创建支持手机和平板的应用程序
创建支持手机和平板的应用程序
目录
引言
一个 Android 应用程序包可以在大量设备上运行,包括手机、平板电脑、PC 等。在本文中,我们将讨论如何使应用程序适应大屏幕,如何有效利用屏幕空间,以及一些让应用更好的技巧和窍门。
背景
当您在较大屏幕上运行应用程序时,您可能会看到有时存在大量未使用的空间,因为该应用程序不是为大屏幕设计的。Android 提供了备用资源机制,为正确的屏幕提供正确的资源,但这还不够。Android 还提供了 Fragment,用于创建多窗格应用程序,通过 Fragment,您可以将应用程序的多个屏幕放入一个屏幕中。
让我们开始吧
Android 3.0 引入了 Fragment。Fragment 是一种可移植的用户界面,它使得创建多窗格 UI 成为可能。它的工作方式类似于 View,您可以将多个 Fragment 添加到单个 Activity 中。每个 Fragment 都有自己的生命周期,与 Activity 的生命周期完全分离,因为您可以在运行时添加或删除它。
为了与旧版 Android 兼容,Android 还提供了支持库,允许您在旧版 Android 上使用新功能,包括 Fragment。在本文中,我们将重点关注支持库中的 Fragment 类(别担心,两个 Fragment 类的行为相同,只有包名不同)。
主从(Master-Detail)风格的应用程序是学习 Fragment 的绝佳例子。许多应用程序都有菜单或链接,当点击它时,应用程序会带您到一个新页面或显示与该菜单/链接相关的一些数据,这被称为主从用户界面。

上图展示了手机上的主从用户界面风格。您会看到主菜单/链接和详细信息分别放置在不同的页面上。

上图展示了平板电脑上的主从用户界面风格。您会看到,在平板电脑或大屏幕设备上,您可以将主页面和详细信息页面合并到单个页面中,是的,它看起来像一个选项卡控件(选项卡控件是主从用户界面的一种实现)。

