C# 波浪模拟器
4.83/5 (62投票s)
使用 VS 2010 C# 制作的实验性波浪模拟程序。
引言

这是一个实验性的波浪模拟程序。它用于在粒子池中产生波浪。例如,可以生成水波。可以实现障碍物。可以模拟波的反射、衍射和相互作用。
背景
我想用我自己的想法在计算机环境中生成波浪。由于您可以对波浪进行深入研究,我将不深入探讨物理学。我只会解释我自己的波浪生成技术。以下是基本概念。
1 - 方形水池
这是波浪生成的地方。它充满了粒子。上面的绿色-蓝色方形表面就是它。
2 - 粒子

粒子类似于像素。它们有序排列,构成整个水池。每个粒子都有高度、速度、加速度、质量和可持续性(抗阻尼)。它们只上下移动。每个粒子在高度上都受到周围 8 个相邻粒子的吸引。在上图的插图中,红色粒子是主粒子,蓝色粒子是相邻粒子。这种吸引力是粒子自然移动的唯一原因。
3 - 振荡器
它用于生成正弦波。它会主动地使某个粒子上下移动,从而吸引相邻粒子,使它们也上下移动。这就形成了一个传播的波。在上图的第一个图像中,底部靠近水平中心的两个振荡器正在运行。
4 - 障碍物
它是一个静态粒子。它不移动。不受任何力影响。它不会吸引其他粒子。在上图的第一个图像中,底部的黄色线条是障碍物。
它是如何工作的?
波浪引擎不使用任何复杂的算法。它仅仅使用以下方法。
Force = Mass * Acceleration;
所有粒子相互吸引。它们只是想在高度上保持接近。请记住,它们只改变高度。它们想处于相同的高度。吸引力与粒子之间的高度差成正比。
当引擎进行计算时,它会检查每一个粒子。如果一个粒子是振荡器或静态粒子,引擎就不会对该粒子进行力计算,然后继续处理下一个。如果粒子是正常的动态粒子,则会进行计算。它从加速度开始。
Acceleration = (H - h) / m;
H 是周围八个(相邻)粒子的平均高度。
h 是被包围粒子的当前高度。
m 是质量。
另一个类似的公式如下。
Acceleration = Math.Sign(H - h) * Math.Pow(Math.Abs(H - h), P) / m;
P 是功率。
现在,它由于高度差而获得了加速度。还有一种阻力。
该公式抵消了加速度。它在某种程度上模拟了阻尼,并阻止了进一步的波浪传播。
Acceleration -= Velocity / Sustainability;
之后,引擎会将加速度限制在一个预设值。因此,绝对加速度不能超过该限制。Limit 对于消除不确定性和溢出是必要的。
if (Acceleration > Limit) Acceleration = Limit; else if (Acceleration < -Limit) Acceleration = -Limit;
现在加速度会影响速度。
Velocity += Acceleration;
速度也影响高度,但不是一次性全部影响。
Height += Velocity / ActionResolution;
限制高度值。
if (Height > Limit) Height = Limit; else if (Height < -Limit) Height = -Limit;
还有一个叫做 ActionResolution 的值,用于防止正反馈。理解这一点很重要,因为如果粒子同时进行所有移动,混乱是不可避免的。那么问题是什么?
1 - 想象两个想要达到相同高度但处于不同高度的粒子。
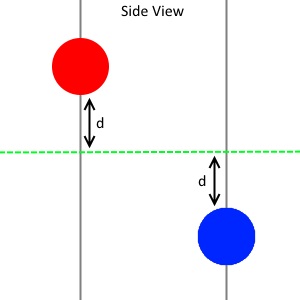
d 是粒子到原点的距离,因此这两个粒子之间的距离为 2d。这种情况会发生什么?它们首先获得很大的加速度。由于阻尼,加速度会降低。加速度影响速度。现在该影响高度了。如果我们同时移动这些粒子,下一刻很可能会变成这样。

它们之间的距离反而变大了,而不是变小了。它们永远不会停止。如果我们不让它们同时移动,它们就会停止。它们必须一步一步地前进,每一步都必须缩短距离。这将防止上述情况发生,最终它们会在相同的高度停止。
在最后一步,所有粒子作为一个整体移动到原点。否则,它们可能会远离原点,因为没有力将它们拉向原点。要做到这一点,将所有粒子的高度值相加,然后将结果除以粒子数量,从而得出粒子的平均高度。我们从每个粒子的身高中减去这个值。
int Total_Height = 0; for (int index = 0; index < Height_Array.Length; index++) Total_Height += Height_Array[index]; for (int index = 0; index < Height_Array.Length; index++) Height_Array[index] -= Total_Height / Height_Array.Length;
计算至此结束。最后,波浪引擎描绘粒子并在控件上进行渲染。
使用代码
有一个名为 WaveEngine.cs 的类来完成所有计算和渲染。首先将其实现到您的项目中。
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Drawing.Imaging;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WaveSimulator
{
public class WaveEngine
{
Bitmap bmp; // This will be our canvas.
