有三个类继承自这个基类,每个类代表一个用于不同目的的令牌模型。ApiApplicationToken 用于身份验证。ApiUserToken 用于授权。ApiRequestToken 用于创建客户端请求。
接口
在库的某些区域需要注入依赖项。为此,定义了所需的接口。使用应用程序应提供所需的令牌来验证和授权 HTTP 请求。接口 **IApiInception** 暴露了调用程序集需要实现的必要方法,这些方法返回处理 HTTP 请求所需的令牌。接口 **IApiException** 用于异常日志记录。每个应用程序都有自己的异常日志记录机制。当使用应用程序中抛出未处理的程序异常时,可以通过实现 IApiException 接口来捕获它。接口 **IApiSignature** 用于计算 HMAC 签名。库本身包含该接口的实现,该实现使用 HMACSHA256 算法来计算 HMAC 签名。可以使用相同的实现,或者通过此接口注入不同的实现(如果需要)。
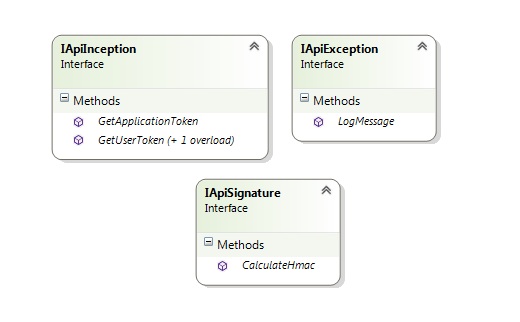
public interface IApiInception
{
ApiApplicationToken GetApplicationToken(string accessToken);
ApiUserToken GetUserToken(string username, string password);
ApiUserToken GetUserToken(string accessToken);
}
public interface IApiException
{
void LogMessage(Exception exception);
}
public interface IApiSignature
{
string CalculateHmac(string secretKey, string stringToSign);
}
依赖注入
定义了一个简单的依赖注入类,它有两个通用的静态方法,允许将对象注入到类中。**RegisterType<TInterface, TClass>** 方法由使用应用程序调用,以将接口类型映射到相应的具体类类型。**GetInstance<TInterface>** 方法由内部类组件调用,以获取已注册接口类型的对象实例。

public class ApiObjectFactory
{
private static readonly Dictionary<string, System.Type> ObjectTypes
= new Dictionary<string, System.Type>();
public static void RegisterType<TInterface, TClass>() where TClass : TInterface
{
var typeInterface = typeof(TInterface);
var typeClass = typeof(TClass);
if (!typeInterface.IsInterface || typeClass.IsInterface || typeClass.IsAbstract)
{
throw new ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode.InvalidOperation);
}
ObjectTypes.Add(typeInterface.Name, typeClass);
}
public static TInterface GetInstance<TInterface>()
{
System.Type type = null;
if (ObjectTypes.TryGetValue(typeof(TInterface).Name, out type))
{
return (TInterface)System.Activator.CreateInstance(type);
}
throw new ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode.MissingRequiredType);
}
}
签名计算
在实现 HMAC 身份验证时,每个 API 请求都需要使用 HMAC 签名进行签名。签名是使用令牌“SecretKey”和消息“StringToSign”计算的。“StringToSign”是使用 URI、请求时间戳和其他 HTTP 头值构造的。计算出的签名被转换为 base64 字符串。这个编码的 base64 字符串是用于签名 HTTP 请求的计算出的签名。

public string CalculateHmac(string secretKey, string stringToSign)
{
byte[] secretBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(secretKey);
byte[] stringBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(stringToSign);
string signature;
using (var hmac = new HMACSHA256(secretBytes))
{
byte[] hash = hmac.ComputeHash(stringBytes);
signature = Convert.ToBase64String(hash);
}
return signature;
}
配置
配置类“ApiConfiguration”实现了单例实例,其属性如下面的类图所示。“RequestValidityInMinutes”属性用于以分钟为单位配置请求的有效性,即任何 HTTP 请求的年龄不能超过 x 分钟。x 值通过 ApiConfiguration 类的实例进行配置。其初始值默认为 10 分钟。这可以由使用应用程序修改。“VersionNamespaceKey”属性用于配置 Web API 版本控制方法。ApiFrame 允许使用两种不同的方法来实现版本控制。可以使用“VersionNamespaceKey”属性进行配置,默认为“area”。

public class ApiConfiguration
{
static ApiConfiguration()
{
Instance = new ApiConfiguration();
Instance.RequestValidityInMinutes = 10;
Instance.VersionNamespaceKey = "area";
}
public static ApiConfiguration Instance { get; private set; }
public double RequestValidityInMinutes { get; set; }
public string VersionNamespaceKey { get; set; }
}
实用程序
该库的这一部分包括实用程序类,如辅助函数、扩展和验证方法,用于访问和验证 HTTP 请求和头。
服务器
服务器组件实现了身份验证和授权所需的筛选器。筛选器会验证 HTTP 请求并识别请求者。在服务器端验证 HTTP 请求涉及三个步骤,如下面的图所示。第一步是使用访问令牌检索密钥令牌。第二步是根据请求参数和密钥令牌计算签名。第三步是验证计算出的签名是否与收到的签名匹配。
安全
下面的类图显示了处理身份验证和授权的服务器组件的设计。
身份验证
身份验证是根据用户名和密码识别用户。ApiFrame 实现了一个名为“ApiAuthentication”的授权筛选器属性,该属性遵循 HMAC 方法,例如通过验证签名来认证用户。它从 HTTP 请求头读取用户名和密码,并使用它们来识别用户。如果用户有效,则会创建一个自定义身份和主体对象。这个自定义主体对象被设置为当前 HttpContext 的 User 属性。
public class ApiAuthentication : AuthorizationFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnAuthorization(HttpActionContext actionContext)
