WCF 路由服务 - 第 II 部分:基于上下文的路由和协议桥接
4.96/5 (18投票s)
本文描述了使用 WCF 路由服务进行的基于上下文的路由和协议桥接。
目录
所有文章
- WCF 路由服务 - 第 IV 部分:服务版本控制和多播
- WCF 路由服务 - 第 III 部分:故障转移和负载均衡
- WCF 路由服务 - 第 II 部分:基于上下文的路由和协议桥接
- WCF 路由服务 - 第一部分:基本概念、简单路由服务与基于内容的路由
引言
在本系列的第一部分中,我介绍了 WCF 路由服务的概念,然后分别描述了它的虚拟终结点、目标服务、消息过滤器和过滤器表配置。然后,我演示了一个简单的路由服务示例,最后解释了使用 WCF RoutingService 进行基于内容的路由。在本系列第二部分中,我将演示使用 WCF RoutingService 进行基于上下文的路由和协议桥接。
基于上下文的路由
在基于上下文的路由中,传入的消息根据消息到达的通道进行路由,而不是通过检查传入消息的内容。
让我们来看一个例子来理解基于上下文的路由。假设我们的 ComplexNumberCalculator 服务有三种类型的客户端(例如Client1、Client2和Client3)。Client1 可以执行所有复数运算,而Client2和Client3只能访问复数的二元和一元运算。因此,在中间件中将分别有三个终结点用于“所有”、“二元”和“一元”复数运算。Client1 将使用一个终结点(例如 'all'),Client2 将使用另一个终结点(例如 'binary'),Client3 将使用最后一个终结点(例如 'unary')。Client1 将消息发送到名为 'all' 的终结点,该终结点必须由中间件路由到处理所有复数运算的服务;Client2 将消息发送到名为 'binary' 的终结点,该终结点必须由中间件路由到处理复数二元运算的服务;Client3 将消息发送到名为 'unary' 的终结点,该终结点必须由中间件路由到处理复数一元运算的服务。

我们的演示服务
为了通过基于上下文的路由实现上述场景,我对我们的 ComplexNumberCalculator 服务进行了一些更改。我定义了两个新的服务契约 IBinaryOperation 和 IUnaryOperation,分别用于复数的二元和一元运算。然后,我定义了一个空的 IComplexNumber 服务契约,并通过实现这两个服务契约来完成。实际上,我已将所有复数运算从 IComplexNumber 服务契约移至 IBinaryOperation 和 IUnaryOperation 服务契约,并将它们按二元和一元运算分组。请参阅下面的服务契约定义-
[ServiceContract]
public interface IBinaryOperation
{
[OperationContract]
Complex Add(Complex x, Complex y);
[OperationContract]
Complex Subtract(Complex x, Complex y);
[OperationContract]
Complex Multiply(Complex x, Complex y);
[OperationContract]
Complex Divide(Complex x, Complex y);
}
[ServiceContract]
public interface IUnaryOperation
{
[OperationContract]
double Modulus(Complex x);
[OperationContract]
double Argument(Complex x);
[OperationContract]
Complex Conjugate(Complex x);
[OperationContract]
Complex Reciprocal(Complex x);
}
[ServiceContract]
public interface IComplexNumber : IBinaryOperation, IUnaryOperation
{
}
下面是上述设计的类图-