BitmapData bd; // This will be used to modify the RGB pixel array of the "bmp".
// "vd" means "vertex data"
float[] vd; // Height map
float[] vdv; // Velocity map
float[] vda; // Acceleration map
float[] vds; // Sustainability map. Sustainability can be thought as anti-damping.
bool[] vd_static; // Static particle map. Particles which will act like a obstacle or wall.
float mass = 0.1f; // Mass of each particle. It is the same for all particles.
float limit = 500f; // Maximum absolute height a particle can reach.
float action_resolution = 20f; // Resolution of movement of particles.
float sustain = 1000f; // Anti-damping. Propagation range increases by increasing this variable. Minimum is 1f.
int delay = 1; // Time-out in milliseconds for force calculations.
float phase1 = 0f; // Current phase value of oscillator1.
float phase2 = 0f; // Current phase value of oscillator2.
float freq1 = 0.2f; // Phase changing rate of oscillator1 per calculation. Frequency increases by increasing this variable.
float freq2 = 0.2f; // Phase changing rate of oscillator2 per calculation. Frequency increases by increasing this variable.
float power = 1.0f; // Power of the output force exerted on each particle. Natural value is 1.0f
BufferedGraphics bufgraph; // Double-buffered graphics for rendering. It minimizes flickering.
BufferedGraphicsContext bufgcont; // Will be used to initialize bufgraph.
Thread ForceCalcT; // Worker thread that will do force calculations.
Mutex mutex; // This will limit the access to variables.
bool work_now = false; // True = Thread must make calculations now, False = Thread must sleep now.
bool highcont = false; // High contrast drawing.
bool disposing = false; // It will be true once the termination starts.
bool osc1active = false; // Is oscillator1 is turned on?
bool osc2active = false; // Is oscillator2 is turned on?
int osc1point = 0; // Location of the oscillator1 in the wave pool. It is an index value.
int osc2point = 0; // Location of the oscillator2 in the wave pool. It is an index value.
int size = 200; // Size of the wave pool. It indicates both the width and height since the pool will always be a square.
Color color1 = Color.Black; // Color of the crest or trough.
Color color2 = Color.Cyan; // Color of the crest or trough.
Color colorstatic = Color.Yellow; // Color of the static particles.
// These variables are used for edge absorbtion. It is used for eliminating reflection from window boundaries.
int absorb_offset = 10; // Offset from each window boundary where the sustainability starts to decrease.
float min_sustain = 2f; // The lowest sustainability value. They are located at the boundaries.
bool edge_absorbtion = true; // If true, the particles near the boundaries will have low sustainability.
Control control; // This will be the control where the engine runs and renders on.