{
// Get the request for the action context
HttpRequestMessage request = actionContext.Request;
// Create an instance of ApiValidation
IApiValidation apiValidation = new ApiValidation();
// Call the validation method to validate the request
apiValidation.ValidateRequest(request);
// Get the access token from the request header parameter and validate
string apiAccessToken = request.GetAccessToken();
// Get the instance of ApiInception
IApiInception apiInception = ApiObjectFactory.GetInstance<IApiInception>();
// Get the application token
ApiApplicationToken applicationToken = apiInception.GetApplicationToken(apiAccessToken);
// Call the validation method to validate the token and signature
apiValidation.ValidateToken(request, applicationToken);
apiValidation.ValidateSignature(request, applicationToken.SecretToken);
// Read the username and password from current http request paramters
var username = HttpContext.Current.Request.Params["Username"];
var password = HttpContext.Current.Request.Params["Password"];
if (username == null || password == null)
{
throw new ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode.MissingRequiredParamter);
}
// Call the service method to get the user details
ApiUserToken user = apiInception.GetUserToken(username, password);
bool isAuthenticated = user != null;
if (isAuthenticated)
{
// Set the user principal for the current http request
string authenticationType = ApiConstants.AUTHTYPE;
IIdentity userIdentity = new ApiIdentity(authenticationType, isAuthenticated, user.Name, user.UserId);
IPrincipal principal = new ApiPrincipal(userIdentity, user.Roles);
HttpContext.Current.User = principal;
}
else
{
throw new ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode.AuthenticationFailed);
}
}
}
Authorization
授权是检查已认证的用户是否被允许执行操作或访问受保护的资源。在 ApiFrame 中,对于授权,我们有一个名为“ApiAuthorization”的授权属性类,它继承自“AuthorizeAttribute”,用于验证签名并通过 HTTP 请求中的用户令牌识别已认证的用户。
public class ApiAuthorization : AuthorizeAttribute
{
public override void OnAuthorization(HttpActionContext actionContext)
{
HttpRequestMessage request = actionContext.Request;
// Get the instnce of ApiValidation
IApiValidation apiValidation = new ApiValidation();
// Call the validation method to validate the request
apiValidation.ValidateRequest(request);
string accessToken = request.GetAccessToken();
// Get the instance of ApiInception
IApiInception apiInception = ApiObjectFactory.GetInstance<IApiInception>();
ApiUserToken user = apiInception.GetUserToken(accessToken);
apiValidation.ValidateToken(request, user);
apiValidation.ValidateSignature(request, user.SecretToken);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(Roles))
{
apiValidation.ValidateRole(Roles, user.Roles);
}
string authenticationType = ApiConstants.AUTHTYPE;
IIdentity userIdentity = new ApiIdentity(authenticationType, true, user.Name, user.UserId);
IPrincipal principal = new ApiPrincipal(userIdentity, user.Roles);
HttpContext.Current.User = principal;
}
}
授权请求
如果使用应用程序不需要对公共 API 方法进行身份验证和授权,但希望允许授权客户端访问,则定义了一个名为“ApiAuthorizedRequest”的授权筛选器属性。可以将其应用于操作方法,以检查请求是否来自授权客户端。
public class ApiAuthorizedRequest : AuthorizationFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnAuthorization(HttpActionContext actionContext)
{
HttpRequestMessage request = actionContext.Request;
// Get the instnce of ApiValidation
IApiValidation apiValidation = new ApiValidation();
// Call the validation method to validate the request
apiValidation.ValidateRequest(request);
string apiAccessToken = request.GetAccessToken();