为小屏幕和大屏幕创建两种布局作为备用资源不是一个好主意,因为您需要复制代码逻辑部分,并且当您想在页面中添加/删除某些内容时,您需要在两个布局文件中都进行操作。

考虑一下将主页面和详细信息页面分别创建,并各自拥有独立的逻辑部分。当应用程序在小屏幕上运行时,只显示主菜单;但当应用程序在大屏幕上运行时,则将详细信息页面附加到屏幕右侧。这个想法被称为多窗格,因为您将多个 UI 窗格放在了单个屏幕上。
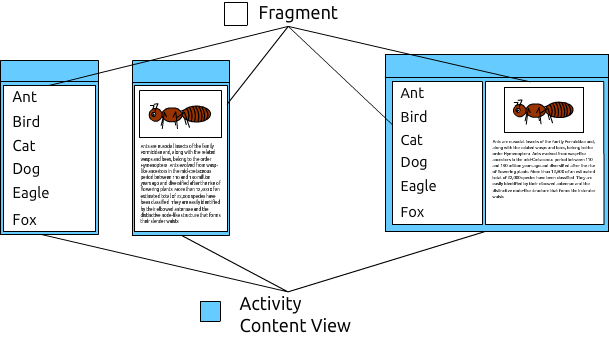
在 Android 上,无法在屏幕上显示多个 Activity,您必须为两个页面创建 Fragment,然后将它们附加到 Activity 中。
任务: 您在本文中的任务是创建一个应用程序,用于显示动物列表及其详细信息,如上图所示。我们将一起学习如何创建它,现在就开始吧!请创建一个不使用任何模板的新应用程序(不添加 Activity),因为我们将自己创建应用程序的所有部分。
如何创建 Fragment?
和 Activity 一样,您需要创建一个派生自 Fragment 的类!
注意: 请使用 android.support.v4.app.Fragment 包中的 Fragment。
要使用支持库中的 Fragment,您需要将该库添加到项目中。如果您使用 Android Studio 作为 IDE,请打开 app 目录中的 build.gradle 文件,然后查看 dependencies 并像这样添加支持库:
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:20.0.0'
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:20.0.0'
}
如果您使用 Eclipse 作为 IDE,您需要将 android-support-v4.jar 文件从 SDK_LOCATION/extras/android/support/v4 复制到您项目的 libs 目录中(并确保 libs 目录存在于您的项目编译类路径中)。
创建 AnimalListFragment。
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
public class AnimalListFragment extends Fragment{
}
然后为这个 Fragment 创建布局。
注意: 为 Fragment 命名布局时,请以 "fragment_" 前缀开头。
fragment_animal_list.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@android:id/list" />
</LinearLayout>
我创建了一个只包含 LinearLayout 和 ListView 的布局,因为我想以列表形式显示动物的名称。
当 Fragment 附加到 Activity 时,Activity 将调用 getView() 方法来获取 Fragment 的 View。因此,您需要在 getView() 方法被调用之前创建 View。Fragment 提供了 onCreateView() 方法用于构建其 View。现在,通过加载(inflate)布局并将其作为方法的结果返回,来实现 onCreateView() 方法。
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_animal_list,null);
return view;
}
注意: 我将 null 值作为 inflate() 方法的第二个参数,因为我现在不想将加载的 View 附加到任何 ViewGroup。(此 Fragment 的宿主 Activity 会自动附加该视图,但如果该 View 已经被附加,则会抛出异常)
接下来,创建 Animal 类来存储动物数据。
public class Animal {
private String name;
private String imageUrl;
private String description;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getImageUrl() {
return imageUrl;
}
public void setImageUrl(String imageUrl) {
this.imageUrl = imageUrl;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
}
我创建了只有 3 个属性的 Animal 类,分别是 name、imageUrl 和 description。(但如果您愿意,可以添加更多属性)
然后,回到 Fragment,创建模拟的 Animal 对象并将其存储在 List 中。(在本文中,我将使用来自维基百科的模拟数据,但在实际应用中,您应该避免使用静态数据)
private List<Animal> generateAnimalList(){
List<Animal> animals = new ArrayList<Animal>(10);
Animal ant = new Animal();
ant.setName("Ant");
ant.setImageUrl("http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/85/WeaverAntDefense.JPG");
ant.setDescription("Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from wasp-like ancestors in the mid-Cretaceous period between 110 and 130 million years ago and diversified after the rise of flowering plants. More than 12,500 of an estimated total of 22,000 species have been classified. They are easily identified by their elbowed antennae and the distinctive node-like structure that forms their slender waists.");
animals.add(ant);
Animal bird = new Animal();
bird.setName("Bird");
bird.setImageUrl("http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/3/32/House_sparrow04.jpg");
bird.setDescription("Birds (class Aves or clade Avialae) are feathered, winged, two-legged, warm-blooded, egg-laying vertebrates. Aves ranks as the tetrapod class with the most living species, approximately ten thousand. Extant birds belong to the subclass Neornithes, living worldwide and ranging in size from the 5 cm (2 in) bee hummingbird to the 2.75 m (9 ft) ostrich. The fossil record indicates that birds emerged within the theropod dinosaurs during the Jurassic period, around 150 million years ago. On 31 July 2014, scientists reported details of the evolution of birds from theropod dinosaurs. Most researchers agree that modern-day birds are the only living members of the Dinosauria clade.");
animals.add(bird);
Animal cat = new Animal();
cat.setName("Cat");
cat.setImageUrl("http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/bb/Kittyply_edit1.jpg/800px-Kittyply_edit1.jpg");
cat.setDescription("The domestic cat is a small, usually furry, domesticated, and carnivorous mammal. It is often called the housecat when kept as an indoor pet, or simply the cat when there is no need to distinguish it from other felids and felines. Cats are often valued by humans for companionship, and their ability to hunt vermin and household pests.");
animals.add(cat);
Animal dog = new Animal();
dog.setName("Dog");
dog.setImageUrl("http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/1/13/Gaia_Basenji.jpg");
dog.setDescription("The domestic dog is a member of the Canidae family of the mammalian order Carnivora. The term \"domestic dog\" is generally used for both domesticated and feral varieties. The dog was the first domesticated animal and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and pet animal in human history. The word \"dog\" can also refer to the male of a canine species, as opposed to the word \"bitch\" which refers to the female of the species.");
animals.add(dog);
return animals;
}
之后,重写 onViewCreated() 方法。您应该在此方法中设置 View 的数据或监听器。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
ListView animalListView = (ListView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.list);
}
现在,我们需要创建 Adapter 来为 ListView 提供数据。
public class AnimalListAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
List<Animal> animalList;
Context context;
public AnimalListAdapter(Context context,List<Animal> animalList){
this.context = context;
this.animalList = animalList;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return animalList==null?0:animalList.size();
}
@Override
public Animal getItem(int i) {
return animalList==null?null:animalList.get(i);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int i) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int i, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
if(view==null)
view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,null);
Animal animal = getItem(i);
TextView nameTextView = (TextView)view.findViewById(android.R.id.text1);
nameTextView.setText(animal.getName());
return view;
}
}
我为 Animal 对象列表创建了一个简单的适配器,这个适配器将使用 android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1 布局来显示列表项。
接下来,回到 Fragment,创建适配器的实例并将其设置给 ListView。
注意: 要从 Fragment 获取 Context 对象,您可以使用 getActivity() 方法来获取该 Fragment 所附加的 Activity 实例。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
ListView animalListView = (ListView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.list);
AnimalListAdapter animalListAdapter = new AnimalListAdapter(getActivity(),generateAnimalList());
animalListView.setAdapter(animalListAdapter);
}
接下来,我们将创建用于显示我们的 Fragment 的 Activity。
Fragment Activity
要将 Fragment 放入 Activity 中,您需要一个 FragmentManager 对象,FragmentManager 允许您管理 Activity 上的 Fragment。