public enum ParticleAttribute
{
Height = 1,
Velocity = 2,
Acceleration = 4,
Sustainability = 8,
Fixity = 16,
All = 32,
}
public float Mass
{
get { return mass; }
set
{
if (value > 0f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
mass = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float Limit
{
get { return limit; }
set
{
if (value > 0f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
limit = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float ActionResolution
{
get { return action_resolution; }
set
{
if (value >= 1f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
action_resolution = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float Sustainability
{
get { return sustain; }
set
{
if (value >= 1f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
sustain = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public int Delay
{
get { return delay; }
set
{
if (value >= 0)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
delay = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float PhaseRate1
{
get { return freq1; }
set
{
if (value > 0f && value < Math.PI * 2f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
freq1 = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float PhaseRate2
{
get { return freq2; }
set
{
if (value > 0f && value < Math.PI * 2f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
freq2 = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float Power
{
get { return power; }
set
{
if (power > 0f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
power = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public int Size
{
get { return size; }
set
{
if (size >= 1f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
size = value;
setPool();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public float EdgeSustainability
{
get { return min_sustain; }
set
{
if (value >= 1f)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
min_sustain = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public int AbsorbtionOffset
{
get { return absorb_offset; }
set
{
if (value > 0 && value < size / 2)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
absorb_offset = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public Color Color1
{
get { return color1; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
color1 = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public Color Color2
{
get { return color2; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
color2 = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public Color ColorStatic
{
get { return colorstatic; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
colorstatic = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public bool HighContrast
{
get { return highcont; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
highcont = value;
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public bool EdgeAbsorbtion
{
get { return edge_absorbtion; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
edge_absorbtion = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public bool Oscillator1Active
{
get { return osc1active; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
osc1active = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public bool Oscillator2Active
{
get { return osc2active; }
set
{
mutex.WaitOne();
osc2active = value;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
public Point Oscillator1Position
{
get { return new Point(osc1point % size, (int)Math.Floor((float)osc1point / (float)size)); }
set
{
if (value.X + value.Y * size < size * size)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
osc1point = value.X + value.Y * size;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
public Point Oscillator2Position
{
get { return new Point(osc2point % size, (int)Math.Floor((float)osc2point / (float)size)); }
set
{
if (value.X + value.Y * size < size * size)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
osc2point = value.X + value.Y * size;
setSustain();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the WaveEngine
/// </summary>
/// <param name="control">The control where the engine renders on.</param>
public WaveEngine(Control control)
{
this.control = control;
control.Resize += new EventHandler(control_Resize);
setPool();
mutex = new Mutex();
ForceCalcT = new Thread(() =>
{
while (!disposing)
{
try
{
while (work_now)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
int beginning = System.Environment.TickCount;
while (System.Environment.TickCount - beginning < delay)
CalculateForces();
generatebitmap();
bufgraph.Graphics.DrawImage(bmp, 0, 0, control.ClientSize.Width, control.ClientSize.Height);
bufgraph.Render();
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
Thread.Sleep(delay);
}
}
catch
{ work_now = false; mutex.ReleaseMutex(); }
Thread.Sleep(0);
}
});
ForceCalcT.Start();
}
void control_Resize(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((Object arg1) =>
{
mutex.WaitOne();
if (bufgraph != null)
bufgraph.Dispose();
if (bufgcont != null)
bufgcont.Dispose();
bufgcont = new BufferedGraphicsContext();
bufgraph = bufgcont.Allocate(control.CreateGraphics(), control.ClientRectangle);
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
});
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets particles' specified attribute(s) to a specified value in a specified rectangular area.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rect">Rectangular area which contains particles.</param>
/// <param name="value">Value to set the particles to.</param>
/// <param name="partatt">Attribute(s) that will be set.</param>
public void SetParticles(Rectangle rect, float value, ParticleAttribute partatt)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
if (rect.X < 0)
rect.X = 0;
if (rect.Y < 0)
rect.Y = 0;
if (rect.Width + rect.X > size)
rect.Width -= (rect.X + rect.Width) - size;
if (rect.Height + rect.Y > size)
rect.Height -= (rect.Y + rect.Height) - size;
bool xh = false, xv = false, xa = false, xs = false, xf = false;
// Let's see which attributes we are gonna deal with.