IApiInception apiInception = ApiObjectFactory.GetInstance<IApiInception>();
// Get the application token
ApiApplicationToken applicationToken = apiInception.GetApplicationToken(apiAccessToken);
apiValidation.ValidateToken(request, applicationToken);
apiValidation.ValidateSignature(request, applicationToken.SecretToken);
}
}
自定义身份和主体
当服务器对用户进行身份验证/授权时,它会创建一个自定义主体(ApiPrincipal),这是一个 IPrincipal 对象,代表代码正在运行的安全上下文。主体包含一个关联的自定义身份对象(ApiIdentity),其中包含有关用户的信息。当进行身份验证/授权时,此安全信息(ApiPrincipal)会为当前的 HTTP 请求(HttpContext.Current.User)设置。下面的代码显示了自定义身份和主体类。
public class ApiIdentity : IIdentity
{
public ApiIdentity(string authenticationType, bool isAuthenticated, string userName, string userId)
{
this.AuthenticationType = authenticationType;
this.IsAuthenticated = isAuthenticated;
this.Name = userName;
this.UserId = userId;
}
public string AuthenticationType { get; private set; }
public bool IsAuthenticated { get; private set; }
public string Name { get; private set; }
public string UserId { get; private set; }
}
public class ApiPrincipal : IPrincipal
{
public ApiPrincipal(IIdentity identity, string roles)
{
this.Identity = identity;
this.Roles = roles.Split(',');
}
public IIdentity Identity { get; private set; }
public string[] Roles { get; private set; }
public bool IsInRole(string roles)
{
return Roles.Intersect(roles.Split(',')).Count() > 0;
}
}
强制使用 HTTPS
通过纯 HTTP 进行通信不安全,即使我们有安全的身份验证方案。启用 SSL 是数据的另一层保护。我们可能需要 HTTPS 来访问一些受保护的资源。ApiFrame 实现了一个名为“ApiHttpsRequired”的授权筛选器,该筛选器会检查 SSL。可用于需要 HTTPS 的 Web API 方法。
public class ApiHttpsRequired : AuthorizationFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnAuthorization(HttpActionContext actionContext)
{
if (actionContext.Request.RequestUri.Scheme != Uri.UriSchemeHttps)
{
throw new ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode.InvalidUriScheme);
}
else
{
base.OnAuthorization(actionContext);
}
}
}
异常
错误代码
一组错误代码定义在一个名为 ApiErrorCode 的枚举类型中,该类型包含 ApiFrame 处理的错误类型的列表。
错误响应
错误响应由 ApiErrorResponse 类创建,该类包含一个静态方法 "GetErrorMessage",该方法返回给定 ApiErrorCode 的 HttpResponseMessage。该方法通过错误代码识别自定义错误,并使用自定义消息、类型和适当的 HttpStatusCode 创建 HttpError。此 HttpError 被序列化并分配给 HttpResponseMesssage 的内容。ApiErrorResponse 类提供了另一个方法 "GetHttpError" 来将 HttpResponseMessage 的内容反序列化为 HttpError。
public class ApiErrorResponse
{
private const string Code = "Code";
private const string Type = "Type";
public static HttpResponseMessage GetErrorMessage(ApiErrorCode errorCode)
{
HttpError error;
switch (errorCode)
{
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidRequestHeader:
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidMD5:
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidSignature:
error = new HttpError("Problem communicating with the application. Invalid Request.");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.ExpectationFailed;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidTimestamp:
error = new HttpError("The date and time is incorrect.");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidScheme:
error = new HttpError("This version of application is outdated.");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.BadRequest;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidUriScheme:
error = new HttpError("There has been problem processing your request.");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.AuthenticationFailed:
error = new HttpError("The username/passowrd you have entered is incorrect");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidToken:
case ApiErrorCode.InvalidRole:
