使用DDD和Repository Unit of Work的Polyglot持久化
使用 DDD 和 Repository Unit of Work 模式处理高绩效企业应用程序中的不同数据存储(SQL、NoSQL 等)
引言
传统的业务应用程序通常使用关系型数据库来存储数据,并将其用作集成点。这需要设计一系列关系表,并在代码中使用单一数据访问层来访问它们,以及使用 ORM 将关系表转换为 OOP 结构。
如今,考虑到关系数据库设计中遇到的一些挑战,这种方式可能无法针对每个业务用例进行优化。在这里没有必要列出此类设计的所有缺点,我们可以找到更多关于此的博文。但让我们给出一个提示:
敏捷性:数据库中的数据结构与应用程序对象模型之间的不匹配会降低生产力。
性能:关系模型旨在占用最少的磁盘空间并消耗最少的资源,这会带来一些副作用和性能限制。
可用性和价格:关系模型中提高可用性会使一致性变得复杂,并且有其成本。
灵活性:并非所有开发人员都熟悉关系模型和模式,在某些情况下,复杂的业务模型需要对 SQL 语言和关系模型有透彻的了解。
在许多捕获大量数据和大量并发请求的企业应用程序中,关系模型未能满足要求。因此,寻找其他替代方案来解决特定的持久化问题,导致许多设计者选择称为 NoSQL 数据库的非关系型系统。
非关系型系统或 NoSQL 数据库可以按一系列功能区域进行分类:键/值、文档数据库、列族数据库、图数据库。每个类别都可以适合一个或多个业务用例场景,由设计者选择最合适的系统。一些 NoSQL 数据库使用文件系统进行持久化,而一些则在内存中。
背景
各种 NoSQL 数据库的出现以及廉价存储空间(磁盘和内存)的充裕,将是设计者和开发人员转向非关系型模型的推动力。
然而,一个显而易见的问题会浮现在脑海:如何设计一个应用程序以便它能够与不同的数据存储进行对话?
我们最终将实现什么?
我们将使用 DDD 和 Repository Unit of Work 模式来设计和构建一个简单的应用程序。该应用程序将在关系型(SQL)和非关系型(NoSQL)数据存储中持久化数据。
作为真实世界的例子,我们将使用一个企业产品商店,假设一个企业(customer)拥有许多组织、部门和员工,他们管理着大量的商品,每个员工都可以搜索、列出、添加、更新和删除商品。此外,应用程序需要存储用户流量,以帮助管理员解决潜在的性能问题。为了满足要求,该应用程序将在云端(Windows Azure)和本地部署。最后,为了演示和测试目的,该应用程序会将所有数据存储在内存中。
选择数据库
在我们的示例产品商店应用程序中,我们可以识别出不同的数据需求。对于每种需求,我们将使用特定的数据库类型,如下所示:
- 客户、组织、部门和用户需要一个安全可靠的数据库来安全地保留层次结构。并且这些实体不会经常更改。因此,我们将它们持久化到关系型数据库中,例如 SQL Server。
- 该应用程序需要存储大量商品,并且必须在可接受的性能下对商品进行过滤、列出和搜索。每个商品包含的信息可能不同。因此,出于这些原因,我们将把商品持久化到 NoSQL 文档数据库中。在这里,我们将使用 MongoDB。
- 该应用程序将允许用户做一些笔记并将它们与其他用户共享。笔记只是文本,可以列出、搜索和过滤。对于笔记,文本将存储在 Lucene 索引中。
- 该应用程序会将商品图像存储在云 Blob 存储中,作为
key/ValueNoSQL 数据库。 - 该应用程序会将错误日志记录并以键/值 NoSQL 数据库的形式存储更改历史记录到云表存储中。
设计和创建解决方案
在开始编码之前,让我们简要介绍一下我们应用程序的高层设计结构。
这是我们解决方案的分层图:

从上面的图我们可以检查应用程序使用的主要层:
- 表示层: ASP.NET MVC5 应用程序,使用 HTML5 AngularJS。
- 分布式服务: MVC 5 Web API 应用程序公开 REST 服务。
- 应用程序管理:管理业务规则。
- 领域对象:核心应用程序业务定义、接口、实体、聚合根。
- 数据:仓储(Repositories)和特定的单元工作(Unit of Work)实现。每个领域实体或聚合根都有一个仓储,每个数据存储类型都有一个单元工作。
- 数据存储:在上图底部,我们看到了应用程序将使用的数据存储:SQL Server、MongoDB、Azure Storage、Lucene 索引和内存中的假存储。
为了检查组件之间的交互,让我们看一下下面的组件图:
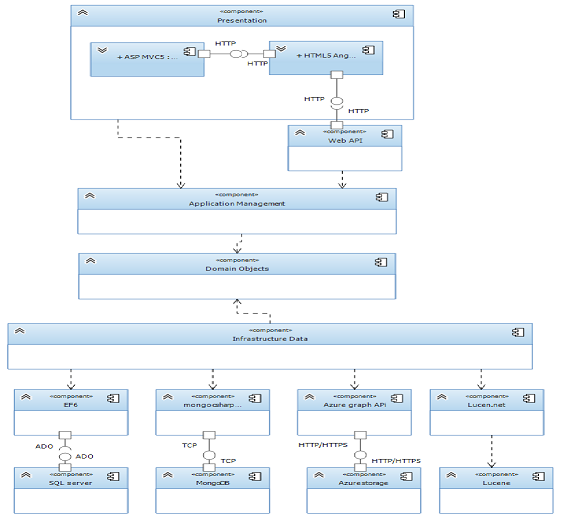
表示层:在表示层,我们可以看到 ASP MVC 5 项目将作为 SPA,使用 HTML5 AngularJS。它还可以使用分布式服务中的直接 Web API 服务,通过 HTTP/HTTPS 进行通信。
分布式 服务: Web API 通过 HTTP/HTTPS 公开 Rest 服务。
应用程序管理:类库,用作 Web API 和 MVC 应用程序的 .NET 引用。
领域对象:类库,用作应用程序管理和基础数据层的 .NET 引用。
基础数据:类库,引用 Domain 对象和一些作为数据存储连接器的库。
- Entity Framework 6 用于 SQL Server。
- Mongocsharpdriver 用于 MongoDB。
- Lucene.net 用于 Lucene 索引。
- Windows Azure Graph API 用于 Azure 存储。
现在让我们放大 Domain 对象层,看看在这个映射图中定义的实体。

您可以在附件的解决方案中找到此图。
代码工作
领域实体
在对我们的示例应用程序进行通用设计描述后,让我们深入研究一些代码。主要关注领域对象定义和基础数据层。其他层可以从附件示例下载。
从领域对象定义开始:在这里,我们将首先为所有实体定义一个基类,其中包含具有某些库属性的通用属性。这是我们基类的代码。
/// <summary>
/// Base class for entities
/// </summary>
public abstract class EntityBase
{
#region Members
Guid _Id;
#endregion
#region Properties
/// <summary>
