Web API 想法 1/3 - 数据流式传输
4.91/5 (202投票s)
与 ASP.NET Web API 相关的项目。通过关于数据流、使用 HTTPS 和扩展 Web API 文档的文章,涉及该技术的大部分方面。

背景
需求和依赖项
- 该解决方案最好使用 VS 2012 (SP4) Ultimate 及更高版本查看。但也可以使用 VS Professional 或 Express 2012 及更高版本查看每个单独的项目。
- .NET Framework 4.5.1 及更高版本
- 大量 Nuget 包。请参阅每个项目的 Nuget **packages.config** 文件
文章将涵盖的内容
- 与 Asp.NET Web API 技术相关
- ActionFilter
- AuthorizationFilter
- DelegateHandler
- 不同的 Web API 路由属性
- MediaTypeFormatter
- OWIN
- 自托管
- Web API 文档及其扩展
- 与 .NET Framework 及其他相关
- Async/Await
- .NET 反射
- 序列化
- ASP.NET Web API/MVC 错误处理
- IIS、HTTPS 和证书
- 设计原则和技术
引言

自 ASP.NET Web API 添加到 .NET Framework 以来已有多年。ASP.NET Web API 构建在 HTTP 协议之上,该协议将 RESTful 服务和数据暴露给外部系统。目标是利用 HTTP 技术将服务扩展到各种平台,而 HTTP 技术得到了许多最终用户应用程序、浏览器、移动设备和其他服务的支持。ASP.NET Web API 是一种请求-响应消息交换模式,其中客户端可以从服务器请求某些信息,服务器将请求响应给客户端。响应可以同步或异步进行。当我们想到 Web API 时,通常会想到几件事。我个人会指出这三个基本要点,而忽略 Web API 的实现。
- 服务及其方法的目的。
- 每个方法的输入(即请求)
- 每个方法的输出(即响应)。
根据约定,ASP.NET Web API 允许您定义与 HTTP 方法(动词)具有匹配语义的方法。例如,如果我们有一个名为 `GetPysicians()` 的方法,那么它与 HTTP 方法的匹配名称将是 `GET`。简而言之,下面的图表显示了每个方法与 HTTP 方法(动词)的匹配情况。

但这种方法可能不适用于不同场景。例如,您可能希望在单个 API 控制器类中定义多个 `GET` 或 `POST` 方法。在这种情况下,框架允许您定义一个动作级路由,将动作包含在 URI 请求中。以下代码显示了如何配置这一点。
public static void Register(HttpConfiguration config)
{
// Web API configuration and services
// Web API routes
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
config.Routes.MapHttpRoute(name: "PhysicianApi",
routeTemplate: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
defaults: new { id = RouteParameter.Optional });
}
但这仍然可能不足以满足其他场景。假设您想要一个方法来从集中式存储库中删除文件,并且您想使用同一方法来获取文件。在这种情况下,Web API 框架允许您使用 `Get` 和 `Delete` HTTP 方法属性来装饰该动作。请参见下图。

请注意,`RemoveFile` 方法可以通过 Delete (`HttpDelete`) 或 Get (`HttpGet`) 动词调用。HTTP 方法属性也有助于为服务方法定义合适的名称。
框架提供的另一个功能是能够提供属性路由模板。这类似于 ASP.NET MVC 路由,不同之处在于它依赖于 HTTP 方法(动词)而不是动作的 URI。这允许您在 Web API 服务下定义几种类型的动作。例如,您可以定义一个带参数的 URI 服务方法。因此,当对服务方法发出请求时,您可以将参数作为请求 URI 的一部分。以下示例代码显示了 `GetPhysicianBySpeciality` 方法上的 Web API 属性路由。
[Route("physician/{speciality}/{physicianID}")]
public PhysicianBase GetPhysicianBySpeciality(string speciality, int physicianID)
{
// Todo : Process the request
}
这样,客户端就可以发送类似 https:///physician/eyecare/1 的请求。有各种类型的路由属性有助于装饰 Web API 控制器及其方法。它们是
| ActionName | 允许您定义动作名称路由 |
| HTTP 方法(HttpGet、HttpPost、AcceptVerbs ...) | 允许您定义 HTTP 方法(动词) |
| NonAction | 阻止调用该动作 |
| 路线 | 允许您定义带/不带参数的模板 |
| RoutePrefix | 允许您定义控制器前缀名称 |
ASP.NET Web API 还包含 `HttpClient`、`HttpRequestMessage` 和 `HttpResponseMessage` 等有用的库和类。请参阅参考部分以获取 Web API 引用的列表。这对于介绍来说已经足够了。在下一节中,我将解释文章的一个主要领域。
数据流
通过互联网执行的频繁操作之一是数据流。ASP.NET Web API 能够处理来自/到服务器/客户端的大量流数据。流数据可以是目录中的文件,也可以是存储在数据库中的二进制数据。在本文中,有两个基本方法,即 `Download` 和 `Upload`,用于完成数据流。下载负责从服务器拉取流数据,而上传负责将流数据保存到服务器。
注意:本文档说明了位于特定(可配置)目录的资源的数据流,并通过 Web API 服务进行流式传输。
参与的项目
WebAPIDataStreamingWebAPIClientPOCOLibrary
在解释代码部分之前,需要在 IIS (7.5) 和 Web API 服务 web.config 文件中进行某些配置。
- 确保 Downloads/Uploads 目录/文件已授予用户(IIS_IUSRS)必要的权限(读取/写入)。
- 确保有足够的内存(RAM)和硬盘空间来处理大文件。
- 对于较大的文件数据,
- 确保在 _web.config_ 文件中配置了 `maxRequestLength` 以及合理的 `executionTimeout`。该值可能取决于允许流式传输的大小。允许的最大文件大小为 2GB。

- 确保在 web.config 文件的 _requestFiltering_ 配置部分下配置了 `maxAllowedContentLength`。此设置的默认值约为 30MB,最大值为 4GB。

注意:为了使用 `maxAllowedContentLength` 配置,需要在 IIS 上启用请求筛选功能。方法如下:- 转到“控制面板”
- 在“程序和功能”菜单的左侧选择“打开或关闭 Windows 功能”
- 选择“Internet Information Services” > “World Wide Web Services” > “Security”
- 启用请求筛选
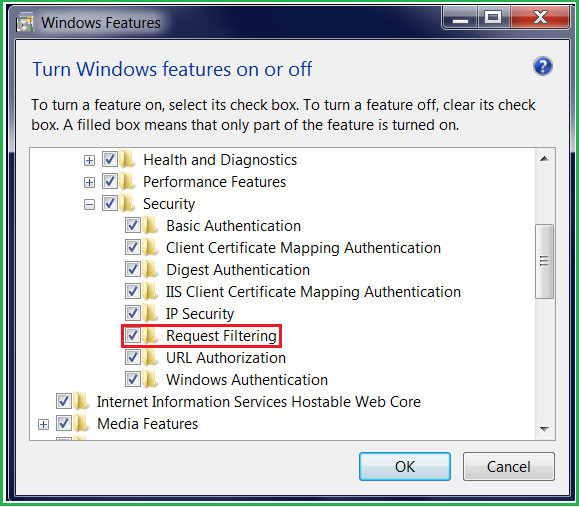
请求筛选的详细信息可以在参考部分找到
- 确保在 _web.config_ 文件中配置了 `maxRequestLength` 以及合理的 `executionTimeout`。该值可能取决于允许流式传输的大小。允许的最大文件大小为 2GB。
/// <summary>
/// File streaming API
/// </summary>
[RoutePrefix("filestreaming")]