error = new HttpError("Authorization has been denied for this request");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.MissingRequiredParamter:
error = new HttpError("The username/passowrd parameter is missing");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
break;
case ApiErrorCode.MissingRequiredType:
error = new HttpError("The required type is not registered");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.Forbidden;
break;
default:
error = new HttpError("Server error.");
error[Code] = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError;
break;
}
error[Type] = errorCode.ToString();
var response = new HttpResponseMessage((HttpStatusCode)error[Code])
{
Content = new StringContent(new JavaScriptSerializer().Serialize(error)),
ReasonPhrase = errorCode.ToString()
};
return response;
}
public static HttpError GetHttpError(HttpResponseMessage response)
{
if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
string responseError = response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result;
var httpError = new JavaScriptSerializer().Deserialize<HttpError>(responseError);
return httpError;
}
return null;
}
}
自定义 HTTP 请求异常
一个名为 "ApiRequestException" 的类继承自 HttpResponseException,它提供了一种定义自定义异常的方法。ApiRequestException 类提供了两个构造函数。一个用于定义 ApiFrame 的内部异常,另一个构造函数允许调用程序集初始化自己的自定义异常。
public class ApiRequestException : HttpRequestException
{
public ApiRequestException(ApiErrorCode errorType)
{
this.ErrorType = errorType;
this.ErrorResponseMessage = ApiErrorResponse.GetErrorMessage(errorType);
}
public ApiRequestException(HttpStatusCode statusCode, string errorMessage, string reasonPhrase)
{
this.ErrorType = ApiErrorCode.InvalidOperation;
this.ErrorResponseMessage = new HttpResponseMessage(statusCode)
{
Content = new StringContent(errorMessage),
ReasonPhrase = reasonPhrase
};
}
public ApiErrorCode ErrorType { get; set; }
public HttpResponseMessage ErrorResponseMessage { get; set; }
}
异常筛选器属性
Web API 异常可以通过异常筛选器进行处理。ApiExceptionAttribute 是一个继承自 ExceptionFilterAttribute 类的异常筛选器,并重写了 OnException 方法。
public class ApiExceptionAttribute : ExceptionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnException(HttpActionExecutedContext context)
{
HttpResponseMessage response;
if (context.Exception is ApiRequestException)
{
ApiRequestException apiException = (ApiRequestException)context.Exception;
response = apiException.ErrorResponseMessage;
}
else
{
ApiObjectFactory.GetInstance<IApiException>().
LogMessage(context.Exception);
response = ApiErrorResponse.GetErrorMessage(ApiErrorCode.InvalidProgramException);
}
context.Response = response;
}
}
版本控制
定义了一个名为“ApiControllerSelector”的自定义类,它实现了 IHttpControllerSelector 来支持版本控制。ApiFrame 提供了使用命名空间或区域版本控制 Web API 的选项。代码摘自此 MSDN 博客[^],并略作修改以兼容 MVC Area。
控制器选择器
Web API 用于选择控制器的接口是 IHttpControllerSelector。该接口上的方法是 SelectController,它为 HttpRequestMessage 选择一个控制器。定义了一个名为“ApiControllerSelector”的自定义类,它实现了 IHttpControllerSelector 来支持版本控制。
public HttpControllerDescriptor SelectController(HttpRequestMessage request)
{
IHttpRouteData routeData = request.GetRouteData();
if (routeData == null)
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
// Get the namespace and controller variables from the route data.
string namespaceName = GetRouteVariable<string>(routeData, ApiConfiguration.Instance.VersionNamespaceKey);
if (namespaceName == null)
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
string controllerName = GetRouteVariable<string>(routeData, ControllerKey);
if (controllerName == null)
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
// Find a matching controller.