接下来,我在我们的控制台宿主应用程序中为 ComplexNumberCalculator 服务配置了三个终结点(每个客户端类型一个),以及一个标准的 mex 终结点-
<services>
<service name="CalculatorService.ComplexNumberCalculator">
<endpoint address="" binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IComplexNumber" />
<endpoint address="binary" binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IBinaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="unary" binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IUnaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="mex" kind="mexEndpoint" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="https://:8081/ComplexNumberService" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
我没有为每种客户端类型创建三个客户端应用程序,而是在单个客户端应用程序中通过配置以下三个客户端终结点来模拟它们-
<client>
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IComplexNumber" name="BasicHttpBinding_IComplexNumber" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IBinaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/unary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IUnaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IUnaryOperation" />
</client>
以下是客户端应用程序代码-
var cfAll = new ChannelFactory<IComplexNumber>("BasicHttpBinding_IComplexNumber");
var cfBinary = new ChannelFactory<IBinaryOperation>("BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr");
var cfUnary = new ChannelFactory<IUnaryOperation>("BasicHttpBinding_IUnaryOperation");
var channelAll = cfAll.CreateChannel();
var channelBinary = cfBinary.CreateChannel();
var channelUnary = cfUnary.CreateChannel();
var z1 = new Complex();
var z2 = new Complex();
z1.Real = 3D;
z1.Imaginary = 4D;
z2.Real = 1D;
z2.Imaginary = -2D;
Console.WriteLine("*** Context Based Routing ***\n");
Console.WriteLine("\nPlease hit any key to run OR enter 'exit' to exit.");
string command = Console.ReadLine();
while (command != "exit")
{
Console.WriteLine("Please hit any key to start Client1: ");
Console.ReadLine();
ComplexNumberArithmetics(channelAll, z1, z2);
Console.WriteLine("Please hit any key to start Client2: ");
Console.ReadLine();
ComplexNumberBinaryArithmetics(channelBinary, z1, z2);
Console.WriteLine("Please hit any key to start Client3: ");
Console.ReadLine();
ComplexNumberUnaryArithmetics(channelUnary, z1);
Console.WriteLine("\nPlease hit any key to re-run OR enter 'exit' to exit.");
command = Console.ReadLine();
}
((IClientChannel)channelAll).Close();
((IClientChannel)channelBinary).Close();
((IClientChannel)channelUnary).Close();
在上面,ComplexNumberArithmetics 方法执行所有复数运算,ComplexNumberBinaryArithmeticss 方法仅执行复数的二元运算,ComplexNumberUnaryArithmetics 方法仅执行复数的一元运算(请参阅示例中的这些方法的代码)。
就是这样。
使用 EndpointName filterType 进行基于上下文的路由
在本节中,我将使用 EndpointName filterType 为基于上下文的路由配置我们的 RoutingService。首先,我为每个客户端类型配置了以下三个虚拟终结点-
<services>
<service name="System.ServiceModel.Routing.RoutingService">
<endpoint address="" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="All" />
<endpoint address="binary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Binary" />
<endpoint address="unary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Unary" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
接下来,我为每个目标服务定义了三个终结点-
<client>
<endpoint address="https://:8081/ComplexNumberService1" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="*" name="AllOperation" />
<endpoint address="https://:8081/ComplexNumberService2" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="*" name="BinaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="https://:8081/ComplexNumberService3" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="*" name="UnaryOperation" />
</client>
接下来,我启用了 RoutingBehavior,然后指定了过滤器表的名称。我通过定义默认行为来实现此目的-
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior name="">
<routing filterTableName="RoutingTable" />
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
然后,我通过将 filterData 属性设置为虚拟终结点名称,并使用 filterType: 'EndpointName',为 RoutingService 的每个虚拟终结点定义了以下过滤器-
<filters>
<filter name="AllOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointName" filterData="All" />
<filter name="BinaryOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointName" filterData="Binary" />
<filter name="UnaryOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointName" filterData="Unary" />
</filters>
最后,我像下面这样在过滤器表 RoutigTable 中将每个过滤器映射到相应的目标服务终结点-
<filterTables>
<filterTable name="RoutingTable">
<add filterName="AllOperationFilter" endpointName="AllOperation" />
<add filterName="BinaryOperationFilter" endpointName="BinaryOperation" />
<add filterName="UnaryOperationFilter" endpointName="UnaryOperation" />
</filterTable>
</filterTables>
在运行我们的演示项目之前,请快速浏览一下此帖子提供的示例项目-

现在,将 ConsoleClient 和 ConsoleHostRouter 项目设置为启动项目,然后按 Ctrl+F5 键运行项目。接下来,从管理员模式的Visual Studio Developer Command Prompt 中运行 WCFRoutingPart2\ComplexNumberServices\StartAllServices.cmd 文件(参见示例代码),以启动 ComplexNumberService1、ComplexNumberService2 和 ComplexNumberService3 服务。现在可以看到具有三个虚拟终结点的 RoutingService-

接下来,按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟我们的 Client1,您可以验证所有复数运算都已由中间件 RoutingService 路由到 ComplexNumberService1 服务。