/// Get or set the persisted object identifier
/// </summary>
[Key]
[Field(Key = true)]
[BsonId]
public virtual Guid Id
{
get
{
return _Id;
}
set
{
_Id = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get or set the Date of Creation
/// </summary>
[DataType(DataType.DateTime)]
public DateTime CreationDate { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Get or set the Date of LastUpdate
/// </summary>
[DataType(DataType.DateTime)]
public DateTime LastUpdateDate { get; set; }
#endregion
}
此类定义了 Id 属性,并带有某些属性。
Key:Entity Framework 的属性,以便该属性将映射到 SQL 主键。BsonI:MongoDB 的属性,以便Id属性将映射为文档标识符。Filed(Key=true):这是 Lucene.net 的属性,用作索引上的文档标识符。
现在这是实体。让我们看看如何为我们的仓储定义合同。这是定义:
/// <summary>
/// Base interface for implement a "Repository Pattern", for
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// </remarks>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity">Type of entity for this repository </typeparam>
public interface IRepository<TEntity>
where TEntity : EntityBase
{
/// <summary>
/// Get the unit of work in this repository
/// </summary>
IUnitOfWork UnitOfWork { get; }
/// <summary>
/// Add item into repository
/// </summary>
/// <param name="item">Item to add to repository</param>
Task AddAsync(TEntity item);
/// <summary>
/// Delete item
/// </summary>
/// <param name="item">Item to delete</param>
Task RemoveAsync(TEntity item);
/// <summary>
/// Get element by entity key
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id">entity key values, the order the are same of order in mapping.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
Task<TEntity> GetElementByIdAsync(Guid id,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken));
/// <summary>
/// Get all elements of type {TEntity} in repository
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pageIndex">Page index</param>
/// <param name="pageCount">Number of elements in each page</param>
/// <param name="orderBy">Order by expression for this query</param>
/// <param name="ascending">Specify if order is ascending</param>
/// <returns>List of selected elements</returns>
Task<IEnumerable<TEntity>> GetPagedElementsAsync<T>(int pageIndex, int pageCount,
Expression<Func<TEntity, T>> orderBy, bool ascending,
CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken));
}
应用程序中使用的所有实体和聚合根将定义一个实现上述合同的仓储类,如我们所见,仓储定义了将在运行时注入的单元工作。因此,对于每个存储,我们将定义其单元工作并将其注入到仓储中。这是单元工作的合同。
public interface IUnitOfWork
: IDisposable
{
/// <summary>
/// Commit all changes made in a container.
/// </summary>
///<remarks>
/// If the entity have fixed properties and any optimistic concurrency problem exists,
/// then an exception is thrown
///</remarks>
void Commit();
......
/// <summary>
/// Commit all changes made in a container Async.