// string key = String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, "{0}.{1}", namespaceName, controllerName);
string key = ApiConfiguration.Instance.VersionNamespaceKey == NamespaceKey ?
String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, "{0}.Controllers.{1}", namespaceName, controllerName) :
String.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, "{0}.{1}", namespaceName, controllerName);
HttpControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor;
if (controllers.Value.TryGetValue(key, out controllerDescriptor))
{
return controllerDescriptor;
}
else if (duplicates.Contains(key))
{
throw new HttpResponseException(
request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError,
"Multiple controllers were found that match this request."));
}
else
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
}
客户端
客户端部分实现了一个网关组件,API 客户端可以使用该组件来调用 WEB API 方法。下面显示了客户端的类图。ApiRequestToken 包含创建 Http 请求所需的属性,该属性作为 Gateway 类组件的 execute 方法的输入参数。网关的主要职责是向服务器发送 HTTP 请求并接收响应。
网关
网关组件负责创建签名后的 HTTP 请求并将其发送到服务器。发送签名后的 HTTP 请求涉及三个步骤,如下面的图所示。第一步是构建包含所有必需请求头参数的 HTTP 请求。第二步是根据请求内容,使用密钥令牌和“StringToSign”消息创建 HMAC-SHA 签名。第三步是将请求和签名发送到服务器。

private HttpResponseMessage SendHttpRequest(ApiRequestToken requestToken)
{
DateTime requestDate = ApiHelper.GetCurrentDateTime();
string contentType = string.Empty;
string contentMD5 = string.Empty;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestToken.Content))
{
contentType = ApiConstants.CONTENTTYPE;
contentMD5 = ApiHelper.ComputeMD5Hash(requestToken.Content);
}
// Step 1: Create the http request
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(requestToken.Verb, requestToken.RelativeUrl);
request.Headers.Date = requestDate;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(requestToken.Content))
{
request.Content = new StringContent(requestToken.Content);
request.Content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue(contentType);
request.Content.Headers.Add("Content-MD5", contentMD5);
}
// Step 2: Sign the request
string stringToSign = ApiHelper.BuildMessageRepresentation(requestToken.Verb.ToString(), contentType, contentMD5, requestDate, ApiConstants.FORWARDSLASH + requestToken.RelativeUrl);
string signature = this.signature.CalculateHmac(requestToken.SecretToken, stringToSign);
string authorizationHeader = ApiHelper.BuildAuthorizationHeader(requestToken.AuthScheme, requestToken.AccessToken, signature);
request.Headers.Add("Authorization", authorizationHeader);
// Step 3: Send the request
using (var client = new HttpClient())
{
client.BaseAddress = new Uri(this.baseUrl);
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Clear();
client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Accept.Add(new MediaTypeWithQualityHeaderValue(ApiConstants.APPJSON));
ServicePointManager.ServerCertificateValidationCallback += (sender, certificate, chain, sslPolicyErrors) => true;
HttpResponseMessage response = client.SendAsync(request).Result;
return response;
}
}
基于请求内容的“消息”(StringToSign)
StringToSign 是一个使用 HTTP 请求元素构造的消息。以下代码示例说明了 StringToSign 的构造方式。Content-MD5 和 Content-Type 仅适用于 HTTP POST 请求。对于 GET、PUT、DELETE 等其他 HTTP 请求,Content 值仅表示为空。
StringToSign = HTTP-VERB + "\n" +
Content-MD5 + "\n" +
Content-Type + "\n" +
TimeStamp + "\n" +
RequestUri;
签名请求
签名请求是将 HMAC 签名添加到 HTTP 请求的授权头中,格式如下:
Authorization: AuthScheme AccessToken:Signature
结论
本文档描述了该库的各个部分及其内容。一篇相关的文章发布在 如何将 ApiFrame 集成到 ASP.NET Web API 应用程序中[^],其中提供了使用 APIFrame 的指南。