接下来,按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟我们的 Client2,您可以验证复数的二元运算已由中间件 RoutingService 路由到 ComplexNumberService2 服务。

最后,按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟我们的 Client3,您可以验证复数的一元运算已由中间件 RoutingService 路由到 ComplexNumberService3 服务。

因此,从这个例子中可以看出,路由是基于消息到达的通道进行的。您也可以通过使用 EndpointAddress 或 EndpointAddressPrefix filterTypes 来检查传入消息的地址来实现基于上下文的路由。
使用 EndpointAddressPrefix filterType 进行基于上下文的路由
在本节中,我将使用 EndpointAddressPrefix filterType 为基于上下文的路由配置我们的 RoutingService。让我们考虑另外两种客户端类型,例如 Client4 和 Client5 来执行复数的二元运算。

因此,我为 Client4 和 Client5 各配置了另外两个虚拟终结点,如下所示-
<services>
<service name="System.ServiceModel.Routing.RoutingService">
<endpoint address="all" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="All" />
<endpoint address="binary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Binary" />
<endpoint address="unary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Unary" />
<endpoint address="binary/another" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="BinaryAnother" />
<endpoint address="binary/another/extra" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="BinaryAnotherExtra" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
然后,我使用 PrefixEndpointAddress filterType 更新了先前定义的过滤器,将 filterData 属性设置为每个复数运算的地址前缀,如下所示-
<filters>
<filter name="AllOperationFilter" filterType="PrefixEndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/all" />
<filter name="BinaryOperationFilter" filterType="PrefixEndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary" />
<filter name="UnaryOperationFilter" filterType="PrefixEndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/unary" />
</filters>
请注意,由于我们使用了 PrefixEndpointAddress filterType,我只为复数的二元运算定义了一个过滤器。因此,所有在虚拟终结点Binary、BinaryAnother和BinaryAnotherExtra上接收的传入消息都将由此过滤器处理,消息将被路由到具有终结点名称BinaryOperation的服务 ComplexNumberService2。
接下来,我配置了客户端应用程序,为上述 RoutingService 虚拟终结点添加了另外两个终结点,如下所示-
<client>
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/all" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IComplexNumber" name="BasicHttpBinding_IComplexNumber" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IBinaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/unary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IUnaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IUnaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary/another" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IBinaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr_Another" />
<endpoint address="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary/another/extra" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="IBinaryOperation" name="BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr_Another_Extra" />
</client>
最后,我对客户端应用程序代码进行了一些更改,以纳入 Client4 和 Client5-
...
var cfBinaryAnother = new ChannelFactory<IBinaryOperation>("BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr_Another");
var cfBinaryAnotherExtra = new ChannelFactory<IBinaryOperation>("BasicHttpBinding_IBinaryOperationr_Another_Extra");
...
var channelBinaryAnother = cfBinaryAnother.CreateChannel();
var channelBinaryAnotherExtra = cfBinaryAnotherExtra.CreateChannel();
...
Console.WriteLine("Please hit any key to start Client4: ");
Console.ReadLine();
ComplexNumberBinaryArithmetics(channelBinaryAnother, z1, z2);
Console.WriteLine("Please hit any key to start Client5: ");
Console.ReadLine();
ComplexNumberBinaryArithmetics(channelBinaryAnotherExtra, z1, z2);
...
((IClientChannel)channelBinaryAnother).Close();
((IClientChannel)channelBinaryAnotherExtra).Close();
...
现在,只需按照上一节中的说明运行演示,您就会发现所有在为复数二元运算定义的虚拟终结点上接收的传入消息都被路由到 ComplexNumberService2 服务。