当存在两种类型的 Fragment(原生和支持库)时,您需要获取正确的 FragmentManager 对象。如果您的 Fragment 派生自 android.app.Fragment,您需要使用 android.app.FragmentManager 中的 FragmentManager;但如果您的 Fragment 派生自 android.support.v4.app.Fragment,则需要使用 android.support.v4.app.FragmentManager 中的 FragmentManager。
Android 3+ 的 android.app.Activity 和 android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity 提供了 getFragmentManager() 方法,该方法返回 android.app.FragmentManager 类的 FragmentManager 对象;但只有 android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity 提供了 getSupportFragmentManager() 方法,该方法返回来自支持库的 FragmentManager 对象。
在本文中,我将创建一个派生自 FragmentActivity 类的 Activity。
注意: ActionBarActivity 是派生自 FragmentActivity 并带有 Action Bar 实现的类。
现在,创建一个派生自 FragmentActivity 的 MainActivity。
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
}
不要忘记将 MainActivity 添加到清单文件中(如果您是手动创建 Activity 类文件的话)。然后将 MainActivity 设置为 main 和 launcher。
AndroidManifest.xml
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
将 Fragment 放入 Activity
要将您的 Fragment 附加到 Activity,您可以直接在布局中添加 <fragment /> 元素,或者编写 Java 代码来动态添加或删除。
<fragment />
您可以直接通过创建 <fragment /> 元素将 Fragment 放入布局文件中,但通过在布局文件中定义 Fragment,您将无法在运行时删除或替换它。
fragment 元素最重要的属性是 android:name,它指向您想要显示的 Fragment 的完整类路径,其他属性与其它视图的通用属性相同。
为 MainActivity 创建布局文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<fragment
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:name="me.vable.android.animallist.fragment.AnimalListFragment"/>
</LinearLayout>
我已将 AnimalListFragment 添加到 MainActivity 的布局文件中。
回到 Activity 文件,并在 onCreate() 中添加 setContentView() 语句以加载布局文件。
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
然后,运行应用!

想要获取 Fragment 的实例吗?
就像 View 一样,如果您将 Fragment 添加到布局文件中,您可以设置它的 id,并且可以通过该 id 获取它的实例。唯一的区别在于,Activity 中没有方法用于获取 Fragment 实例,您需要获取 FragmentManager 的实例,然后调用 findFragmentById() 方法。
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Fragment animalListFragment = getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.fragment_animal_list);
}
}
注意: 请不要忘记确保您已导入正确的 Fragment 类,Android Studio 可能会建议导入 android.app.Fragment,但如果您使用的是 android.support.v4.app.Fragment,则需要手动导入它。
现在您的屏幕上有了动物列表,接下来我们将学习如何在 Java 代码中动态添加 Fragment。
通过 Java 代码将 Fragment 放入 Activity
您也可以使用 Java 代码在运行时添加、删除或替换 Fragment。

如果您的应用有一些功能需要在运行时更改某些 Fragment,例如当用户点击右侧 Fragment 中的设置菜单时,左侧的 Fragment 将被替换为设置 Fragment,您需要通过 Java 代码来实现。
要通过 Java 代码将 Fragment 放入 Activity,您需要为 Fragment 提供一个容器视图(View)。我建议您使用 FrameLayout,因为它简单,而且将多个 Fragment 放在单个容器中不是一个好主意,因为这样很难管理它们。