if ((ParticleAttribute.All & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.All)
{
xh = true; xv = true; xa = true; xs = true; xf = true;
}
else
{
if ((ParticleAttribute.Height & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.Height)
xh = true;
if ((ParticleAttribute.Velocity & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.Velocity)
xv = true;
if ((ParticleAttribute.Acceleration & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.Acceleration)
xa = true;
if ((ParticleAttribute.Sustainability & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.Sustainability)
xs = true;
if ((ParticleAttribute.Fixity & partatt) == ParticleAttribute.Fixity)
xf = true;
}
for (int y = rect.Y * size; y < rect.Y * size + rect.Height * size; y += size)
{
for (int x = rect.X; x < rect.X + rect.Width; x++)
{
if (xh)
vd[x + y] = value;
if (xv)
vdv[x + y] = value;
if (xa)
vda[x + y] = value;
if (xs)
vds[x + y] = value;
if (xf)
vd_static[x + y] = Convert.ToBoolean(value);
}
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
/// <summary>
/// Gives a float array of specified attribute of particles in a specified rectangular area.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rect">Rectangular area which contains particles.</param>
/// <param name="partatt">Attribute whose array will be given. Only one attribute can be specified and "All" cannot be specified.</param>
public float[] GetParticles(Rectangle rect, ParticleAttribute partatt)
{
float[] result = new float[1];
bool xh = false, xv = false, xa = false, xs = false, xf = false;
if ((int)partatt == 1 || (int)partatt == 2 || (int)partatt == 4 || (int)partatt == 8 || (int)partatt == 16)
{
mutex.WaitOne();
if (rect.X < 0)
rect.X = 0;
if (rect.Y < 0)
rect.Y = 0;
if (rect.Width + rect.X > size)
rect.Width -= (rect.X + rect.Width) - size;
if (rect.Height + rect.Y > size)
rect.Height -= (rect.Y + rect.Height) - size;
result = new float[rect.Width * rect.Height];
if (partatt == ParticleAttribute.Height)
xh = true;
if (partatt == ParticleAttribute.Velocity)
xv = true;
if (partatt == ParticleAttribute.Acceleration)
xa = true;
if (partatt == ParticleAttribute.Sustainability)
xs = true;
if (partatt == ParticleAttribute.Fixity)
xf = true;
int r = 0;
for (int y = rect.Y * size; y < rect.Y * size + rect.Height * size; y += size)
{
for (int x = rect.X; x < rect.X + rect.Width; x++)
{
if (xh)
result[r] = vd[x + y];
if (xv)
result[r] = vdv[x + y];
if (xa)
result[r] = vda[x + y];
if (xs)
result[r] = vds[x + y];
if (xf)
result[r] = Convert.ToSingle(vd_static[x + y]);
r += 1;
}
}
mutex.ReleaseMutex();
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts the force calculation.
/// </summary>
public void Run()
{
work_now = true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Suspends the force calculation indefinitely.
/// </summary>
public void Stop()
{
work_now = false;
}
public void Dispose()
{
work_now = false;
disposing = true;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem((Object arg1) =>
{
mutex.WaitOne();
bmp.Dispose();
mutex.Close();
});
}
void CalculateForces()
{
float total_height = 0;// This will be used to shift the height center of the whole particle system to the origin.
// This loop calculates the forces exerted on the particles.
for (int index = 0; index < vd.Length; index += 1)
{
// If this is a static particle, it will not move at all. Continue with the next particle.
if (vd_static[index])
{
vd[index] = 0;
vdv[index] = 0;
vda[index] = 0;
continue;
}
if (index == osc1point && osc1active)
{
// This is where the oscillator1 is located. It is currently active.
// So this particle only serves as an oscillator for neighbor particles.
// It will not be affected by any forces. It will just move up and down.
vdv[index] = 0;
vda[index] = 0;
vd[index] = limit * (float)Math.Sin(phase1);
phase1 += freq1;
if (phase1 >= 2f * (float)Math.PI)
phase1 -= (float)Math.PI * 2f;
continue;
}
if (index == osc2point && osc2active)
{
vdv[index] = 0;
vda[index] = 0;
vd[index] = limit * (float)Math.Sin(phase2);
phase2 += freq2;
if (phase2 >= 2f * (float)Math.PI)
phase2 -= (float)Math.PI * 2f;
continue;
}
// So this particle is neither an oscillator nor static. So let's calculate the force.
// Reset the acceleration. We do this because acceleration dynamically changes with the force.
vda[index] = 0;
// Sum up all the height values so we will find the average height of the system.
// This doesn't contribute to the force calculation. It is immaterial.
total_height += vd[index];
// Now we will find out the average height of the 8 neighbor particles.
// So we will know where the current particle will be attracted to.
// "heights" is the sum of all the height values of neighbor particles.
float heights = 0;
// "num_of_part" is the number of particles which contributed to the "heights".
int num_of_part = 0;
//// UP
if (!(index >= 0 && index < size)) // Make sure that this point is not on a boundary.
{
if (!vd_static[index - size]) // Make sure that the neighbor particle is not static.
