ASP.NET Web API 中的 HTTP 304 Not Modified
5.00/5 (2投票s)
一个示例项目,演示如何在 Web API 中“手动”控制 HTTP 缓存。
引言
上一篇文章: HTTP 304 Not Modified - An Introduction
在我上一篇文章中,我们讨论了由HTTP 304 Not Modified状态码提供的基本 HTTP 缓存机制以及几个相关的标头。该机制可以概括为一句话:
引用如果某物未更改,则不发送。
本文将展示一个在 ASP.NET Web API 中实现的示例项目。
背景
这个示例项目是我几个月前创建的一个教学材料,旨在向人们展示如何创建支持 HTTP 304 的 Web API Controller 以及如何使用 jQuery 来消费它。该项目中的场景是让用户查看和编辑公司员工数据。用户在下拉框中选择一名员工后,从服务器查询或缓存到浏览器中的数据将显示在左侧,关键响应标头将显示在右侧,如图 1 所示。
图 1
内容引用自 https://www.valvesoftware.com/company/people.html
在接下来的章节中,我们将从后端到前端,从幕后的设计模式到创建 API Controller。最后一部分,我们将转向 jQuery 部分作为结尾。
观察者模式
观察者设计模式在此示例项目中起着至关重要的作用。其基本思想是观察实例的变化并接收通知。图 2 是显示其在此项目中如何使用的简化 UML 图。
图 2
被观察的主体是Employee类的实例。这是用户将查看和编辑的内容。Employee实现了INotifyPropertyChanged接口,因此EmployeeChangeObserver可以通过订阅PropertyChanged事件来观察它。一旦事件被调用,EmployeeChangeObserver会立即使用时间戳和Guid标记它,并更新其LastChange属性。正如您在Change类中的属性名称中看到的,时间戳将用作**Last-Modified**标头值,Guid将用作**ETag**标头值,用于未来的 HTTP 请求。
以下是Employee类(部分成员已省略)。每当属性更改时,都会调用PropertyChanged事件。
public class Employee : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
#region Fields
private Guid id;
private string firstName;
private string lastName;
// Other fields abbreviated.
#endregion
#region Properties
public Guid ID
{
get { return this.id; }
set { this.ChangeProperty(ref this.id, value, "ID"); }
}
public string FirstName
{
get { return this.firstName; }
set { this.ChangeProperty(ref this.firstName, value, "FirstName"); }
}
public string LastName
{
get { return this.lastName; }
set { this.ChangeProperty(ref this.lastName, value, "LastName"); }
}
// Other properties abbreviated.
#endregion
#region Event
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
#endregion
#region Event Raiser
protected virtual void OnPropertyChanged(PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (this.PropertyChanged != null)
this.PropertyChanged(this, e);
}
#endregion
#region Others
protected void ChangeProperty<T>(ref T currentValue, T newValue,
string propertyName)
{
if (!EqualityComparer<T>.Default.Equals(currentValue, newValue))
{
currentValue = newValue;
this.OnPropertyChanged(new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
#endregion
}
接下来,我们创建一个通用的ChangeObserver<TItem>类来观察任何实现INotifyPropertyChanged接口的实例。每当调用PropertyChanged事件时,Change属性将使用DateTime.UtcNow和Guid.NewGuid()值进行更新。
public abstract class ChangeObserver<TItem>
where TItem : class, INotifyPropertyChanged
{
#region Field
private readonly TItem item;
private Change lastChange;
#endregion
#region Property
public TItem Item
{
get { return this.item; }
}
public Change LastChange
{
get { return this.lastChange; }
}
#endregion
#region Constructure
// Default constructor abbreviated.
public ChangeObserver(TItem item, Change lastChange)
{
if (item == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("item");
this.item = item;
this.item.PropertyChanged += this.item_PropertyChanged;
this.lastChange = lastChange;
}
#endregion
#region Event Handler
private void item_PropertyChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
// Update the latest change information whenever the change occurs.