回到我们的应用,当用户选择动物时,在手机上会通过用动物详情替换动物列表来显示该动物的详情,但在平板电脑上,我们将在屏幕右侧显示动物详情。这意味着我们的应用将不使用静态 Fragment(布局中的 fragment 元素)。
在 MainActivity 的布局文件中,将 fragment 元素替换为 FrameLayout。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/framelayout_left"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
然后我们需要为平板电脑再创建一个布局文件。
为平板电脑创建布局目录
(您可以简单地在 res 目录下手动创建 layout-large 目录)
在 res 上右键单击,选择 New > Android resource directory

然后,将 Resource Type 设置为 layout。

之后,在 Available qualifiers 中选择 Size,点击 >> 按钮,然后将 Screen size 选项更改为 large。

按 OK 按钮,您将在 res 目录下看到 layout-large 目录。

然后在 layout-large 目录中创建 Activity 的布局文件,其名称与手机的布局文件相同。

现在,当在平板电脑上运行应用程序时,layout-large 中的布局文件将被加载。
接下来,向新布局中添加视图。对于平板电脑,动物列表和详情将显示在同一屏幕上,您需要在左侧和右侧添加两个 FrameLayout 来显示 Fragment。
注意: 您需要将左侧 FrameLayout 的 id 设置为与手机布局中的 FrameLayout 相同,并限制其宽度。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/framelayout_left"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</FrameLayout>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/framelayout_right"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
之后,转到 Activity 文件。在 onCreate() 方法中,创建一个新的 AnimalListFragment 实例。
AnimalListFragment animalListFragment = new AnimalListFragment();
然后获取 FragmentManager 实例用于管理 fragment。(我使用了来自支持库的 FragmentManager)
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
以下是您应该了解的 FragmentManager 的方法:
beginTransaction()- 返回FragmentTransaction的实例,用于添加、删除、替换以及对 fragment 的其他操作。getFragments()- 返回当前上下文中的Fragment列表。*仅支持库中的 FragmentManager 提供*findFragmentById()- 使用资源 id 查找特定的Fragment实例。findFragmentByTag()- 使用标签查找特定的Fragment实例。
现在,我们将获取 FragmentTransaction 对象。
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
FragmentTransaction 的重要方法:
add()- 将Fragment添加到指定的容器中。remove()- 删除一个特定的Fragment。replace()- 删除指定容器中的所有Fragment并添加一个新的Fragment。addToBackStack()- 在提交后将此事务添加到返回栈中,以便您可以撤销此事务。commit()- 安排此事务的提交,此事务的所有命令不会在提交后立即执行,而是在主线程准备就绪时执行。
注意: 在您提交事务之前,事务中的所有命令都不会被安排执行。
然后,我们将把 Fragment 添加到左侧的 FrameLayout 中。
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_left,animalListFragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
运行应用!

在手机上,您将得到与静态 Fragment 相同的结果。

在平板电脑上运行应用时,您会看到右侧有一片空白区域,因为我们还没有创建并添加详情 Fragment。
创建一个名为 AnimalDetailFragment 的新 Fragment。
public class AnimalDetailFragment extends Fragment {
}
然后,为这个 Fragment 创建视图。添加一个 ImageView 和一个 TextView。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview_animal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:src="@drawable/android3"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview_description"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="16dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:text="@string/lorem_ipsum"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageview_animal"/>
</RelativeLayout>
</ScrollView>
我使用 ScrollView 作为根 View,因为我不知道内容的长度,如果内容太长,用户可以向下滚动。并且我创建了 Lorem ipsum 字符串来模拟屏幕内容。

这是我设置给 ImageView src 的图片。
接下来,回到 AnimalDetailFragment 并重写 onCreateView() 方法,加载布局并将其作为方法结果返回。
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_animal_detail,null);
return view;
}
之后,回到 MainActivity,并将这个 Fragment 放入 Activity 内容视图的右侧 FrameLayout 中。
注意: 在放置 Fragment 之前,您必须检查容器 View 是否存在,因为当您有多个布局文件以支持多种设备时,有时某些布局中的某些 View 在另一个布局中并不存在。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
AnimalListFragment animalListFragment = new AnimalListFragment();
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_left,animalListFragment);
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)!=null){
AnimalDetailFragment animalDetailFragment = new AnimalDetailFragment();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_right,animalDetailFragment);
}
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
运行应用!