{
heights += vd[index - size];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// UPPER-RIGHT
if (!((index + 1) % size == 0 || (index >= 0 && index < size)))
{
if (!vd_static[index - size + 1])
{
heights += vd[index - size + 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// RIGHT
if (!((index + 1) % size == 0))
{
if (!vd_static[index + 1])
{
heights += vd[index + 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// LOWER-RIGHT
if (!((index + 1) % size == 0 || (index >= (size * size) - size && index < (size * size))))
{
if (!vd_static[index + size + 1])
{
heights += vd[index + size + 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// DOWN
if (!(index >= (size * size) - size && index < (size * size)))
{
if (!vd_static[index + size])
{
heights += vd[index + size];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// LOWER-LEFT
if (!(index % size == 0 || (index >= (size * size) - size && index < (size * size))))
{
if (!vd_static[index + size - 1])
{
heights += vd[index + size - 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
//// LEFT
if (!(index % size == 0))
{
if (!vd_static[index - 1])
{
heights += vd[index - 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
// UPPER-LEFT
if (!(index % size == 0 || (index >= 0 && index < size)))
{
if (!vd_static[index - size - 1])
{
heights += vd[index - size - 1];
num_of_part += 1;
}
}
if (num_of_part != 0)
{
heights /= (float)num_of_part;
if (power != 1.0f)
vda[index] += Math.Sign(heights - vd[index]) * (float)Math.Pow(Math.Abs(vd[index] - heights), power) / mass;
else
vda[index] += -(vd[index] - heights) / mass;
}
// Damping takes place.
vda[index] -= vdv[index] / vds[index];
// Don't let things go beyond their limit.
// This makes sense. It eliminates a critic uncertainty.
if (vda[index] > limit)
vda[index] = limit;
else if (vda[index] < -limit)
vda[index] = -limit;
}
// Now we have finished with the force calculation.
// Origin height is zero. So "shifting" is the distance between the system average height and the origin.
float shifting = -total_height / (float)vd.Length;
// We are taking the final steps in this loop
for (int index = 0; index < vd.Length; index += 1)
{
// Acceleration feeds velocity. Don't forget that we took care of the damping before.
vdv[index] += vda[index];
// Here is the purpose of "action_resolution":
// It is used to divide movements.
// If the particle goes along the road at once, a chaos is most likely unavoidable.
if (vd[index] + vdv[index] / action_resolution > limit)
vd[index] = limit;
else if (vd[index] + vdv[index] / action_resolution <= limit && vd[index] + vdv[index] / action_resolution >= -limit)
vd[index] += vdv[index] / action_resolution; // Velocity feeds height.
else
vd[index] = -limit;
// Here is the last step on shifting the whole system to the origin point.
vd[index] += shifting;
}
}
void generatebitmap()
{
if (bmp == null || bmp.Width != size)
bmp = new Bitmap(size, size, PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb); // 24 bit RGB. No need for alpha channel.
// Get the bitmap data of "bmp".
bd = bmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, size, size), System.Drawing.Imaging.ImageLockMode.WriteOnly, System.Drawing.Imaging.PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb);
IntPtr ptr = bd.Scan0; // Get the address of the first line in "bd"
int bytes = bd.Stride * bd.Height; // "Stride" gives the size of a line in bytes.
byte[] rgbdata = new byte[bytes];
// It's time for the coloration of the height.
for (int index = 0; index < vd.Length; index++)
{
// Brightness. This value is the 'brightness' of the height.
// Now we see why "limit" makes sense.
byte bright = (byte)(((float)vd[index] + limit) / (float)((limit * 2f) / 255f));
if (vd_static[index])
{
rgbdata[index * 3] = ColorStatic.B;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 1] = ColorStatic.G;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 2] = ColorStatic.R;
}
else
{
if (highcont)
{
byte red_average = (byte)((float)(color1.R + color2.R) / 2f);
byte green_average = (byte)((float)(color1.G + color2.G) / 2f);
byte blue_average = (byte)((float)(color1.B + color2.B) / 2f);
if (vd[index] > 0)
{
rgbdata[index * 3] = color1.B;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 1] = color1.G;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 2] = color1.R;
}
else if (vd[index] < 0)
{
rgbdata[index * 3] = color2.B;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 1] = color2.G;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 2] = color2.R;
}
else if (vd[index] == 0)
{
rgbdata[index * 3] = blue_average;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 1] = green_average;
rgbdata[index * 3 + 2] = red_average;
}
}
else
{
float brightr1 = (float)bright / 255f;
float brightr2 = 1f - (float)bright / 255f;
rgbdata[index * 3] = (byte)((float)color1.B * brightr1 + (float)color2.B * brightr2);
rgbdata[index * 3 + 1] = (byte)((float)color1.G * brightr1 + (float)color2.G * brightr2);
rgbdata[index * 3 + 2] = (byte)((float)color1.R * brightr1 + (float)color2.R * brightr2);
}
}
}
// At last, we overwrite and release the bitmap data.