/// </summary>
///<remarks>
/// If the entity have fixed properties and any optimistic concurrency problem exists,
/// then an exception is thrown
///</remarks>
Task CommitAsync( CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken));
......
/// <summary>
/// Commit all changes made in a container Async.
/// </summary>
///<remarks>
/// If the entity have fixed properties and any optimistic concurrency problem exists,
/// then 'client changes' are refreshed - Client wins
///</remarks>
Task CommitAndRefreshChangesAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken));
访问数据存储
对于每个数据存储,我们将定义其单元工作,以便可以将其注入到特定的仓储中。首先,在领域对象层,我们定义了一个单元工作的合同,因此这里的单元工作将实现它。
以关系型数据库(SQL Server)为例,这可能是最常见的。在这里,我们将使用 Entity Framework 并创建一个实现基本合同并继承 Entity Framework DBContext 的单元工作。上面是此示例中使用的代码。
public class MainBCUnitOfWork : DbContext, IMainBCUnitOfWork
{
#region Fileds
private IDbSet<Customer> _customers;
private IDbSet<Address> _addresses;
private IDbSet<Department> _departments;
private IDbSet<Organization> _organizations;
.......
#region Properties
public IDbSet<Customer> Customers
{
get
{
if (this._customers == null)
this._customers = (IDbSet<Customer>)this.Set<Customer>();
return this._customers;
}
}
public IDbSet<Department> Departments
{
get
{
if (this._departments == null)
this._departments = (IDbSet<Department>)this.Set<Department>();
return this._departments;
}
}
..............
#endregion
.........
public virtual IQueryable<TEntity> CreateSet<TEntity>() where TEntity : class,new()
{
return (IDbSet<TEntity>)this.Set<TEntity>();
}
public virtual void Commit()
{
try
{
this.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException ex)
{
throw this.GetDBValidationExptions(ex);
}
}
...............
public async Task CommitAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default(CancellationToken))
{
cancellationToken.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
try
{
await this.SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException ex)
{
throw this.GetDBValidationExptions(ex);
}
}
........................
}
类的完整定义可以在附件的代码中找到。
对于存储在 SQL Server 数据库中的每个实体,都定义了一个 IDBSet 属性。create set 方法将用于检索数据。
同样,我们将使用 MongoDB C# 驱动程序(可以作为 Nuget 包添加)为 MongoDB 定义一个单元工作。这是使用的代码。
public class MongoUnitOfWork : IMongoUnitOfWork
{
#region Fields
string _dbHostName;
string _dbName;
MongoDatabase _database;
......
#region properties
public string DbName
{
get {
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(this._dbName))
{
this._dbName = "polyGlotDemo";
}
return _dbName;
}
set { _dbName = value; }
}
public string DbHostName
{
get {
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(this._dbHostName))
{
this._dbHostName = "127.0.0.1";
}
return _dbHostName;
}
set { _dbHostName = value; }
}
public MongoDatabase Database
{
get { return _database; }
set { _database = value; }
}
public IDbSet<DepartmentAggregate> Departments { get; set; }
#endregion
#region Ctor
public MongoUnitOfWork()
{
var pack = new ConventionPack();
pack.Add(new CamelCaseElementNameConvention());
ConventionRegistry.Register("MongoUnitOfWorkPack", pack, (t) => true);
string connectionString = "mongodb://" + t
MongoClientSettings settings = MongoClientSettings.FromUrl(new MongoUrl(connectionString));
settings.WriteConcern.Journal = true;
var mongoClient = new MongoClient(settings);
var mongoServer = mongoClient.GetServer();
if (!mongoServer.DatabaseExists(this.DbName))
{
throw new MongoException(string.Format
(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, Messages.DatabaseDoesNotExist, this.DbName));
}
this.Database = mongoServer.GetDatabase(this.DbName);
var coll = this.Database.GetCollection<
DepartmentAggregate>("DepartmentAggregate");
//coll.RemoveAll();
foreach (var dep in data.DepartmentAggregates)
{
if (!coll.AsQueryable().Any(x => x.Id == dep.Id))
{
coll.Insert<DepartmentAggregate>(dep);
}
}
this.Departments = new MemorySet<DepartmentAggregate>();
}
#endregion
.........
}
#endregion
类的完整定义可以在附件的代码中找到。
对于其他存储和单元工作,您可以浏览代码。逻辑是相同的。
运行示例
以下是使用附件示例的一些先决条件:
- 从 https://mongodb.ac.cn/downloads 下载 MongoDB。
- 启动 MongoDB 并创建一个数据库和集合。
- Visual Studio Ultimate(如果您想打开建模项目)。
- Azure SDK 2.5:模拟 Azure 存储。
- 以管理员身份运行 Visual Studio。
- 运行 Azure 解决方案。
- 使用 Nuget 恢复任何丢失的包。
关注点
应用程序示例,使用 DDD、Windows Azure、MongoDB、Lucene.net 等管理多个存储和多个环境。
希望这个例子能有所帮助,欢迎提出任何评论。
