Android 中语音和音频处理的初学者指南
4.73/5 (5投票s)
通过最简单的 Android 音频教程,学习文本转语音、语音识别、音频录制和音频播放
目录
1. 背景
2. 准备应用
3. 文本转语音
4. 语音识别
4.1 语音识别 Intent
4.2 使用 SpeechRecognizer 类
5. 使用 Audio Recorder
6. 音频信号处理
7. 结论
1. 背景
语音和音频是当今应用程序中最重要的方面。语音识别、文本转语音是一些让你的应用更具直观性的功能。此外,了解音频录制和播放也很有帮助!例如,你想通过简单的文本向用户呈现一个 Toast,想象一下也能将其读出来是多么直观?
或者想象一下将语音命令与应用的菜单选项关联起来是多么直观?我敢肯定你的用户会觉得更有趣,并且会喜欢具有这些创新功能的应用。
然而,我在 Google Play 上看到,很多应用都没有利用这些功能。同时,在互联网上搜索也找不到很多关于 Android 语音和音频处理的完整教程。因此,我决定写一篇非常基础的教程,帮助你理解 Android 中音频和语音处理的原理,并帮助你开始着手!
2. 准备应用
照例,我们将尽量保持 UI 简洁,专注于让功能正常工作。首先来看看 UI。

图 2.1 应用的最终 UI
所以,我们的 UI 主要有一个跨越整个表单的 EditText。它有一个带有三个选项的菜单:第一个用于语音识别,第二个用于语音合成或文本转语音,第三个用于音频录制。当我们选择“录制”菜单时,标题将变为“停止”。因此,用户现在可以选择同一个菜单来停止录制。
我们将首先在 Eclipse 中创建一个 Android 项目,最小 SDK 要求为 14,目标 SDK 要求为 14。我们将项目命名为 SpeechAndAudio,包名为 com.integratedideas。但我强烈建议你使用自己的包名。
这是我们的 res/layout/activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="VoiceRecognition Demo!" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edWords"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="0.38"
android:gravity="top"
android:ems="10" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
</LinearLayout>
注意 EditText 的 `android:gravity="top"` 用法。没有这一行,光标将位于控件的中间,输入也将从中间开始。
如图 2.1 所示,我们还必须有一个显示元素的菜单。我们已经通过我们关于“文章菜单、多个 Intent、资源管理”的 Android 教程 学会了如何处理菜单。
所以我们将编辑 res/menu/main.xml 并将其修改为如下所示的 main.xml。
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:context="com.integratedideas.speechandaudio.MainActivity" >
<item
android:id="@+id/menuVoiceRecog"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:showAsAction="never"
android:title="Speech Recognition"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/menuTTS"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:showAsAction="never"
android:title="Text to Speech"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/menuRecord"
android:orderInCategory="100"
android:showAsAction="never"
android:title="Record"/>
</menu>
我们有三个菜单项:menuVoiceRecog、menuTTS、menuRecord,分别用于语音识别、文本转语音和录制音频。让我们也在 MainActivity 中声明一个 edWords 实例,并使用 findViewById 将其初始化为 activity_main.xml 的 edWord。
我们还将更新我们的 MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
EditText edWords;
private void showToast(String message)
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edWords=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.edWords);
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data)
{
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
}
请注意,我们添加了 `onActivityResult` 方法,因为我们将使用 Intent。在准备好应用环境后,就可以直接着手进行语音合成或文本转语音部分了。
另外,请注意我们添加了一个简单的 `showToast()` 方法,它接受一个字符串并在 toast 中显示。Toast basically is a short lived dialog in Android which appears at the bottom of the form, remains visible for some period of time and then vanishes. It's a great way of letting user know the response of certain actions. (Toast basically is a short lived dialog in Android which appears at the bottom of the form, remains visible for some period of time and then vanishes. It's a great way of letting user know the response of certain actions.)