Interlocked.Exchange(ref this.lastChange, new Change(DateTime.UtcNow, Guid.NewGuid()));
}
#endregion
}
第三,我们创建了一个EmployeeChangeObserver类,它派生自ChangeObserver<TItem>,专门用于观察Employee实例。
public class EmployeeChangeObserver : ChangeObserver<Employee>
{
public EmployeeChangeObserver(Employee item)
: base(item)
{
}
public EmployeeChangeObserver(Employee item, Change lastModified)
: base(item, lastModified)
{
}
}
以上是我们应用观察者设计模式所需的一切。下一节,我们将继续 Web API 部分。
在 Web API 中的实现
我们的 Web API 定义在ValuesController类中。它提供了几个方法,能够选择、创建和更新Employee类的实例。ValuesControllerExtensions类定义了一组静态方法,允许ValuesController用几行代码完成 HTTP 缓存。
我们先来看看ValuesControllerExtensions。扩展方法EndIfNotModified(HttpRequestMessage, DateTime)决定是否需要进一步处理请求。我们还有一个CreateResponse<T>(HttpRequestMessage, HttpStatusCode, T, DateTime)方法,它会添加 HTTP 缓存所需的所有响应标头。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Headers;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace HttpCaching.Controllers
{
public static class ValuesControllerExtensions
{
// Some methods abbreviated.
public static void EndIfNotModified(this HttpRequestMessage request, DateTime lastModified)
{
if (request == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("request");
var ifModifiedSince = request.Headers.IfModifiedSince;
if (ifModifiedSince != null && ifModifiedSince.Value.DateTime >= lastModified)
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotModified);
}
public static HttpResponseMessage CreateResponse<T>(this HttpRequestMessage request,
HttpStatusCode statusCode, T value, DateTime lastModified, TimeSpan expires)
{
if (request == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("request");
var response = request.CreateResponse<T>(statusCode, value);
response.Headers.CacheControl = new CacheControlHeaderValue();
response.Content.Headers.LastModified = new DateTimeOffset(lastModified);
response.Content.Headers.Expires = new DateTimeOffset(DateTime.UtcNow
+ expires.Duration());
return response;
}
}
}
这两个扩展方法组合背后的逻辑可以概括为以下图表,这在上一篇文章中您可能已经很熟悉了。

图 3
有了这些扩展方法,在ValuesController下构建一个支持 HTTP 缓存的方法就容易多了。正如您在Select(Guid)方法中看到的:
using HttpCaching.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Concurrent;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Helpers;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace HttpCaching.Controllers
{
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
#region Fields
public static readonly ConcurrentDictionary<Guid, EmployeeChangeObserver> Employees;
public static readonly TimeSpan DefaultExpires;
#endregion
#region Constructor
static ValuesController()
{
// Read JSON data from text file as the default content of the dictionary.
var fileInfo = new FileInfo(HttpContext.Current.Server.MapPath("~/App_Data/Valve.txt"));
var lastChange = new Change(fileInfo.LastWriteTimeUtc, Guid.NewGuid());
var employees = Json.Decode<Employee[]>(File.ReadAllText(fileInfo.FullName)).
ToDictionary(c => c.ID, c => new EmployeeChangeObserver(c, lastChange));
Employees = new ConcurrentDictionary<Guid, EmployeeChangeObserver>(employees);
// The default expiration time in clients' cache is 1 minute.
DefaultExpires = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1);
}
#endregion
#region Methods
[HttpGet]
public HttpResponseMessage Select(Guid id)
{
var employee = Employees.EndIfNotFound(id);
var lastChange = employee.LastChange;
// If change information is not available, will end here.
if (lastChange == null)
return base.Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, employee.Item);
// If nothing changed, will raise an HttpResponseException in status 304.
base.Request.EndIfNotModified(lastChange.LastModifiedUtc);
// Give the latest change information.
return base.Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, employee.Item,
lastChange.LastModifiedUtc, DefaultExpires);
}
// Other methods abbreviated.
#endregion
}
}
这就是我们在此需要EmployeeChangeObserver.LastChange属性的地方。得益于观察者设计模式,每当调用Select(Guid)方法时,它总是指示所选的Employee对象是否在过去发生过更改。它还提供了我们为EndIfNotModified(HttpRequestMessage, DateTime)和CreateResponse<T>(HttpRequestMessage, HttpStatusCode, T, DateTime)方法所需的参数。
在 jQuery 中调用 Web API
现在我们可以使用 jQuery 来消费 Web API 了。在图 1中,当选择框“Employee”发生变化时,会触发带有选中 ID 的selectEmployee(id)函数。它的任务是从服务器或缓存中检索员工信息,并用它填充表单。
function selectEmployee(id) {
$.ajax("/../api/values/select", {
data: { ID: id },
type: "GET",
ifModified: true, // Remember to turn this option on.
statusCode: {
304: function() {
$("#statusCode").val(304);
$("#cacheMessage").text("The content is rendered from cache.");
},
200: function () {
$("#statusCode").val(200);
$("#cacheMessage").text("The content is rendered from server.");
}
},
success: function (data, textStatus, jqXHR) {
// Parameter data is null if status is 304.
if (jqXHR.status == 304) {
// Render data from cache.
data = jQuery.data(mainForm, id);
} else {
// Save data into cache.
jQuery.data(mainForm, data["ID"], data);
}
$("#firstName").val(data["FirstName"]);
$("#lastName").val(data["LastName"]);
$("#alias").val(data["Alias"]);
$("#steamId").val(data["SteamID"]);
$("#sex").val(data["Sex"]);
$("#description").val(data["Description"]);
// Show response headers.