在手机上,没有任何变化。

在平板电脑上,您将在屏幕右侧看到 AnimalDetailFragment 的 View。看起来不太美观?现在试试更改动物列表的背景颜色!
将 AnimalListFragment 的布局复制到 layout-large 目录,然后编辑该副本。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#F4B700"
>
<ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@android:id/list"
/>
</LinearLayout>
再次运行应用!

看起来好一些了,但还不够,哈哈哈 :D 试着自己把它做得更漂亮吧!
然后,当用户点击动物列表项时,它应该高亮显示,以明确该项已被选中。再次进入平板电脑的动物列表布局,并为 ListView 添加 listSelector 属性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#F4B700"
>
<ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@android:id/list"
android:listSelector="@android:color/white"
/>
</LinearLayout>
再次运行应用!并尝试选择动物。

好了,现在我们的 UI 差不多完成了。
向 Fragment 传递数据
与 Activity 类似,您可以将 Bundle 对象传递给 Fragment。Bundle 是一个键值集合,主要用于在实例化期间将数据传递给 Activity/Fragment。对于 Fragment,您可以通过调用 setArguments() 方法来传递 Bundle 对象。
注意: Fragment 的 setArguments() 方法只能在 Fragment 被附加之前调用。参数将在 Fragment 状态之间保留。
在我们的应用中,我们将把 Animal 对象传递给 AnimalDetailFragment,然后在 View 创建后,我们会将数据添加到 UI 中。
重写 AnimalDetailFragment 的 onViewCreated() 方法,并通过调用 getArguments() 方法获取参数对象。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
}
请确保 Animal 类派生自 Serializable 标记接口,因为要将复杂类型添加到 bundle 中,您需要使其可序列化。
public class Animal implements Serializable {
...
}
然后回到 AnimalDetailFragment,并从参数中获取 Animal 对象。
注意: 要从 Bundle 中获取内容,您需要知道它们的键,并且应该在使用前检查该键是否存在。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
if(bundle.containsKey("animal")) {
Animal animal = (Animal)bundle.getSerializable("animal");
}
}
之后,如果 Animal 对象存在,我们将使用它来设置 View 的数据。
我将使用 Picasso 库来加载动物图片。在 Android Studio 中,您可以通过进入 app 目录下的 build.gradle 文件,并在 dependencies 列表中添加 "compile 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.3.4'" 来添加此库。(如果您使用 Eclipse 作为 IDE,您需要下载 jar 文件并将其放入 libs 目录,并确保 libs 目录出现在编译类路径中)
dependencies {
compile fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
compile 'com.android.support:appcompat-v7:20.0.0'
compile 'com.android.support:support-v4:20.0.0'
compile 'com.squareup.picasso:picasso:2.3.4'
}
当图片从互联网加载时,我们需要在清单文件中添加网络访问权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
回到 AnimalDetailFragment,尝试将图片设置到 ImageView 并设置描述文本。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
if(bundle.containsKey("animal")) {
Animal animal = (Animal)bundle.getSerializable("animal");
ImageView animalImageView = (ImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.imageview_animal);
TextView descriptionTextView = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.textview_description);
Picasso.with(getActivity()).load(animal.getImageUrl()).placeholder(R.drawable.android3).into(animalImageView);
descriptionTextView.setText(animal.getDescription());
}
}
然后转到 MainActivity,创建一个假的 Animal 对象,并将其传递给 AnimalDetailFragment。
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)!=null){
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.setName("Penguin");
animal.setImageUrl("http://www.emperor-penguin.com/penguin-chick.jpg");
animal.setDescription("Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin ");
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("animal",animal);
AnimalDetailFragment animalDetailFragment = new AnimalDetailFragment();
animalDetailFragment.setArguments(bundle);
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_right,animalDetailFragment);
}
在平板电脑上运行应用!