3. 文本转语音
文本转语音是一种系统可以为给定句子合成语音的概念。人工智能语音以自然的方式读出句子中的单词。
`android.speech.tts` 有一个 `TextToSpeech` 类,它能帮助我们实现 TTS。它需要与支持的 Locale 或你希望 TTS 引擎发音的语言进行初始化。一旦初始化,你就可以调用 `speak` 方法来朗读你传递给该方法的文本。
所以,让我们在类中声明一个 TextToSpeech 对象,并在 `onCreate` 方法中初始化其 `onClickListener`。
TextToSpeech tts;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edWords=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.edWords);
tts=new TextToSpeech(getApplicationContext(), new TextToSpeech.OnInitListener() {
@Override
public void onInit(int status)
{
tts.setLanguage(Locale.US);
}
});
}
我使用了 `Locale.US`,你可以查看其他的 Locale。只需删除 `Locale.US` 中的 `.US`,然后输入 `.`,它就会弹出其他 Locale。
tts 有两个变量可以改变语音的生成方式:**Pitch** 和 **SpeechRate**。Pitch 是生成语音的中心频率,SpeechRate 是说话的速度。两者的取值范围都是 (0-1.0f)。1.0f 的 SpeechRate 是最快的,0.0f 是最慢的。同样,高 pitch 意味着高频率,产生柔和的女声。
所以,现在让我们修改 `onOptionsItemSelected` 方法并集成语音合成。
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
// Handle action bar item clicks here. The action bar will
// automatically handle clicks on the Home/Up button, so long
// as you specify a parent activity in AndroidManifest.xml.
int id = item.getItemId();
switch(id)
{
case R.id.menuVoiceRecog:
break;
case R.id.menuTTS:
tts.setPitch(.8f);
tts.setSpeechRate(.1f);
tts.speak(edWords.getText().toString().trim(), TextToSpeech.QUEUE_FLUSH, null);
break;
case R.id.menuRecord:
break;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
如你所见,我们调用了 `speak` 方法,并将 `edWords` 中的文本作为第一个参数传递,引擎将根据指定的 pitch 和 rate 进行朗读。如果你不指定它们的值,TTS 将假定一个默认值。
现在构建并运行你的应用程序,并在你的设备上运行,就像我们 这里 学到的那样。我不会真的费心集成到模拟器中,因为归根结底,你会在设备上进行测试。
4. 语音识别
语音识别可以通过两种方式实现:第一种是使用 Intent,第二种是作为服务。基于 Intent 的方法是从菜单触发的。所以当你想要检测到语音时,你启动一个语音识别 Intent,它在你说话时保持活动状态,然后它会识别出你说的话。
4.1 语音识别 Intent
所以,让我们在 `onOptionSelection` 方法中准备 `menuVoiceRecog` 的 case。
case R.id.menuVoiceRecog:
Intent intent = new Intent(RecognizerIntent.ACTION_RECOGNIZE_SPEECH);
intent.putExtra(RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_LANGUAGE_MODEL,
RecognizerIntent.LANGUAGE_MODEL_FREE_FORM);
intent.putExtra(RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_PROMPT, "Voice recognition Demo...");
startActivityForResult(intent, REQUEST_CODE);
break;
每当我们处理 Intent 时,都需要一个 REQUEST_CODE,以便在 `onActivityResult` 中可以找出是哪个 Intent 的结果到达了。所以,让我们在类中声明一个整数变量。
static final int REQUEST_CODE=1;
所以,当你选择这个菜单选项时,会出现一个新的 Intent,它会提示你说话。在你停止说话后,它的结果将通过 `onActivityResult` 提供。
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data)
{
if (requestCode == REQUEST_CODE && resultCode == RESULT_OK)
{
// Populate the wordsList with the String values the recognition engine thought it heard
ArrayList<String> matches = data.getStringArrayListExtra(
RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_RESULTS);
showToast(matches.get(0));
edWords.setText(edWords.getText().toString().trim()+" "+matches.get(0));
}
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
}