$("#lastModified").val(jqXHR.getResponseHeader("Last-Modified"));
$("#expires").val(jqXHR.getResponseHeader("Expires"));
$("#eTag").val(jqXHR.getResponseHeader("ETag"));
}
});
}
// Other functions abbreviated.
在回调函数success中,我们将从服务器接收到的数据存储到缓存中,并使用data()函数从缓存中调用数据。请注意,我们在上一篇文章中讨论过,HTTP 状态 304 的消息正文是空的。因此,参数data是null,您不应该访问它。
那么它是如何工作的呢?
让我们看看该项目在浏览器中是如何实际工作的。我们在 Chrome 中浏览/Home/Index,按 F12 打开开发者工具,然后返回浏览器并选择员工Gabe Newell。
图 3
请记住,这是我们第一次选择Gabe Newell(如图 3 所示)。请求和响应标头如图 4 所示。
图 4
接下来,让我们尝试选择另一位员工,然后再次选择Gabe Newell,或者点击“刷新”按钮,看看开发者工具中发生了什么。
图 5
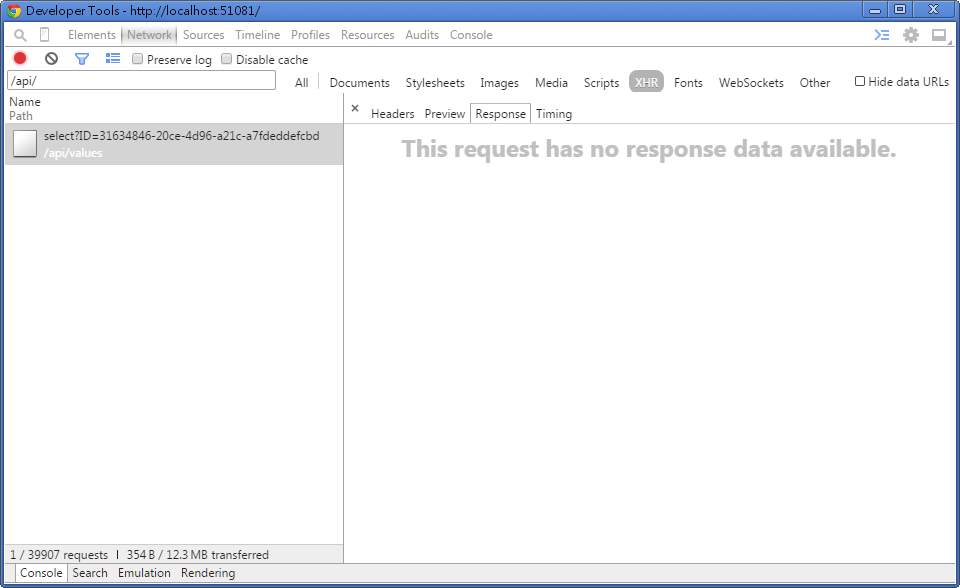
请注意,请求中存在If-Modified-Since标头。该值与我们在图 4 中看到的Last-Modified完全相等。这次我们收到了一个HTTP 304 Not Modified响应,因为自Sat, 07 Feb 2015 08:58:32 GMT以来数据没有更改。当然,响应正文是空的。
图 6
结论
我希望这个项目能让您大致了解,HTTP 缓存不仅适用于静态资源,还可以通过“手动”控制标头来应用于动态内容。当您回顾创建的 Web API 或设计新的 Web API 时,如果内容是可观察的,您可能会酌情考虑让您的 API 支持 HTTP 缓存。
您可能已经注意到,上面几节中没有提到一些内容。以下是您可以自己尝试的几点。
- 在此示例项目中,我们使用**Last-Modified**标头来实现 HTTP 缓存。但是请记住我们在上一篇文章中讨论过的,还有另一个选项**ETag**可供选择。尝试修改
ValuesController.Select(Guid)方法并达到相同的效果。 - 在此示例中,
Employee实例最初从 Valve.txt 加载,更改不会保存在文件中。尝试设计并将其替换为实际的数据库表,并将更改保存下来。
延伸阅读
- HTTP 标头字段定义 - http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec14.html
- jQuery.data() - https://api.jqueryjs.cn/jquery.data/