协议桥接
通常,两个服务如果配置相同的绑定,就可以相互通信。但如果两个服务使用的绑定不同呢?它们是否可以以任何方式相互通信?理论上有两种可能的通信方式。第一种选择是更新客户端应用程序以匹配后端服务的绑定。但这并非总是可行,例如在互操作性场景中。第二种选择是重新配置后端服务以匹配客户端应用程序想要通信的绑定。但这同样并非总是可行,例如,如果您不拥有该服务,这将导致可维护性问题,您将需要公开更多的终结点。
协议桥接消除了这些情况,服务始终以与以前相同的方式与客户端应用程序通信。这种解耦非常有帮助,因为它确保了额外的通信需求不会影响后端服务。
但请注意,路由服务中的通信形状必须始终是对称的,即如果客户端和路由服务之间的通信是请求-响应类型,那么路由服务和后端服务之间的通信也必须是请求-响应类型。如果客户端应用程序和路由服务之间的通信是请求-响应类型,而路由服务和后端服务之间的通信是单向类型(反之亦然),那么就没有意义了。
在所有之前的示例中,我都在客户端与路由器之间以及路由器与目标服务之间使用了相同的 basicHttpBinding。WCF RoutingService 还为跨大多数 WCF 绑定进行通信提供了强大的支持。例如,您可以将路由器配置为使用 basicHttpBinding,以便客户端应用程序可以通过 basicHttpBinding 与其通信,但路由器使用 NetTcpBinding、NetNamedPipeBinding 或 udpBinding 与目标服务通信。
让我们重新考虑“基于上下文的路由”部分中的先前示例,并为协议桥接演示重新配置它。假设 ComplexNumberCalculator 服务使用 udpBinding、NetTcpBinding 和 NetNamedPipeBinding 绑定公开了三个终结点,分别对应 IComplexNumber、IBinaryOperation 和 IUnaryOperation 服务契约;并且路由器使用 basicHttpBinding 配置了虚拟终结点,以便与客户端应用程序通信。
因此,Client1、Client2 和 Client3 将使用 basicHttpBinding 与路由器通信,而路由器将分别使用 udpBinding、NetTcpBinding 和 NetNamedPipeBinding 与Client1、Client2 和 Client3 的目标服务通信。

因此,根据上述示例,我首先像下面这样,使用 udpBinding、NetTcpBinding 和 NetNamedPipeBinding 绑定为 ComplexNumberCalculator 服务配置了以下三个终结点,以及一个标准的 mex 终结点-
<services>
<service name="CalculatorService.ComplexNumberCalculator">
<endpoint address="udp" binding="udpBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IComplexNumber" />
<endpoint address="tcp" binding="netTcpBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IBinaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="pipe" binding="netNamedPipeBinding" contract="CalculatorService.IUnaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="mex" kind="mexEndpoint" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="soap.udp://224.1.1.1:40000/ComplexNumberService" />
<add baseAddress="net.tcp://:8081/ComplexNumberService" />
<add baseAddress="net.pipe:///ComplexNumberService" />
<add baseAddress="https://:8082/ComplexNumberService" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
接下来,我为每个客户端类型重新配置了 RoutingService,具有以下三个虚拟终结点-
<services>
<service name="System.ServiceModel.Routing.RoutingService">
<endpoint address="all" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="All" />
<endpoint address="binary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Binary" />
<endpoint address="unary" binding="basicHttpBinding"
contract="System.ServiceModel.Routing.IRequestReplyRouter" name="Unary" />
<host>
<baseAddresses>
<add baseAddress="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router" />
</baseAddresses>
</host>
</service>
</services>
接下来,我为每个目标服务重新定义了三个终结点-
<client>
<endpoint address="soap.udp://224.1.1.1:40000/ComplexNumberService/udp" binding="udpBinding"
contract="*" name="AllOperation" />
<endpoint address="net.tcp://:8081/ComplexNumberService/tcp" binding="netTcpBinding"
contract="*" name="BinaryOperation" />
<endpoint address="net.pipe:///ComplexNumberService/pipe" binding="netNamedPipeBinding"
contract="*" name="UnaryOperation" />
</client>
然后,我通过将 filterData 属性设置为虚拟终结点的地址,并使用 filterType: 'EndpointAddress',为 RoutingService 的每个虚拟终结点重新定义了以下过滤器-
<filters>
<filter name="AllOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/all" />
<filter name="BinaryOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/binary" />
<filter name="UnaryOperationFilter" filterType="EndpointAddress" filterData="https://:8080/RoutingService/Router/unary" />
</filters>
最后,我还对客户端应用程序代码进行了一些更改。您可以在此帖子附带的示例应用程序中找到它们。
全部完成。现在,将 ConsoleClient、ConsoleHostComplexNo 和 ConsoleHostRouter 项目设置为启动项目,然后按 Ctrl+F5 键运行项目。现在,查看带有三个终结点以及标准 mex 终结点(ConsoleHostComplexNo)的目标服务 ComplexNumberCalculator-