System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.Copy(rgbdata, 0, ptr, bytes);
bmp.UnlockBits(bd);
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets sustainability of each particle.
/// </summary>
void setSustain()
{
if (edge_absorbtion)
{
// We will fill "vds" array with "sustain" then we will deal with elements near to window boundaries.
// Since we want the sustainability to decrease towards the edges, "min_sustain" can't be bigger than "sustain".
if (min_sustain > sustain)
{
min_sustain = 1.0f; // even "sustain" can't be less than 1.0f so this is a reliable value.
}
// Sustainability reduction fields should not mix with each other. So the maximum offset is the middle-screen.
if (absorb_offset >= size / 2)
{
absorb_offset = size / 2 - 1;
}
// This value is sustainability decreasion rate per row/column. The decreasion is linear.
float dec = (sustain - min_sustain) / (float)absorb_offset;
// This one stores the current sustainability.
float cur = min_sustain;
// First, we fill "vds" array with "sustain".
for (int i = 0; i < vds.Length - 1; i++)
vds[i] = sustain;
// This loop sets up the sustainability values for the top.
for (int off = 0; off <= absorb_offset; off++)
{
// Process each row/column from the edge to the offset.
for (int x = off; x < size - off; x++)
{
// Process each sustainability element in the current row/column
vds[x + off * size] = cur;
}
cur += dec;
}
cur = sustain; // Reset the current sustainability.
// This loop sets up the sustainability values for the bottom.
for (int off = 0; off <= absorb_offset; off++)
{
for (int x = absorb_offset - off; x < size - (absorb_offset - off); x++)
{
vds[x + off * size + size * (size - absorb_offset - 1)] = cur;
}
cur -= dec;
}
cur = sustain;
// This loop sets up the sustainability values for the left.
for (int off = 0; off <= absorb_offset; off++)
{
for (int x = absorb_offset - off; x < size - (absorb_offset - off); x++)
{
vds[x * size + (absorb_offset - off)] = cur;
}
cur -= dec;
}
cur = sustain;
// This loop sets up the sustainability values for the right.
for (int off = 0; off <= absorb_offset; off++)
{
for (int x = absorb_offset - off; x < size - (absorb_offset - off); x++)
{
vds[x * size + off + size - absorb_offset - 1] = cur;
}
cur -= dec;
}
}
else
{
// The only thing to do is to fill "vds" array with "sustain" in this case.
for (int i = 0; i < vds.Length; i++)
vds[i] = sustain;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Initializes the wave pool system.
/// </summary>
void setPool()
{
if (bufgraph != null)
bufgraph.Dispose();
if (bufgcont != null)
bufgcont.Dispose();
bufgcont = new BufferedGraphicsContext();
bufgraph = bufgcont.Allocate(control.CreateGraphics(), control.ClientRectangle);
vd = new float[size * size];
vdv = new float[size * size];
vda = new float[size * size];
vd_static = new bool[size * size];
