使用 Entity Framework 6.1 (Code First) 的通用数据访问助手
4.73/5 (18投票s)
泛型数据访问助手
引言
此助手的目标是使用实体框架 (CodeFirst) 开发一个通用的 - 即可重用的 - 数据访问助手,而其动机是使用 泛型 和 委托 来消除冗余代码。
该助手分为两部分,第一部分是查询(检索)业务,第二部分是将更改保存到数据库,这些更改以同步和异步方式实现。
背景
此助手建议使用以下技术 .NET 4.5 (C#5)、Entity Framework 6 (CodeFirst)。此外,您需要对 async / await 代码有适度的了解。
详细信息
此处的通用意味着将 泛型 应用于接受委托的方法 - 如果不返回,则类型为 Action ,如果返回结果,则类型为 Func - 作为参数,该参数又采用 DBContext 类型的参数作为您的具体类继承的基类。
每个方法都封装了以下逻辑,具体取决于其角色
- 使用
using初始化具体的实体框架上下文 - 使用锁定 (
Default) 或解锁 (IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted) 表开始事务范围 try/catch主体- 委托执行
- 提交和回滚逻辑,如果它是由一组事务组成的原子事务
- 结果返回类型布尔值,指示查询/保存状态,或者使用泛型预定义的类型。
- 异步逻辑
- 记录异常
所有这些逻辑都不会写入您的基于业务的数据访问逻辑中,因此消除了冗余代码。
动机
当我们编写使用 EF & Linq 访问数据库的简单逻辑时,它看起来像这样
public static List<Employee> GeAllEmployees()
{
try
{
using (var northwindContext = new NorthwindDBContext())
{
var query = from e in northwindContext.Employees select e;
return query.ToList();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log Error
}
}
因此,我必须使用新的业务(例如 GetEmployeeOrders )使此代码变得冗余。此外,如果我必须访问另一个数据库,这意味着另一个 DBContext ,我必须使此逻辑变得冗余 !!
在这里, 泛型 和 委托 是解决这两个问题的方案。因此,我创建了一个名为 DALHelper 的 public static class ,其中包含以下七个 static 方法。
1 查询
所有检索方法也可以用于将更改保存到数据库。
1.1 默认
以下代码段正在 锁定 表,这是初始化新 DbContext 的默认行为。
public static bool GenericRetrival<T>(Action<T> action) where T : DbContext, new()
{
try
{
using (var context = new T())
{
action(context);
return true;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log Error
return false;
}
}
用法
public List<Employee> GeAllEmployees()
{
List<Employee> result= null;
bool success = DALHelper.GenericRetrival<NorthwindDBContext>((northwindContext) =>
{
result = (from e in northwindContext.Employees select e).ToList();
});
return result;
}
1.2 使用 泛型结果 查询
这里我们将 TResult 标识为 DBContext 类型的泛型,类型为 Func 的委托将返回 TResult 类型的对象。
public static TResult GenericResultRetrival<T, TResult>(Func<T, TResult> func) where T : DbContext, new()
where TResult : new()
{
try
{
using (var context = new T())
{
TResult res = func(context);
return res;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log Error
return default(TResult);
}
}
用法
public List<Employee> GeAllEmployees()
{
List<Employee> result = DALHelper.GenericResultRetrival<NorthwindDBContext,List<Employee>>((northwindContext) =>
{
return (from e in northwindContext.Employees select e).ToList();
});
return result;
}
1.3 异步 查询
public static async Task<TResult> GenericRetrivalAsync<T,
TResult>(Func<T, Task<TResult>> func)
where T : DbContext, new()
where TResult : new()
{
try
{
using (var context = new T())
{
return await func(context);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Log Error
return default(TResult);
}
}
用法
public async Task<List<Employee>> GetAllEmployeesAsync()
{
return await DALHelper.GenericRetrivalAsync<NorthwindDBContext, List<Employee>>(async (northwindContext) =>
{
return await (from e in northwindContext.Employees select e).ToListAsync();
});
}
1.4 长时间 查询,不锁定 表(异步)
public static async Task<TResult>
GenericResultNoLockLongRetrivalAsync<T,TResult>(Func<T, Task<TResult>> func)
where T : DbContext, new()
where TResult : new()
{
try
{
using (var context = new T())
{
((IObjectContextAdapter)context).ObjectContext.CommandTimeout = 0;
using (var dbContextTransaction =
context.Database.BeginTransaction(IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted))
{
return await func(context);
}
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Log Error
return default(TResult);
}
}
1.5 从 两个 上下文异步查询
public static async Task<object>
GenericTwiceContextsRetrivalAsync<T1, T2>(Func<T1, T2, Task<object>> func)
where T1 : DbContext, new()
where T2 : DbContext, new()
{
try
{
using (var context1 = new T1())
{
using (
var dbContextTransaction1 = context1.Database.BeginTransaction(IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted))
{
using (var context2 = new T2())
{
using (
var dbContextTransaction2 =
context2.Database.BeginTransaction(IsolationLevel.ReadUncommitted)
)
{
return await func(context1, context2);
}
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception exception)
{
// Log Error
return null;
}
}
用法
public async Task<object> GetDistributedDataAsync()
{
return await DALHelper.GenericTwiceContextsRetrivalAsync<NorthwindDBContext, AdventureWorkDBContext>(async
(northwindContext, advantureContext) =>
{
var employees = (from e in northwindContext.Employees select e).ToListAsync();
var cutomers = (from c in advantureContext.Customers select c).ToListAsync();
await Task.WhenAll(employees, cutomers);
return new
{
EmployeeList = employees.Result,
PersonList = cutomers.Result
};
});
}
因此,设计将是
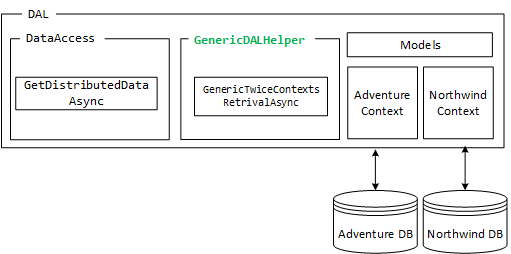
2 保存
2.1 通用安全保存
我称它为 安全 ,因为它可以将一组事务视为具有提交/回滚逻辑的 原子 。
public static bool GenericSafeTransaction<T>(Action<T> action) where T : DbContext, new()
{
using (var context = new T())
{
using (var dbContextTransaction = context.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
action(context);
dbContextTransaction.Commit();
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
dbContextTransaction.Rollback();
// Log Error
return false;
}
}
}
}
用法
public bool AddMultipleRecords(Employee newEmp, Supplier newSup)
{
return DALHelper.GenericSafeTransaction<NorthwindDBContextgt;(northwindContext =>
{
northwindContext.Employees.Add(newEmp);
northwindContext.SaveChanges();
northwindContext.Suppliers.Add(newSup);
northwindContext.SaveChanges();
});
}
2.2 异步 保存
public static async Task<int?> GenericSafeTransactionAsync<T>(Action<T> action)
where T : DbContext, new()
{
using (var context = new T())
{
using (var dbContextTransaction = context.Database.BeginTransaction())
{
try
{
action(context);
int affectedRecords = await context.SaveChangesAsync();
dbContextTransaction.Commit();
return affectedRecords;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
dbContextTransaction.Rollback();
// Log Error
return null;
}
}
}
}
用法
return await DALHelper.GenericSafeTransactionAsync<NorthwindDBContext>( async (northwindContext) =>
{
northwindContext.Employees.Add(newEmp);
});