接下来,按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟HTTP到UDP的协议桥接,您可以验证Client1使用 basicHttpBinding 与路由器通信,然后路由器使用 udpBinding 与 complexNumberCalculator 服务的“udp”终结点通信。

接下来,再次按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟HTTP到TCP的协议桥接,您可以验证Client2使用 basicHttpBinding 与路由器通信,然后路由器使用 netTcpBinding 与 complexNumberCalculator 服务的“tcp”终结点通信。
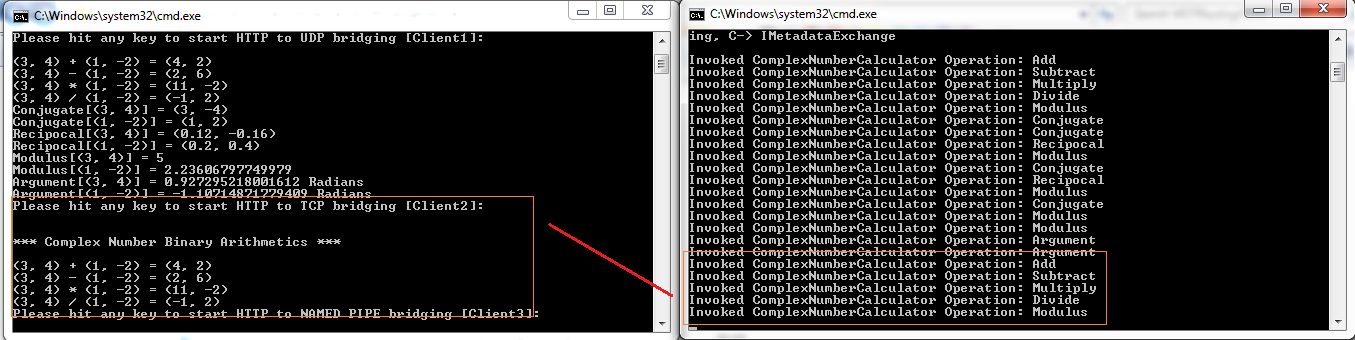
接下来,再次按控制台客户端窗口中的任意键以模拟HTTP到NamedPipe的协议桥接,您可以验证Client3使用 basicHttpBinding 与路由器通信,然后路由器使用 netNamedPipeBinding 与 complexNumberCalculator 服务的“pipe”终结点通信。

请注意,在 RoutingService 的上下文中,协议桥接有两个关键方面:传输介质转换(意味着客户端和服务不必在电线上通信时使用相同的传输。)和协议转换(意味着隐式处理任何必要的通信协议转换,例如从SOAP 1.1 [basicHttpBinding] 到SOAP 1.2 [NetTcpBinding])。
结论
在这篇文章中,我探讨了使用 EndpointName 和 PrefixEndpointAddress 过滤器类型的基于上下文的路由。然后,我解释了协议桥接的概念。我已尽最大努力通过演示应用程序来展示这些概念。在下一篇文章中,我将探讨更多概念,如多播、负载均衡等。在此之前,祝您编码愉快。
历史记录
- 2014 年 6 月 7 日 -- 文章更新(在“所有文章”部分为系列的第四部分添加了新条目)
- 2014 年 5 月 28 日 - 文章更新(在“所有帖子”部分添加了系列第三篇文章的新条目)
- 2014 年 5 月 27 日 - 文章更新(更新了“所有帖子”部分系列第一篇文章的 URL)
- 2014 年 5 月 24 日 - 文章更新
- (更新了文章标题)
- (更新了“所有帖子”部分的条目)
- 2014 年 5 月 23 日 - 文章更新(上传了更新后的示例代码)
- 2014 年 5 月 22 日 - 文章更新
- (更新了“使用 EndpointName filterType 进行基于上下文的路由”部分,增加了启用 RoutingBehavior 的内容)
- (更正了拼写错误)
- 2014 年 5 月 21 日 - 文章更新(更新了“所有帖子”部分的条目)
- 2014 年 5 月 20 日 - 文章更新
- (重新排列了“所有帖子”部分的条目)
- (添加了目录部分)
- 2014 年 5 月 19 日 - 发布原始版本