Intent 返回的匹配结果是一个带有 EXTRA_RESULTS 标签的数组。其中 0 索引的元素是最佳匹配,第一个元素是第二佳匹配,依此类推。即使你说了几个词,整个识别结果也会作为第一个字符串提供。所以我们捕获这个字符串并将其追加到我们的 editText 中。

图 2.2:通过 Intent 进行语音识别的结果
你可以看到“all the citizens”被错误地识别为“i am in cities”。
在处理完 Intent(实际上用处不大)后,是时候创建一个持续监控语音并不断检测它的进程了。
4.2 使用 SpeechRecognizer 类
你可能已经注意到,当你触发语音识别过程时,它会启动一个 Intent,这有时非常烦人。为了在后台运行语音识别,你可以使用 SpeechRecognizer 类的对象,通过工厂方法 `SpeechRecognizer.createSpeechRecognizer(Context)` 进行初始化,并使用 `setRecognizationListener` 设置一个新的监听器。
此外,你还需要在一个处理与语音识别相关的事件的类中实现 `RecognitionListener`。
class listener implements RecognitionListener
{
public void onReadyForSpeech(Bundle params)
{
Log.d(TAG, "onReadyForSpeech");
}
public void onBeginningOfSpeech()
{
Log.d(TAG, "onBeginningOfSpeech");
}
public void onRmsChanged(float rmsdB)
{
Log.d(TAG, "onRmsChanged");
}
public void onBufferReceived(byte[] buffer)
{
Log.d(TAG, "onBufferReceived");
}
public void onEndOfSpeech()
{
Log.d(TAG, "onEndofSpeech");
}
public void onError(int error)
{
Log.d(TAG, "error " + error);
}
public void onResults(Bundle results)
{
String str = new String();
Log.d(TAG, "onResults " + results);
ArrayList data = results.getStringArrayList(SpeechRecognizer.RESULTS_RECOGNITION);
str = data.get(0).toString();
edWords.setText(edWords.getText().toString()+" "+str);
}
public void onPartialResults(Bundle partialResults)
{
Log.d(TAG, "onPartialResults");
}
public void onEvent(int eventType, Bundle params)
{
Log.d(TAG, "onEvent " + eventType);
}
}
我们关心的处理器是 `onResult`,我们在其中获取识别出的单词(或单词),并将其追加到 `edWords` 控件中。
SpeechRecognizer 对象 sr 可以按以下方式初始化。
sr= SpeechRecognizer.createSpeechRecognizer(this);
sr.setRecognitionListener(new listener());
最后,在菜单点击事件监听器中,可以使 sr 开始监听。
Intent intent = new Intent(RecognizerIntent.ACTION_RECOGNIZE_SPEECH);
intent.putExtra(RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_LANGUAGE_MODEL,RecognizerIntent.LANGUAGE_MODEL_FREE_FORM);
intent.putExtra(RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_CALLING_PACKAGE,"voice.recognition.test");
intent.putExtra(RecognizerIntent.EXTRA_MAX_RESULTS,5);
sr.startListening(intent);
这与 4.1 中讨论的唯一的显著区别是,我们在这里启动的是一个监听器,而不是启动一个 Activity。
引用注意
请记住,此解决方案从 Android 4.1 Jelly Beans 及更高版本开始不再完全可用。从那个版本开始,当你启动语音识别时,它会以一声哔声开始,并在大约 4 秒的暂停后自动分派对象。在这种情况下,你必须扩展 `RecognitionService`,检查是否存在静音期。在错误处理程序中,将声音静音半秒并重新启动服务。这个解决方法不适合初学者教程,超出了本文的范围。
5. 使用 Audio Recorder
你需要授予应用录制音频的权限。你还需要访问写入外部文件夹的权限,以便能够存储录制的音频。
所以,编辑你的 manifest 文件并添加以下行:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO"/>
为了能够将音频文件存储在 SD 卡的某个文件夹中,我们将首先在 SD 卡的 Music 文件夹中创建一个文件夹。我们已经知道 如何设置外部文件夹中的应用目录。
//////////////// Preparing Directory////////
try
{
Log.d("Starting", "Checking up directory");
File mediaStorageDir = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_MUSIC), "SpeechAndAudio");
// This location works best if you want the created images to be shared
// between applications and persist after your app has been uninstalled.