vds = new float[size * size];
setSustain();
}
}
}
现在,我们可以在 Form 中使用它。让我们先从这个开始。
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WaveSimulator
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
}
在全局范围内声明该类的实例。
WaveEngine we;
在初始化期间初始化 we。在参数中指定 this。
we = new WaveEngine(this);
现在我们可以在任何想要运行的地方运行它。让我们在初始化后立即运行它。
we.Run();
我们还需要在程序终止时处理 we。否则,程序将继续运行。以下代码对我来说效果很好。
private void MainForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
we.Dispose();
}
就这样。执行程序。您会看到一个类似这样的窗口。

这是最终的代码。
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WaveSimulator
{
public partial class MainForm : Form
{
WaveEngine we;
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
we = new WaveEngine(this);
we.Run();
}
private void MainForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
we.Dispose();
}
}
}
目前没有任何动作。我们需要更改粒子的一个属性才能看到一些动作。我们可以通过激活一个振荡器来实现。最多可以同时运行两个振荡器。
我们可以单击窗口在鼠标位置激活一个振荡器。这个效果会很好。
private void MainForm_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
we.Oscillator1Position = new Point((int)(((float)e.X / (float)ClientSize.Width) * (float)we.Size), (int)(((float)e.Y / (float)ClientSize.Height) * (float)we.Size));
we.Oscillator1Active = true;
}
执行程序并在窗口中的任何位置单击。您将看到波浪。为了使其更有趣,请在初始化 we 后添加以下命令。
we.EdgeAbsorbtion = false;
现在波浪应该会从窗口边界反弹。

由于该类及其注释相当直观,我们将不逐一介绍。您可以下载源代码或演示。该项目完全使用了该类。除了主窗口,它还包含以下内容。

一个 Adjustments 窗口,用于控制所有属性。还有一个 1DView 窗口,用于查看水池的任何横截面区域。它提供了水池的侧视图。

关注点
当我开始制作这个项目时,我认为它可能不起作用,或者最多只能勉强工作,但当我意识到它的工作方式如此简单时,我感到很惊讶。我曾考虑过用弹簧将每个粒子拉向原点,但那失败了。总有些地方出错。大多数时候,我遇到一个令人讨厌的场景,如下所示。我称之为“混乱”,因为它确实感觉如此。

这种情况的原因是低运动分辨率导致的积极反馈,但这花了我很长时间才意识到。两个粒子首先互相吸引,获得很大的加速度,并以非常剧烈的方式移动。最终它们之间的距离比以前更大。在这种情况下,它们必须获得更大的加速度。因此,它们在每次移动中都在互相远离,而不是靠近。这导致了混乱。
我还遇到一个看似简单但却难以克服的问题。那就是吸收波浪以防止反射。在一个具有均匀可持续性的水池中,波浪会简单地从窗口边缘反弹。起初看到这一点很有趣,但很快我就想消除它。我试图让边缘附近的粒子静止,但这一点用都没有。我尝试了很多次,但都失败了。过了一段时间,我真的绞尽脑汁地思考:“什么可以吸收波浪?摩擦?当然不是……等等……等一下……为什么不是摩擦?边界上的高而光滑的摩擦……是的!为什么不试试呢?”它起作用了,但吸收参数高度依赖于粒子的属性。
还有一件令人讨厌的事情,我还没有弄清楚。当一个粒子吸引其他八个相邻粒子,并且该粒子本身也被它们吸引时,我们需要考虑每个粒子之间的距离。对吗?不幸的是,考虑距离会导致某些事情出错。

上面是一个说明图,显示了相邻粒子之间可能的两种距离。一种是 1 个单位,另一种是根号 2 个单位。根据距离,距离平方根为 2 的粒子之间的吸引力应该更小,而距离为 1 的粒子之间的吸引力应该更大,因此距离与吸引力成反比。考虑到这种情况会导致问题。我将合力除以距离,但这实际上并没有起作用。
历史
2014 年 5 月 27 日 - 重要更新
1 - 从属性和许多函数中删除了 QueueUserWorkItem 函数。它们以前使用线程是因为我不想这些操作暂停 UI,但这些多线程操作经常导致意外结果。
WaveEngine we = new WaveEngine(); we.Size = 100; int x = we.Size;
x 最终是多少?它不是 100。如果此代码在没有任何中断的情况下执行,x 不会等于 100。这是因为属性设置是多线程的。在我们检索 Size 之前,线程无法完成操作。如果不想暂停 UI,则需要用户提供的线程。
2 - 删除了 SwitchStaticDynamic 函数。将改用 SetParticles 函数。
3 - 向 ParticleAttribute 枚举添加了“固定性”。这使得可以使用 SetParticles 函数在动态和静态粒子之间进行转换。
次要修复和改进。
重要提示: 当我在一台现代计算机上尝试我的程序时,我对其 CPU 性能感到震惊。我自己的电脑几乎有 10 年了,配备 1 GB RAM 和 2.01 GHz 双核 AMD CPU。我在一台配备 Intel i7 3.4 GHz 四核 CPU 的台式电脑上测试了我的程序。与我电脑上的模拟速度相比,这是一个极其快速的模拟。它非常快,但我希望通过平滑的 FPS 来减慢它的速度。我调整了 Delay,但这并没有给我一个平滑的 FPS。最后,我增加了 Size,因此粒子数量增加了。这增加了 CPU 的负载,最终渲染变得平滑而缓慢。Size 非常大,速度仍然令人满意。因此,如果您的 CPU 非常快和/或您认为模拟速度非常快,请增加 Size。另一个选择是增加运动分辨率。