[RequestModelValidator]
public class StreamFilesController : ApiController
{
/// <summary>
/// Get File meta data
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">FileName value</param>
/// <returns>FileMeta data response.</returns>
[Route("getfilemetadata")]
public HttpResponseMessage GetFileMetaData(string fileName)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
/// <summary>
/// Search file and return its meta data in all download directories
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">FileName value</param>
/// <returns>List of file meta datas response</returns>
[HttpGet]
[Route("searchfileindownloaddirectory")]
public HttpResponseMessage SearchFileInDownloadDirectory(string fileName)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
/// <summary>
/// Asynchronous Download file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">FileName value</param>
/// <returns>Tasked File stream response</returns>
[Route("downloadasync")]
[HttpGet]
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> DownloadFileAsync(string fileName)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
/// <summary>
/// Download file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">FileName value</param>
/// <returns>File stream response</returns>
[Route("download")]
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage DownloadFile(string fileName)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
/// <summary>
/// Upload file(s)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the server</param>
/// <returns>Message response</returns>
[Route("upload")]
[HttpPost]
public HttpResponseMessage UploadFile(bool overWrite)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
/// <summary>
/// Asynchronous Upload file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the server</param>
/// <returns>Tasked Message response</returns>
[Route("uploadasync")]
[HttpPost]
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> UploadFileAsync(bool overWrite)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
}
`Download` 服务方法首先检查请求的文件名是否存在于目标文件路径中。如果文件未找到,它将返回一个错误响应对象,提示“文件未找到”。如果成功,它会将内容读取为字节,并以 `application/octet-stream` MIME 内容类型附加到响应对象。
/// <summary>
/// Download file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="fileName">FileName value<param>
/// <returns>File stream response<returns>
[Route("download")]
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage DownloadFile(string fileName)
{
HttpResponseMessage response = Request.CreateResponse();
FileMetaData metaData = new FileMetaData();
try
{
string filePath = Path.Combine(this.GetDownloadPath(), @"\", fileName);
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(filePath);
if (!fileInfo.Exists)
{
metaData.FileResponseMessage.IsExists = false;
metaData.FileResponseMessage.Content = string.Format("{0} file is not found !", fileName);
response = Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, metaData, new MediaTypeHeaderValue("text/json"));
}
else
{
response.Headers.AcceptRanges.Add("bytes");
response.StatusCode = HttpStatusCode.OK;
response.Content = new StreamContent(fileInfo.ReadStream());
response.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition = new ContentDispositionHeaderValue("attachment");
response.Content.Headers.ContentDisposition.FileName = fileName;
response.Content.Headers.ContentType = new MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/octet-stream");
response.Content.Headers.ContentLength = fileInfo.Length;
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Log exception and return gracefully