现在,我们可以向 Fragment 传递数据了。
在 Fragment 和 Activity 之间通信
在 Activity 中,如果您有 Fragment 的实例,您可以通过调用 Fragment 的方法直接与其通信。反之,您也可以从 Fragment 中获取 Activity 实例,并直接调用 Activity 的方法。然而,由于 Fragment 可以被附加到任何 Activity 上,它不应该依赖于某个特定的 Activity。因此,我们不会直接调用 Activity 的方法,而是会创建一个用于与 Activity 通信的接口(监听器),这样每个想要从 Fragment 接收消息的 Activity 都必须实现该接口。
定义接口
在我们的应用中,当用户点击动物列表项时,应用程序将显示该动物的详细信息。为了让我们的应用正常工作,我们需要创建一个接口来通知 Activity 用户已选择动物。
我们的接口很简单,我们只需要一个方法,用于通知 Activity 列表中的一个项目被选中了。现在就去 AnimalListFragment 创建这个接口吧!
public interface OnFragmentInteractionListener {
public void onAnimalSelected(Animal animal);
}
附加监听器
当 Fragment 附加到 Activity 上时,我们应该获取接口(监听器)对象并存储起来以备后用。重写 onAttach() 方法,并检查 Activity 是否派生自 OnFragmentInteractionListener,如果是,则将其赋值给一个变量。
注意: onAttach() 方法将在 Fragment 被附加到 Activity 时调用。
注意: 您可以使用 instanceof 关键字来测试类是否派生自某个类。
OnFragmentInteractionListener listener;
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
if(activity instanceof OnFragmentInteractionListener){
listener = (OnFragmentInteractionListener) activity;
}
}
现在,当您将 Fragment 放在 Activity 上时,如果该 Activity 派生自此接口,您将获得一个 OnFragmentInteractionListener 的实例。
当 Fragment 从 Activity 分离时,您也应该移除监听器,以防止意外调用监听器方法。重写 onDetach() 方法并将监听器设置为 null。
注意: onDetach() 方法将在 Fragment 从 Activity 分离时调用。
@Override
public void onDetach() {
super.onDetach();
listener = null;
}
调用监听器方法
当列表项被选中时,我们将通过调用 OnFragmentInteractionListener 的 onAnimalSelected() 方法来通知 Activity。
为 ListView 实现 OnItemClickListener。
@Override
public void onViewCreated(View view, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState);
ListView animalListView = (ListView) view.findViewById(android.R.id.list);
AnimalListAdapter animalListAdapter = new AnimalListAdapter(getActivity(),generateAnimalList());
animalListView.setAdapter(animalListAdapter);
animalListView.setOnItemClickListener(onAnimalListViewItemClickListener);
}
AdapterView.OnItemClickListener onAnimalListViewItemClickListener = new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int i, long l) {
}
};
当 onItemClick() 被调用时,调用 onAnimalSelected()。
AdapterView.OnItemClickListener onAnimalListViewItemClickListener = new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int i, long l) {
Animal animal = (Animal)adapterView.getItemAtPosition(i);
if(listener!=null)
listener.onAnimalSelected(animal);
}
};
注意: 在调用 onAnimalSelected() 方法之前,请确保监听器不为 null。
实现监听器
现在,我们将在 MainActivity 中实现 OnFragmentInteractionListener。转到 MainActivity,并在类签名中添加 "implements AnimalListFragment.OnFragmentInteractionListener"。
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements AnimalListFragment.OnFragmentInteractionListener {
...
}
IDE 会要求您实现该接口的方法,确认后您将得到 onAnimalSelected() 方法。(如果 IDE 没有要求实现,请您自己动手)
@Override
public void onAnimalSelected(Animal animal) {
}
接下来,当 onAnimalSelected() 被调用时,请求 FragmentManager 显示 AnimalDetailFragment。在手机上,我们将用 AnimalDetailFragment 替换 AnimalListFragment;但在平板电脑上,我们将用一个新的替换掉现有的右侧 Fragment。
@Override
public void onAnimalSelected(Animal animal) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
int containerViewId = R.id.framelayout_left;
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)!=null)
containerViewId = R.id.framelayout_right;
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("animal",animal);
AnimalDetailFragment animalDetailFragment = new AnimalDetailFragment();
animalDetailFragment.setArguments(bundle);
fragmentTransaction.replace(containerViewId,animalDetailFragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
运行应用并尝试选择动物!


您会发现,当您选择动物时,其详情会随之改变以匹配该动物!