// Create the storage directory if it does not exist
if (! mediaStorageDir.exists())
{
if (! mediaStorageDir.mkdir())
{
Log.e("Directory Creation Failed",mediaStorageDir.toString());
}
else
{
Log.i("Directory Creation","Success");
}
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Log.e("Directory Creation",ex.getMessage());
}
filePath=Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_MUSIC).getPath()+"/"+"SpeechAndAudio/";
/////////////////////////////////////////////
在设置好存储文件的目录后,我们将直接着手实现录制。这是我们的工作流程:
1) 点击“菜单-录制”后,菜单标题应更改为“停止”。
2) 在录制时,初始化一个 MediaRecorder 对象以在文件中录制音频流。我们将从当前时间戳生成文件名。
3) 录制完成后,使用 MediaPlayer 对象播放刚刚录制的文件。
这是 `onOptionItemSelected` 方法中 `menuRecord` 的代码。
case R.id.menuRecord:
if(item.getTitle().equals("Record"))
{// Record
fileName = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddhhmm'.3gp'").format(new Date());
fname=filePath+fileName;
item.setTitle("Stop");
recorder = new MediaRecorder();
recorder.setAudioSource(MediaRecorder.AudioSource.MIC);
recorder.setOutputFormat(MediaRecorder.OutputFormat.THREE_GPP);
recorder.setOutputFile(fname);
recorder.setAudioEncoder(MediaRecorder.AudioEncoder.AMR_NB);
try {
recorder.prepare();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("In Recording", "prepare() failed");
}
recorder.start();
}
else
{
item.setTitle("Record");
recorder.stop();
recorder.release();
recorder = null;
//Stop
////////////// Now Play/////////////
player = new MediaPlayer();
try {
player.setDataSource(fname);
player.prepare();
player.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e("Player Exception", "prepare() failed");
}
}
break;
所以现在你所有录制的音频文件都将存储在 sdcard/Music/SpeechAndAudio 文件夹中,你也可以离线播放!
6. 音频信号处理