metaData = new FileMetaData();
metaData.FileResponseMessage.Content = ProcessException(exception);
response = Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError, metaData, new MediaTypeHeaderValue("text/json"));
}
return response;
}
`Upload` 服务方法基于 `multipart/form-data` MIME 内容类型工作。首先,它检查 HTTP 请求内容类型是否为 multipart 类型。如果成功,它会将内容长度与允许上传的最大文件大小进行比较。如果成功,它将开始将请求内容上传到目标位置。操作完成后,它会向用户发送适当的响应消息。执行上传的代码片段如下所示。
/// <summary>
/// Upload file(s)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the server.</param>
/// <returns>Message response</returns>
[Route("upload")]
[HttpPost]
public HttpResponseMessage UploadFile(bool overWrite)
{
HttpResponseMessage response = Request.CreateResponse();
List<FileResponseMessage> fileResponseMessages = new List<FileResponseMessage>();
FileResponseMessage fileResponseMessage = new FileResponseMessage { IsExists = false };
try
{
if (!Request.Content.IsMimeMultipartContent())
{
fileResponseMessage.Content = "Upload data request is not valid !";
fileResponseMessages.Add(fileResponseMessage);
response = Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.UnsupportedMediaType, fileResponseMessages, new MediaTypeHeaderValue("text/json"));
}
else
{
response = ProcessUploadRequest(overWrite);
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Log exception and return gracefully
fileResponseMessage = new FileResponseMessage { IsExists = false };
fileResponseMessage.Content = ProcessException(exception);
fileResponseMessages.Add(fileResponseMessage);
response = Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError, fileResponseMessages, new MediaTypeHeaderValue("text/json"));
}
return response;
}
/// <summary>
/// Asynchronous Upload file
/// </summary>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the server.<param>
/// <returns>Tasked Message response</returns>
[Route("uploadasync")]
[HttpPost]
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> UploadFileAsync(bool overWrite)
{
return await new TaskFactory().StartNew(
() =>
{
return UploadFile(overWrite);
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Process upload request in the server
/// </summary>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the server.</param>
/// </returns>List of message object</returns>
private HttpResponseMessage ProcessUploadRequest(bool overWrite)
{
// .........................................
// Full code available in the source control
// .........................................
}
调用下载和上传文件方法的客户端应用程序是一个控制台应用程序。该应用程序通过 `HttpClient` 和相关类使用文件流 Web API 服务。基本上,下载文件代码会创建一个带有正确文件名的下载 HTTP 请求对象,并将请求发送到服务器。
/// <summary>
/// Download file
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Awaitable Task object</returns>
private static async Task DownloadFile()
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine("Please specify file name with extension and Press Enter :- ");
string fileName = Console.ReadLine();
string localDownloadPath = string.Concat(@"c:\", fileName); // the path can be configurable
bool overWrite = true;
string actionURL = string.Concat("downloadasync?fileName=", fileName);
try
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Start downloading @ {0}, {1} time ",
DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString(),
DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString()));
using (HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient())
{
httpClient.BaseAddress = baseStreamingURL;
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, actionURL);
await httpClient.SendAsync(request, HttpCompletionOption.ResponseHeadersRead).