在手机上,当您点击动物名称时,会显示动物的详细信息,但无法返回到动物列表 T^T
返回栈
当 Fragment 被替换时,默认情况下您无法返回到前一个 Fragment,但您可以通过 addToBackStack() 方法将 FragmentTransaction 添加到返回栈来实现这一点。
注意: 当用户按下返回按钮时,返回栈中的 FragmentTransaction 将反向执行。
我们将尝试仅在用户在手机上运行应用时,在提交 Fragment 替换操作之前,将 FragmentTransaction 添加到返回栈中。
@Override
public void onAnimalSelected(Animal animal) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
int containerViewId = R.id.framelayout_left;
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)!=null)
containerViewId = R.id.framelayout_right;
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("animal",animal);
AnimalDetailFragment animalDetailFragment = new AnimalDetailFragment();
animalDetailFragment.setArguments(bundle);
fragmentTransaction.replace(containerViewId,animalDetailFragment);
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)==null)
fragmentTransaction.addToBackStack(null);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
在手机上重新运行应用!

现在,您可以在详情页面按返回按钮回到动物列表了。
我们的应用差不多完成了,但还有一些您应该知道的事情。
Fragment 生命周期

**图片来自官方文档**
由于 Fragment 有其自身的生命周期,您应该知道在哪个状态下应该做什么。
以下是当您将 Fragment 附加到 Activity 时会调用的回调方法
onAttach()- 当Fragment附加到 Activity 时调用。onCreate()- 用于初始化Fragment时调用。onCreateView()- 为Fragment创建一个视图,视图创建后onViewCreated()方法会立即调用。onActivityCreated()- 通知Activity.onCreate()已完成。onViewStateRestored()- 告知从已保存的状态中恢复数据。onStart()- 在Fragment对用户可见后调用。onResume()- 在Fragment完全活跃时调用。
以下是当 Fragment 不再使用时会调用的回调方法
onPause()- 当Fragment不再与用户交互时调用。应在此状态下保存数据。onStop()- 当Fragment不再可见时调用。onDestroyView()- 当视图被销毁时调用。onDestroy()- 用于进行最终清理时调用。onDetach()- 当Fragment不再附加到Activity时调用。
警告
当您在手机上运行我们的应用时,您会发现如果您选择一个动物然后旋转设备,动物列表会覆盖在详情页面之上。

每次 Activity 重新创建时,每个 FragmentTransaction 都会被存储以便重新执行。例如,当设备方向改变时,Activity 会重新创建,然后屏幕旋转之前所做的每个 FragmentTransaction 都会自动重新执行。听起来不错,但问题是,如果您在 Activity 的 onCreate() 方法中添加 Fragment,您的 Fragment 将会覆盖在因 FragmentTransaction 重新执行而产生的 Fragment 之上。
您可以通过检查 Activity.onCreate() 的 Bundle 参数来解决这个问题。如果 Bundle 为 null,则意味着这是 onCreate() 第一次被调用,您可以执行 FragmentTransaction。但如果 Bundle 不为 null,则不要执行任何 FragmentTransaction 以避免该问题。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
/* Inflate View and restore saved state here*/
if(savedInstanceState!=null)
return;
/* FragmentTransaction here*/
}
回到我们的 MainActivity 并进行编辑。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
if(savedInstanceState!=null)
return;
AnimalListFragment animalListFragment = new AnimalListFragment();
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_left,animalListFragment);
if(findViewById(R.id.framelayout_right)!=null){
Animal animal = new Animal();
animal.setName("Penguin");
animal.setImageUrl("http://www.emperor-penguin.com/penguin-chick.jpg");
animal.setDescription("Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin Penguin ");
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putSerializable("animal",animal);
AnimalDetailFragment animalDetailFragment = new AnimalDetailFragment();
animalDetailFragment.setArguments(bundle);
fragmentTransaction.add(R.id.framelayout_right,animalDetailFragment);
}
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
运行应用并再试一次!

现在,问题解决了,哈哈哈。
进一步学习
比您今天学到的东西更重要的是您明天将要学什么。在本文中,我只谈论了 Fragment 的基本用法,但 Fragment 有许多有趣的实现,您应该学习它们。
选项卡 (Tabs) - 大多数选项卡的实现都使用 Fragment 作为内容。
ViewPager - 想要实现横向页面滚动吗?ViewPager 就是答案,它的工作方式类似于 ListView,但 ViewPager 中的项目是 Fragment。
导航抽屉 (Navigation Drawer) - 许多应用都有导航抽屉,例如 Facebook。将侧边菜单移至导航抽屉是个好主意。
希望您享受您的 Android 应用开发生活。
历史
- 2014年10月5日 初次发布
- 2014年10月6日 修正部分措辞