处理语音和音频是 Android 中一个重要的部分。有几种数字信号处理算法,从简单的音高检测到改变信号的基频。Google 最近发布了一个基于 NDK 的音频信号处理库,名为 patchfield。但是,还有一个优秀的音频信号处理库,它纯 Java 编写,名为 TarsosDsp。
你可以进入 `/latest` 文件夹并下载 TarsosDSP-Android-latest-bin.jar。将这个库复制到你的项目 `lib` 文件夹中。清理并构建你的项目,以便开始在 Android 中进行音频信号处理。
我展示了一个简单但非常有效的音高检测算法。首先,我们添加一个名为 menuAudioProcessing 的菜单项。在 `onOptionsItemSelected` 方法中,我们为这个菜单选项添加一个 case。
case R.id.menuAudioProcess:
AudioDispatcher dispatcher = AudioDispatcherFactory.fromDefaultMicrophone(22050,1024,0);
PitchDetectionHandler pdh = new PitchDetectionHandler() {
@Override
public void handlePitch(PitchDetectionResult result,AudioEvent e)
{
final float pitchInHz = result.getPitch();
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run()
{
TextView text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvMessage);
text.setText("" + pitchInHz);
}
});
}
};
AudioProcessor p = new PitchProcessor(PitchEstimationAlgorithm.FFT_YIN, 22050, 1024, pdh);
dispatcher.addAudioProcessor(p);
new Thread(dispatcher,"Audio Dispatcher").start();
一旦你选择这个选项,你需要说话,你会在文本视图中看到非常高的音高值,当你停止时,音高值会变成负数,如下图所示。
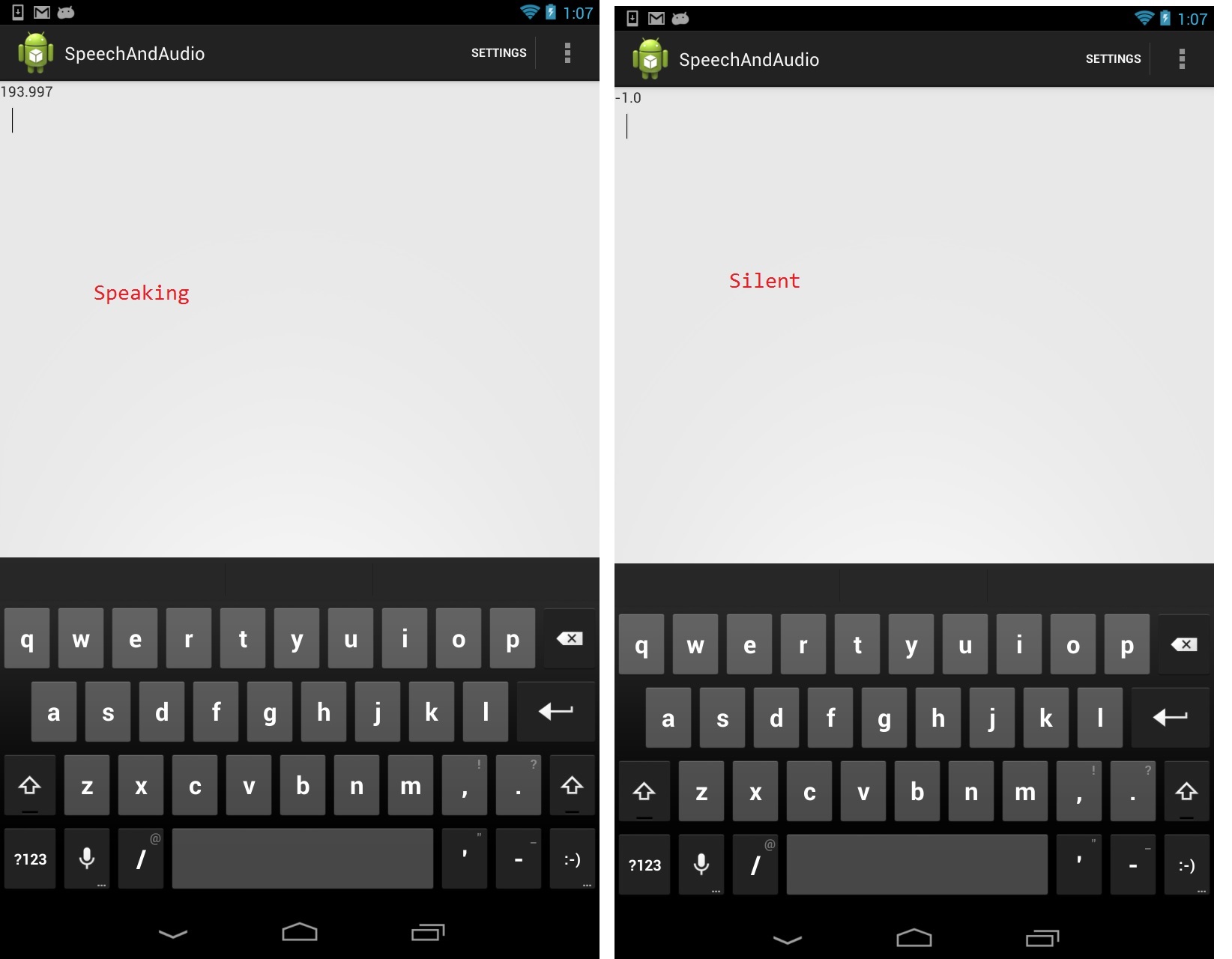
图 8.1:使用 TarsosDSP 在 Android 中进行音频信号处理的音高检测
以这个例子为起点,你可以尝试其他的信号处理功能。你只需要做的就是向 `dispatcher` 对象添加一个 `handler`,其中 `handler` 是不同的音频处理算法。使用 TarsosDSP 中任何实现 AudioProcessor 的类的一般方法是,首先从你的音频数据创建一个 AudioEvent,然后调用 AudioProcessor 的 `process` 方法。事件处理完毕后,你可以检查 AudioEvent 缓冲区的内容,或者在某些情况下,监听特定的事件/回调,例如 PercussionOnsetDetector 的 OnsetHandler 及其 handleOnset() 方法。
7. 结论
音频信号处理和音频处理是 Android 中多媒体相关应用的一个非常重要的方面。尽管 Android 提供了简单而有效的处理方法,但互联网上关于如何有效地在 Android 中执行音频和声音相关工作的教程并不多。
我想写一篇关于 Android 语音和音频信号处理的初学者教程,可以作为音频处理的起点。你可以通过集成文本转语音和音高检测来构建智能应用程序。语音识别可以由音高检测触发。所以你可以用音频做一些有趣的事情。希望本教程能鼓励你在你的应用中更多地使用音频功能。