ContinueWith((response)
=>
{
Console.WriteLine();
try
{
ProcessDownloadResponse(localDownloadPath, overWrite, response);
}
catch (AggregateException aggregateException)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Exception : ", aggregateException));
}
});
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Process download response object
/// </summary>
/// <param name="localDownloadFilePath">Local download file path</param>
/// <param name="overWrite">An indicator to overwrite a file if it exist in the client.</param>
/// <param name="response">Awaitable HttpResponseMessage task value</param>
private static void ProcessDownloadResponse(string localDownloadFilePath, bool overWrite,
Task<HttpResponseMessage> response)
{
if (response.Result.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
response.Result.Content.DownloadFile(localDownloadFilePath, overWrite).
ContinueWith((downloadmessage)
=>
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine(downloadmessage.TryResult());
});
}
else
{
ProcessFailResponse(response);
}
}
请注意上面的代码。`HttpClient` 对象发送请求并等待响应,以便仅发送响应头(`HttpCompletionOption.ResponseHeadersRead`),而不是文件的整个响应内容。一旦读取了响应头,它将对内容执行必要的验证,如果成功,将执行实际的文件下载方法。
这是调用上传文件流 Web API 服务方法的代码。与下载方法类似,它会创建一个带有 multipart 表单数据内容类型的请求对象,并将请求发送到服务器。内容经过验证并发送到服务器以进行进一步处理。
/// <summary>
/// Upload file
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Awaitable task object</returns>
private static async Task UploadFile()
{
try
{
string uploadRequestURI = "uploadasync?overWrite=true";
MultipartFormDataContent formDataContent = new MultipartFormDataContent();
// Validate the file and add to MultipartFormDataContent object
formDataContent.AddUploadFile(@"c:\nophoto.png");
formDataContent.AddUploadFile(@"c:\ReadMe.txt");
if (!formDataContent.HasContent()) // No files found to be uploaded
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write(formDataContent.GetUploadFileErrorMesage());
return;
}
else
{
string uploadErrorMessage = formDataContent.GetUploadFileErrorMesage();
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(uploadErrorMessage)) // Some files couldn't be found
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.Write(uploadErrorMessage);
}
HttpRequestMessage request = new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Post, uploadRequestURI);
request.Content = formDataContent;
using (HttpClient httpClient = new HttpClient())
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Start uploading @ {0}, {1} time ",
DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString(),
DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString()));
httpClient.BaseAddress = baseStreamingURL;
await httpClient.SendAsync(request).
ContinueWith((response)
=>
{
try
{
ProcessUploadResponse(response);
}
catch (AggregateException aggregateException)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Exception : ", aggregateException));
}
});
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Process download response object
/// </summary>
/// <param name="response">Awaitable HttpResponseMessage task value</param>
private static void ProcessUploadResponse(Task<HttpResponseMessage> response)
{
if (response.Result.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
string uploadMessage = string.Format("\nUpload completed @ {0}, {1} time ",
DateTime.Now.ToLongDateString(),
DateTime.Now.ToLongTimeString());
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Green;
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}\nUpload Message : \n{1}", uploadMessage,
JsonConvert.SerializeObject(response.Result.Content.ReadAsAsync<List<FileResponseMessage>>().TryResult(), Formatting.Indented)));
}
else
{
ProcessFailResponse(response);
}
}
数据流项目还包含未在本文中明确解释的扩展类和方法。下载源代码并进行探索。
下一步
下一节将介绍 使用 HTTPS
参考文献
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Representational_state_transfer
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Request-response
- http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616
- http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh849329(v=vs.108).aspx
- http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits
- http://www.ASP.NET/web-api/
- http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb727008.aspx
历史和 GitHub 版本
- WebAPI Thoughts @ GitHub
- 更新于 2014 年 11 月 4 日
- 更新于 2014 年 11 月 18 日
- 更新于 2014 年 11 月 20 日
- 2015 年 10 月 18 日更新 - 文章代码格式问题
